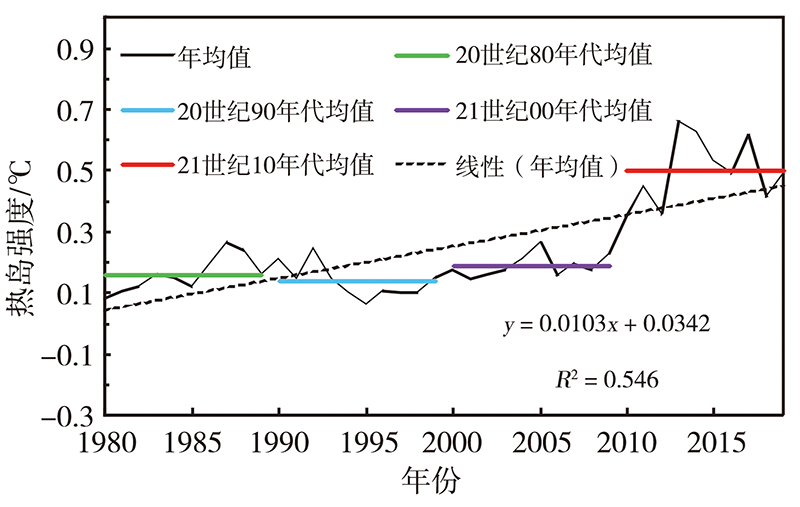
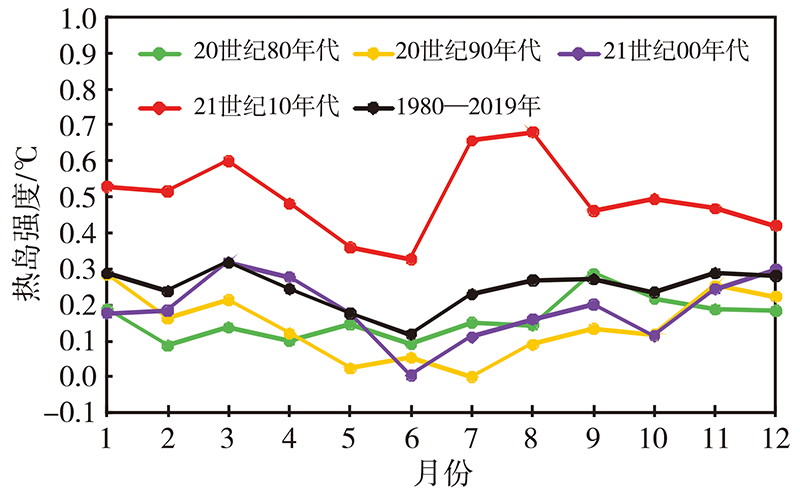
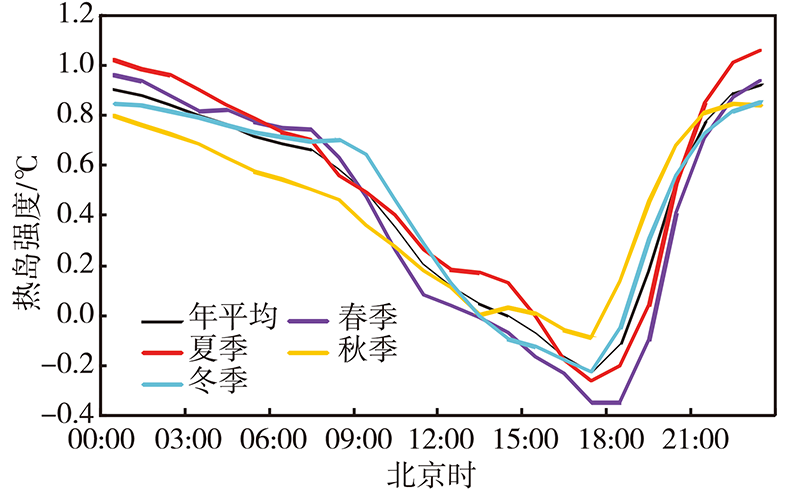
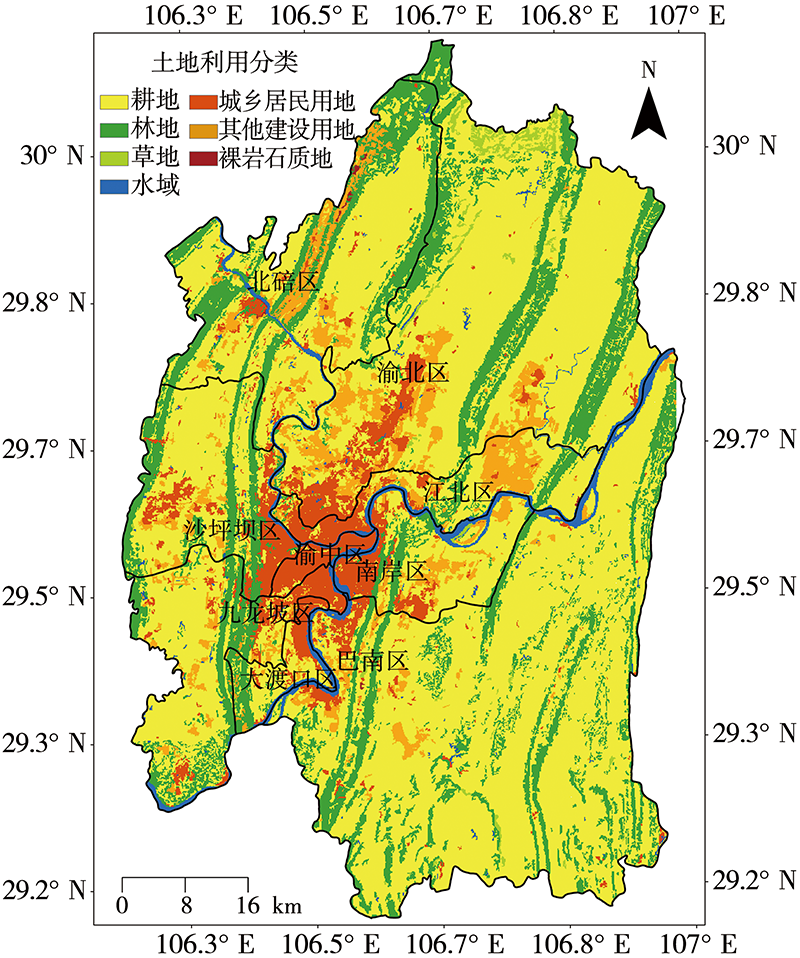
| [1] |
HE X D, WANG J, FENG J M, et al. Observational and modeling study of interactions between urban heat island and heatwave in Beijing[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 247, 119169. DOI:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119169.
|
| [2] |
RIZVI S H, ALAM K, IQBAL M J. Spatio-temporal variations in urban heat island and its interaction with heat wave[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 2019, 185: 50-57.
|
| [3] |
WARD K, LAUF S, KLEINSCHMIT B, et al. Heat waves and urban heat islands in Europe: a review of relevant drivers[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 569:527-539.
|
| [4] |
金丽娜, 李雄飞, 杜萌萌, 等. 基于FY-3卫星数据的西安市城市热岛特征分析[J]. 气象与环境科学, 2019, 42(4):74-82.
|
| [5] |
宋轩, 段金龙, 杜丽平. 城市热岛效应研究概况[J]. 气象与环境科学, 2009, 32(3):68-72.
|
| [6] |
杨续超, 陈锋, 祝炜平, 等. 城市化对浙江省夏季极端高温事件的影响[J]. 热带气象学报, 2014, 30(4):719-726.
|
| [7] |
谈建国, 郑有飞, 彭丽, 等. 城市热岛对上海夏季高温热浪的影响[J]. 高原气象, 2008, 27(增刊1):144-149.
|
| [8] |
LI H D, SODOUDI S, LIU J F, et al. Temporal variation of urban aerosol pollution island and its relationship with urban heat island[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2020, 241, 104957.DOI:10.1016/j.atmosres.2020.104957.
|
| [9] |
史军, 梁萍, 万齐林, 等. 城市气候效应研究进展[J]. 热带气象学报, 2011, 27(6):942-951.
|
| [10] |
朱焱, 刘红年, 沈建, 等. 苏州城市热岛对污染扩散的影响[J]. 高原气象, 2016, 35(6):1584-1594.
|
| [11] |
PENG J, HU Y X, DONG J Q, et al. Quantifying spatial morphology and connectivity of urban heat islands in a megacity: a radius approach[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 714, 136792. DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136792.
|
| [12] |
WANG W M, LIU K, TANG R, et al. Remote sensing image-based analysis of the urban heat island effect in Shenzhen, China[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C, 2019, 110:168-175.
|
| [13] |
董良鹏, 江志红, 沈素红. 近十年长江三角洲城市热岛变化及其与城市群发展的关系[J]. 大气科学学报, 2014, 37(2):146-154.
|
| [14] |
卞子浩, 马超群, 王迪, 等. 西安地区热岛效应与景观生态格局相关性研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2016, 34(2):342-348.
|
| [15] |
丁硕毅, 乔冠瑾, 郭媛媛, 等. 珠三角城市群热岛及其气象影响因子研究[J]. 热带气象学报, 2015, 31(5):681-690.
|
| [16] |
邓玉娇, 王捷纯, 何全军, 等. 基于MODIS资料分析近15年广州城市热岛特征及演变规律[J]. 热带气象学报, 2018, 34(6):755-762.
|
| [17] |
尚建设, 李本亮, 孙小丽, 等. 济南市夏季城市热岛效应特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2018, 36(1):70-74.
|
| [18] |
刘伟东, 尤焕苓, 孙丹. 1971—2010年京津冀大城市热岛效应多时间尺度分析[J]. 气象, 2016, 42(5):598-606.
|
| [19] |
黄利萍, 苗峻峰, 刘月琨. 天津城市热岛效应的时空变化特征[J]. 大气科学学报, 2012, 35(5):620-632.
|
| [20] |
吴遥, 唐红玉, 蒋兴文, 等. 重庆市一次特强区域性高温天气过程诊断[J]. 干旱气象, 2019, 37(5):817-826.
|
| [21] |
周长春, 汪丽, 郭善云, 等. 四川盆地高温热浪时空特征及预报模型研究[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 2014, 34(3): 51-57.
|
| [22] |
易佳, 田永中, 高阳华, 等. 基于RS的山地城市热岛效应及其与土地覆被变化关系研究——以重庆市主城区为例[J]. 云南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 28(6):62-69.
|
| [23] |
但尚铭, 安海锋, 但玻, 等. 基于AVHRR和DEM的重庆城市热岛效应分析[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2009, 18(7):680-685.
|
| [24] |
李成范, 刘岚, 周廷刚, 等. 基于定量遥感技术的重庆市热岛效应[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2009, 18(1):60-65.
|
| [25] |
陶于祥, 许凯丰, 易宗旺, 等. 基于半变异函数的城市热岛空间异质性分析[J]. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 40(10):145-152.
|
| [26] |
何泽能, 李永华, 陈志军, 等. 重庆市2006年夏季城市热岛分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 2008, 24(5):527-532.
|
| [27] |
何泽能, 杨世琦, 唐晓萍, 等. 重庆市城市热岛研究的现状需求和建议[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 2010, 30(4):85-88.
|
| [28] |
何泽能, 高阳华, 上官昌贵, 等. 盛夏重庆下垫面温度及对热岛效应的影响浅析[J]. 气象灾害防御, 2018, 25(2):14-17.
|
| [29] |
孙永, 王咏薇, 高阳华, 等. 复杂地形条件下城市热岛及局地环流特征的数值模拟[J]. 大气科学学报, 2019, 42(2):280-292.
|
| [30] |
朱丽, 苗峻峰, 高阳华. 重庆城市热岛环流结构和湍流特征的数值模拟[J]. 大气科学, 2020, 44(3):657-678.
|
| [31] |
吴兑, 邓雪娇. 环境气象学与特种气象预报[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2001:15-16.
|
| [32] |
PENG Y D, LI W S, LUO X B, et al. A geographically and temporally weighted regression model for spatial downscaling of MODIS land surface temperatures over urban heterogeneous regions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience & Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(7):5012-5027.
|
| [33] |
张勇, 余涛, 顾行发, 等. CBERS-02 IRMSS热红外数据地表温度反演及其在城市热岛效应定量化分析中的应用[J]. 遥感学报, 2006, 10(5):789-797.
|
| [34] |
赵小锋, 叶红. 热岛效应季节动态随城市化进程演变的遥感监测[J]. 生态环境学报, 2009, 18(5):1817-1821.
|
| [35] |
罗小波, 陈丹, 刘明皓, 等. 基于HJ-1B/IRS的重庆市热岛效应监测应用[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2011, 13(6):833-839.
|
 ), ZHANG Dejun1,2, YE Qinyu1,2, CHEN Zhijun1,2, YANG Shiqi1,2, GAO Yanghua1,2
), ZHANG Dejun1,2, YE Qinyu1,2, CHEN Zhijun1,2, YANG Shiqi1,2, GAO Yanghua1,2
 ), 张德军1,2, 叶勤玉1,2, 陈志军1,2, 杨世琦1,2, 高阳华1,2
), 张德军1,2, 叶勤玉1,2, 陈志军1,2, 杨世琦1,2, 高阳华1,2