干旱气象 ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (4): 540-549.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-04-0540
近50 a黑龙江省5—9月气象干旱及大气环流异常特征
王莹1( ), 张舒1(
), 张舒1( ), 徐永清2, 阙粼婧3, 李新华1, 黄英伟1, 陈雪1, 王蕾1
), 徐永清2, 阙粼婧3, 李新华1, 黄英伟1, 陈雪1, 王蕾1
- 1.黑龙江省气象服务中心,黑龙江 哈尔滨 150030
2.黑龙江省气候中心,黑龙江 哈尔滨 150030
3.北京玖天气象科技有限公司,北京 100191
-
收稿日期:2023-02-28修回日期:2023-05-15出版日期:2023-08-31发布日期:2023-08-29 -
通讯作者:张舒(1986—),女,硕士,高级工程师,主要从事环境气象、农业气象研究。E-mail:417386287@qq.com。 -
作者简介:王莹(1983—),女,硕士,高级工程师,主要从事气象服务及气象灾害研究。E-mail:61949683@qq.com。 -
基金资助:中国气象局气象能力提升联合研究专项(22NLTSY001);黑龙江省自然科学基金项目(LH2022D022);中国气象局沈阳大气环境研究所联合开放基金项目(2021SYIAEKFMS10)
Meteorological drought and atmospheric circulation anomalies characteristics in Heilongjiang Province from May to September in recent 50 years
WANG Ying1( ), ZHANG Shu1(
), ZHANG Shu1( ), XU Yongqing2, QUE Linjing3, LI Xinhua1, HUANG Yingwei1, CHEN Xue1, WANG Lei1
), XU Yongqing2, QUE Linjing3, LI Xinhua1, HUANG Yingwei1, CHEN Xue1, WANG Lei1
- 1. Heilongjiang Meteorological Service Center, Harbin 150030, China
2. Heilongjiang Climate Center, Harbin 150030, China
3. Beijing Jiutian Meteorological Technology Co., Ltd, Beijing 100191, China
-
Received:2023-02-28Revised:2023-05-15Online:2023-08-31Published:2023-08-29
摘要:
黑龙江省是我国主要的粮食生产基地,研究该区域干旱气候特征对科学开展旱灾防御治理具有重要作用。基于1971—2020年农作物生长季(5—9月)黑龙江省80个国家气象站逐日气温、降水资料,计算黑龙江省逐日气象干旱综合指数(Meteorological Drought Composite Index,MCI),分析黑龙江省中旱、重旱、特旱日数时空分布特征,进一步对比分析典型干旱、湿润年的环流特征。结果表明:1971—2020年5—9月,黑龙江省大兴安岭南部、松嫩平原西部是干旱多发区;干旱日数月际空间分布西多东少、中部腹地局部偏多;中旱、重旱、特旱日数年代际特征明显且均呈减少趋势,中旱减少趋势最明显,变化速率为-1.7 d·(10 a)-1。典型干旱年与典型湿润年的环流存在显著差异,典型干旱年,贝加尔湖以西地区受反气旋控制,黑龙江上空受西风带气流控制,盛行下沉气流,不利于冷暖空气交汇,水汽输送通道不明显,水汽难以到达黑龙江地区;典型湿润年情况则相反。
中图分类号:
引用本文
王莹, 张舒, 徐永清, 阙粼婧, 李新华, 黄英伟, 陈雪, 王蕾. 近50 a黑龙江省5—9月气象干旱及大气环流异常特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(4): 540-549.
WANG Ying, ZHANG Shu, XU Yongqing, QUE Linjing, LI Xinhua, HUANG Yingwei, CHEN Xue, WANG Lei. Meteorological drought and atmospheric circulation anomalies characteristics in Heilongjiang Province from May to September in recent 50 years[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(4): 540-549.
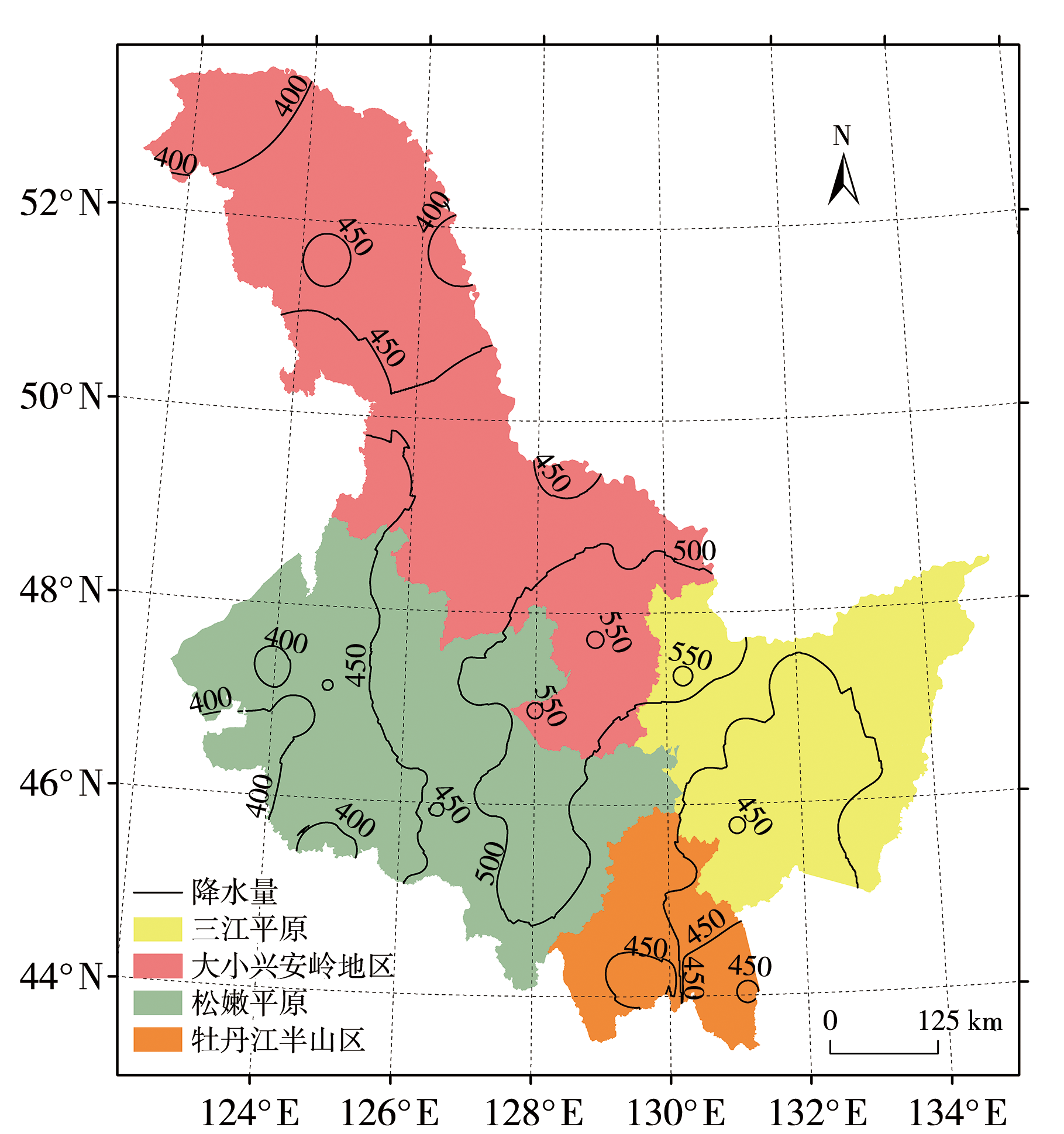
图1 黑龙江省地理分区(填色区)及1990—2020年降水气候态(黑色等值线,单位:mm)分布
Fig.1 Geographical zoning (color filled areas) and distribution of precipitation climate state (black isolines, Unit: mm) during 1990-2020 in Heilongjiang Province
| 等级 | 类型 | MCI | 干旱影响程度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 无旱 | MCI>-0.5 | 地表湿润,作物水分供应充足;地表水资源充足,能满足人们生产、生活需要 |
| 2 | 轻旱 | -1.0<MCI≤-0.5 | 地表空气干燥,土壤出现水分轻度不足,作物轻微缺水,叶色不正;水资源出现短缺,但对生产、生活影响不大 |
| 3 | 中旱 | -1.5<MCI≤-1.0 | 土壤表面干燥,土壤出现水分不足,作物叶片出现萎蔫现象;水资源短缺,对生产、生活造成影响 |
| 4 | 重旱 | -2.0<MCI≤-1.5 | 土壤水分持续严重不足,出现干土层(1~10 cm),作物出现枯死现象;河流出现断流,水资源严重不足,对生产、生活造成较重影响 |
| 5 | 特旱 | MCI≤-2.0 | 土壤水分持续严重不足,出现较厚干土层(大于10 cm),作物出现大面积枯死;多条河流出现断流,水资源严重不足,对生产、生活造成严重影响 |
表1 基于气象干旱综合指数MCI的干旱等级划分
Tab.1 Classification of drought grades based on meteorological drought composite index (MCI)
| 等级 | 类型 | MCI | 干旱影响程度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 无旱 | MCI>-0.5 | 地表湿润,作物水分供应充足;地表水资源充足,能满足人们生产、生活需要 |
| 2 | 轻旱 | -1.0<MCI≤-0.5 | 地表空气干燥,土壤出现水分轻度不足,作物轻微缺水,叶色不正;水资源出现短缺,但对生产、生活影响不大 |
| 3 | 中旱 | -1.5<MCI≤-1.0 | 土壤表面干燥,土壤出现水分不足,作物叶片出现萎蔫现象;水资源短缺,对生产、生活造成影响 |
| 4 | 重旱 | -2.0<MCI≤-1.5 | 土壤水分持续严重不足,出现干土层(1~10 cm),作物出现枯死现象;河流出现断流,水资源严重不足,对生产、生活造成较重影响 |
| 5 | 特旱 | MCI≤-2.0 | 土壤水分持续严重不足,出现较厚干土层(大于10 cm),作物出现大面积枯死;多条河流出现断流,水资源严重不足,对生产、生活造成严重影响 |
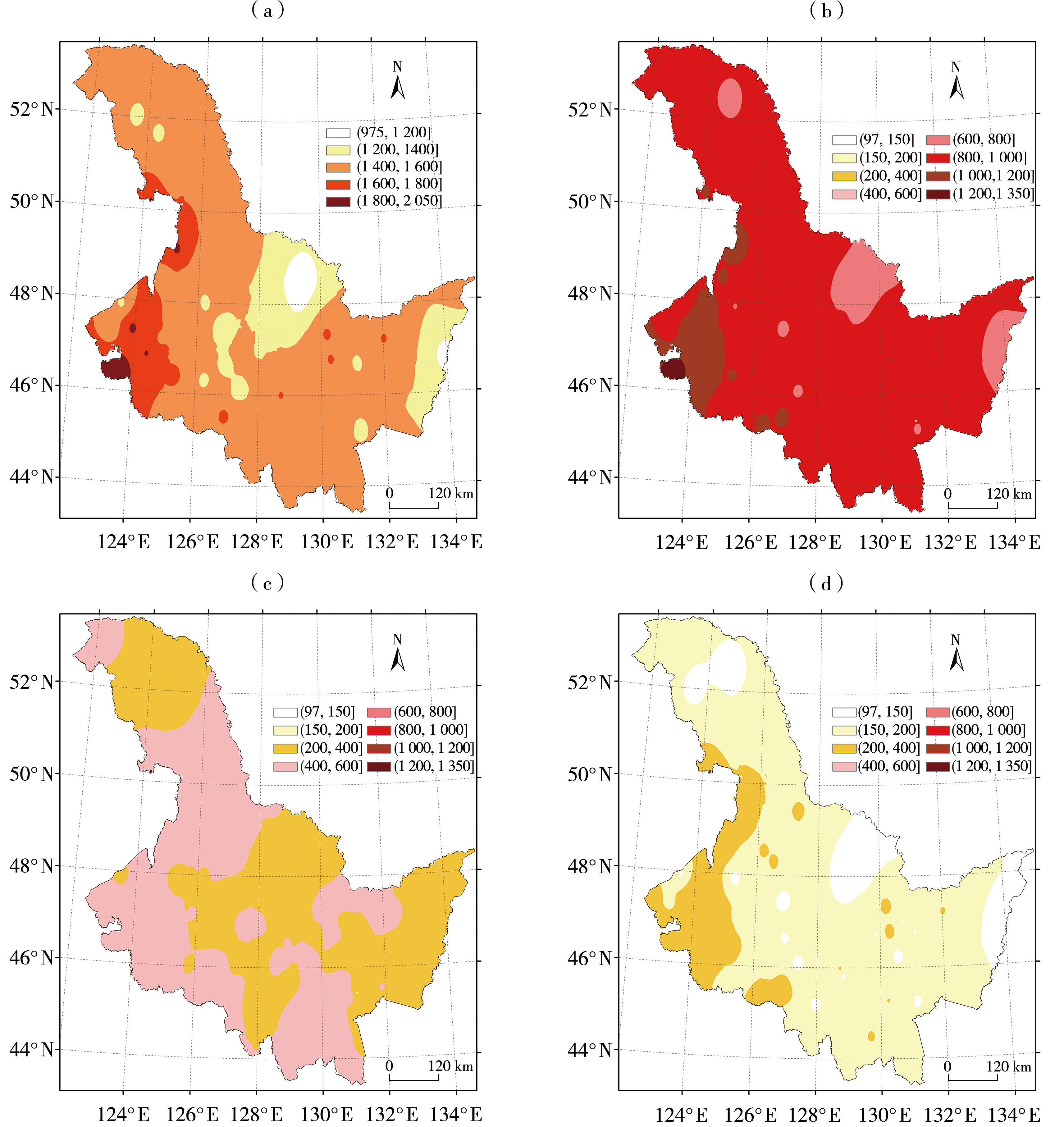
图2 1970—2020年5—9月黑龙江省中旱及以上(a)和中旱(b)、重旱(c)、特旱(d)日数空间分布(单位:d)
Fig.2 Spatial distribution of days of moderate drought and above (a), moderate drought (b), severe drought (c) and extreme drought (d) in Heilongjiang Province from May to September during 1970-2020 (Unit: d)

图3 1970—2020年5月(a、b、c)、6月(d、e、f)、8月(g、h、i)黑龙江省中旱(a、d、g)、重旱(b、e、h)、特旱(c、f、i)日数空间分布(单位:d)
Fig.3 Spatial distribution of days of moderate drought (a, d, g), severe drought (b, e, h) and extreme drought (c, f, i) in Heilongjiang Province in May (a, b, c), June (d, e, f) and August (g, h, i) from 1970 to 2020 (Unit: d)

图4 20世纪70年代(a、b、c)、90年代(d、e、f)及21世纪10年代(g、h、i)5—9月黑龙江省中旱(a、d、g)、重旱(b、e、h)、特旱(c、f、i)日数空间分布(单位:d)
Fig.4 The spatial distribution of days of moderate drought (a, d, g), severe drought (b, e, h) and extreme drought (c, f, i) in Heilongjiang Province from May to September in the 1970s (a, b, c), 1990s (d, e, f) and 2010s (g, h, i) (Unit: d)

图5 1970—2020年5—9月黑龙江省平均中旱(a)、重旱(b)、特旱(c)日数年际变化
Fig.5 Inter-annual variation of moderate (a), severe (b) and extreme (c) drought days in Heilongjiang Province from May to September during 1970-2020
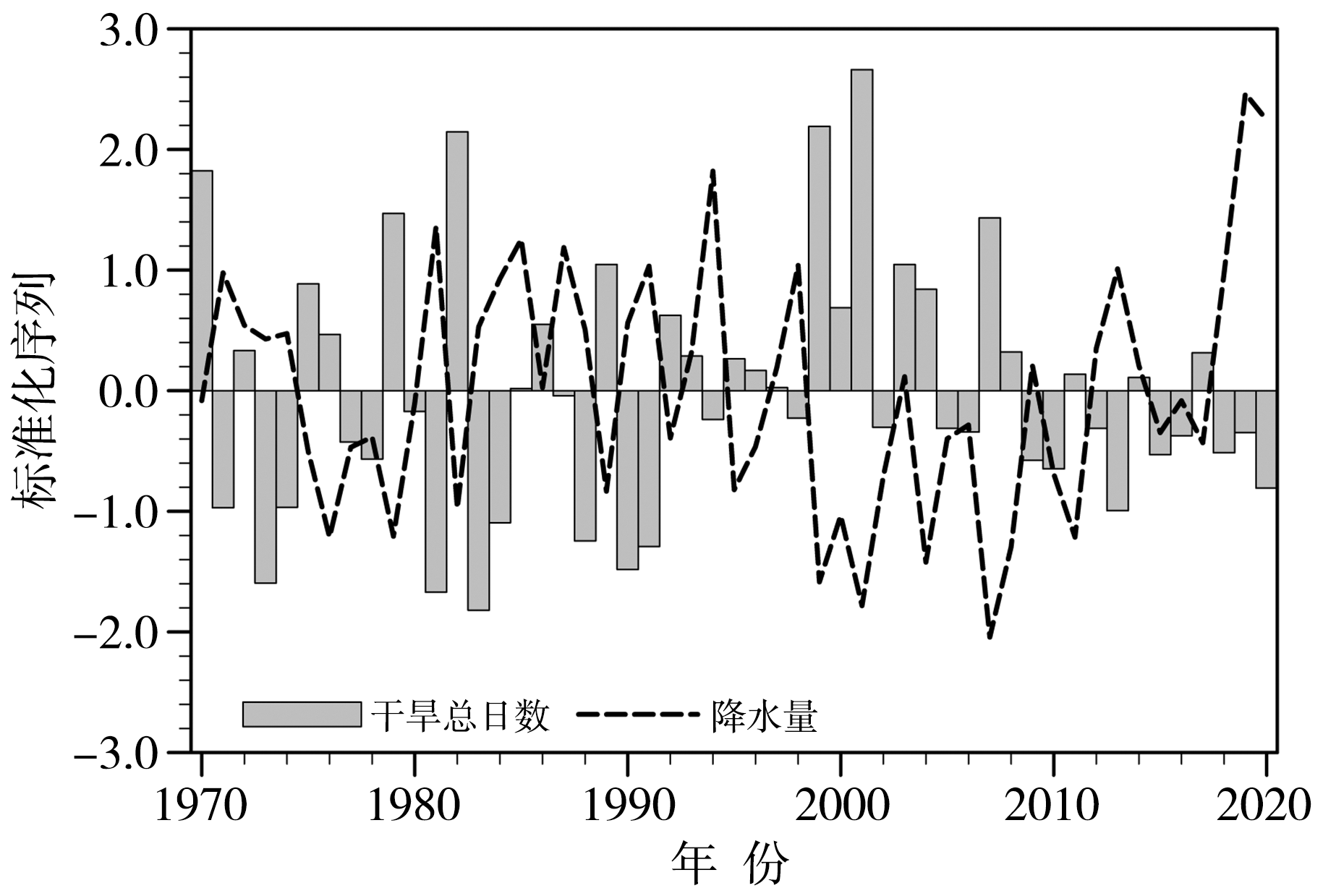
图6 1970—2020年5—9月黑龙江省中旱及以上等级干旱日数与降水量标准化时间序列
Fig.6 The standardized time series of days of moderate drought and above and precipitation in Heilongjiang Province from May to September during1970-2020

图7 黑龙江省典型干旱年(a、b)与湿润年(c、d)500 hPa高度距平场(a、c,单位:gpm)、850 hPa风场距平(b、d,单位:m s-1)合成分析及其差值场(e,单位:gpm;f,单位:m s-1) (打点区域通过α=0.10的显著性检验。下同)
Fig.7 Synthetic analysis of 500 hPa height anomaly field (a, c, Unit: gpm), 850 hPa wind field anomaly (b, d, Unit: m s-1) in typical dry year (a, b) and wet year (c, d) in Heilongjiang Province and their difference field (e, Unit: gpm; f, Unit: m s-1) (The dotting area passes the significance test at α=0.10. the same as below)

图8 典型干旱年(a)与典型湿润年(b)整层水汽通量距平合成分析及其差值场(c)(单位:kg·m-1·s-1)
Fig.8 Synthetic analysis of whole layer water vapor flux anomaly in typical dry years (a) and wet years (b) in Heilongjiang Province and their difference field (c) (Unit: kg·m-1·s-1)
| [1] | 敖雪, 翟晴飞, 崔妍, 等, 2020. 不同升温情景下中国东北地区平均气候和极端气候事件变化预估[J]. 气象与环境学报, 36(5): 40-51. |
| [2] | 陈敏, 颜鹏程, 张铁军, 等, 2022. 基于MCI的1961—2016年中国北方不同等级干旱趋势研究[J]. 甘肃科技, 38(16): 33-37. |
| [3] | 冯波, 闫佰忠, 章光新, 2014. 松花江流域水文干旱联合概率分布特征研究[J]. 节水灌溉, (5): 38-42+47. |
| [4] | 高峰, 王宝书, 2008. 全球变暖与东北地区气温变化研究[J]. 海洋预报, 25(1): 26-30. |
| [5] | 郭梦, 张奇莹, 钱会, 等, 2019. 基于SPEI干旱指数的陕西省干旱时空分布特征分析[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 30(3): 127-132+138. |
| [6] |
郭晓丽, 陈素华, 2018. 内蒙古中部地区春玉米水分亏缺时空特征[J]. 干旱气象, 36(2): 295-300.
DOI |
| [7] | 李析男, 谢平, 李彬彬, 等, 2014. 变化环境下不同等级干旱事件发生概率的计算方法——以无定河流域为例[J]. 水利学报, 45(5): 585-594. |
| [8] | 李雪纯, 赵君, 徐进超, 2018. 基于降水距平百分率的安徽省近50 a干旱时空分布特征分析[J]. 中国农村水利水电, (9): 133-136+143. |
| [9] | 廖要明, 张存杰, 2017. 基于MCI的中国干旱时空分布及灾情变化特征[J]. 气象, 43(11): 1 402-1 409. |
| [10] | 刘玉莲, 于宏敏, 2012. 基于CI指数的黑龙江省作物生长关键期干旱变化[J]. 气象与环境学报, 28(1): 48-54. |
| [11] | 刘玉汐, 任景全, 孙月, 等, 2020. 1971—2016年东北地区农业气象灾害损失变化特征及影响[J]. 干旱气象, 38(4): 647-654. |
| [12] | 马建勇, 许吟隆, 潘婕, 2012. 基于SPI与相对湿润度指数的1961—2009年东北地区5—9月干旱趋势分析[J]. 气象与环境学报, 28(3): 90-95. |
| [13] | 马柱国, 符淙斌, 2006. 1951—2004年中国北方干旱化基本事实[J]. 科学通报, 51(20): 2 429-2 439. |
| [14] | 马柱国, 符淙斌, 2007. 20世纪下半叶全球干旱化的事实及其与大尺度背景的联系[J]. 中国科学D辑: 地球科学, 37 (2): 222-233. |
| [15] | 孟鑫, 智协飞, 2016. 东北地区夏季干旱的年际—年代际变化特征[J]. 大气科学学报, 39(4): 562-568. |
| [16] | 木沙·如孜, 雷晓云, 白云岗, 等, 2014. 塔里木河流域旱灾发生规律[J]. 干旱区研究, 31(2): 274-278. |
| [17] | 钱正安, 吴统文, 宋敏红, 等, 2001. 干旱灾害和我国西北干旱气候的研究进展及问题[J]. 地球科学进展, 16(1): 28-38. |
| [18] | 申双和, 张方敏, 盛琼, 2009. 1975—2004年中国湿润指数时空变化特征[J]. 农业工程学报, 25(1): 11-15. |
| [19] | 孙力, 安刚, 廉毅, 等, 2002. 中国东北地区夏季旱涝的大气环流异常特征[J]. 气候与环境研究, 7(1): 102-113. |
| [20] | 汪秀清, 陈长胜, 张智勇, 等, 2006. 东北地区夏季旱涝的区域特征及水汽异常输送[J]. 自然灾害学报, 15(4): 53-58. |
| [21] |
王素萍, 王劲松, 张强, 等, 2020. 多种干旱指数在中国北方的适用性及其差异原因初探[J]. 高原气象, 39(3): 628-640.
DOI |
| [22] |
王亚平, 黄耀, 张稳, 2008. 中国东北三省1960—2005年地表干燥度变化趋势[J]. 地球科学进展, 23(6): 619-626.
DOI |
| [23] |
王莺, 张强, 王劲松, 等, 2022. 21世纪以来干旱研究的若干新进展与展望[J]. 干旱气象, 40(4): 549-566.
DOI |
| [24] | 王盈, 2020. 五种干旱指数在呼和浩特市地区的适用性研究[D]. 内蒙古: 内蒙古农业大学: 8-12. |
| [25] | 韦潇宇, 胡琦, 马雪晴, 等, 2018. 基于SPEI的华北平原夏玉米生长季干旱时空变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 36(4): 554-560. |
| [26] | 魏凤英, 张婷, 2009. 东北地区干旱强度频率分布特征及其环流背景[J]. 自然灾害学报, 18(3): 1-7. |
| [27] | 吴黎, 解文欢, 张有智, 等, 2022. 基于温度植被干旱指数的黑龙江省20年干旱时空特征研究[J]. 水土保持研究, 29(5): 358-363. |
| [28] |
薛亮, 袁淑杰, 王劲松, 2023. 我国不同区域气象干旱成因研究进展与展望[J]. 干旱气象, 41(1): 1-13.
DOI |
| [29] | 杨霏云, 郑秋红, 罗蒋梅, 等, 2015. 实用农业气象指标[M]. 北京: 气象出版社: 21-23. |
| [30] | 杨文通, 张丽媛, 高宇, 2022. 东北三省农业旱灾特征及重现期分析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 36(10): 133-141. |
| [31] | 于宏敏, 刘玉莲, 高永刚, 等, 2012. 松花江流域气候变化影响评估报告[M]. 北京: 气象出版社: 3-7. |
| [32] | 张强, 韩兰英, 郝小翠, 等, 2015. 气候变化对中国农业旱灾损失率的影响及其南北区域差异性[J]. 气象学报, 73(6): 1 092-1 103. |
| [33] | 张强, 姚玉璧, 李耀辉, 等, 2020. 中国干旱事件成因和变化规律的研究进展与展望[J]. 气象学报, 78(3): 500-521. |
| [34] | 张强, 张良, 崔显成, 等, 2011. 干旱监测与评价技术的发展及其科学挑战[J]. 地球科学进展, 26(7): 763-778. |
| [35] | 赵茹欣, 王会肖, 杨会彩, 等, 2017. 基于标准降水指数的黑龙江省气象干旱特征分析[J]. 节水灌溉, (12): 56-62+67. |
| [36] | 赵一磊, 任福民, 李栋梁, 等, 2013. 基于有效降水干旱指数的改进研究[J]. 气象, 39(5): 600-607. |
| [37] | 中国气象局, 2017. 气象干旱等级: GB/T20481—2017[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| [38] | 邹旭恺, 张强, 2008. 近半个世纪我国干旱变化的初步研究[J]. 应用气象学报, 19(6): 679-687. |
| [39] |
LIU Z Q, JIANG L P, SHI C X, et al, 2023. CRA-40/Atmosphere: the first-generation Chinese atmospheric reanalysis(1979-2018): system description and performance evaluation[J]. Journal of Meteorological Research, 37(1): 1-19.
DOI |
| [40] |
OBASI G O P, 1994. WMO’s Role in the international decade for natural disaster reduction[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 75(9): 1 655-1 661.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
YU X J, ZHANG L X, ZHOU T J, et al, 2021. The Asian subtropical westerly jet stream in CRA-40, ERA5, and CFSR reanalysis data: comparative assessment[J]. Journal of Meteorological Research, 35(1): 46-63.
DOI |
| [42] |
ZHAO D, ZHANG L X, ZHOU T J, et al, 2021. Contributions of local and remote atmospheric moisture fluxes to east China precipitation estimated from CRA-40 reanalysis[J]. Journal of Meteorological Research, 35(1): 32-45.
DOI |
| [43] |
ZHOU H, LIU Y B, 2016. SPI based meteorological drought assessment over a humid basin: effects of processing schemes[J]. Water, 8(9), 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8090373.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 姚彦伶 , 王 悦 , 陈权亮 , 廖雨静. 青藏高原中东部极端降水的时空变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(5): 714-722. |
| [2] | 乜虹, 保广裕, 戴升, 张晓云, 王凯. 青海共和盆地PM10质量浓度变化特征及其影响因子研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(2): 301-308. |
| [3] | 娄德君, 李永生, 王永光, 陈晨, 张健. 2020年7月黑龙江极端少雨成因初探[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(3): 396-405. |
| [4] | 焦洋, 张永婧, 尹承美, 褚颖佳. 山东夏季暴雨对青藏高原东南部及邻近区域春季大气热源变化的响应[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(3): 406-414. |
| [5] | 徐玮平, 孟祥新, 顾伟宗, 伯忠凯. 山东春季极端低温与前冬北大西洋海温的关系[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(2): 202-211. |
| [6] | 许婷婷, 杨霞, 周鸿奎. 1981—2019年新疆区域性高温天气过程时空特征及其环流分型[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(2): 212-221. |
| [7] | 何芬, 赖绍钧, 池艳珍, 潘航, 曹蓉, 鲍瑞娟. 福建省2018年3—6月干旱环流的变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(1): 22-29. |
| [8] | 于静,王莺,高亚敏,齐佳慧,付铭. 基于MOD16产品的科尔沁草原地表蒸散时空变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(5): 831-837. |
| [9] | 肖晶晶, 马浩, 张育慧, 贺忠华, 李娜, 温泉沛, 李正泉. 1905—2018年浙江地温序列构建及其变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(3): 386-393. |
| [10] | 高睿娜, 王素艳, 高娜, 左河疆. CI和MCI干旱指数在宁夏的适应性对比[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(2): 185-192. |
| [11] | 王健疆, 马浩, 余丽萍, 龚理卿, 汪晨. 2019年浙江省秋旱大气环流特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(1): 1-7. |
| [12] | 侯琼, 苗百岭, 王英舜, 董春丽. 水分胁迫对半干旱典型草原土壤水分变化特征的影响[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(6): 987-993. |
| [13] | 檀艳静, 胡程达, 史桂芬. 黄淮海区域参考作物蒸散量的时空变化特征及影响因素#br#[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(5): 794-803. |
| [14] | 段修荣, 罗伟, 郭海燕. 1963—2017年四川自贡市不同历时年最大降水量变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(1): 40-49. |
| [15] | 马有绚, 李万志, 王丽霞, 白文蓉, 王紫文. 基于SPI的青海省春季干旱时空演变特征及环流诊断[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(03): 362-370. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
