干旱气象 ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (1): 64-72.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-01-0064
基于微波辐射计资料的祁连山东段大气水汽和液态水时空变化特征
把黎1,2( ), 奚立宗1(
), 奚立宗1( ), 蔡迪花3, 庞朝云1, 张鑫海4, 尹春5
), 蔡迪花3, 庞朝云1, 张鑫海4, 尹春5
- 1.甘肃省人工影响天气办公室,甘肃 兰州 730020
2.中国气象局云雾物理环境重点实验室,北京 100081
3.中国气象局兰州干旱气象研究所,甘肃 兰州 730020
4.甘肃省永登县气象局,甘肃 永登 730300
5.甘肃省气象服务中心,甘肃 兰州 730020
Spatial and temporal variation characteristics of atmospheric water vapor and liquid water in eastern section of the Qilian Mountains based on microwave radiometer data
BA Li1,2( ), XI Lizong1(
), XI Lizong1( ), CAI Dihua3, PANG Zhaoyun1, ZHANG Xinhai4, YIN Chun5
), CAI Dihua3, PANG Zhaoyun1, ZHANG Xinhai4, YIN Chun5
- 1. Gansu Weather Modification Office, Lanzhou 730020, China
2. Key Laboratory for Cloud Physics of China Meteorological Administration, Beijing 100081, China
3. Institute of Arid Meteorology, CMA, Lanzhou 730020, China
4. Yongdeng Meteorological Bureau of Gansu Province, Yongdeng 730300, Gansu, China
5. Meteorological Service Center of Gansu Province, Lanzhou 730020, China
摘要:
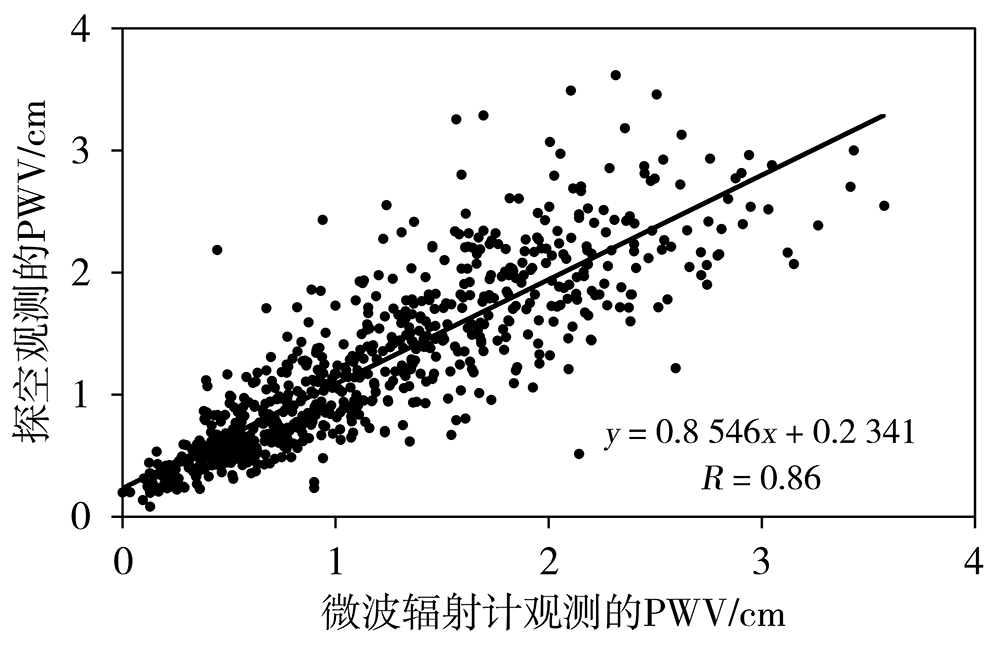
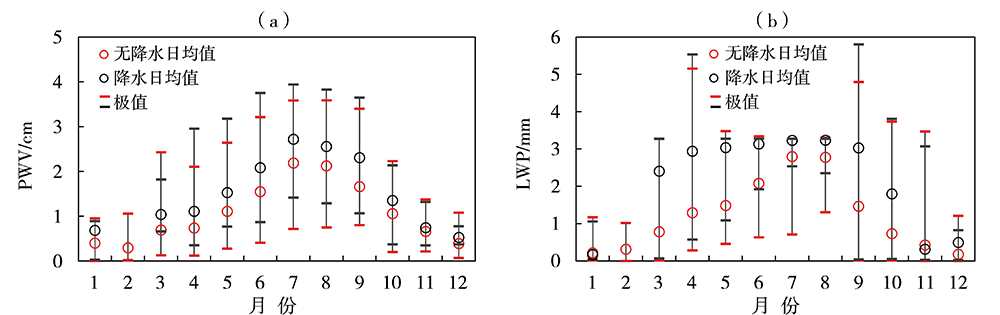
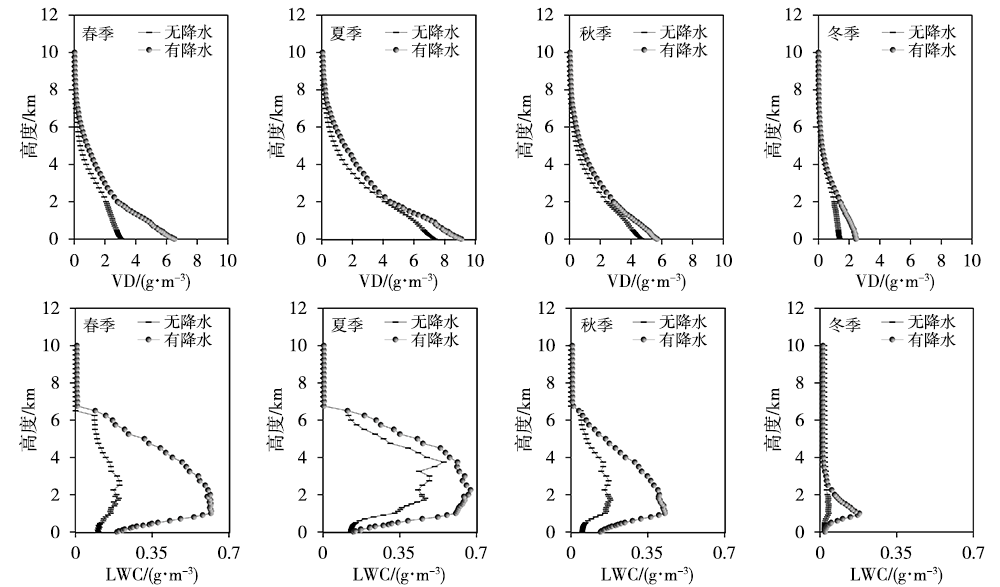
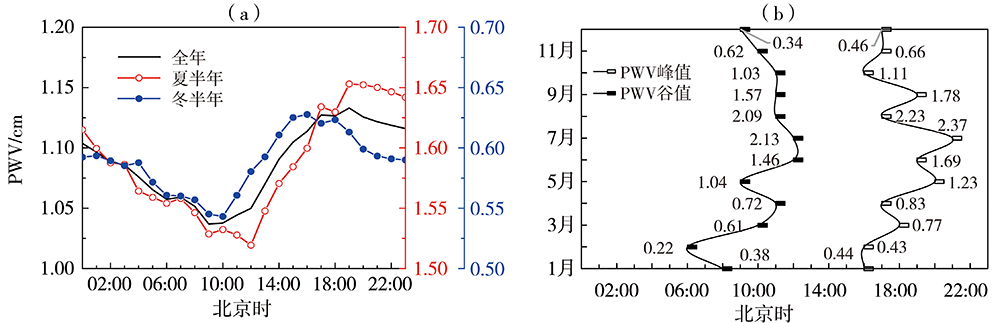
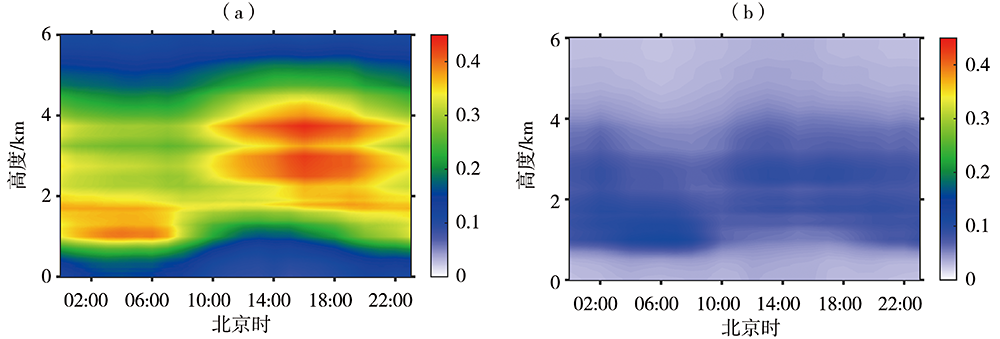
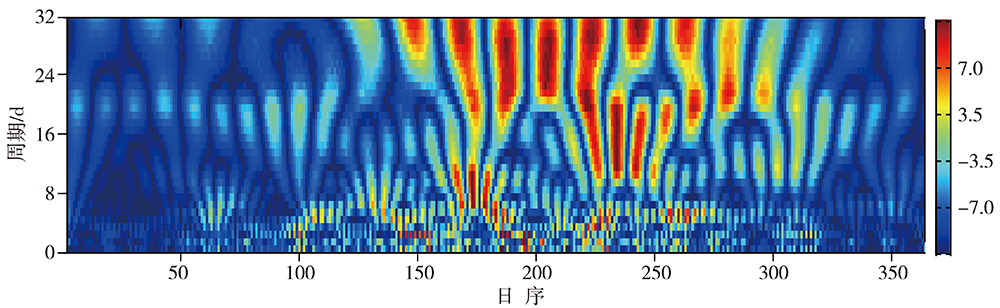
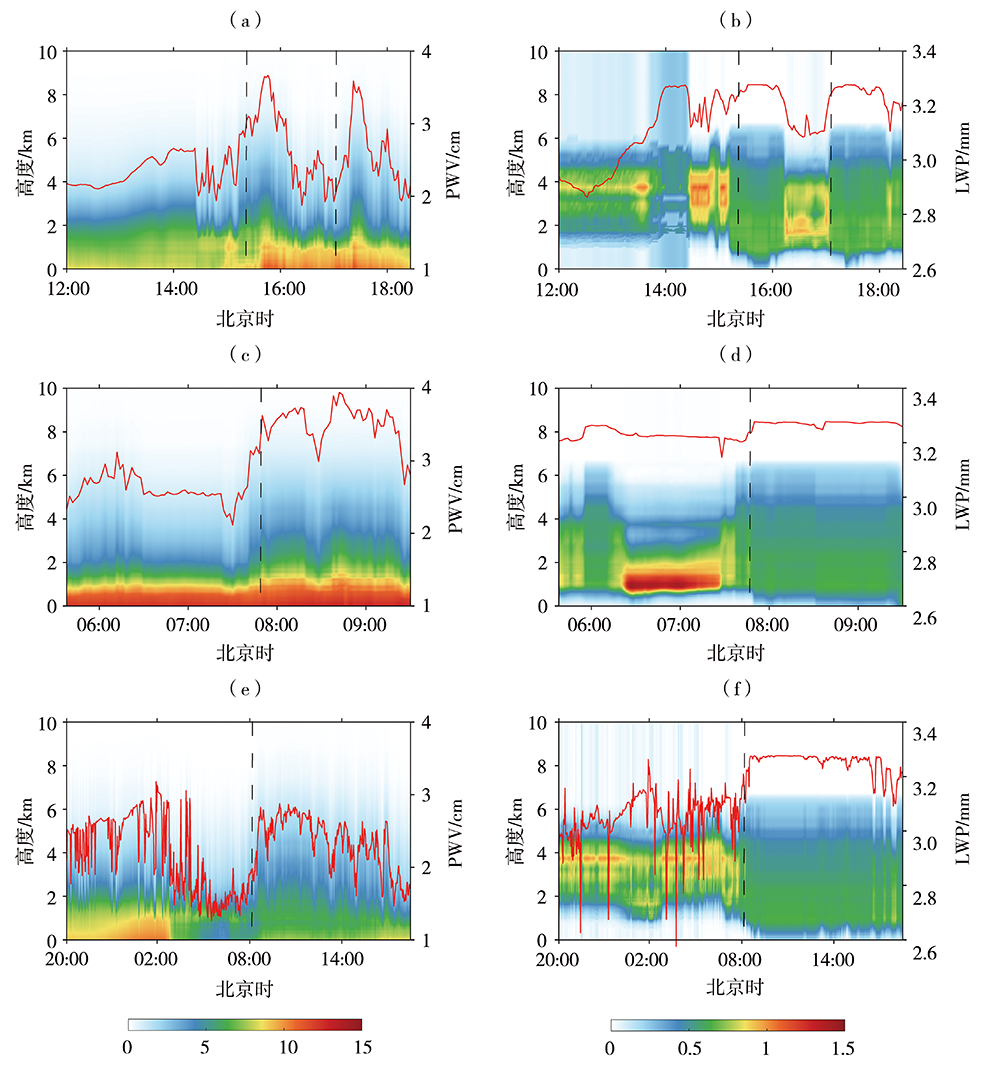
气候变暖背景下全球干旱风险升高,而对气候变化高敏感的中国西北干旱半干旱区尤为突出,严重制约着区域经济的可持续发展,科学开发空中云水资源是解决该区域水资源短缺的有效途径。利用甘肃永登国家气象观测站地基多通道微波辐射计资料和常规气象观测资料,研究祁连山东段大气水汽和液态水的时空分布及不同性质降水前演变特征。结果表明:(1)受大气环流、地形、边界层及局地和区域天气气候条件等多因素影响,祁连山东段98%以上的水汽集中在6.0 km以下,大气水汽密度随高度下降,液态水含量则随高度先增后减。降水天气背景下,水汽密度及液态水含量明显增大,且液态水含量最大值出现高度有所降低。(2)水汽及液态水存在明显的季节变化,夏季大气可降水量远大于冬季,夏季液态水垂直伸展高度及最大值出现高度均大于冬季。(3)水汽及液态水日变化明显,且存在季节差异。水汽日峰值出现在下午至傍晚,谷值出现在清晨至中午;夏半年峰值及谷值出现时间较冬半年迟,且峰谷值变化幅度更大。液态水垂直伸展高度白天高于夜间,且夏半年垂直分布较冬半年深厚。(4)大气可降水量存在10~20 d和8 d左右的主周期,夏、秋季4~7 d和21~32 d的周期变化也比较明显。(5)不同类型降水前水汽及液态水均存在跃增现象,但跃增量、跃增时间及高度存在差异。其中,7—8月积层混合云降水前跃增时间最早,积云降水前跃增量最大、跃增高度最高,而暖云降水前跃增高度明显偏低。
中图分类号: