干旱气象 ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (1): 123-131.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-01-0123
银川市大气边界层逆温影响因素及其与冬季PM2.5的关系
陈荣1,2( ), 王建英1,3(
), 王建英1,3( ), 杨文军1,4, 陈敏1,2, 王谦1,2, 李琨1,2
), 杨文军1,4, 陈敏1,2, 王谦1,2, 李琨1,2
- 1.中国气象局旱区特色农业气象灾害监测预警与风险管理重点实验室,宁夏气象防灾减灾重点实验室,宁夏 银川 750002
2.宁夏银川市气象局,宁夏 银川 750002
3.宁夏气象服务中心,宁夏 银川 750002
4.宁夏贺兰县气象局,宁夏 贺兰 750200
Influence factors of atmospheric boundary layer inversion in Yinchuan City and the relation with PM2.5 in winter
CHEN Rong1,2( ), WANG Jianying1,3(
), WANG Jianying1,3( ), YANG Wenjun1,4, CHEN Min1,2, WANG Qian1,2, LI Kun1,2
), YANG Wenjun1,4, CHEN Min1,2, WANG Qian1,2, LI Kun1,2
- 1. Key Laboratory for Meteorological Disaster Monitoring and Early Warning and Risk Management of Characteristic Agriculture in Arid Regions, CMA, Key Laboratory of Meteorological Disaster Preventing and Reducing of Ningxia, Yinchuan 750002, China
2. Yinchuan Meteorological Bureau of Ningxia, Yinchuan 750002, China
3. Ningxia Meteorological Service Center, Yinchuan 750002, China
4. Helan Meteorological Station of Ningxia, Helan 750200, China
摘要:
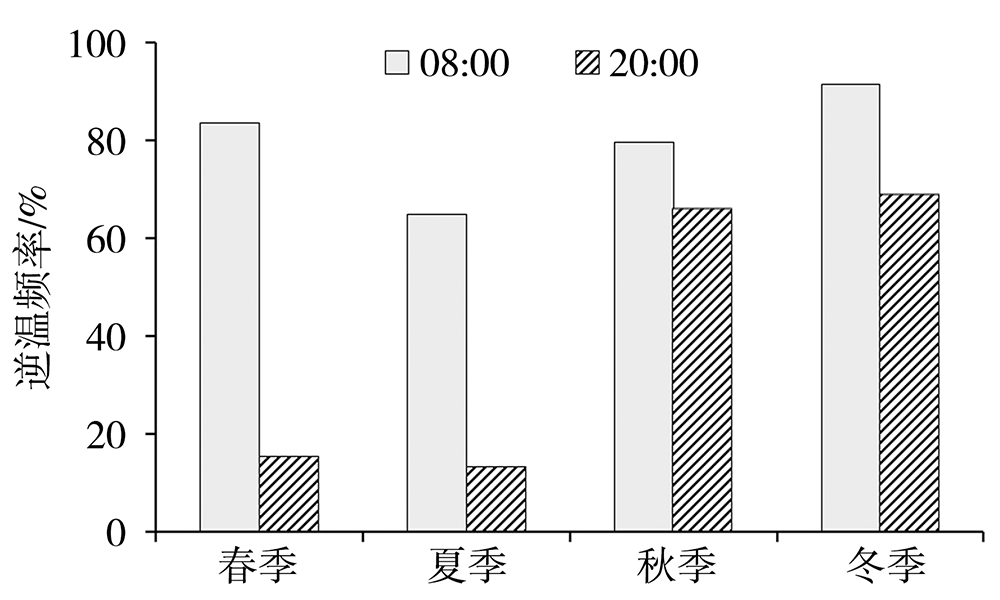
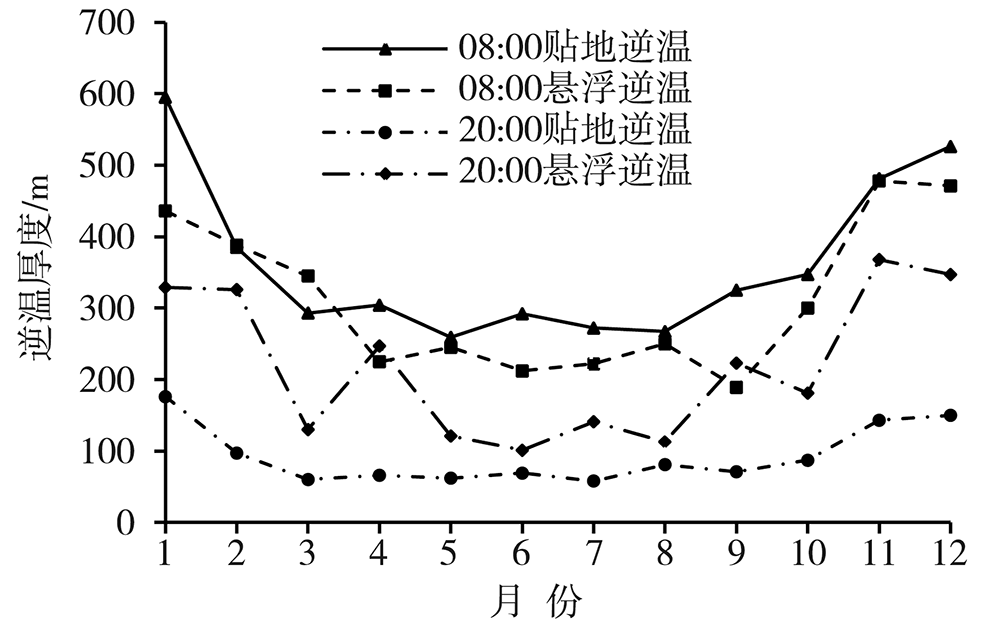
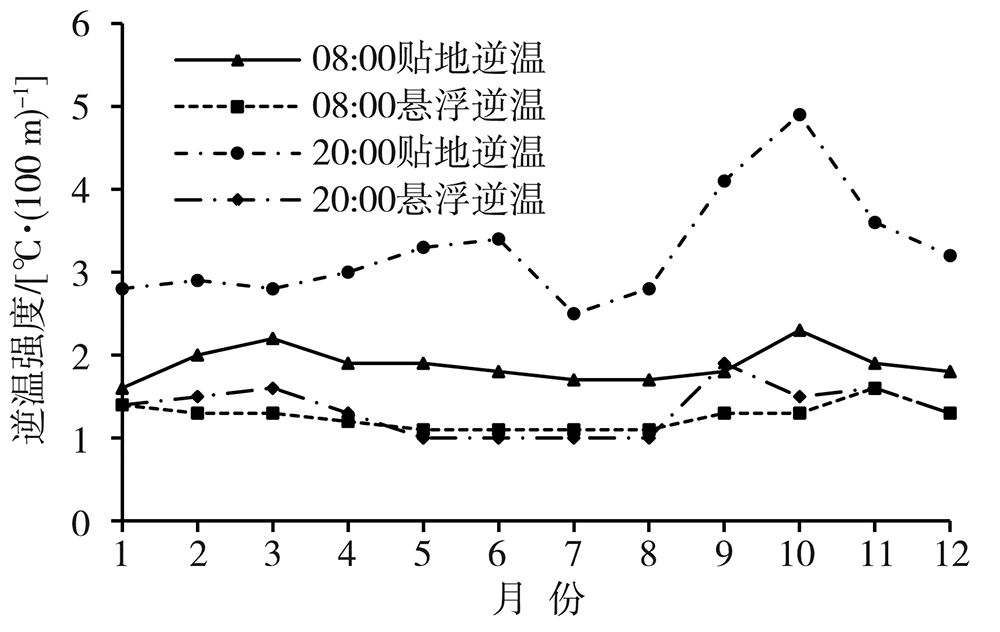
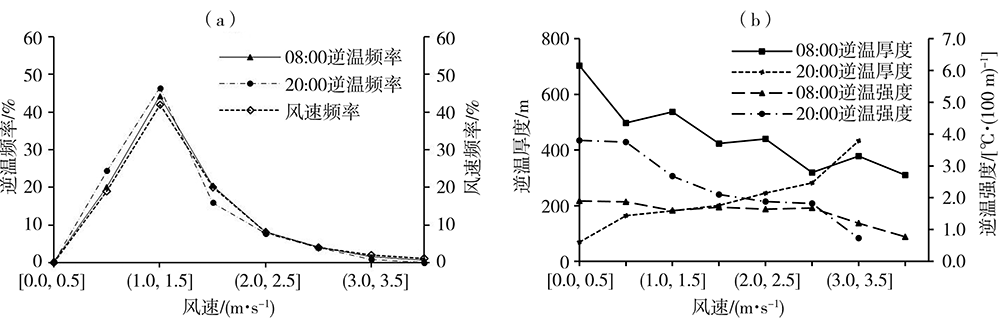
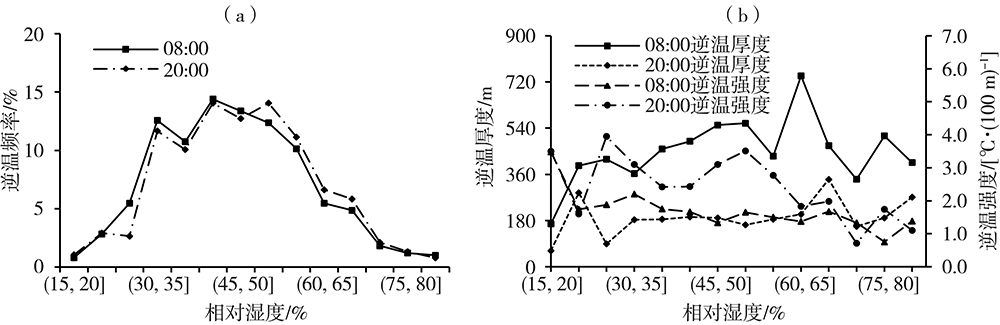
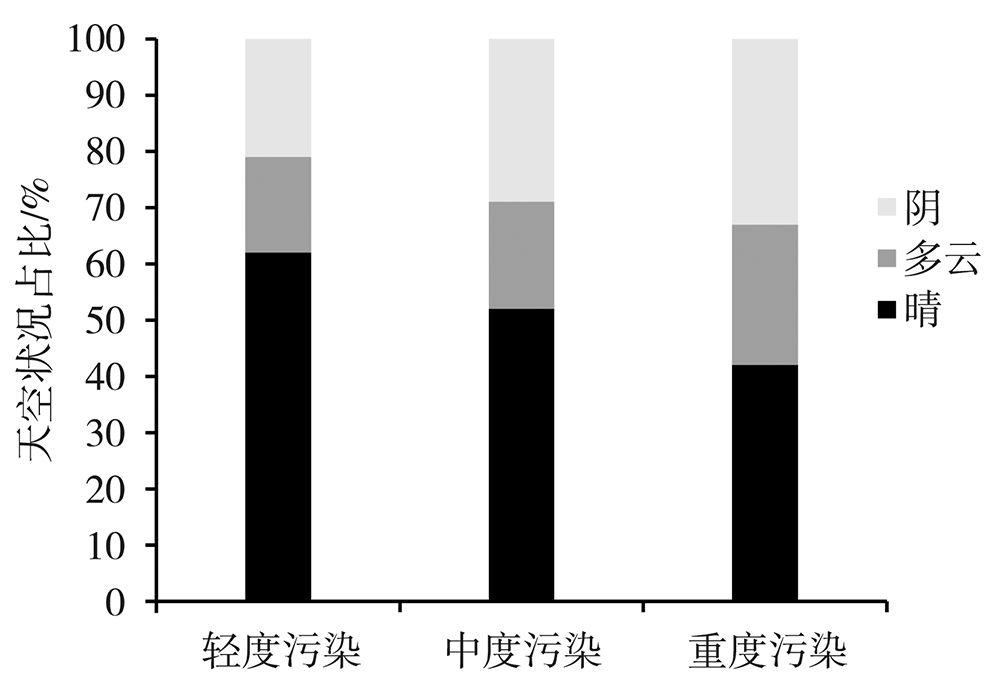
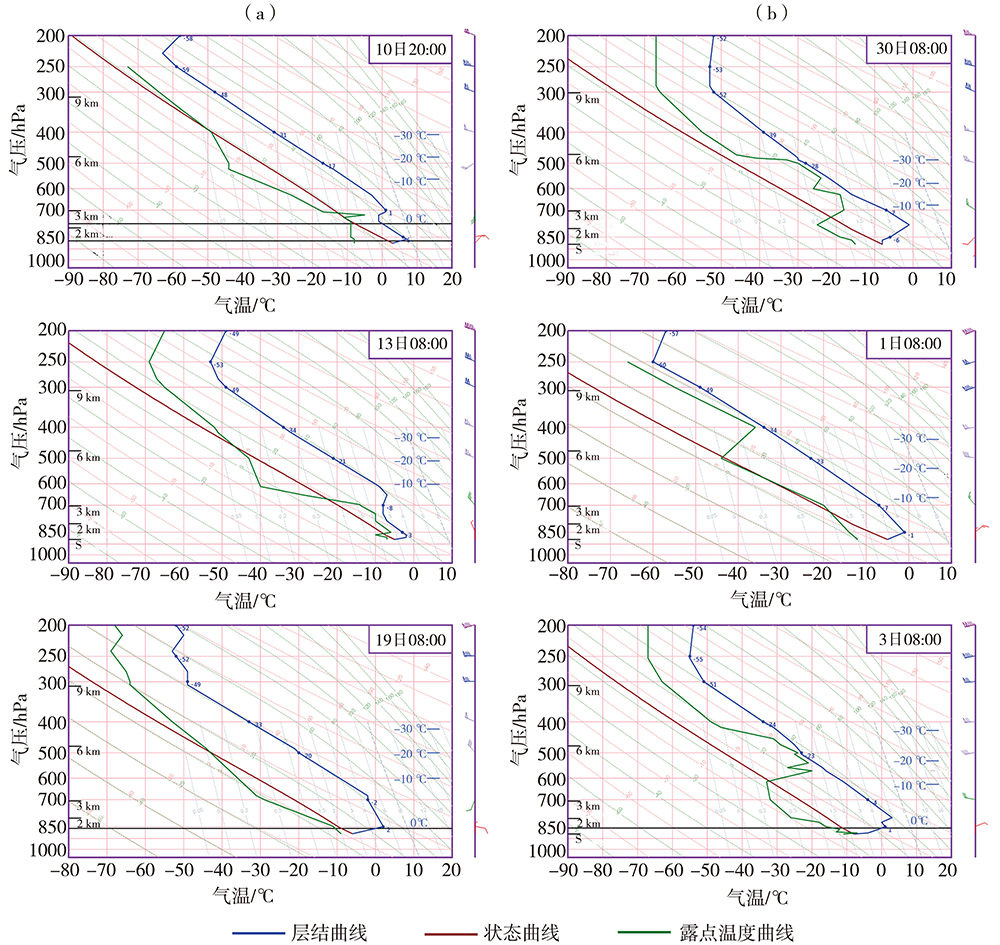
为了探究银川市大气边界层逆温特征和影响因素及其与冬季PM2.5污染的关系,利用2015—2020年银川气象站探空、地面气象观测资料及银川市空气质量监测数据,在分析银川市大气边界层逆温及地面气象要素特征基础上,以冬季为研究时段,探讨逆温与地面气象要素对PM2.5污染的影响。结果表明:(1)银川市清晨大气边界层较傍晚更易出现逆温,且逆温多为贴地逆温,贴地逆温较悬浮逆温强度大、厚度小;逆温频率和厚度冬季最大、夏季最小,逆温强度秋季最强、夏季最弱。(2)冬季晴天,地面平均风速1.0~1.5 m·s-1、相对湿度30%~60%的气象条件下易出现逆温。(3)贴地逆温是影响冬季PM2.5污染天气的主要气象因素之一,当逆温厚度超过596 m、强度超过1.4 ℃·(100 m)-1时,易出现PM2.5污染天气,且随着逆温厚度增大、强度增强,污染加重。(4)冬季PM2.5污染天气下,清晨天空状况多为晴天,通常地面平均风速小于1.3 m·s-1、相对湿度大于54%,且随着湿度增大污染加重。(5)边界层高度与PM2.5质量浓度存在显著负相关,边界层高度越低,PM2.5污染越重。
中图分类号: