Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (1): 11-18.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2024)-01-0011
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Cause analysis of flood-drought alternation event in July 2022 in arid and semi-arid region of Inner Mongolia
LIU Wei1,2( ), ZHAO Yanli2(
), ZHAO Yanli2( ), GAO Jing1,2, LI Linhui3, WANG Huimin2
), GAO Jing1,2, LI Linhui3, WANG Huimin2
- 1. Key Open Laboratory for Northeast China Cold Vortex Research,Shenyang 110166,China
2. Inner Mongolia Climate Center,Hohhot 010051,China
3. Inner Mongolia Meteorological Service,Hohhot 010051,China
-
Received:2023-04-11Revised:2023-06-06Online:2024-02-29Published:2024-03-06
2022年7月内蒙古干旱半干旱区涝—旱转折事件的成因分析
刘炜1,2( ), 赵艳丽2(
), 赵艳丽2( ), 高晶1,2, 李林惠3, 王慧敏2
), 高晶1,2, 李林惠3, 王慧敏2
- 1.东北冷涡研究重点开放实验室,辽宁 沈阳 110166
2.内蒙古自治区气候中心,内蒙古 呼和浩特 010051
3.内蒙古自治区气象局,内蒙古 呼和浩特 010051
-
通讯作者:赵艳丽(1969—),女,内蒙古满洲里人,硕士,正高级工程师,主要从事气象灾害监测、预报预警和评估研究。E-mail: 861952609@qq.com。 -
作者简介:刘炜(1986—),女,内蒙古呼和浩特人,硕士,高级工程师,主要从事气候预测与异常机理诊断方面的研究。E-mail: liuwei.05@163.com。 -
基金资助:中国气象局沈阳大气环境研究所联合开放基金项目(2022SYIAEKFMS08);中国气象局沈阳大气环境研究所联合开放基金项目(2021SYIAEKFMS13);内蒙古气象局科技创新项目(nmqxkjcx202444);内蒙古自治区科技重大专项专题(2020ZD0013-02);内蒙古自治区科技计划项目(2020GG0017);内蒙古自治区自然科学基金项目(2022LHMS04004)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LIU Wei, ZHAO Yanli, GAO Jing, LI Linhui, WANG Huimin. Cause analysis of flood-drought alternation event in July 2022 in arid and semi-arid region of Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(1): 11-18.
刘炜, 赵艳丽, 高晶, 李林惠, 王慧敏. 2022年7月内蒙古干旱半干旱区涝—旱转折事件的成因分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(1): 11-18.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2024)-01-0011

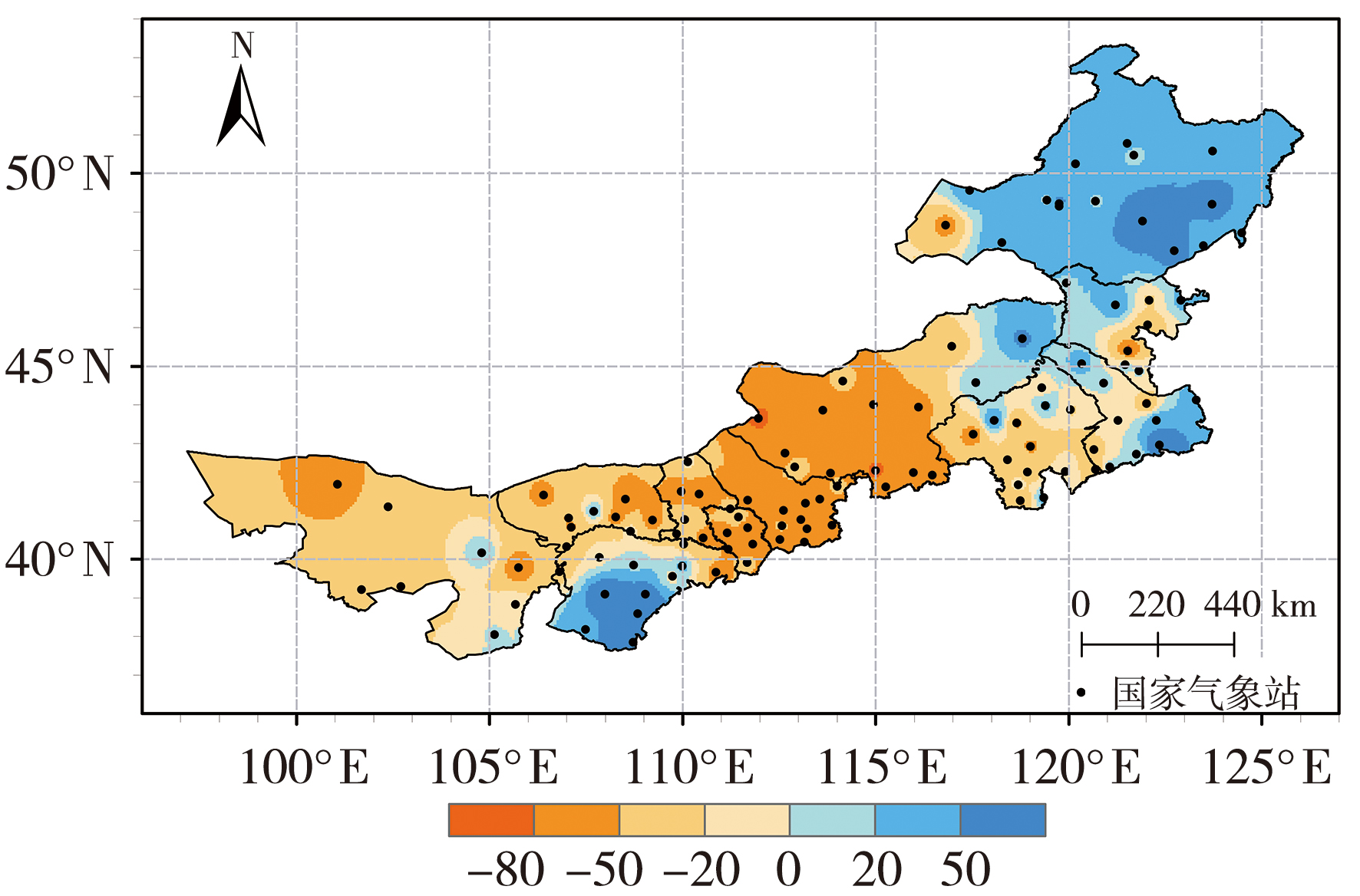
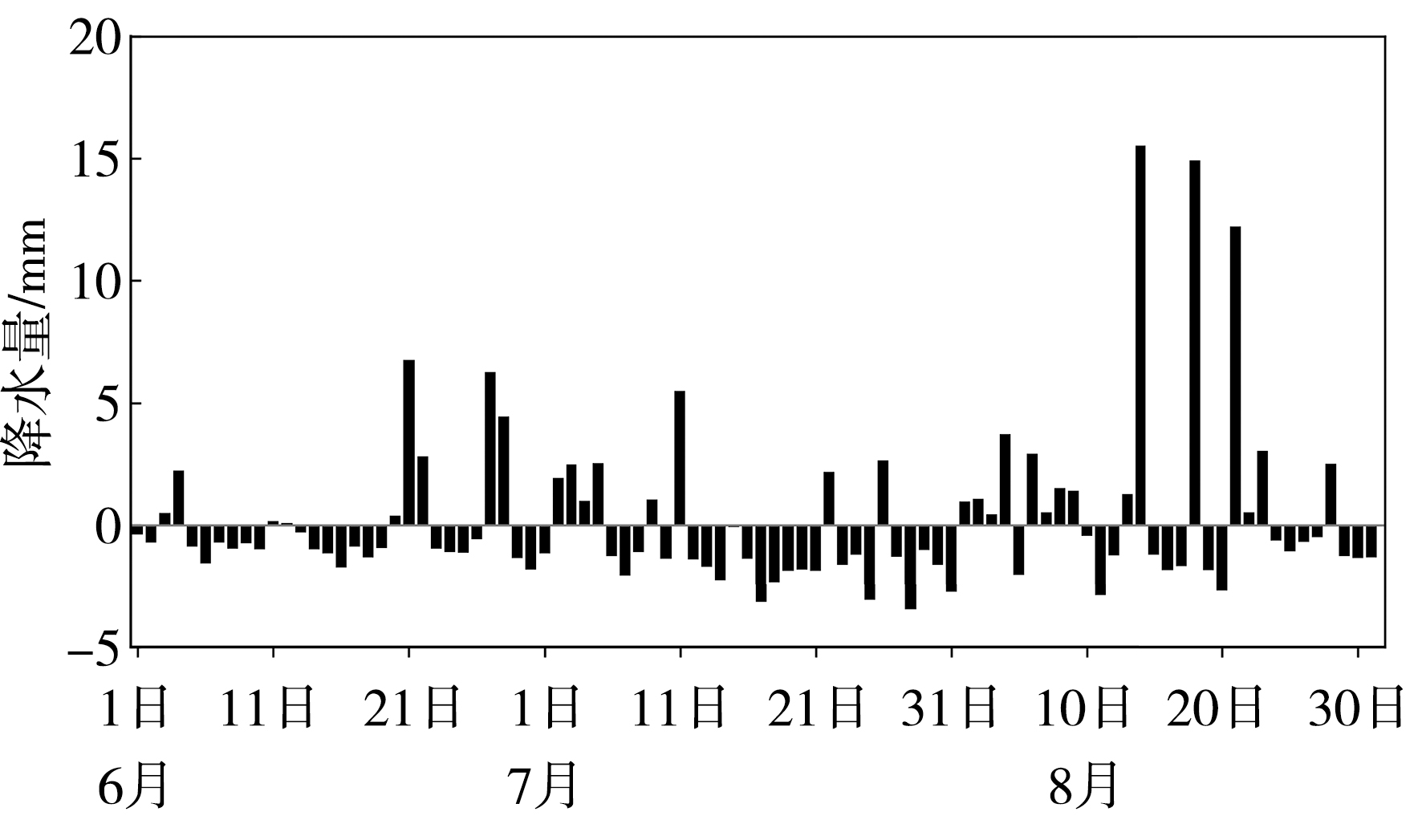
Fig.2 Spatial distribution of the first REOF mode (a) and its normalized time coefficients (b) of precipitation in July during 1991-2022 (The red rectangle box for the location of midwest Inner Mongolia. the same as below)
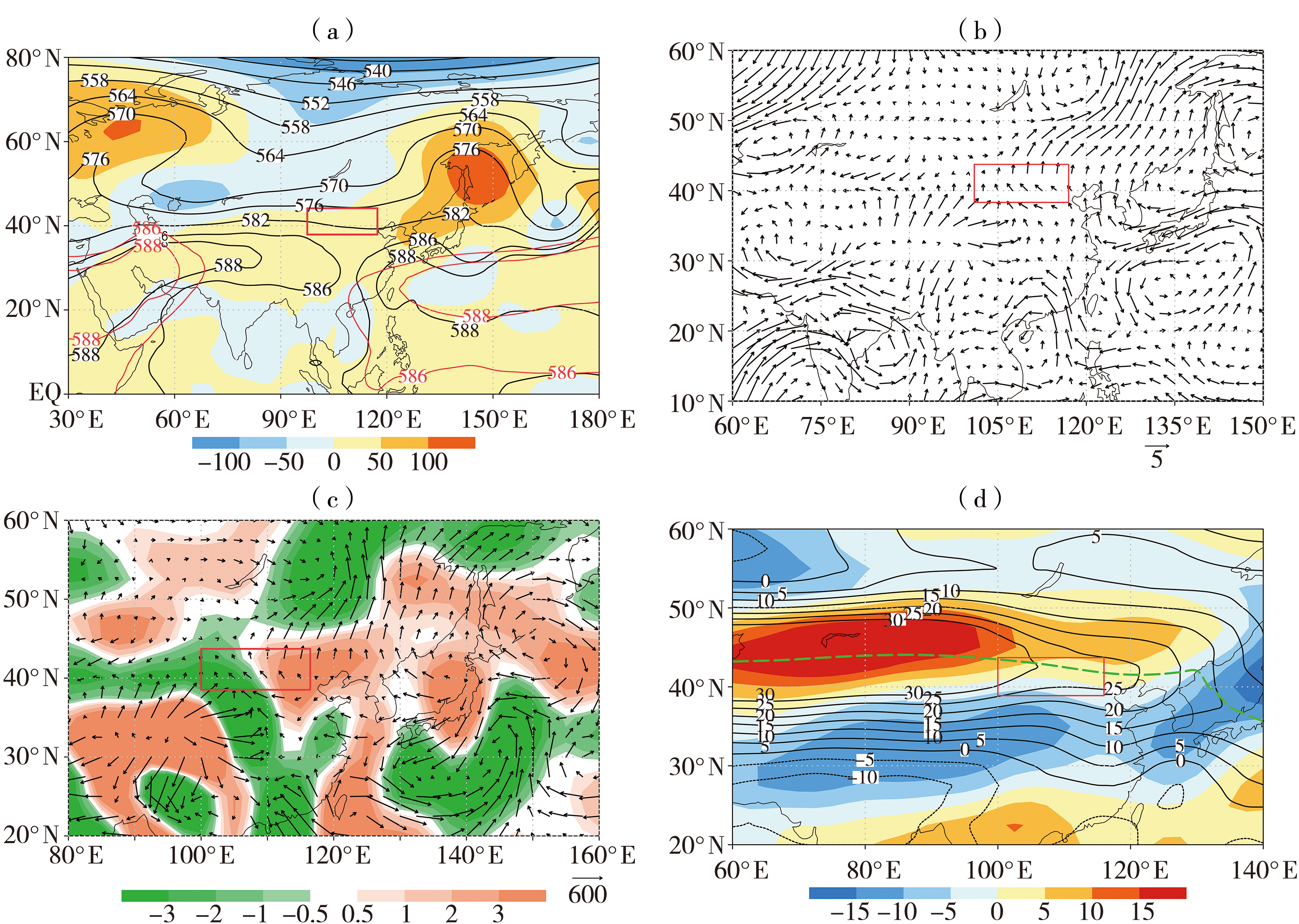
Fig.4 The 500 hPa geopotential height field (contours) and its anomalies field (color shaded) (a, Unit: dagpm), 850 hPa wind field anomalies (b, Unit: m·s-1), integral water vapor flux over the whole troposphere (vectors, Unit: kg·m-1·s-1) and its divergence (color shaded, Unit: 10-5 kg·m-2·s-1) anomaly field (c), 200 hPa zonal wind field (contours) and its anomalies (color shaded) in East Asia area (d, Unit: m·s-1) from 1 to 11 July 2022 (the red solid lines for climatological mean line of 586 and 588 dagpm, the green thick dashed line for the location of westerly jet axis. the same as below)

Fig.5 The average meridional circulation(stream lines,Unit: m·s-1) and vertical velocity(color shaded,Unit: 10-2 Pa·s-1) profile over the range of 100.0°E-117.5°E from 1 to 11 July 2022 (The midwest of Inner Mongolia is located between the two red lines. the same as below)

Fig.6 The 500 hPa geopotential height field (contours) and its anomalies field (color shaded) (a, Unit: dagpm), 850 hPa wind field anomalies (b, Unit: m·s-1), integral water vapor flux over the whole troposphere (vectors, Unit: kg·m-1·s-1) and its divergence (color shaded, Unit: 10-5kg·m-2·s-1) anomaly (c), 200 hPa zonal wind field (contours) and its anomalies (color shaded) in East Asia area (d, Unit: m·s-1) from 12 to 31 July 2022

Fig.7 The average meridional circulation(stream lines,Unit: m·s-1) and vertical velocity(color shaded,Unit: 10-2 Pa·s-1) profile over the range of during 100.0°E-117.5°E from 12 to 31 July 2022

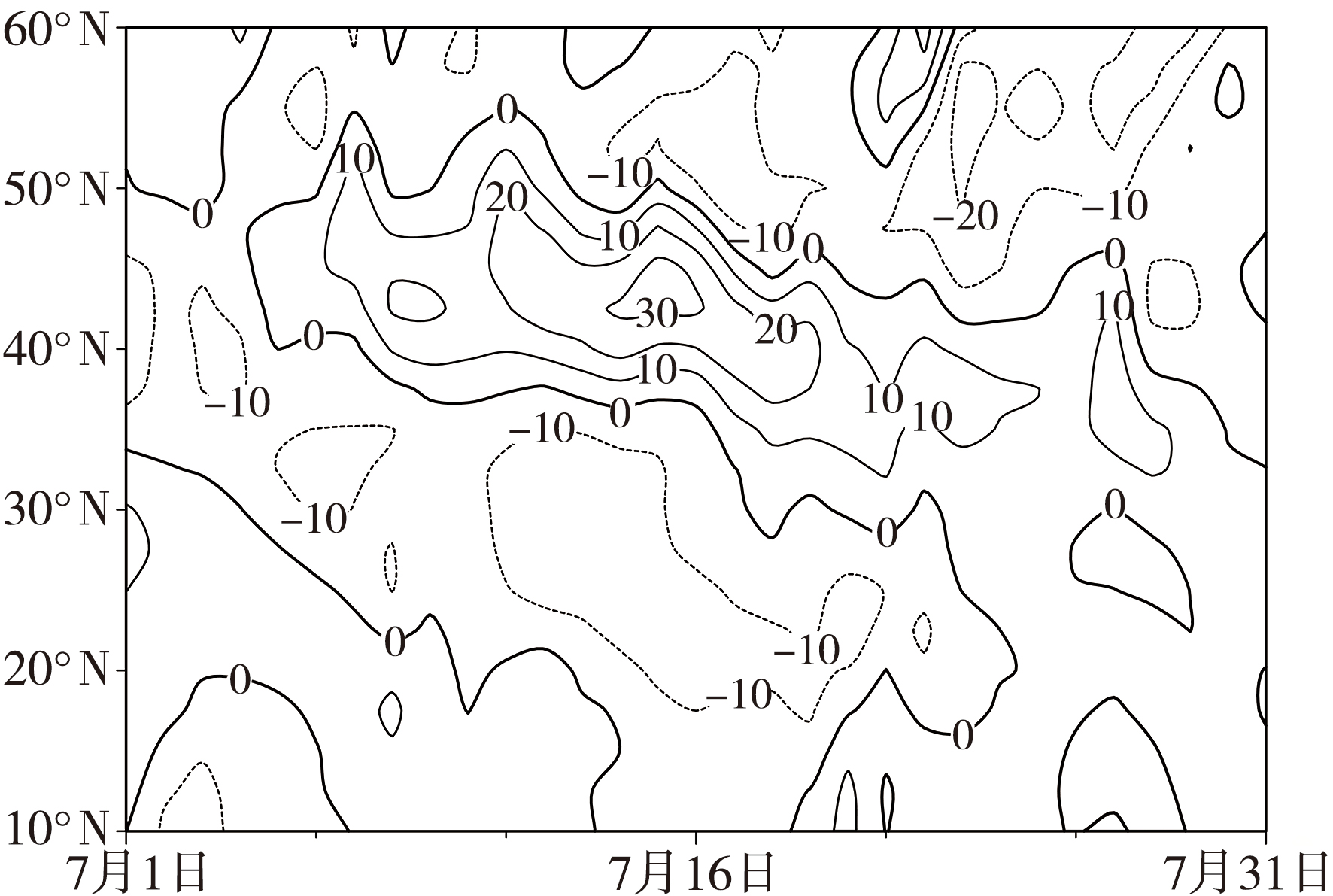
Fig.9 The difference field of the averaged geopotential height between 1-11 and 12-31 July 2022 (Unit: gpm) (the dotted areas passing the significant test at α=0.05. the same as below)

Fig.10 Composited sea surface temperature anomaly fields in flood-drought alternation years from 1990 to 2022 (a) and the sea surface temperature anomaly field in July 2022 (b) in middle and western Inner Mongolia(Unit: ℃)
| [1] | 陈廷芝, 尤莉, 古月, 2010. 2009年汛期内蒙古干旱少雨成因[J]. 干旱气象, 28(2): 167-172. |
| [2] | 陈廷芝, 尤莉, 古月, 等, 2012. 2010年夏季内蒙古干旱高温成因分析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 26(1): 88-92. |
| [3] | 封国林, 杨涵洧, 张世轩, 等, 2012. 2011年春末夏初长江中下游地区旱涝急转成因初探[J]. 大气科学, 36(5): 1 009-1 026. |
| [4] |
董祝雷, 白美兰, 衣娜娜, 2018. 内蒙古夏季降水与亚洲纬向环流的联系[J]. 干旱气象, 36(2): 256-262.
DOI |
| [5] |
郭其蕴, 1983. 东亚夏季风强度指数及其变化的分析[J]. 地理学报, 38(3): 207-217.
DOI |
| [6] | 侯琼, 乌兰巴特尔, 2006. 内蒙古典型草原区近40年气候变化及其对土壤水分的影响[J]. 气象科技, 34(1): 102-106. |
| [7] | 黄荣辉, 蔡榕硕, 陈际龙, 等, 2006. 我国旱涝气候灾害的年代际变化及其与东亚气候系统变化的关系[J]. 大气科学, 30(5): 730-743. |
| [8] |
焦敏, 李辑, 王阳, 等, 2018. 2014年盛夏辽宁异常少雨的大尺度环流特征[J]. 干旱气象, 36(5): 751-757.
DOI |
| [9] | 李栋梁, 邵鹏程, 王慧, 2013. 1951-2009年东亚副热带夏季风北边缘位置的地域特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 33(5): 230-238. |
| [10] | 李栋梁, 吕兰芝, 2002. 中国农牧交错带的气候特征与演变[J]. 中国沙漠, 22 (5): 76-81. |
| [11] | 李栋梁, 张茜, 姚慧茹, 等, 2016. 北印度夏季风与中国河套及邻近地区盛夏降水的联系[J]. 高原气象, 35(6): 1 512-1 523. |
| [12] |
李忆平, 张金玉, 岳平, 等, 2022. 2022年夏季长江流域重大干旱特征及其成因研究[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5): 733-747.
DOI |
| [13] | 李崇银, 王作台, 林士哲, 等, 2004. 东亚夏季风活动与东亚高空西风急流位置北跳关系的研究[J]. 大气科学, 28(5): 641-658. |
| [14] | 李妍, 布和朝鲁, 林大伟, 等, 2016. 内蒙古夏季降水变率的优势模态及其环流特征[J]. 大气科学, 40(4): 756-776. |
| [15] | 李海英, 高晶, 张宇, 等, 2019. 内蒙古春季降水的气候特征及预测思路[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 13(4): 79-87. |
| [16] |
林纾, 李红英, 黄鹏程, 等, 2022. 2022年夏季我国高温干旱特征及其环流形势分析[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5): 748-763.
DOI |
| [17] | 刘炜, 赵艳丽, 2020. 内蒙古中西部地区2018年夏季异常多雨成因[J]. 干旱气象, 38(5): 709-715. |
| [18] | 刘炜, 赵艳丽, 冯晓晶, 2021. 内蒙古地区夏季旱涝急转环流异常特征及其预测[J]. 干旱气象, 39(2): 203-214. |
| [19] | 陆日宇, 林中达, 张耀存, 2013. 夏季东亚高空急流的变化及其对东亚季风的影响[J]. 大气科学, 37(2): 331-340. |
| [20] | 廖清海, 高守亭, 王会军, 等, 2004. 北半球夏季副热带西风急流变异及其对东亚夏季风气候异常的影响[J]. 地球物理学报, 47(1): 10-18. |
| [21] |
娄德君, 李永生, 王永光, 等, 2022. 2020年7月黑龙江极端少雨成因初探[J]. 干旱气象, 40(3): 396-405.
DOI |
| [22] | 马清霞, 2002. 内蒙古地区2001年夏季气候特征及前兆信号分析[J]. 气象, 28(12): 11-14. |
| [23] | 马清霞, 高晶, 包福祥, 2013. 2012年汛期内蒙古大范围降水偏多成因分析[J]. 内蒙古气象, (6): 3-6. |
| [24] | 罗哲贤, 2005. 中国西北干旱气候动力学引论[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [25] |
邵鹏程, 李栋梁, 王春学, 2015. 近50年黄河流域夏季降水的时空变化及其与东亚副热带西风急流的关系[J]. 高原气象, 34(2): 347-356.
DOI |
| [26] | 武炳义, 张人禾, 2011. 东亚夏季风年际变率及其与中、高纬度大气环流以及外强迫异常的联系[J]. 气象学报, 69(2): 219-233. |
| [27] | 武荣盛, 侯琼, 杨玉辉, 等, 2021. 多时间尺度气象干旱指数在内蒙古典型草原的适应性研究[J]. 干旱气象, 39(2): 177-184. |
| [28] | 杨莲梅, 张庆云, 2007. 夏季东亚西风急流扰动异常与副热带高压关系研究[J]. 应用气象学报, 18(4): 452-459. |
| [29] | 姚慧茹, 李栋梁, 王慧, 2017. 1981—2012年西北东部夏季降水不同强度雨日变化及其环流特征的对比分析. 气象学报, 75(3): 384-399. |
| [30] | 宣守丽, 张庆云, 孙淑清, 等, 2013. 夏季逐月东亚高空急流异常对我国降水的影响[J]. 气候与环境研究, 18 (6): 781-792. |
| [31] | 张培忠, 杨素兰, 1996. 阻塞高压活动的气候变化及其对中国某些地区旱涝的影响[J]. 气象学报, 54(5): 633-640. |
| [32] | 张庆云, 宣守丽, 孙淑清, 2018. 夏季东亚高空副热带西风急流季节内异常的环流特征及前兆信号[J]. 大气科学, 42(4): 935-950. |
| [33] | KALNAY E, KANAMITSU M, KISTLER R, et al, 1996. The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 77(3): 437-471. |
| [34] | LU R Y, 2004. Associations among the components of the East Asian summer monsoon system in the meridional direction[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan Ser Ⅱ, 82(1): 155-165. |
| [35] | LIN Z D, LU R Y, 2005. Interannual meridional displacement of the East Asian upper-tropospheric jet stream in summer[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 22(2): 199-211. |
| [36] | SMITH T M, REYNOLDS R W, 2004. Improved extended reconstruction of SST (1854-1997)[J]. Journal of Climate, 17(12): 2 466-2 477. |
| [1] | LUO Xiaoling, YANG Mei, ZHAO Huihua, LI Yanying, JIANG Jufang, FU Fenqi. Influence analysis of El Niño event on temperature, precipitation and meteorological drought in Wuwei, Gansu [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(6): 849-859. |
| [2] | MA Siyuan, JIN Yan, ZHANG Si, WANG Chuqin, MA Zhimin. Different impacts of El Niño/Southern Oscillation events on autumn meteorological drought in Yunnan Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(6): 860-872. |
| [3] | WANG Yun, WANG Lijuan, LU Xiaojuan, ZHANG Jinyu, WANG Zhilan, SHA Sha, HU Die, YANG Yang, YAN Pengcheng, LI Yiping. Analysis of the characteristics and causes of drought in China in the first half of 2023 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(6): 884-896. |
| [4] | ZHAO Huizhen, HE Tao, GUO Ruixia, WANG Chengfu, ZHANG Yanrong, LI Qi. Meteorological drought variation characteristics in the Gannan Plateau based on standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(5): 688-696. |
| [5] | WANG Ying, ZHANG Shu, XU Yongqing, QUE Linjing, LI Xinhua, HUANG Yingwei, CHEN Xue, WANG Lei. Meteorological drought and atmospheric circulation anomalies characteristics in Heilongjiang Province from May to September in recent 50 years [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(4): 540-549. |
| [6] | CAI Yiheng, LI Shuai, ZHANG Qiang, DENG Biao, LUO Yu, SUN Rui. Spatio-temporal variation of drought in Sichuan Province from 1997 to 2021 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(2): 241-250. |
| [7] | JIANG Shujie, CHENG Ying, FANG Nan, ZHOU Yuquan, SHAN Zhonghua, ZHANG Lei. Construction of artificial precipitation demand level index of the reservoir based on drought and water level characteristics [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(2): 341-349. |
| [8] | XUE Liang, YUAN Shujie, WANG Jinsong. Progress and prospects of research on causes of meteorological drought in different regions in China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(1): 1-13. |
| [9] | WU Rongsheng, HOU Qiong, YANG Yuhui, FENG Xuyu, LI Bin, ZHENG Fengjie. Applicability Evaluation of Multi-time-scales Meteorological Drought Indexes in Typical Steppe of Inner Mongolia [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(2): 177-184. |
| [10] | GAO Ruina, WANG Suyan, GAO Na, ZUO Hejiang. Application Comparison of CI and MCI Drought Indexes in Ningxia [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(2): 185-192. |
| [11] | SHI Shangyu, WANG Fei, JIN Kai, DING Wenbin. Response of Vegetation Index to Meteorological Drought over Loess Plateau [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(1): 1-13. |
| [12] | YUE Yanyu1, WU Cuihong1, ZHOU Yue2, CHEN Sainan1, QIN Pengcheng2. Weather Feature and Service Points of Extreme High Temperature Under Different Circulation Situation [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(6): 1027-. |
| [13] | LI Yiping, LI Yaohui. Advances in Adaptability of Meteorological Drought Indices in China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(5): 709-723. |
| [14] | SUN Linhua,FENG Jianying,LI Zhunlong,XU Juan,ZHANG Ming. Design and Implementation of Test Platform on the Meteorological Drought Monitoring and Early Warning Service in China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2014, 32(1): 142-146. |
| [15] | WANG Suyan,ZHENG Guangfen,LI Xin,LI Zhenglin,YANG Jianling,FENG Jianmin. Modification of CI Comprehensive Meteorological Drought Index and Its Application in Ningxia [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2013, 31(3): 561-569. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||