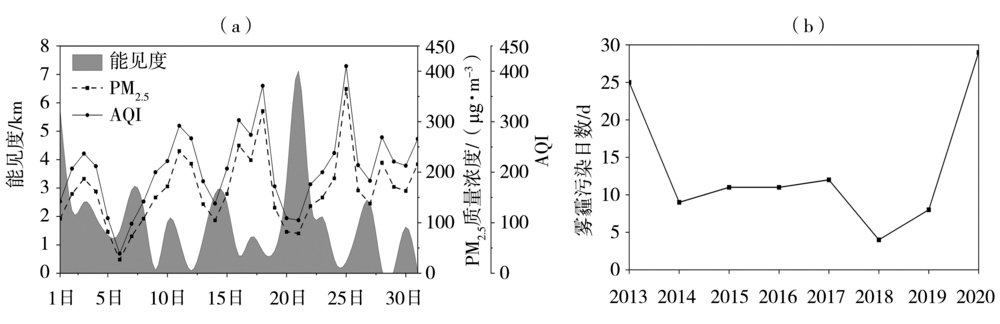
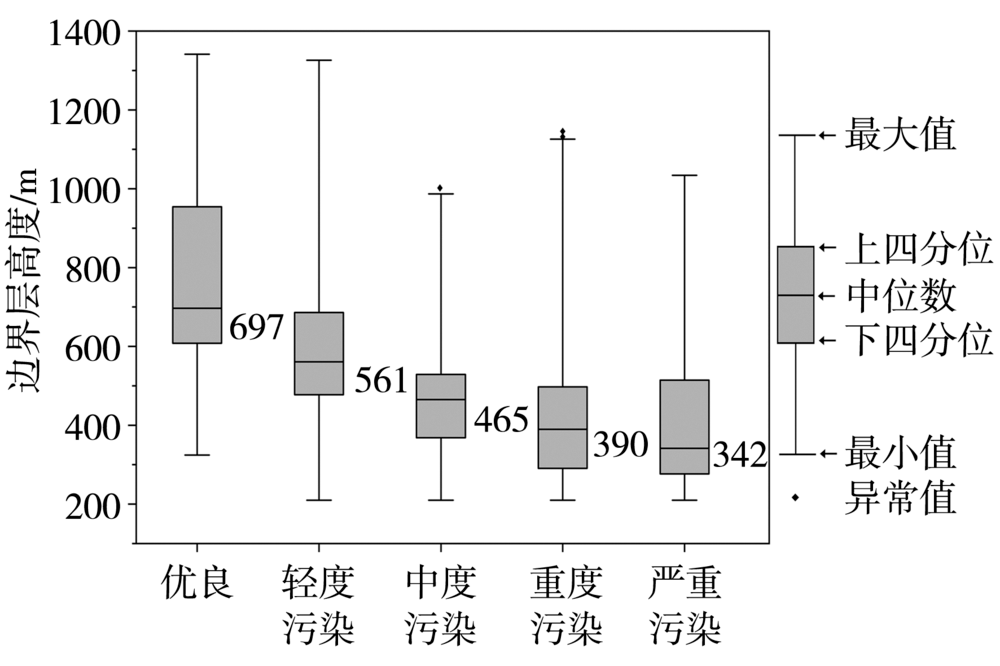
| [1] |
中国气象局. 地面气象观测规范[Z]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2003:21-27.
|
| [2] |
吴兑, 吴晓京, 朱小祥. 雾和霾[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2009.
|
| [3] |
DENG Z Z, ZHAO C S, MA N, et al. Size-resolved and bulk activation properties of aerosols in the North China plain: the importance of aerosol size distribution in the prediction of CCN number concentration[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Discussions, 2011, 11(1):3835-3846.
|
| [4] |
ZHANG Q, MENG J, QUAN J, et al. Impact of aerosol composition on cloud condensation nuclei activity[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2012, 12(268):3783-3790.
|
| [5] |
张人禾, 李强, 张若楠. 2013年1月中国东部持续性强雾霾天气产生的气象条件分析[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2014, 44(1):27-36.
|
| [6] |
李美琪, 郭蕊, 贾小卫, 等. 冀中南一次持续性大雾过程成因及维持机制[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(4):591-600.
|
| [7] |
罗贵东, 陈怡蓓, 郑文全. 达州市2016年元旦期间持续重污染天气气象条件分析[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 2017, 37(2):58-64.
|
| [8] |
杨康权, 龙柯吉, 肖递祥. 成都地区一次持续性污染过程天气特征分析[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 2016, 36(4):75-78.
|
| [9] |
赵敬国, 王式功, 王嘉媛, 等. 兰州市空气污染与气象条件关系分析[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 49(4):491-496.
|
| [10] |
范洋, 樊曙先, 张红亮, 等. 临安冬夏季SO2、NO2和O3体积分数特征及与气象条件的关系[J]. 大气科学学报, 2013, 36(1):121-128.
|
| [11] |
邹旭东, 杨洪斌, 张云海, 等. 1951─2012年沈阳市气象条件变化及其与空气污染的关系分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2015, 24(1):76-83.
|
| [12] |
李子华, 黄建平, 孙博阳, 等. 辐射雾发展的爆发性特征[J]. 大气科学, 1999, 19(5):623-631.
|
| [13] |
徐敬, 丁国安, 颜鹏, 等. 北京地区PM2.5的成分特征及来源分析[J]. 应用气象学报, 2007, 18(5):645-654.
|
| [14] |
戴永立, 陶俊, 林泽健, 等. 2006-2009年我国超大城市霾天气特征及影响因子分析[J]. 环境科学, 2013, 34(8):2925-2932.
|
| [15] |
杨东贞, 于海青, 丁国安, 等. 北京北郊冬季低空大气气溶胶分析[J]. 应用气象学报, 2002(增刊1):113-126.
|
| [16] |
范烨, 郭学良, 付丹红, 等. 北京及周边地区2004年8、9月间大气气溶胶分布特征观测分析[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2007, 12(1):49-62.
|
| [17] |
王丛梅, 杨永胜, 李永占, 等. 2013年1月河北省中南部严重污染的气象条件及成因分析[J]. 环境科学研究, 2013, 26(7):695-702.
|
| [18] |
苟玉清, 许东蓓. 成都市2017年12月下旬重污染过程及气象条件特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2018, 36(6):1012-1019.
|
| [19] |
郭立平, 乔林, 石茗化, 等. 河北廊坊市连续重污染天气的气象条件分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2015, 33(3):497-504.
|
| [20] |
张琪敏, 赵景波. 2004年中国典型城市大气污染现状及污染差异分析[J]. 贵州师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 25(2):33-36.
|
| [21] |
王玮, 汤大钢, 刘红杰, 等. 中国PM2.5污染状况和污染特征的研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2000, 20(1):1-5.
|
| [22] |
唐宜西, 张小玲, 熊亚军, 等. 北京一次持续霾天气过程气象特征分析[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2013, 29(5):12-19.
|
| [23] |
徐丽娜, 李忠, 胡亚男, 等. 2019年冬季呼和浩特市大气污染频发的气象条件分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(1):112-118.
|
| [24] |
邢雅婷, 王帅, 赵玲. 呼和浩特市城区大气污染物浓度变化特征分析[J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(5):1139-1149.
|
| [25] |
王韵杰, 张少君, 郝吉明. 中国大气污染治理: 进展·挑战·路径[J]. 环境科学研究, 2019, 32(10):1755-1762.
|
| [26] |
王鹏. 2013-2017年呼和浩特市大气污染时空变化特征[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学, 2019.
|
| [27] |
中国环境科学研究院, 中国环境监测总站. 环境空气质量指数(AQI)技术规定(试行): HJ 633-2012[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2012.
|
| [28] |
危诗敏, 冯鑫媛, 王式功, 等. 四川盆地多层逆温特征及其对大气污染的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(3):1005-1013.
|
| [29] |
周璐. 长沙市空气质量与气象条件的关系研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2018.
|
| [30] |
张珺, 宋晓辉. 2014年邯郸大气环境特征及气象条件影响因子分析[J]. 气象与环境科学, 2016, 39(2):63-68.
|
| [31] |
高怡, 张美根. 2013年1月华北地区重雾霾过程及其成因的模拟分析[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2014, 19(2):140-152.
|
| [32] |
吴兑, 廖国莲, 邓雪娇, 等. 珠江三角洲霾天气的近地层输送条件研究[J]. 应用气象学报, 2008, 19(1):1-9.
|
| [33] |
邓长菊, 尹晓惠, 甘璐. 北京雾与霾天气大气液态水含量和相对湿度层结特征分析[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2014, 19(2):193-199.
|
| [34] |
《大气科学词典》编委会. 大气科学词典[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 1994:576-576.
|
| [35] |
陈少勇, 夏权, 王劲松, 等. 西北地区晚霜冻结束日的气候变化特征及其影响因子[J]. 中国农业气象, 2013, 34(1):8-13.
|
| [36] |
王生林, 余优森. 甘肃农业霜冻灾害及其防御对策研究[J]. 甘肃农业大学学报, 2001, 36(2):226-231.
|
| [37] |
陈瑞敏, 吴雁, 康文英, 等. 连续雾霾天气污染物浓度变化及天气形势特征分析[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2014, 19(2):209-218.
|
| [38] |
徐冉, 张恒德, 杨孝文, 等. 北京地区秋冬季大气污染特征及成因分析[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(8):3405-3414.
|
| [39] |
张周祥. 秋冬季北京北部重污染事件PM1化学组分特征及气象因素的贡献[D]. 北京: 中国气象科学研究院, 2017.
|
 ), TONG Tong, JIANG Jiayu, WANG Junxiu, ZHAO Yiyong
), TONG Tong, JIANG Jiayu, WANG Junxiu, ZHAO Yiyong