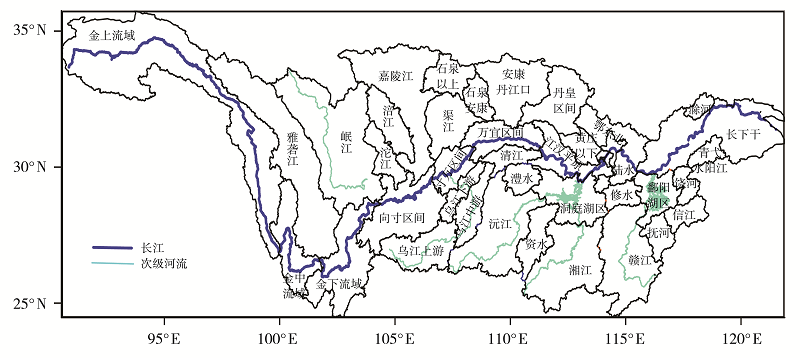
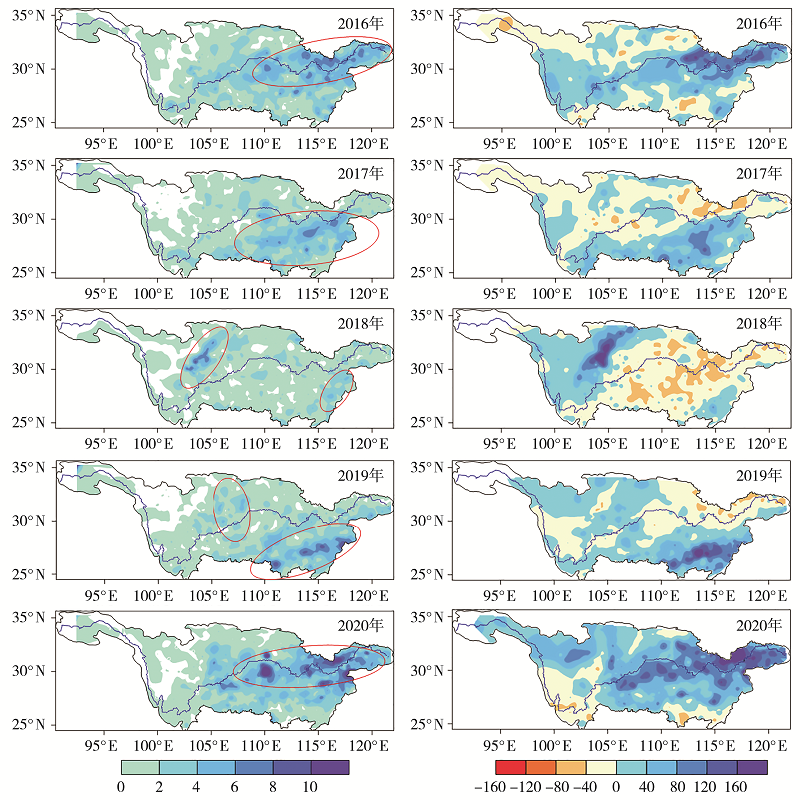
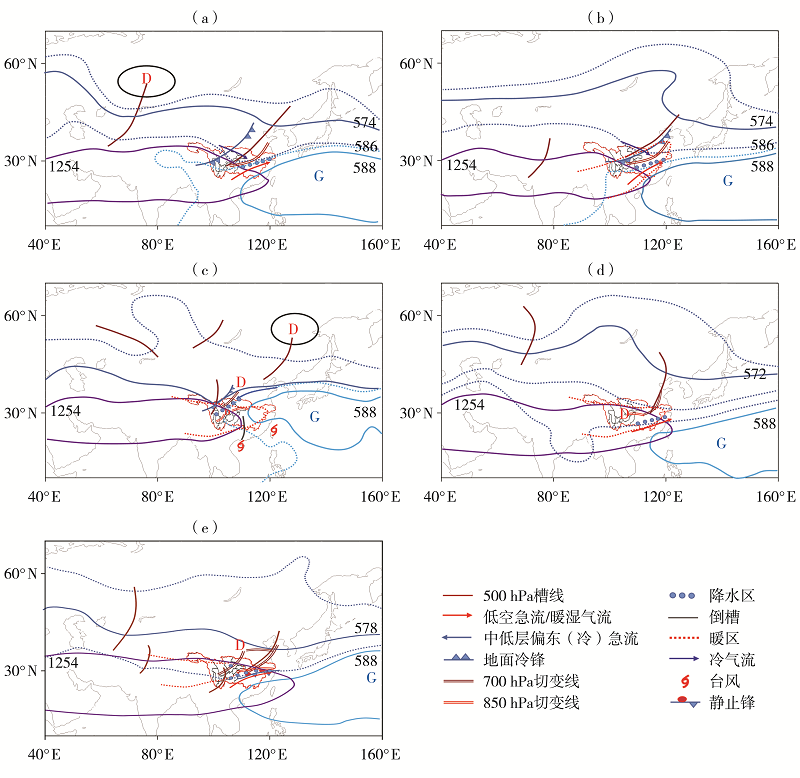
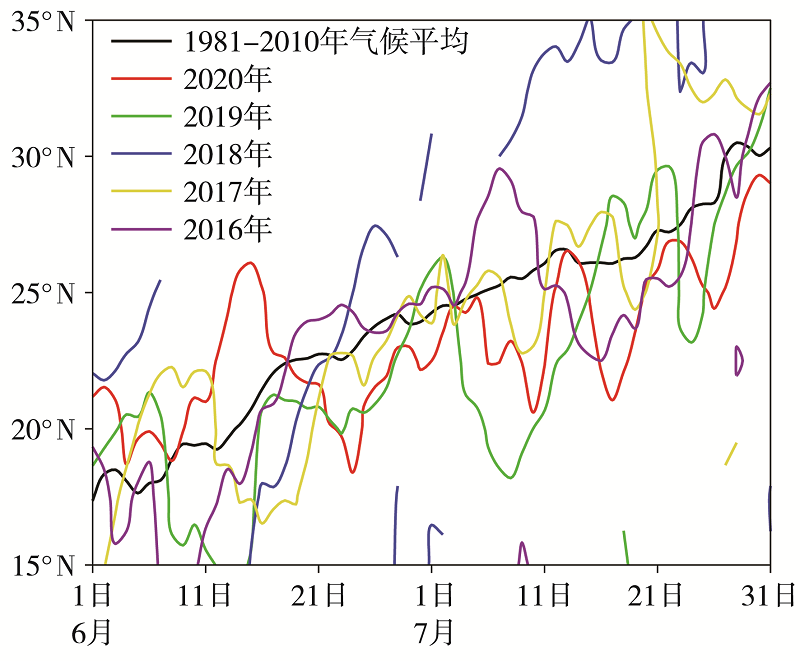
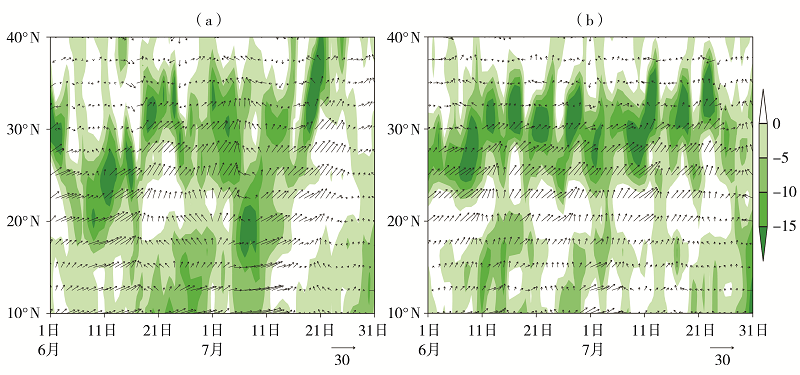
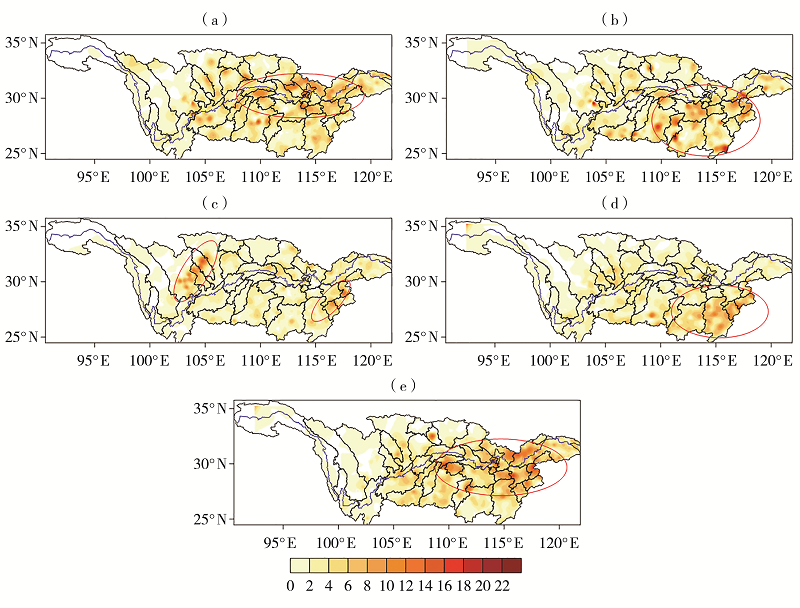
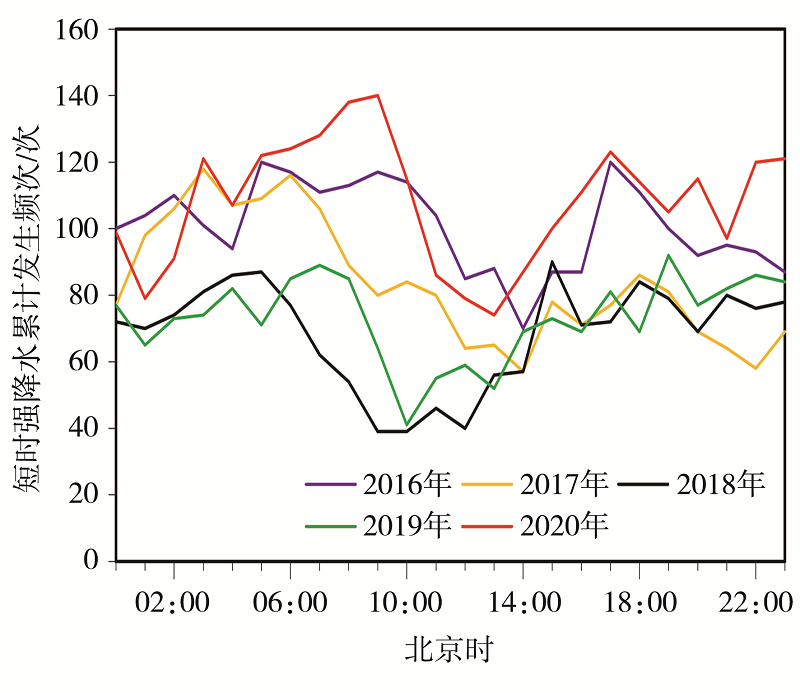
| [1] |
吴胜军, 杜耕, 王学雷, 等. 长江洪水特征分析[C]// 2004年重力学与固体潮学术研讨会暨祝贺许厚泽院士70寿辰研讨会, 2004:1040-1044.
|
| [2] |
邓宏兵. 长江流域洪灾探析[J]. 华中师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2002, 36(1):117-120.
|
| [3] |
袁媛, 高辉, 贾小龙, 等. 2014—2016年超强厄尔尼诺事件的气候影响[J]. 气象, 2016, 42(5):532-539.
|
| [4] |
李维京. 1999年大气环流异常及其对中国气候异常的影响[J]. 气象, 1998, 25(4):20-25.
|
| [5] |
牛若芸, 金荣花. 2008年梅雨异常大尺度环流成因分析[J]. 高原气象, 2009, 28(6):1326-1334.
|
| [6] |
金荣花, 陈涛, 鲍媛媛, 等. 2007年梅汛期异常降水的大尺度环流成因分析[J]. 气象, 2008, 34(4):79-85.
|
| [7] |
赵俊虎, 陈丽娟, 王东阡. 2016年我国梅雨异常特征及成因分析[J]. 大气科学, 2018, 42(5):1055-1066.
|
| [8] |
袁媛, 高辉, 柳艳菊. 2016年夏季我国东部降水异常特征及成因简析[J]. 气象, 2017, 43(1):115-121.
|
| [9] |
权婉晴, 何立富. 2016年7月大气环流和天气分析[J]. 气象, 2016, 42(10):1283-1288.
|
| [10] |
赵晓琳. 2018年我国梅雨特征及梅雨期降水异常成因分析[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2019, 42(3):29-33.
|
| [11] |
赵娴婷, 廖移山, 闵爱荣, 等. 2016年4—10月我国主要暴雨天气过程简述[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2017, 36(2):182-191.
|
| [12] |
封国林, 杨涵洧, 张世轩, 等. 2011年春末夏初长江中下游地区旱涝急转成因初探[J]. 大气科学, 2012, 36(5):1009-1026.
|
| [13] |
水利部长江水利委员会水文局. 2016年长江暴雨洪水[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2019.
|
| [14] |
中国气象局. 暴雨年鉴(2008)[M]. 北京: 气象出版社,2011.
|
| [15] |
俞小鼎. 短时强降水临近预报的思路与方法[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2013, 32(3):202-209.
|
| [16] |
王晓芳. 长江中下游地区梅雨期线状中尺度对流系统分析Ⅱ: 环境特征[J]. 气象学报, 2012, 70(5):924-935.
|
| [17] |
张家国, 王珏, 吴涛, 等. 长江中游地区极端降水主要天气系统类型分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2018, 37(1):15-23.
|
| [18] |
赵云发, 崔讲学. 长江中上游流域洪水天气特征分析[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2018.
|
| [19] |
陶诗言, 赵煜佳, 陈晓敏. 东亚的梅雨期与亚洲上空大气环流季节变化的关系[J]. 气象学报, 1985, 29(2):119-134.
|
| [20] |
陶诗言, 卫捷. 再论夏季西太平洋副热带高压的西伸北跳[J]. 应用气象学报, 2001, 17(5):513-525.
|
| [21] |
陶诗言, 张庆云, 张顺利. 夏季北太平洋副热带高压系统的活动[J]. 气象学报, 2001, 59(6):748-758.
|
| [22] |
徐海明, 何金海, 周兵. 江淮入梅前后大气环流的演变特征和西太平洋副高北跳西伸的可能机制[J]. 应用气象学报, 2001, 12(2):150-158.
|
| [23] |
吴国雄, 丑纪范, 刘屹岷, 等. 副热带高压研究进展及展望[J]. 大气科学, 2003, 27(4):503-517.
|
| [24] |
王芬, 张娇艳, 谷晓平, 等. 西太平洋副热带高压不同特征指数与贵州夏季降水的关系[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2017, 36(4):348-356.
|
| [25] |
陈丽娟, 顾薇, 龚振淞, 等. 影响2018年汛期气候的先兆信号及预测效果评估[J]. 气象, 2019, 45(4):553-564.
|
| [26] |
顾薇, 陈丽娟. 2018年夏季海洋大气特征及对我国气候的影响[J]. 气象, 2019, 45(1):126-134.
|
| [27] |
李崇银, 王作台, 林士哲, 等. 东亚夏季风活动与东亚高空西风急流位置北跳关系的研究[J]. 大气科学, 2004, 28(5):641-658.
|
| [28] |
张耀存, 况雪源. 东亚副热带西风急流位置变化与亚洲夏季风爆发的关系[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2008, 27(2):3-9.
|
| [29] |
孙继松, 戴建华, 何立富. 强对流天气预报的基本原理与技术方法——中国强对流天气预报手册[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2014.
|
| [30] |
段旭, 张秀年, 许美玲, 等. 云南及其周边地区中尺度对流系统时空分布特征[J]. 气象学报, 2004, 62(2):244-250.
|
 ), LI Shuangjun, MENG Yingjie(
), LI Shuangjun, MENG Yingjie( )
)