干旱气象 ›› 2025, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (2): 186-194.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-02-0186
1961—2023年黑龙江省多尺度干旱时空特征
刘玉莲1,2( ), 李秀芬3, 康恒元4(
), 李秀芬3, 康恒元4( ), 孙爽1,2, 袁芳5, 周贺玲6, 沈月钊7
), 孙爽1,2, 袁芳5, 周贺玲6, 沈月钊7
- 1.黑龙江省气候中心,黑龙江 哈尔滨 150030
2.五营国家气候观象台,黑龙江 五营 153000
3.黑龙江省气象科学研究所,黑龙江 哈尔滨 150030
4.黑龙江省哈尔滨市气象局,黑龙江 哈尔滨 150028
5.中国气象局气象干部培训学院湖北分院,湖北 武汉 430074
6.河北省廊坊市气象局,河北 廊坊 131001
7.黑龙江省五常市气象局,黑龙江 五常 150040
Multi-scale drought spatiotemporal characteristics in Heilongjiang Province from 1961 to 2023
LIU Yulian1,2( ), LI Xiufen3, KANG Hengyuan4(
), LI Xiufen3, KANG Hengyuan4( ), SUN Shuang1,2, YUAN Fang5, ZHOU Heling6, SHEN Yuezhao7
), SUN Shuang1,2, YUAN Fang5, ZHOU Heling6, SHEN Yuezhao7
- 1. Climate Center of Heilongjiang Province, Harbin 150030, China
2. Wuying National Climatological Observatory, Wuying 153000, Heilongjiang, China
3. Heilongjiang Province Institute of Meteorological Sciences, Harbin 150030, China
4. Harbin Meteorological Bureau of Heilongjiang Province, Harbin 150028, China
5. Training Centre, CMA, Hubei Branch, Wuhan 430074, China
6. Langfang Meteorological Bureau of Hebei Province, Langfang 131001, Hebei, China
7. Wuchang Meteorological Bureau of Heilongjiang Province , Wuchang 150040, Heilongjiang, China
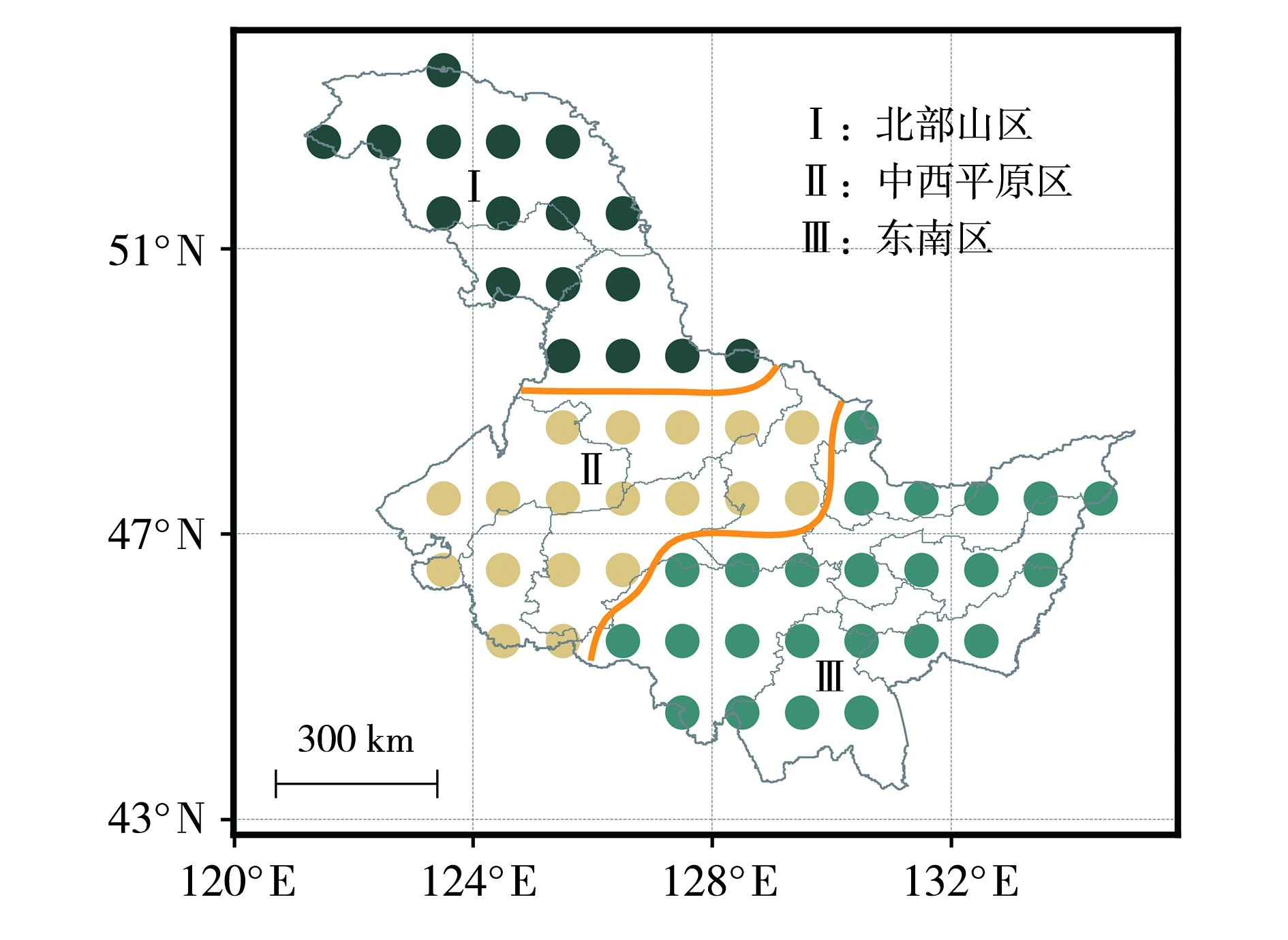
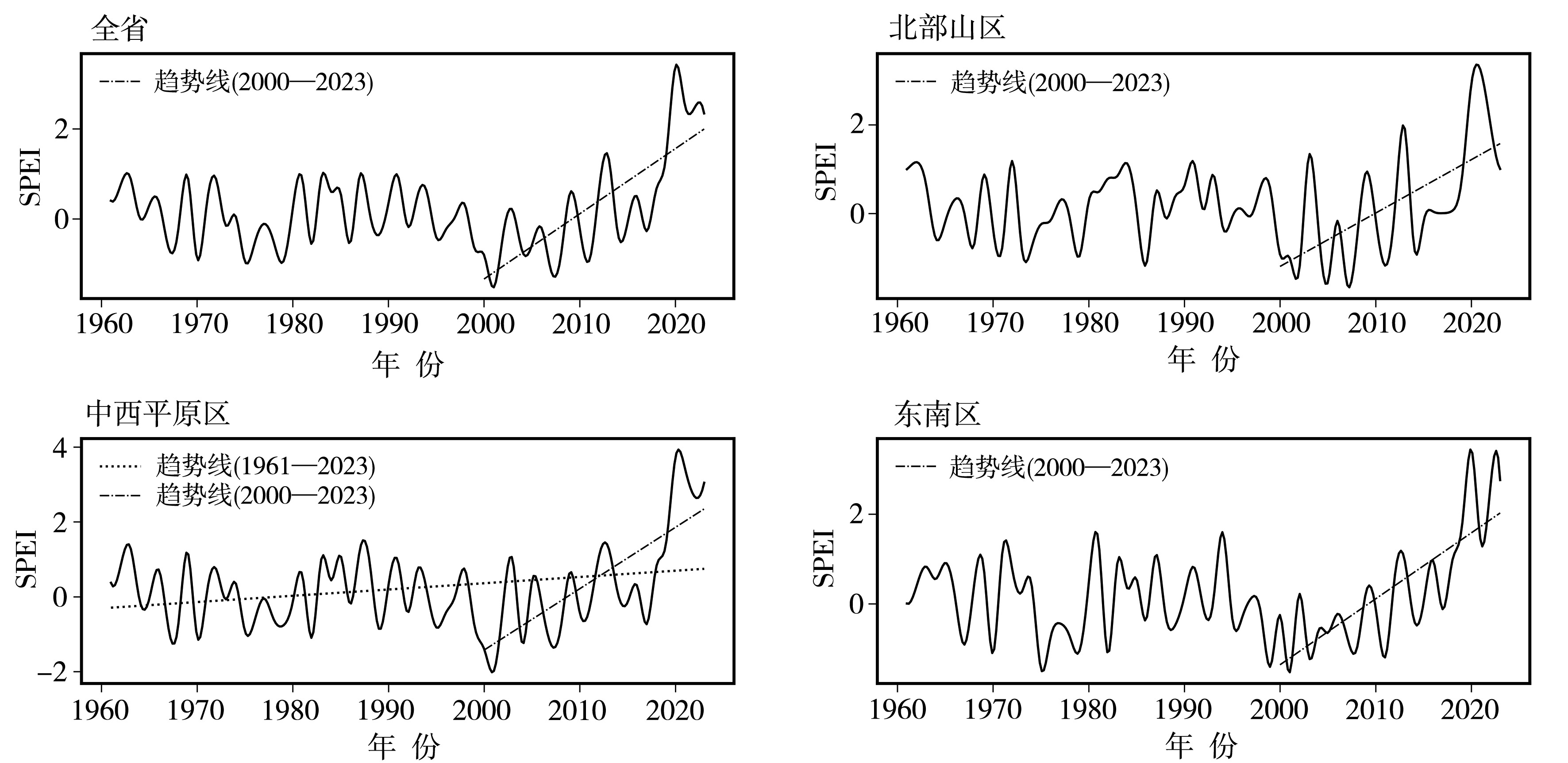
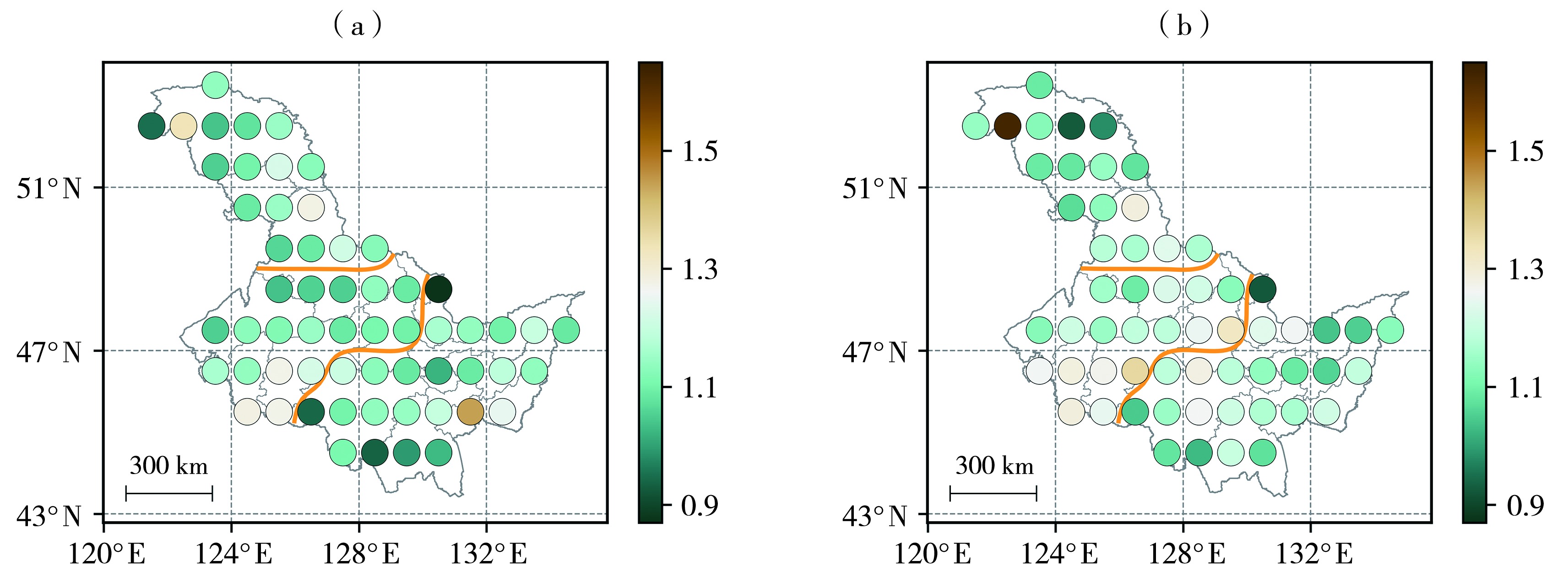
摘要: 明确气候变化背景下黑龙江省多尺度干旱时空特征,对于防灾减灾、保障粮食安全至关重要。基于1961—2023年黑龙江省水平分辨率为1°×1°的NCEP(National Center for Environmental Prediction)和GPCC(Global Precipitation Climatology Centre)月尺度格点气象数据,计算不同时间尺度的标准化降水蒸散指数(Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index,SPEI),使用K-means聚类方法,将黑龙江省分为3个区域,分析1961—2023年黑龙江省不同干旱分区、多时间尺度气象干旱时空特征。结果表明:1961—2023年黑龙江省SPEI指数表现出明显的波动,北部山区4月SPEI呈现显著减小趋势,而中西平原区和东南区在不同时间尺度下SPEI呈增加趋势,表明黑龙江省不同区域的干湿状况存在显著的空间差异。黑龙江省气象干旱主要以大范围群发的形式出现,有两个明显的高发期,分别是1967—1989年和1999—2011年;夏季干旱影响范围普遍大于春季。最近气候期(1991—2020年)黑龙江省的干旱频次增加、强度增强,这一趋势对区域的生态安全和可持续发展构成了挑战。
中图分类号: