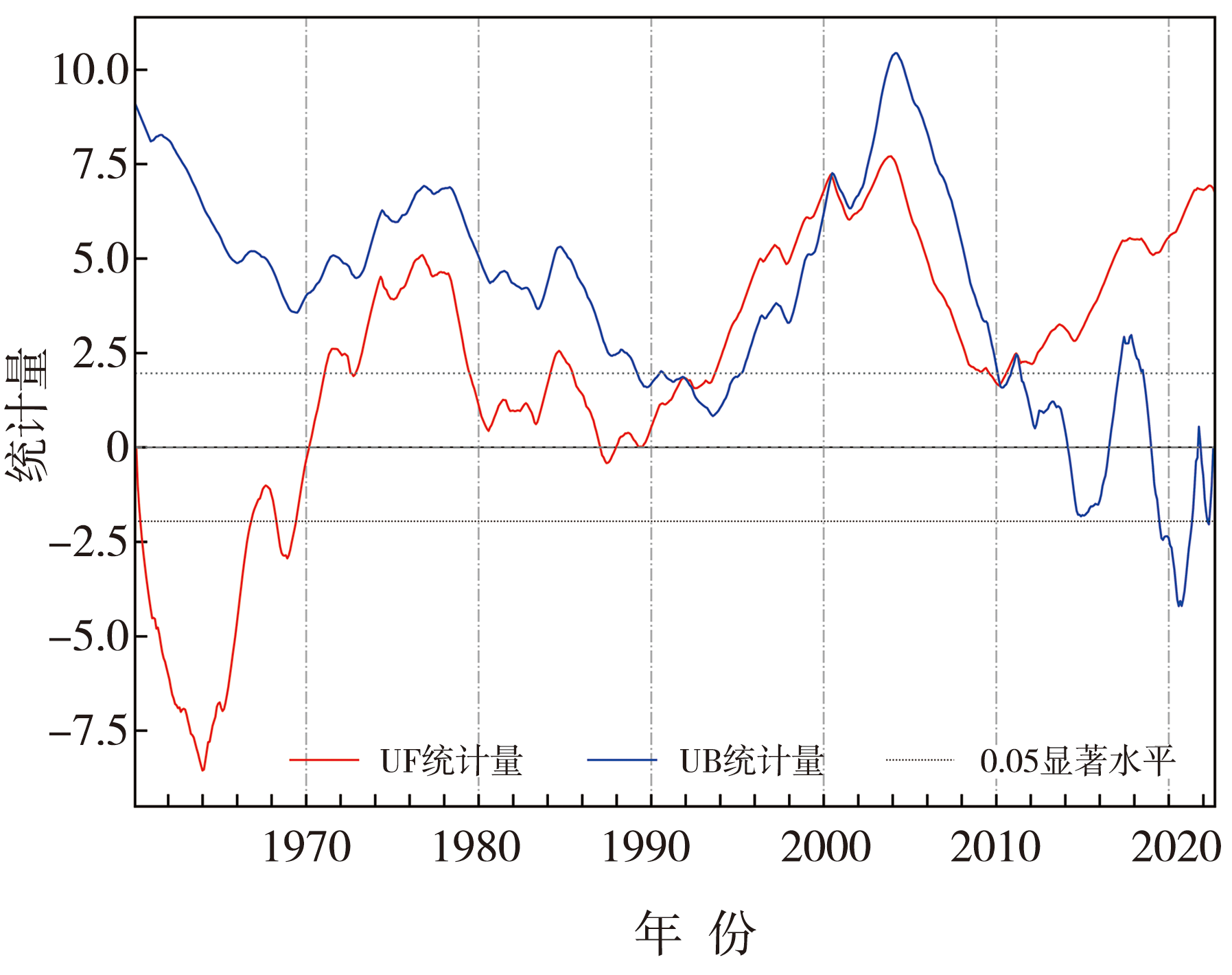
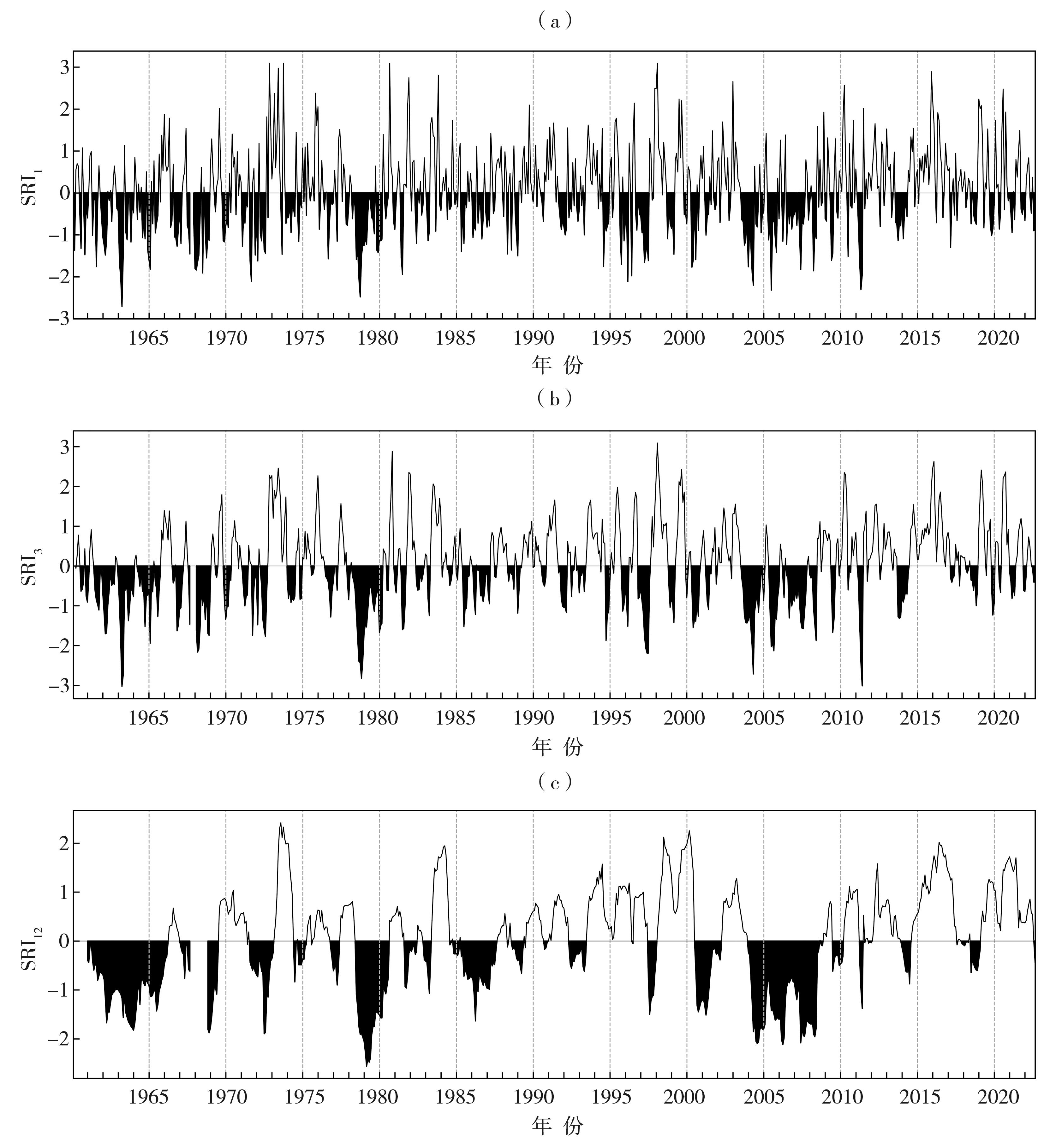
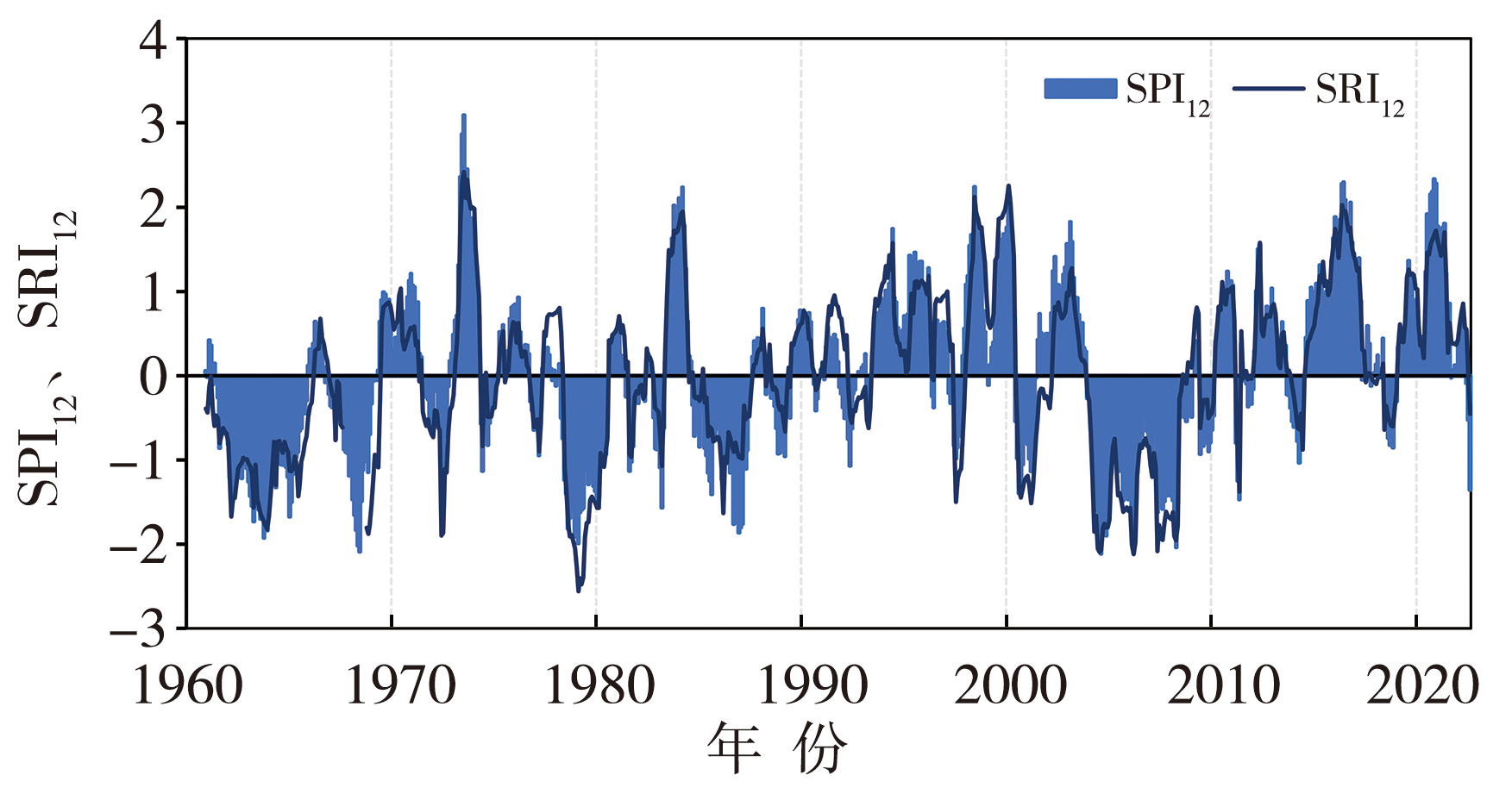
| [1] |
曹欣荣, 2014. 浙江省气象干旱规律分析研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学.
|
| [2] |
樊高峰, 苗长明, 毛燕军, 等, 2008. 浙江干旱特征及其与区域气候变化关系[J]. 气象科技, 36(2): 180-184.
|
| [3] |
高放, 刘冀, 陈威, 等, 2023. 淮河流域上游分区气象-水文干旱传播特征及响应概率研究[J]. 水土保持研究, 30(5): 257-265.
|
| [4] |
国家气候中心,中国气象局预报与网络司,中国气象局兰州干旱气象研究所, 2017. 气象干旱等级:GB/T 20 481—2017[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社.
|
| [5] |
韩会明, 孙军红, 2022. 赣江流域气象水文干旱传播特征分析[J]. 中国农村水利水电(12): 101-106.
DOI
|
| [6] |
胡彩虹, 赵留香, 王艺璇, 等, 2016. 气象、农业和水文干旱之间关联性分析[J]. 气象与环境科学, 39(4): 1-6.
|
| [7] |
姜舒婕, 程莹, 方楠, 等, 2023. 基于干旱和水位特征构建水库人工增雨需求指数[J]. 干旱气象, 41(2): 341-349.
DOI
|
| [8] |
李帅, 曾凌, 张存杰, 等, 2023. 长江上游近120年来气象干旱和水文干旱时空变化关系及其传递特征[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 19(3): 263-277.
|
| [9] |
林盛吉, 2011. 基于统计降尺度模型的钱塘江流域干旱预测和评估[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学.
|
| [10] |
马岚, 2019. 气象干旱向水文干旱传播的动态变化及其驱动力研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学.
|
| [11] |
潘婧茹, 2015. 台风暴雨及其雨水资源对苏北旱情的缓解作用的研究[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学.
|
| [12] |
潘娅英, 骆月珍, 王亚男, 等, 2018. 新安江流域降水、径流演变特征分析[J]. 水土保持研究, 25(6): 121-125.
|
| [13] |
皮卫阳, 赵雪花, 祝雪萍, 2018. 汾河上游水文干旱与气象干旱的关系[J]. 水电能源科学, 36(9): 19-22.
|
| [14] |
石朋, 詹慧婕, 瞿思敏, 等, 2022. 黄河源区气象干旱与水文干旱关联性分析[J]. 水资源保护, 38(3): 80-86.
|
| [15] |
宋艳玲, 2022. 全球干旱指数研究进展[J]. 应用气象学报, 33(5): 513-526.
|
| [16] |
粟晓玲, 张更喜, 冯凯, 2019. 干旱指数研究进展与展望[J]. 水利与建筑工程学报, 17(5): 9-18.
|
| [17] |
孙军红, 韩会明, 2023. 赣江源气象干旱向水文干旱的传播及降水短缺阈值分析[J]. 水电能源科学, 41(12): 5-9.
|
| [18] |
王乐, 刘德地, 李天元, 等, 2015. 基于多变量M-K检验的北江流域降水趋势分析[J]. 水文, 35(4): 85-90.
|
| [19] |
王莺, 张强, 王劲松, 等, 2022. 21世纪以来干旱研究的若干新进展与展望[J]. 干旱气象, 40(4): 549-566.
DOI
|
| [20] |
吴志勇, 程丹丹, 何海, 等, 2021. 综合干旱指数研究进展[J]. 水资源保护, 37(1): 36-45.
|
| [21] |
武慧敏, 吕爱锋, 张文翔, 2022. 巴音河流域水文干旱对气象干旱的响应[J]. 南水北调与水利科技(中英文), 20(3): 459-467.
|
| [22] |
薛亮, 袁淑杰, 王劲松, 2023. 我国不同区域气象干旱成因研究进展与展望[J]. 干旱气象, 41(1): 1-13.
DOI
|
| [23] |
杨铭珂, 贺中华, 张浪, 等, 2021. 不同时间尺度下气象干旱向水文干旱传播过程[J]. 水土保持学报, 35(6): 350-360.
|
| [24] |
杨扬, 赵伟明, 胡颖冰, 等, 2023. “衡邵娄干旱走廊”干旱时空演变特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 41(4): 550-559.
DOI
|
| [25] |
袁星, 王钰淼, 张苗, 等, 2020. 关于骤旱研究的一些思考[J]. 大气科学学报, 43(6): 1 086-1 095.
|
| [26] |
张建龙, 王龙, 杨蕊, 等, 2014. 南盘江流域水文干旱对气象干旱的响应特征[J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 12(3): 29-32.
|
| [27] |
张强, 韩兰英, 张立阳, 等, 2014. 论气候变暖背景下干旱和干旱灾害风险特征与管理策略[J]. 地球科学进展, 29(1):80-91.
DOI
|
| [28] |
张强, 李栋梁, 姚玉璧, 等, 2024. 干旱形成机制与预测理论方法及其灾害风险特征研究进展与展望[J]. 气象学报, 82(1): 1-21.
|
| [29] |
张强, 王劲松, 姚玉璧, 等, 2017. 干旱灾害风险及其管理[M]. 北京: 气象出版社.
|
| [30] |
张强, 姚玉璧, 李耀辉, 等, 2020. 中国干旱事件成因和变化规律的研究进展与展望[J]. 气象学报, 78(3):500-521.
|
| [31] |
章诞武, 丛振涛, 倪广恒, 2013. 基于中国气象资料的趋势检验方法对比分析[J]. 水科学进展, 24(4): 490-496.
|
| [32] |
AGHAKOUCHAK A, CHIANG F, HUNING L S, et al, 2020. Climate extremes and compound hazards in a warming world[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 48: 519-548.
|
| [33] |
BURN D H, ELNUR M A H, 2002. Detection of hydrologic trends and variability[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 255(1/2/3/4): 107-122.
|
| [34] |
LIU L, HONG Y, BEDNARCZYK C N, et al, 2012. Hydro-climatological drought analyses and projections using meteorological and hydrological drought indices: A case study in Blue River Basin, Oklahoma[J]. Water Resources Management, 26(10): 2 761-2 779.
|
| [35] |
WU J F, LIU Z Y, YAO H X, et al, 2018. Impacts of reservoir operations on multi-scale correlations between hydrological drought and meteorological drought[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 563: 726-736.
|
 ), 张露萱1, 李福刚2, 张珏1, 张玮玮1, 李强2
), 张露萱1, 李福刚2, 张珏1, 张玮玮1, 李强2
 ), ZHANG Luxuan1, LI Fugang2, ZHANG Jue1, ZHANG Weiwei1, LI Qiang2
), ZHANG Luxuan1, LI Fugang2, ZHANG Jue1, ZHANG Weiwei1, LI Qiang2