Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2021, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (06): 911-920.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2021)-06-0911
• Articl • Previous Articles Next Articles
Analysis of cause of abnormally high temperature in Hainan Island in spring 2019
XING Caiying1,2( ), WU Shengan1,2(
), WU Shengan1,2( ), HU Deqiang1,2, ZHU Jingjing1,2
), HU Deqiang1,2, ZHU Jingjing1,2
- 1. Key Laboratory of South China Sea Meteorological Disaster Prevention and Mitigation of Hainan Province, Haikou 570203, China
2. Climate Center of Hainan Province, Haikou 570203, China
-
Received:2020-10-30Revised:2021-04-28Online:2021-12-30Published:2021-12-31 -
Contact:WU Shengan
2019年春季海南岛异常高温成因分析
邢彩盈1,2( ), 吴胜安1,2(
), 吴胜安1,2( ), 胡德强1,2, 朱晶晶1,2
), 胡德强1,2, 朱晶晶1,2
- 1.海南省南海气象防灾减灾重点实验室,海南 海口 570203
2.海南省气候中心,海南 海口 570203
-
通讯作者:吴胜安 -
作者简介:邢彩盈(1987— ),女,硕士,高级工程师,主要从事气候统计和短期气候预测研究. E-mail: 18876777858@163.com。 -
基金资助:海南省自然科学基金项目(2019RC360);海南省气象局科研项目(hnqxSJ202106);中国气象局预报员专项项目共同资助(CMAYBY2020-103)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
XING Caiying, WU Shengan, HU Deqiang, ZHU Jingjing. Analysis of cause of abnormally high temperature in Hainan Island in spring 2019[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(06): 911-920.
邢彩盈, 吴胜安, 胡德强, 朱晶晶. 2019年春季海南岛异常高温成因分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(06): 911-920.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2021)-06-0911
| 等级 | 判别标准 |
|---|---|
| 轻度 | 日最高气温大于等于35 ℃的日数持续3~4 d |
| 中度 | 日最高气温大于等于35 ℃的日数持续5~7 d |
| 重度 | 日最高气温大于等于35 ℃的日数持续8 d以上 |
Tab.1 Classification criteria of grade of high temperature and heatwave events
| 等级 | 判别标准 |
|---|---|
| 轻度 | 日最高气温大于等于35 ℃的日数持续3~4 d |
| 中度 | 日最高气温大于等于35 ℃的日数持续5~7 d |
| 重度 | 日最高气温大于等于35 ℃的日数持续8 d以上 |
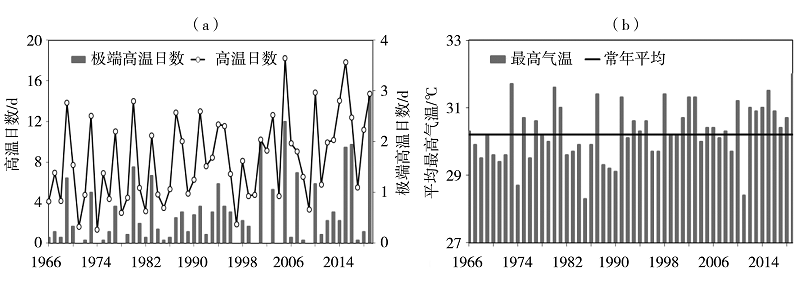
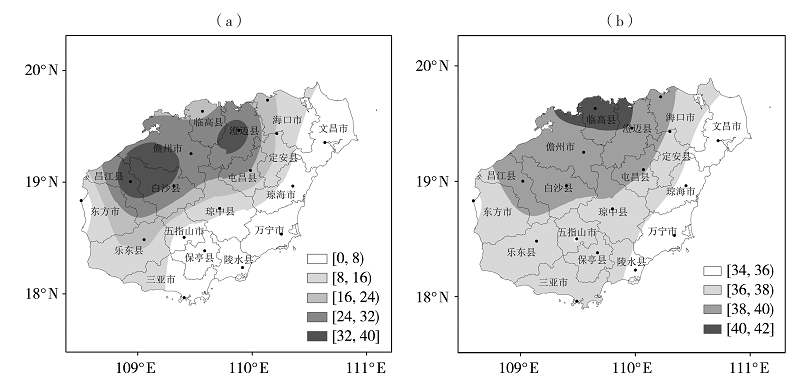
Fig.2 The inter-annual variation of high temperature days, extremely high temperature days (a) and maximum temperature (b) averaged over the Hainan Island in spring from 1966 to 2019
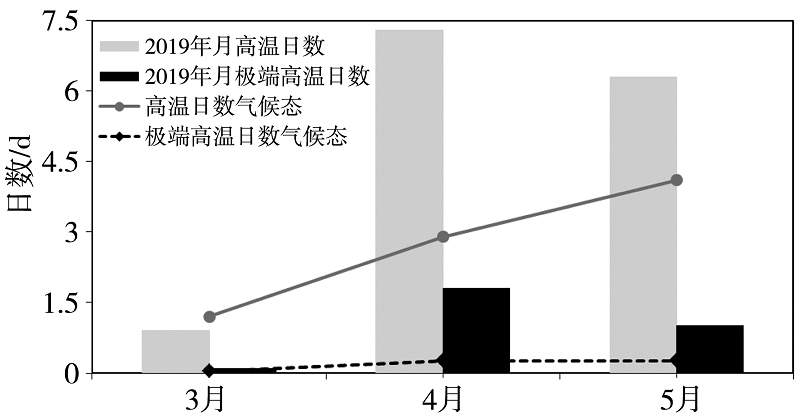
Fig.3 The comparison of monthly high temperature days, extremely high temperature days in spring 2019 and climate state averaged over the Hainan Island
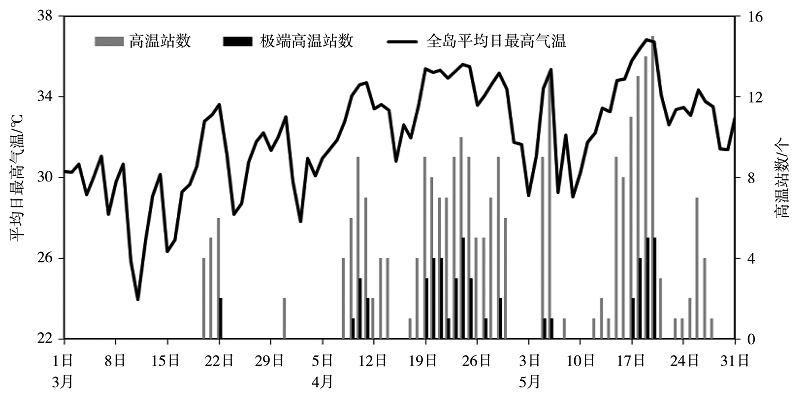
Fig.4 The variation of daily high temperature stations, extremely high temperature stations and average maximum temperature in the Hainan Island from March 1 to May 31 in 2019
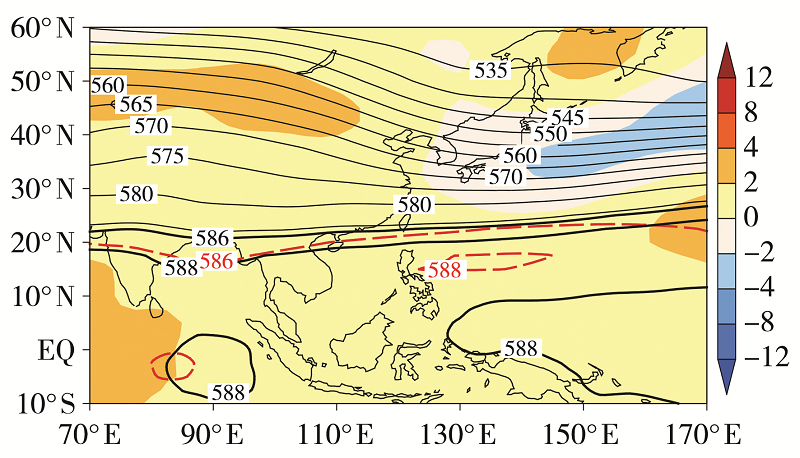
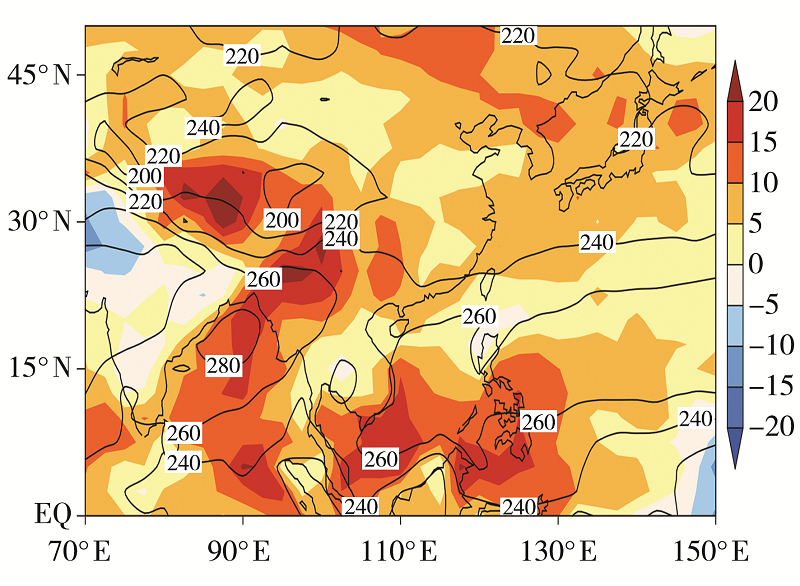
Fig.5 The 500 hPa geopotential height (isolines) and its anomaly field (the shaded) in spring 2019 (Unit: dagpm) (the black thick solid isolines for 586 dagpm and 588 dagpm in 2019, red thick dashed isolines for climate state of 586 dagpm and 588 dagpm)
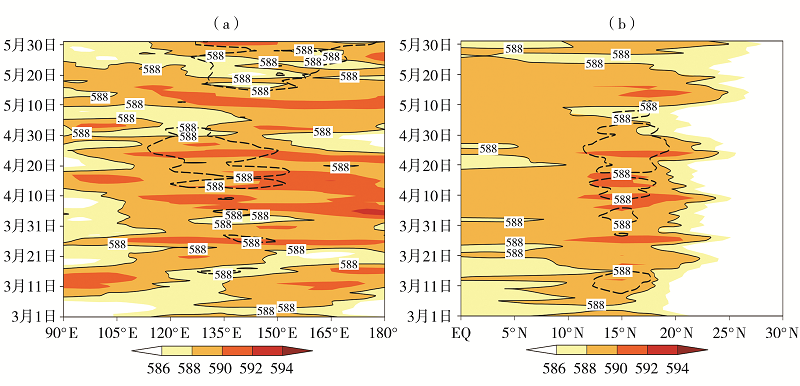
Fig.6 Longitude-time cross-section averaged over 15°N-22°N (a) and latitude-time cross-section averaged over 115°E-125°E (b) of 500 hPa geopotential height (Unit: dagpm) from March 1 to May 31 in 2019 (the solid isolines for 588 dagpm in 2019, the dashed isolines for climate state of 588 dagpm)
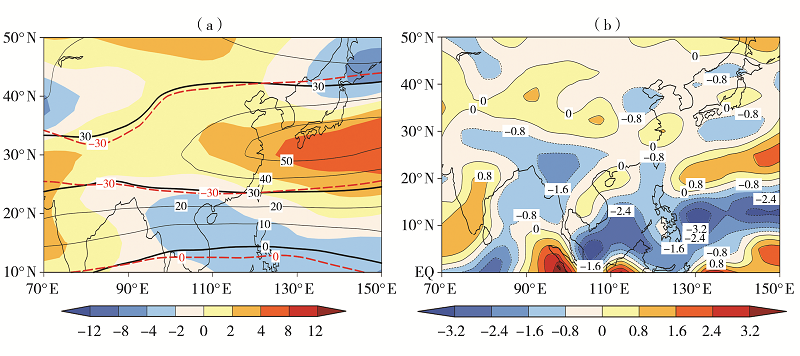
Fig.7 The 200 hPa zonal wind (isolines) and its anomaly field (the shaded) (Unit: m·s-1) (a, thick solid isolines for 0 and 30 m·s-1 in 2019, thick dashed isolines for climate state of 0 and 30 m·s-1) and 200 hPa divergence anomaly field (b, Unit: 10-6 s-1) in spring 2019
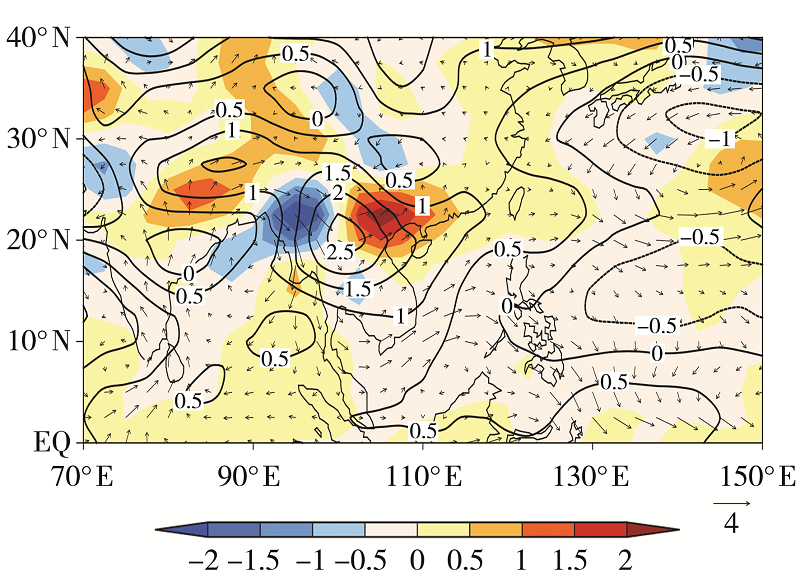
Fig.8 Distribution of anomaly field of 850 hPa temperature (isolines, Unit: K), wind (wind vectors, Unit: m·s-1) and temperature advection(the shaded, Unit: 105 K·s-1) in spring 2019
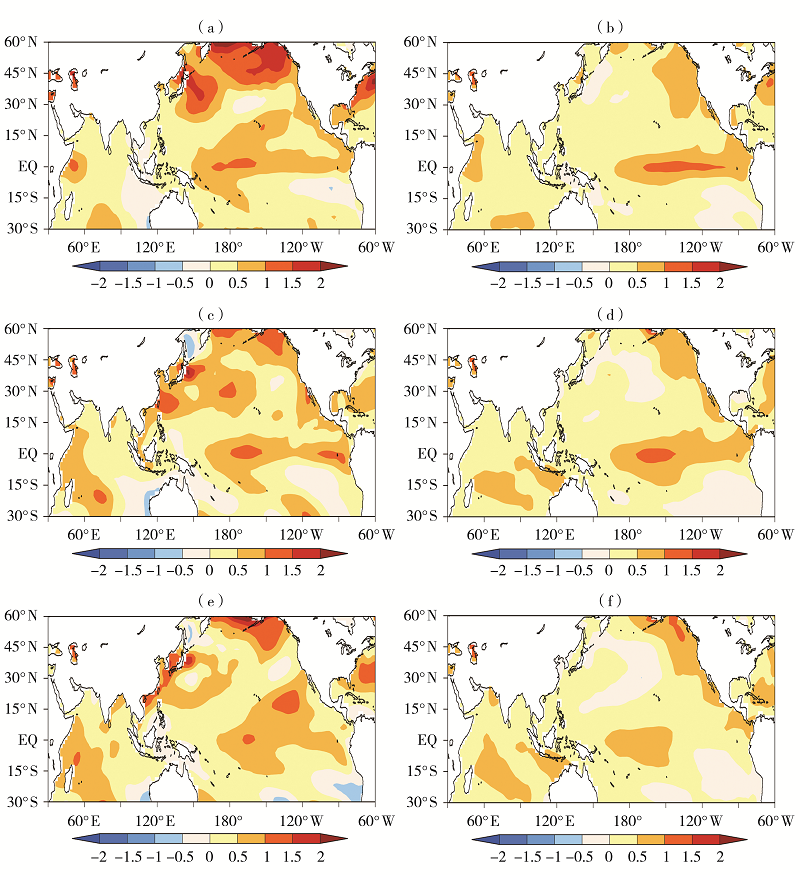
Fig.10 The SST anomaly fields in previous autumn (a,b), winter (c,d) and spring (e,f) in 2019 (a,c,e) and in anomalously high temperature years since 2000 (b,d,f) (Unit: ℃)
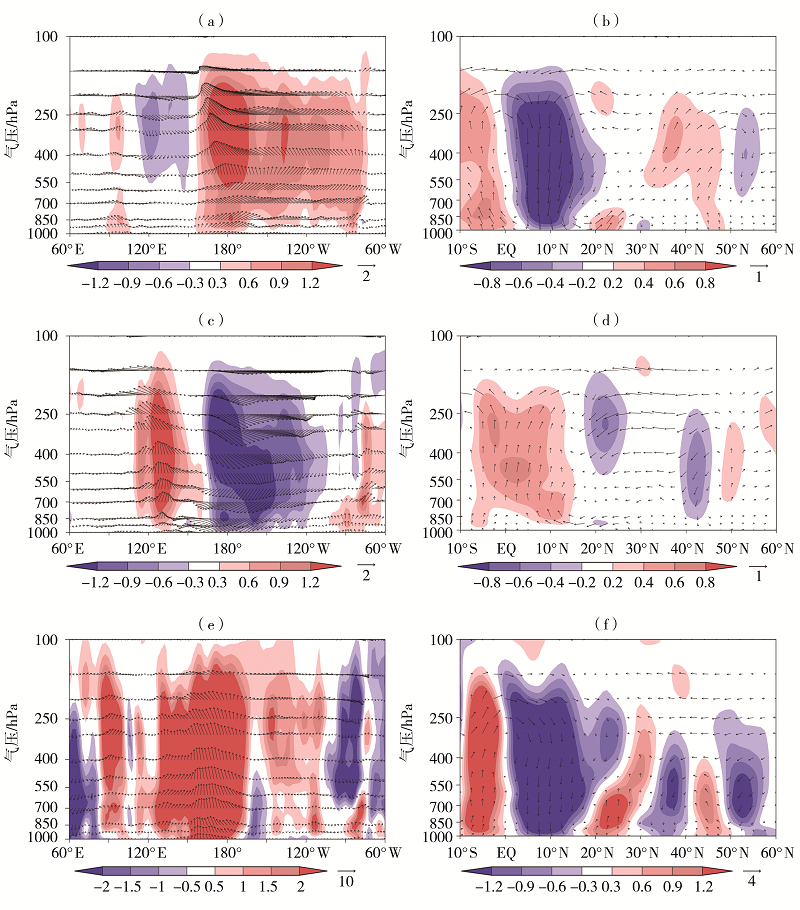
Fig.11 The Walker circulation anomaly fields averaged over 5°S-5°N (a,c,e, composition of u component and ω component) and Hadley circulation anomaly fields averaged over 100°E-120°E (b,d,f, composition of v component and ω component) in subsequent spring of El Niño (a,b) and La Niña (c,d) years since 1981 and in spring 2019 (e,f) (Unit of u and v is m·s-1,Unit of ω is 10-2 Pa·s-1; the shaded for vertical velocity anomaly)
| [1] | 邢彩盈, 张京红, 吴胜安. 近50年海南岛高温日数和热浪的气候特征[J]. 中国农学通报, 2017, 33(22):107-112. |
| [2] | 杨辉, 李崇银. 2003年夏季中国江南异常高温的分析研究[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2005, 10(1):80-85. |
| [3] | 彭海燕, 周曾奎, 赵永玲, 等. 2003年夏季长江中下游地区异常高温的分析[J]. 气象科学, 2005, 25(4):355-361. |
| [4] | 罗伯良, 李易芝. 2013年夏季湖南严重高温干旱及其大气环流异常[J]. 干旱气象, 2014, 32(4):593-598. |
| [5] | 彭京备, 刘舸, 孙淑清. 2013年我国南方持续性高温天气及副热带高压异常维持的成因分析[J]. 大气科学, 2016, 40(5):897-906. |
| [6] | 夏扬, 徐海明. 2013年长江中下游地区夏季高温事件的环流特征及成因[J]. 气象科学, 2017, 37(1):60-69. |
| [7] | 彭京备, 张庆云, 布和朝鲁. 2006年川渝地区高温干旱特征及其成因分析[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2007, 12(3):464-474. |
| [8] | 陈丽华, 周率, 党建涛, 等. 2006年盛夏川渝地区高温干旱气候形成的物理机制研究[J]. 气象, 2010, 36(5):85-91. |
| [9] | 张志薇, 王式功, 尚可政, 等. 华中地区近50年高温事件及大气环流成因分析[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 47(2):50-55. |
| [10] | 彭莉莉, 戴泽军, 罗伯良, 等. 2013年夏季西太平洋副高异常特征及其对湖南高温干旱的影响[J]. 干旱气象, 2015, 33(2):195-201. |
| [11] | 张曦, 黎鑫. 湖南省夏季高温热浪时空分布特征及其成因[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2017, 22(6):747-756. |
| [12] | 贾子康, 郑志海, 封国林. 中国南方地区盛夏高温类型及其对应的大尺度环流和海温异常[J]. 气象学报, 2020, 78(6):928-944. |
| [13] | 张英华, 李艳, 李德帅, 等. 中国东部夏季极端高温的空间分布特征及其环流型[J]. 高原气象, 2016, 35(2):469-483. |
| [14] | 袁媛, 丁婷, 高辉, 等. 我国南方盛夏气温主模态特征及其与海温异常的联系[J]. 大气科学, 2018, 42(6):1245-1262. |
| [15] |
HU K M, HUANG G, QU X, et al. The impact of Indian Ocean variability on high temperature extremes across the southern Yangtze River valley in late summer[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2012, 29(1):91-100.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
HU K M, HUANG G, WU R G. A strengthened influence of ENSO on August high temperature extremes over the southern Yangtze River valley since the late 1980s[J]. Journal of Climate, 2013, 26(7):2205-2221.
DOI URL |
| [17] | 刘嘉慧敏, 郑然, 娄盼星, 等. 2017年7月陕西高温热浪天气成因及前期信号初探[J]. 干旱气象, 2019, 37(2):233-242. |
| [18] | 杨涵洧, 封国林. 2013年盛夏中国持续性高温事件诊断分析[J]. 高原气象, 2016, 35(2):484-494. |
| [19] | 袁媛, 李崇银. 热带印度洋海温异常不同模态对南海夏季风爆发的可能影响[J]. 大气科学, 2009, 33(2):325-336. |
| [20] | 袁媛, 高辉, 贾小龙, 等. 2014—2016年超强厄尔尼诺事件的气候影响[J]. 气象, 2016, 42(5):532-539. |
| [21] | 晏红明, 李清泉, 袁媛, 等. 夏季西北太平洋大气环流异常及其与热带印度洋—太平洋海温变化的关系[J]. 地球物理学报, 2013, 56(8):2542-2557. |
| [22] | 邹海波, 吴珊珊, 单九生, 等. 2013年盛夏中国中东部高温天气的成因分析[J]. 气象学报, 2015, 73(3):481-495. |
| [23] | 许祖清. 海南高温分布特征[J]. 气象研究与应用, 2008, 29(3):12-13. |
| [24] | 符式红, 郑艳. 2014年海南岛持续性异常高温成因分析[J]. 气象研究与应用, 2017, 38(2):27-30. |
| [25] | 张永领, 陈小丽, 黄彦彬, 等. 海南异常高温的气候特征及其海气背景[J]. 气象科技, 2005, 33(2):147-151. |
| [26] | 任芝花, 余予, 邹凤玲, 等. 部分地面要素历史基础气象资料质量检测[J]. 应用气象学报, 2012, 23(6):739-747. |
| [27] |
KALNAY E, KANAMITSU M, KISTLER R, et al. The NCEP/NCAR 40year reanalysis project[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 1996, 77:437-472.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
HUANG B, BANZON V F, FREEMAN E, et al. Extended reconstructed sea surface temperature version 4 (ERSST.v4). Part I: upgrades and intercomparisons[J]. Journal of Climate, 2015, 28(3):911-930.
DOI URL |
| [29] | 刘芸芸, 李维京, 艾婉秀, 等. 月尺度西太平洋副热带高压指数的重建与应用[J]. 应用气象学报, 2012, 23(4):414-423. |
| [30] |
CHAMBERS D P, TAPLEY B D, Stewart R H. Anomalous warming in the Indian Ocean coincident with El Niño[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1999, 104:3035-304.
DOI URL |
| [31] | 国家气候中心. 厄尔尼诺/拉尼娜事件判别方法: QX/T 370—2017[S]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2017. |
| [32] | 谈建国, 陆晨, 陈正洪. 高温热浪与人体健康[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2009. |
| [33] |
YUAN Y, YANG S. Impacts of different types of El Niño on the East Asian climate: focus on ENSO cycles[J]. Journal of Climate, 2012, 25(21):7702-7722.
DOI URL |
| [34] | 杨莲梅, 张庆云. 夏季东亚西风急流扰动异常与副热带高压关系研究[J]. 应用气象学报, 2007, 18(4):452-459. |
| [35] | 黄荣辉, 孙凤英. 热带西太平洋暖池的热状态及其上空的对流活动对东亚夏季气候异常的影响[J]. 大气科学, 1994, 18(2):141-151. |
| [36] | 刘芸芸, 陈丽娟. 2019年春季我国主要气候异常特征及可能成因分析[J]. 气象, 2019, 45(10):1483-1493. |
| [37] | 张庆云, 王媛. 冬夏东亚季风环流对太平洋热状况的响应[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2006, 11(4):487-498. |
| [38] |
XIE S P, HU K M, HADNER J, et al. Indian Ocean capacitor effect on Indo-Western Pacific climate during the summer following El Niño[J]. Journal of Climate, 2009, 22:730-747.
DOI URL |
| [39] | WATANABE M, JIN F F. Role of Indian ocean warming in the development of Philippine sea anticyclone during ENSO[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2002, 29(10):1478. DOI: 10.1029/2001GL014318. |
| [40] |
YUAN Y, YANG S, ZHANG Z Q. Different evolutions of the Philippine Sea anticyclone between the eastern and central Pacific El Niño: possible effects of Indian Ocean SST[J]. Journal of Climate, 2012, 25(22):7867-7783.
DOI URL |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||