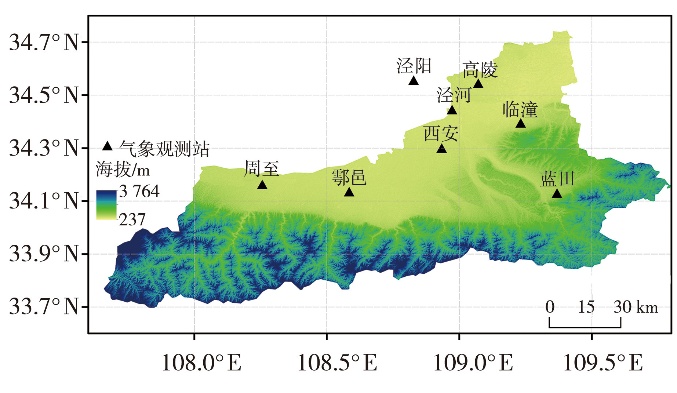
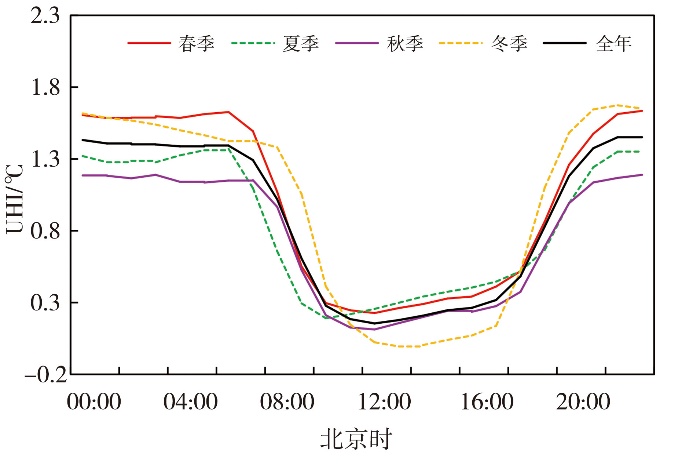
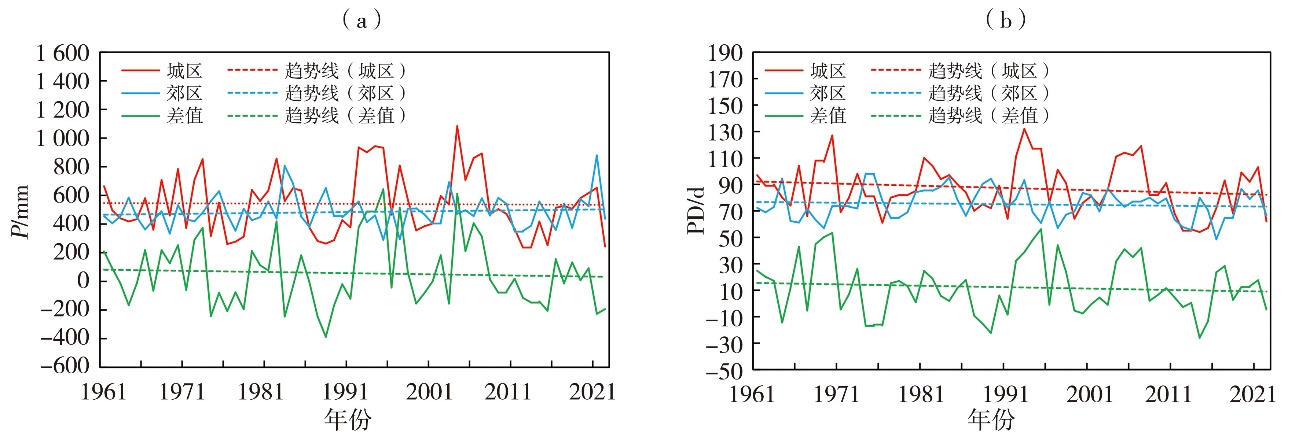
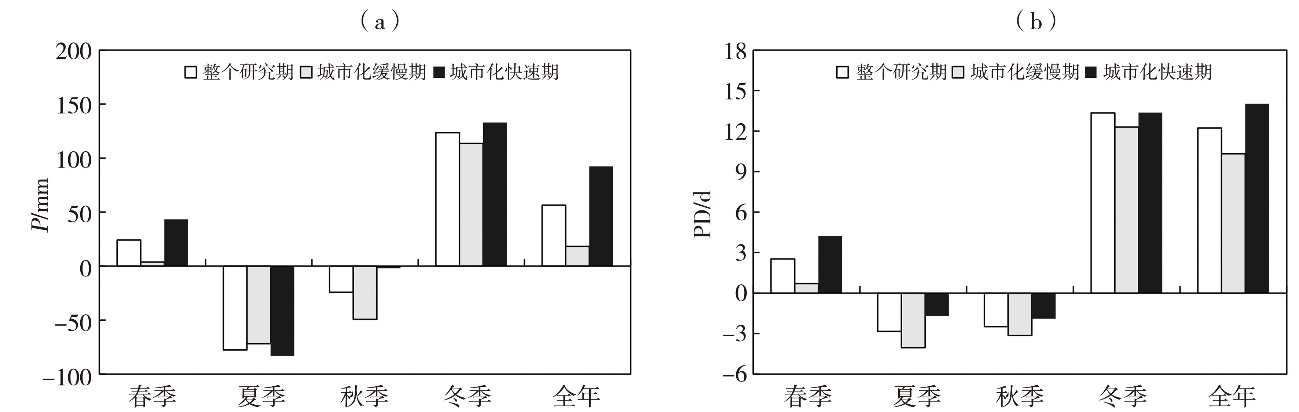
Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2025, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (3): 403-412.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-03-0403
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Impact of urbanization on the climate environment in Xi’an over the past 60 years
SHEN Jiaojiao1,2( ), HAO Sujuan1(
), HAO Sujuan1( ), JIN Lina3, ZHANG Yabin4, FAN Dandan2,5, GUO Qi1
), JIN Lina3, ZHANG Yabin4, FAN Dandan2,5, GUO Qi1
- 1. Shaanxi Meteorological Service Center, Xi’an 710014, China
2. China Meteorological Administration Eco-Environment and Meteorology for the Qinling Mountains and Loess Plateau Key Laboratory, Xi’an 710016, China
3. Xi’an Meteorological Bureau of Shaanxi Province, Xi’an 710016, China
4. Meteorological Institute of Shaanxi Province, Xi’an 710016, China
5. Shaanxi Meteorological Information Center, Xi’an 710014, China
-
Received:2024-08-29Revised:2025-04-15Online:2025-06-30Published:2025-07-12
近60 a西安城市化对气候环境的影响
沈姣姣1,2( ), 郝苏娟1(
), 郝苏娟1( ), 金丽娜3, 张雅斌4, 樊丹丹2,5, 郭琦1
), 金丽娜3, 张雅斌4, 樊丹丹2,5, 郭琦1
- 1.陕西省气象服务中心,陕西 西安 710014
2.中国气象局秦岭和黄土高原生态环境气象重点开放实验室,陕西 西安 710016
3.陕西省西安市气象局,陕西 西安 710016
4.陕西省气象科学研究所,陕西 西安 710016
5.陕西省气象信息中心,陕西 西安 710014
-
通讯作者:郝苏娟 -
作者简介:沈姣姣(1986—),女,博士,高级工程师,主要从事城市化气候效应研究。E-mail:jiaojiaoshen19@163.com。 -
基金资助:中国气象局秦岭和黄土高原生态环境重点开放实验室面上课题(2024G-7);陕西省科技厅重点研发计划项目(2024SF-YBXM-675)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
SHEN Jiaojiao, HAO Sujuan, JIN Lina, ZHANG Yabin, FAN Dandan, GUO Qi. Impact of urbanization on the climate environment in Xi’an over the past 60 years[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(3): 403-412.
沈姣姣, 郝苏娟, 金丽娜, 张雅斌, 樊丹丹, 郭琦. 近60 a西安城市化对气候环境的影响[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(3): 403-412.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-03-0403
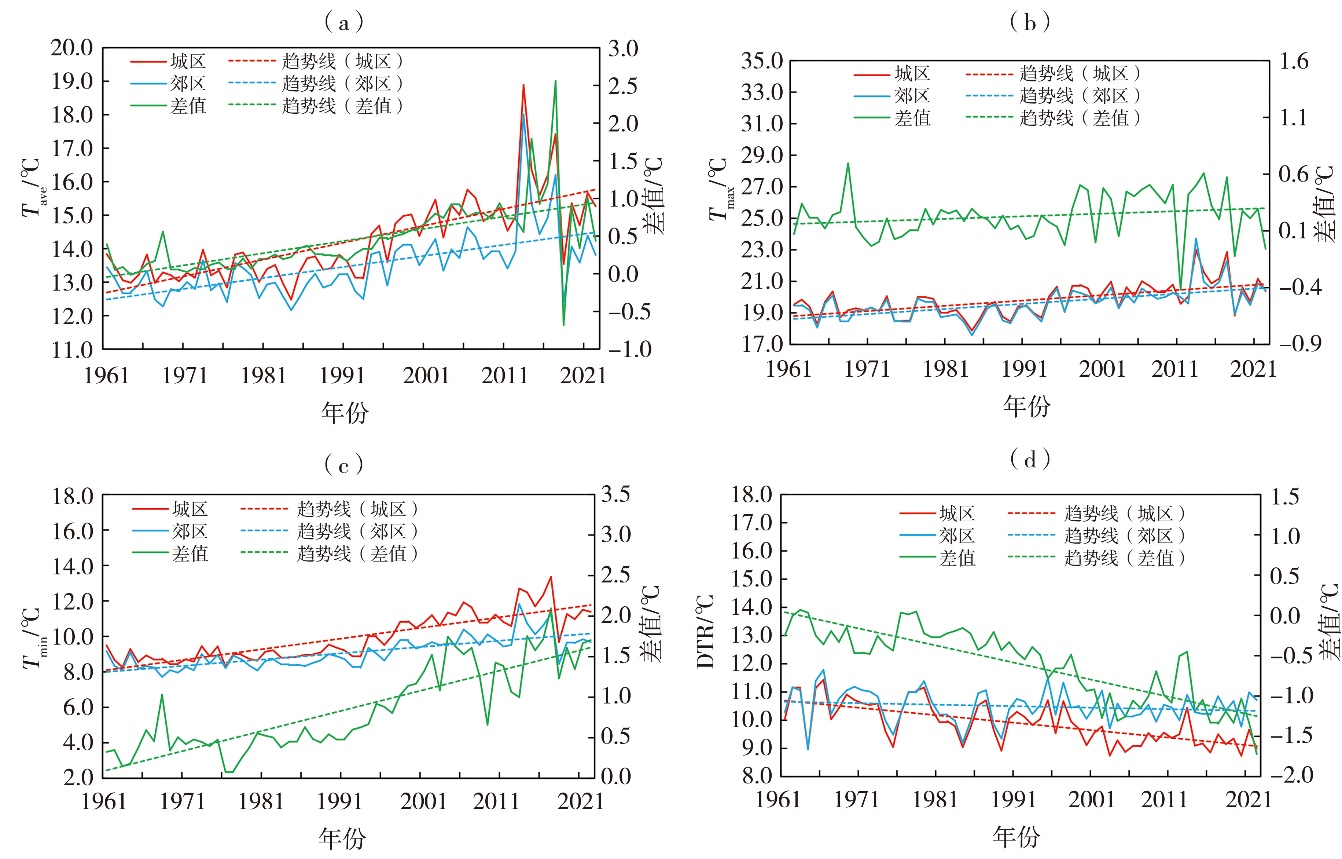
Fig.2 The inter-annual variation of Tave (a), Tmax (b), Tmin (c), DTR (d) and their difference between urban and suburban areas in Xi’an during 1961-2022
| 年份 | UHPI | 热岛面积比例/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 强热岛 | 较强热岛 | 弱热岛 | 无热岛 | ||
| 2020 | 0.30 | 25.4 | 11.7 | 10.5 | 13.8 |
| 2022 | 0.30 | 27.1 | 12.1 | 8.6 | 12.6 |
| 2023 | 0.35 | 27.1 | 13.7 | 8.0 | 12.4 |
Tab.1 UHPI and area proportion of different levels in Xi’an in 2020, 2022 and 2023
| 年份 | UHPI | 热岛面积比例/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 强热岛 | 较强热岛 | 弱热岛 | 无热岛 | ||
| 2020 | 0.30 | 25.4 | 11.7 | 10.5 | 13.8 |
| 2022 | 0.30 | 27.1 | 12.1 | 8.6 | 12.6 |
| 2023 | 0.35 | 27.1 | 13.7 | 8.0 | 12.4 |
| 气象要素 | 时段 | 城市化缓慢期 | 城市化快速期 | 整个研究期 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 城区 | 郊区 | 差值 | 城区 | 郊区 | 差值 | 城区 | 郊区 | 差值 | ||
| Tave | 全年 | 0.04 | -0.04 | 0.08** | 0.68*** | 0.43** | 0.25*** | 0.51*** | 0.32*** | 0.19*** |
| 春季 | 0.09 | -0.12 | 0.21*** | 0.66** | 0.44* | 0.22*** | 0.60*** | 0.34*** | 0.26*** | |
| 夏季 | -0.47*** | -0.61*** | 0.14*** | 0.37** | 0.19 | 0.18*** | 0.27*** | 0.09 | 0.18*** | |
| 秋季 | 0.27* | 0.20 | 0.07*** | 0.46*** | 0.32** | 0.14** | 0.37*** | 0.23*** | 0.14*** | |
| 冬季 | 0.29* | 0.32* | -0.03 | 0.45** | 0.41* | 0.04 | 0.49*** | 0.38*** | 0.11*** | |
| Tmax | 全年 | -0.18 | -0.17 | 0.01 | 0.53** | 0.45** | 0.08*** | 0.37*** | 0.33*** | 0.04*** |
| 春季 | -0.12 | -0.21 | 0.09** | 0.70** | 0.66* | 0.04 | 0.52*** | 0.45*** | 0.07*** | |
| 夏季 | -0.81*** | -0.75*** | -0.05 | 0.29 | 0.19 | 0.10** | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.01 | |
| 秋季 | 0.26 | 0.25 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.13 | -0.03 | 0.25*** | 0.22*** | 0.03 | |
| 冬季 | -0.05 | -0.04 | -0.01 | 0.36 | 0.61** | -0.24 | 0.33*** | 0.37*** | -0.03 | |
| Tmin | 全年 | 0.13 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.84*** | 0.05*** | 0.34*** | 0.63*** | 0.37*** | 0.26*** |
| 春季 | 0.18 | -0.03 | 0.21*** | 0.69** | 0.38 | 0.31*** | 0.69*** | 0.33*** | 0.36*** | |
| 夏季 | -0.18 | -0.26** | 0.08** | 0.53*** | 0.26** | 0.27*** | 0.47*** | 0.23*** | 0.24*** | |
| 秋季 | 0.18 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0.76*** | 0.54*** | 0.22*** | 0.48*** | 0.29*** | 0.20*** | |
| 冬季 | 0.36** | 0.49*** | -0.13*** | 0.51** | 0.35* | 0.16 | 0.55*** | 0.39*** | 0.16*** | |
| DTR | 全年 | -0.31** | -0.27* | -0.05 | -0.31*** | -0.08 | -0.24*** | -0.26*** | -0.05*** | -0.21*** |
| 春季 | -0.29 | -0.17 | -0.12** | 0.01 | 0.25 | -0.24*** | -0.16*** | 0.11 | -0.28*** | |
| 夏季 | -0.63*** | -0.50*** | -0.13** | -0.24 | -0.09 | -0.15*** | -0.37*** | -0.15** | -0.22*** | |
| 秋季 | 0.07 | 0.11 | -0.04 | -0.66*** | -0.42** | -0.24*** | -0.24*** | -0.08 | -0.16*** | |
| 冬季 | -0.41* | -0.52* | 0.11** | -0.15 | 0.22 | -0.37*** | -0.22** | -0.03 | -0.18*** | |
Tab.2 Variation trends of temperature in different stages of urbanization development in Xi’an during 1961-2022 单位:℃·(10 a)-1
| 气象要素 | 时段 | 城市化缓慢期 | 城市化快速期 | 整个研究期 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 城区 | 郊区 | 差值 | 城区 | 郊区 | 差值 | 城区 | 郊区 | 差值 | ||
| Tave | 全年 | 0.04 | -0.04 | 0.08** | 0.68*** | 0.43** | 0.25*** | 0.51*** | 0.32*** | 0.19*** |
| 春季 | 0.09 | -0.12 | 0.21*** | 0.66** | 0.44* | 0.22*** | 0.60*** | 0.34*** | 0.26*** | |
| 夏季 | -0.47*** | -0.61*** | 0.14*** | 0.37** | 0.19 | 0.18*** | 0.27*** | 0.09 | 0.18*** | |
| 秋季 | 0.27* | 0.20 | 0.07*** | 0.46*** | 0.32** | 0.14** | 0.37*** | 0.23*** | 0.14*** | |
| 冬季 | 0.29* | 0.32* | -0.03 | 0.45** | 0.41* | 0.04 | 0.49*** | 0.38*** | 0.11*** | |
| Tmax | 全年 | -0.18 | -0.17 | 0.01 | 0.53** | 0.45** | 0.08*** | 0.37*** | 0.33*** | 0.04*** |
| 春季 | -0.12 | -0.21 | 0.09** | 0.70** | 0.66* | 0.04 | 0.52*** | 0.45*** | 0.07*** | |
| 夏季 | -0.81*** | -0.75*** | -0.05 | 0.29 | 0.19 | 0.10** | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.01 | |
| 秋季 | 0.26 | 0.25 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.13 | -0.03 | 0.25*** | 0.22*** | 0.03 | |
| 冬季 | -0.05 | -0.04 | -0.01 | 0.36 | 0.61** | -0.24 | 0.33*** | 0.37*** | -0.03 | |
| Tmin | 全年 | 0.13 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.84*** | 0.05*** | 0.34*** | 0.63*** | 0.37*** | 0.26*** |
| 春季 | 0.18 | -0.03 | 0.21*** | 0.69** | 0.38 | 0.31*** | 0.69*** | 0.33*** | 0.36*** | |
| 夏季 | -0.18 | -0.26** | 0.08** | 0.53*** | 0.26** | 0.27*** | 0.47*** | 0.23*** | 0.24*** | |
| 秋季 | 0.18 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0.76*** | 0.54*** | 0.22*** | 0.48*** | 0.29*** | 0.20*** | |
| 冬季 | 0.36** | 0.49*** | -0.13*** | 0.51** | 0.35* | 0.16 | 0.55*** | 0.39*** | 0.16*** | |
| DTR | 全年 | -0.31** | -0.27* | -0.05 | -0.31*** | -0.08 | -0.24*** | -0.26*** | -0.05*** | -0.21*** |
| 春季 | -0.29 | -0.17 | -0.12** | 0.01 | 0.25 | -0.24*** | -0.16*** | 0.11 | -0.28*** | |
| 夏季 | -0.63*** | -0.50*** | -0.13** | -0.24 | -0.09 | -0.15*** | -0.37*** | -0.15** | -0.22*** | |
| 秋季 | 0.07 | 0.11 | -0.04 | -0.66*** | -0.42** | -0.24*** | -0.24*** | -0.08 | -0.16*** | |
| 冬季 | -0.41* | -0.52* | 0.11** | -0.15 | 0.22 | -0.37*** | -0.22** | -0.03 | -0.18*** | |
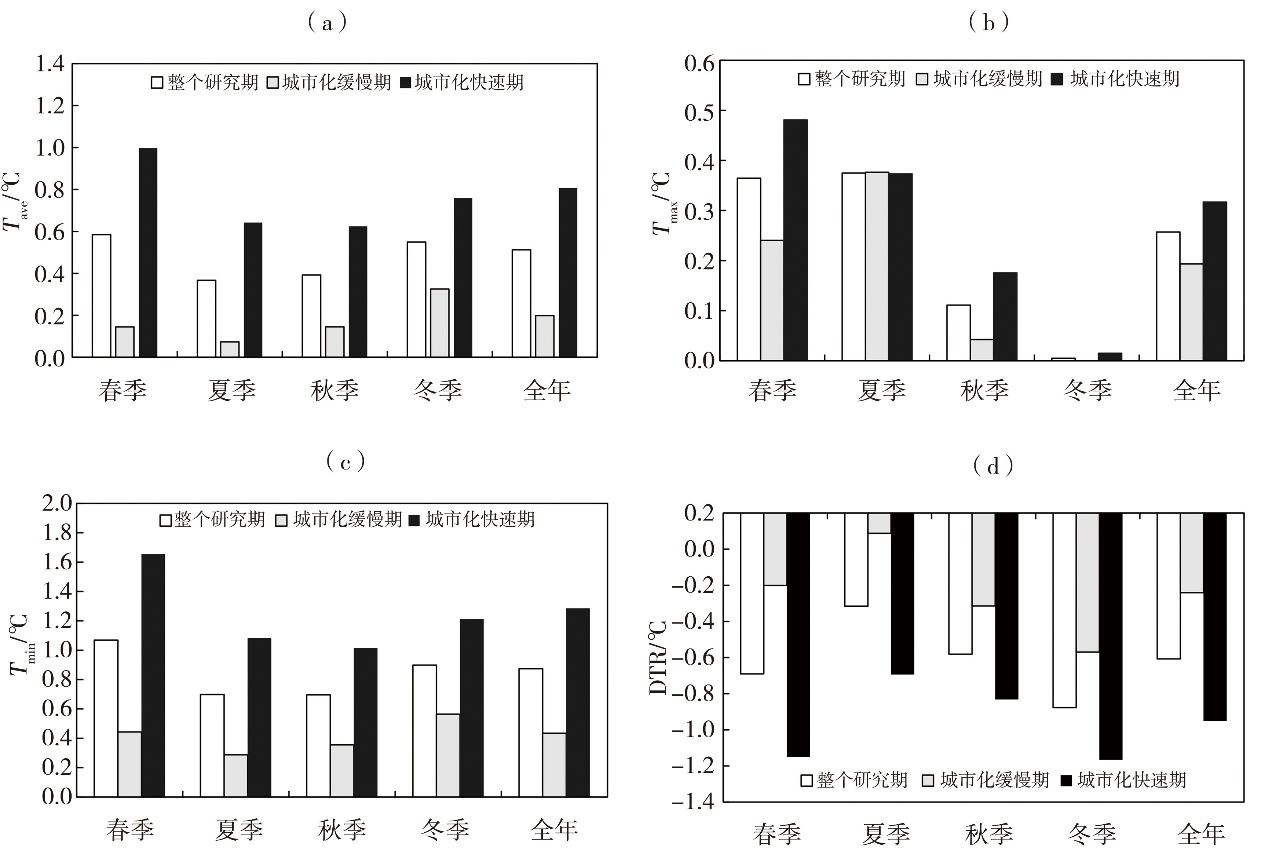
Fig.3 Difference of Tave (a), Tmax (b), Tmin (c) and DTR (d) between urban and suburban areas in different stages of urbanization development in Xi’an during 1961-2022
| 城市化发展阶段 | 降水量等级 | 城区 | 郊区 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P/mm | PD/d | RI/(mm·d-1) | P/mm | PD/d | RI/(mm·d-1) | ||
| 城市化缓慢期 | 小雨 | 182.0 | 71.2 | 2.6 | 159.3 | 61.5 | 2.6 |
| 中雨 | 202.3 | 13.1 | 15.2 | 191.5 | 12.1 | 15.8 | |
| 大雨及以上 | 120.9 | 3.3 | 36.4 | 137.2 | 3.7 | 37.3 | |
| 总降雨 | 505.3 | 87.5 | 5.7 | 487.0 | 77.2 | 6.3 | |
| 城市化快速期 | 小雨 | 179.6 | 67.7 | 2.6 | 151.0 | 57.5 | 2.6 |
| 中雨 | 232.0 | 14.9 | 15.4 | 173.6 | 11.2 | 15.4 | |
| 大雨及以上 | 161.7 | 4.3 | 37.0 | 158.4 | 4.1 | 38.1 | |
| 总降雨 | 573.3 | 86.9 | 6.4 | 481.0 | 72.9 | 6.6 | |
Tab.3 The P, PD and RI of different levels of precipitation between urban and suburban areas in different stages of urbanization development in Xi’an during 1961-2022
| 城市化发展阶段 | 降水量等级 | 城区 | 郊区 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P/mm | PD/d | RI/(mm·d-1) | P/mm | PD/d | RI/(mm·d-1) | ||
| 城市化缓慢期 | 小雨 | 182.0 | 71.2 | 2.6 | 159.3 | 61.5 | 2.6 |
| 中雨 | 202.3 | 13.1 | 15.2 | 191.5 | 12.1 | 15.8 | |
| 大雨及以上 | 120.9 | 3.3 | 36.4 | 137.2 | 3.7 | 37.3 | |
| 总降雨 | 505.3 | 87.5 | 5.7 | 487.0 | 77.2 | 6.3 | |
| 城市化快速期 | 小雨 | 179.6 | 67.7 | 2.6 | 151.0 | 57.5 | 2.6 |
| 中雨 | 232.0 | 14.9 | 15.4 | 173.6 | 11.2 | 15.4 | |
| 大雨及以上 | 161.7 | 4.3 | 37.0 | 158.4 | 4.1 | 38.1 | |
| 总降雨 | 573.3 | 86.9 | 6.4 | 481.0 | 72.9 | 6.6 | |
| 区域 | 时段 | 城市化缓慢期 | 城市化快速期 | 整个研究期 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SD/[h·(10 a)-1] | RH/[%·(10 a)-1] | SD/[h·(10 a)-1] | RH/[%·(10 a)-1] | SD/[h·(10 a)-1] | RH/[%·(10 a)-1] | ||
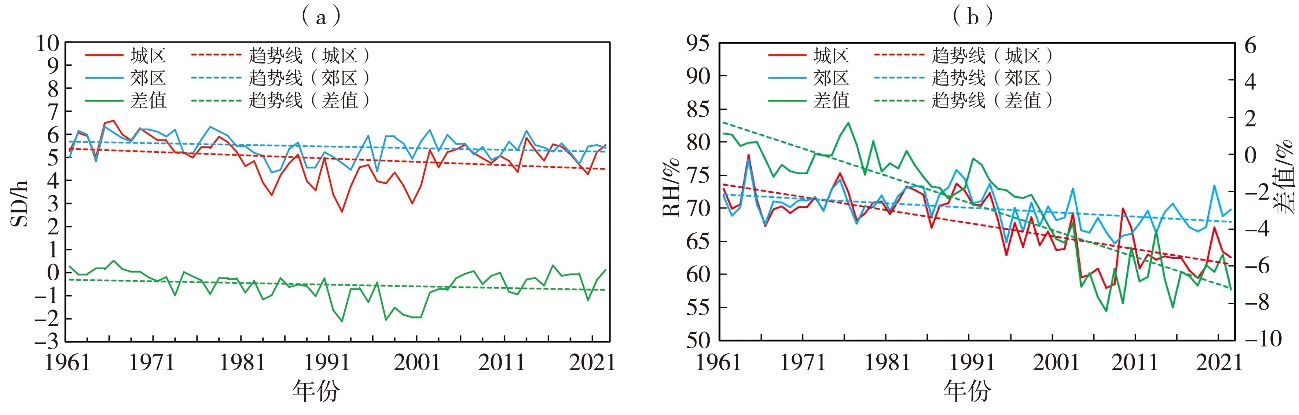
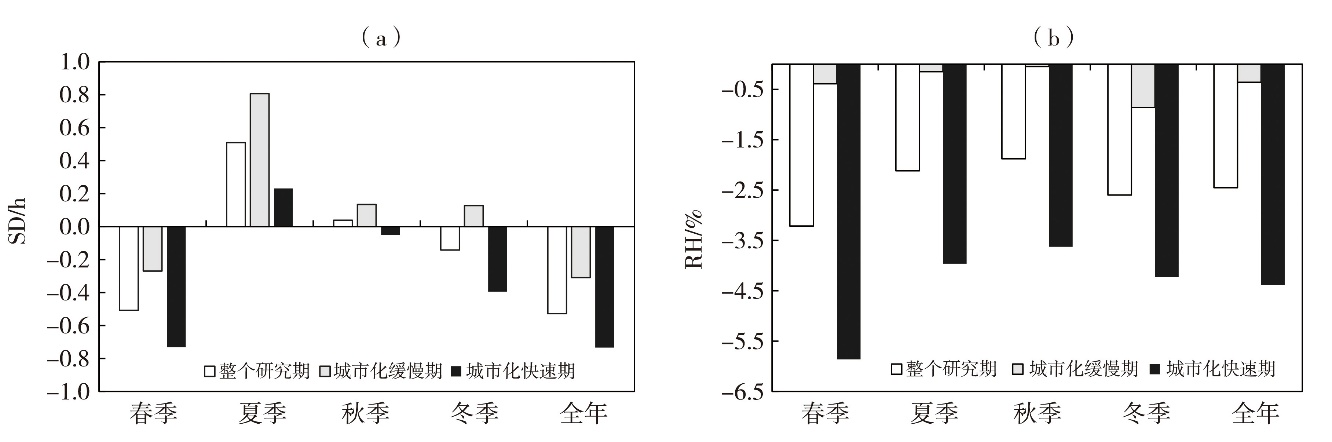
| 城区 | 全年 | -0.69*** | 0.03 | 0.55*** | -2.23*** | -0.14** | -1.97*** |
| 春季 | -0.58*** | -0.91 | 0.84*** | -4.84*** | 0.03 | -3.62*** | |
| 夏季 | -1.11*** | 2.29*** | 0.23 | -1.17 | -0.33*** | -1.08*** | |
| 秋季 | -0.41* | -1.56* | 0.33 | -0.50 | -0.13 | -1.55*** | |
| 冬季 | -0.67*** | 0.30 | 0.88*** | -4.29*** | -0.13* | -2.24*** | |
| 郊区 | 全年 | -0.36*** | 0.77* | 0.06 | -0.42 | -0.07** | -0.68*** |
| 春季 | -0.19 | 0.43 | 0.39** | -3.28*** | 0.12** | -1.93*** | |
| 夏季 | -0.51*** | 3.20*** | 0.01 | -0.13 | -0.16*** | 0.09 | |
| 秋季 | -0.08 | -0.89 | -0.18 | 1.51** | -0.12** | -0.33 | |
| 冬季 | -0.40*** | 0.43 | 0.17* | -1.26 | -0.07* | -1.00*** | |
Tab.4 The variation trends of SD and RH between urban and suburban areas in different stages of urbanization development in Xi’an during 1961-2022
| 区域 | 时段 | 城市化缓慢期 | 城市化快速期 | 整个研究期 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SD/[h·(10 a)-1] | RH/[%·(10 a)-1] | SD/[h·(10 a)-1] | RH/[%·(10 a)-1] | SD/[h·(10 a)-1] | RH/[%·(10 a)-1] | ||
| 城区 | 全年 | -0.69*** | 0.03 | 0.55*** | -2.23*** | -0.14** | -1.97*** |
| 春季 | -0.58*** | -0.91 | 0.84*** | -4.84*** | 0.03 | -3.62*** | |
| 夏季 | -1.11*** | 2.29*** | 0.23 | -1.17 | -0.33*** | -1.08*** | |
| 秋季 | -0.41* | -1.56* | 0.33 | -0.50 | -0.13 | -1.55*** | |
| 冬季 | -0.67*** | 0.30 | 0.88*** | -4.29*** | -0.13* | -2.24*** | |
| 郊区 | 全年 | -0.36*** | 0.77* | 0.06 | -0.42 | -0.07** | -0.68*** |
| 春季 | -0.19 | 0.43 | 0.39** | -3.28*** | 0.12** | -1.93*** | |
| 夏季 | -0.51*** | 3.20*** | 0.01 | -0.13 | -0.16*** | 0.09 | |
| 秋季 | -0.08 | -0.89 | -0.18 | 1.51** | -0.12** | -0.33 | |
| 冬季 | -0.40*** | 0.43 | 0.17* | -1.26 | -0.07* | -1.00*** | |
| [1] | 冯瑞, 杨丽萍, 侯成磊, 等, 2022. 基于随机森林的陕西省西安市近地表气温估算[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 44(1): 102-113. |
| [2] | 何萍, 江艳萍, 李矜霄, 等, 2017. 城市化对云南高原楚雄市近年来雨岛效应的影响研究[J]. 干旱区地理, 40(5): 933-941. |
| [3] |
何泽能, 张德军, 叶勤玉, 等, 2022. 近40 a重庆城市热岛特征及其与天气状况的关系[J]. 干旱气象, 40(4): 683-689.
DOI |
| [4] | 金丽娜, 李雄飞, 2021. 2014—2017年西安市城市热岛、冷岛精细化时空特征分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 15(1): 97-102. |
| [5] | 金丽娜, 李雄飞, 杜萌萌, 等, 2019. 基于FY-3卫星数据的西安市城市热岛特征分析[J]. 气象与环境科学, 42(4): 74-82. |
| [6] | 李鹏, 徐宗学, 张瑞, 等, 2020. 济南市极端降水特性与雨岛效应分析[J]. 北京师范大学学报:自然科学版, 56(6): 822-830. |
| [7] | 李宇, 周德成, 闫章美, 2021. 中国84个主要城市大气热岛效应的时空变化特征及影响因子[J]. 环境科学, 42(10): 5 037-5 045. |
| [8] | 李宇, 周德成, 闫章美, 等, 2022. 中国主要城市的城市化对局地增温的贡献[J]. 环境科学, 43(5): 2 822-2 830. |
| [9] | 刘小明, 闫浩文, 周亮, 等, 2020. 丝绸之路沿线节点城市扩张空间演变分析研究:以西安、兰州和乌鲁木齐为例[J]. 测绘与空间地理信息, 43(3): 178-180. |
| [10] | 刘宇峰, 原志华, 孔伟, 等, 2015. 1993—2012年西安城区城市热岛效应强度变化趋势及影响因素分析[J]. 自然资源学报, 30(6): 974-985. |
| [11] | 彭嘉栋, 赵辉, 陈晓晨, 2017. 长沙城市化进程对局地气候的影响[J]. 气象与环境科学, 40(4): 42-48. |
| [12] |
尚建设, 李本亮, 孙小丽, 等, 2018. 济南市夏季城市热岛效应特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 36(1): 70-74.
DOI |
| [13] | 唐晓萍, 张德军, 赵漫, 等, 2023. 近20年重庆沙坪坝城市热岛效应变化特征[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 43(2): 105-112. |
| [14] |
王辉, 陈欣, 茹菁宇, 等, 2024. 高原山地城市降水结构演变特征及城市效应: 以昆明市为例[J]. 长江科学院院报, 41(7): 25-33.
DOI |
| [15] | 王建鹏, 孙继松, 杜继稳, 等, 2009. 西安地区气温的年代际变化及其受城市化进程的影响[J]. 气候与环境研究, 14(4): 434-444. |
| [16] | 王建鹏, 孙继松, 王式功, 等, 2011. 盆地地形下西安城市热岛效应对周边降水的影响[J]. 干旱气象, 29(2): 168-173. |
| [17] | 魏凤英, 2022. 现代气候统计诊断与预测技术[M]. 第3版. 北京: 气象出版社: 77-82. |
| [18] |
杨仕琪, 王冀, 窦银银, 等, 2023. 1916—2020年北京城市变迁及其与区域气候演化的关系[J]. 地理学报, 78(3): 620-639.
DOI |
| [19] | 杨智威, 陈颖彪, 吴志峰, 等, 2019. 粤港澳大湾区城市热岛空间格局及影响因子多元建模[J]. 资源科学, 41(6): 1 154-1 166. |
| [20] | 姚玉龙, 2014. 西北绿洲典型城市地表温度的时空变化特征与成因分析[D]. 兰州: 西北师范大学. |
| [21] | 郁珍艳, 樊高峰, 李正泉, 等, 2020. 基于加密观测资料的杭州城市热环境及闷热特征分析[J]. 气象科技, 48(4): 570-578. |
| [22] | 张君枝, 梁雅楠, 王冀, 等, 2024. 1981—2020年北京城市热岛效应时空特征及其影响因素分析[J]. 大气科学学报, 47(4): 581-591. |
| [23] | 张树钦, 黄哲帆, 唐若莹, 等, 2022. 广东汕头市近十年来城市热岛效应分析[J]. 中国海洋大学学报: 自然科学版, 52(8): 19-30. |
| [24] | 张文静, 吴素良, 郝丽, 等, 2019. 西安城市热岛效应变化特征分析[J]. 陕西气象(1): 18-21. |
| [25] | 张小玲, 刘梦娜, 青泉, 等, 2022. 1960—2018年成都地区极端气温变化及城市化贡献分析[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 42(1): 10-17. |
| [26] |
张渝晨, 田宏伟, 2023. 近17 a郑州城市热岛时空演变及驱动机制分析[J]. 干旱气象, 41(3): 403-412.
DOI |
| [27] | 赵旋, 吴遥, 冯勇, 等, 2021. 成都城市化发展对局地气候的影响[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 41(4): 100-107. |
| [28] | 赵志敏, 徐华君, 王虎贤, 2007. 城市化对“城市浑浊岛效应”影响分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 1(6): 7-9. |
| [29] | 郑祚芳, 任国玉, 2018. 北京地区大气湿度变化及城市化影响分析[J]. 气象, 44(11): 1 471-1 478. |
| [30] | 中国气象局气候变化中心, 2024. 中国气候变化蓝皮书(2024)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 15-23. |
| [31] | 周鹏, 谢元礼, 高志远, 等, 2020. 西安市不透水面的变化及其驱动力[J]. 水土保持通报, 40(3): 274-281. |
| [32] | 周淑贞, 1988. 上海城市气候中的“五岛”效应[J]. 中国科学, 11: 1 226-1 234. |
| [33] | 周雅清, 任国玉, 2009. 城市化对华北地区最高、最低气温和日较差变化趋势的影响[J]. 高原气象, 28(5): 1 158-1 166. |
| [34] | BUO I, SAGRIS V, BURDUN I, et al, 2021. Estimating the expansion of urban areas and urban heat islands (UHI) in Ghana: A case study[J]. Natural Hazards, 105(2): 1 299-1 321. |
| [35] | HE X D, WANG J, FENG J M, et al, 2020. Observational and modeling study of interactions between urban heat island and heatwave in Beijing[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 247: 119169. DOI:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119169. |
| [36] | IPCC, 2021. Summary for policymakers. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis[M]. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Inter-Governmental Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge University Press: 3-32. |
| [37] | YU X J, GU X H, KONG D D, et al, 2022. Asymmetrical shift toward less light and more heavy precipitation in an urban agglomeration of East China: Intensification by urbanization[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 49(4): e2021GL 097046. DOI:10.1029/2021GL097046. |
| [1] | CHEN Min, CHEN Yuying, CHEN Rong, CHEN Yuxi, YANG Yuanyuan. Classification and meteorological element evolution of rainstorm in the eastern Helan Mountain foothills [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(3): 413-423. |
| [2] | PAN Liujie, LIANG Mian, QI Chunjuan, LI Peirong, ZHU Qingliang. Characteristics of meteorological elements and objective forecast verification at the key venues of “the 14th National Games” [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(3): 491-502. |
| [3] | CHEN Rong, WANG Jianying, YANG Wenjun, CHEN Min, WANG Qian, LI Kun. Influence factors of atmospheric boundary layer inversion in Yinchuan City and the relation with PM2.5 in winter [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(1): 123-131. |
| [4] | QI Yajie, CHEN Min, ZHONG Jiqin, FAN Shuiyong, LIU Ruiting, GUO Chunwei. Effect Evaluation of Short-term Forecast of Surface Meteorological Elements by Using RMAPS-ST Coupled Urban Canopy Model in North China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(5): 859-868. |
| [5] | TAN Changrong1, GUO Xiaoning, CHEN Qi, LI Jinhai,YOU Sangjie, MA Xuelian, MA Yuancang, QI Caihong. Study on Surface Ozone Characteristics and Its Influencing Factors in Xining [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(1): 31-39. |
| [6] | . Variation Characteristic of Main Meteorological Elements During Summer Sand-Dust Storm Processes in East of Hexi Corridor [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(3): 427-. |
| [7] | WANG Jianpeng, XUE Chunfang, HUANG Shaoni,WANG Dan, PAN Liujie, CHENG Lu. Sensitivity Test of Impact of Urbanization and Anthropogenic Heat on Meteorological Elements in Xi’an [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(3): 434-443. |
| [8] | . Change Character of Weather Elements at Tazhong of Xinjiang [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2011, 29(3): 315-321. |
| [9] | LIU Shi-Xiang, DAO Jian-Gong, ZHANG Tie-Jun, CHANG Da-Cheng, FU Xiao-Gong, ZHANG Jing, SONG Xiu-Ling. Verification and Assessment of Autumn Short - term Objective Forecast of Meteorological Elements in Northwest China [J]. J4, 2010, 28(3): 346-351. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||