干旱气象 ›› 2025, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (1): 126-132.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2025)-01-0126
内蒙古中部地区层状云微物理特征及可播度分析
许志丽1( ), 徐亮亮2, 毕力格1(
), 徐亮亮2, 毕力格1( ), 史金丽1, 辛悦1, 刘沫彤3
), 史金丽1, 辛悦1, 刘沫彤3
- 1.内蒙古自治区人工影响天气中心,内蒙古 呼和浩特 010051
2.内蒙古自治区气象数据中心,内蒙古 呼和浩特 010051
3.内蒙古自治区赤峰市气象局,内蒙古 赤峰 024000
Analysis on microphysical characteristics and seedability of stratiform clouds in middle region of Inner Mongolia
XU Zhili1( ), XU Liangliang2, BI Lige1(
), XU Liangliang2, BI Lige1( ), SHI Jinli1, XIN Yue1, LIU Motong3
), SHI Jinli1, XIN Yue1, LIU Motong3
- 1. Inner Mongolia Weather Modification,Hohhot 010051,China
2. Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Meteorological Data Center,Hohhot 010051,China
3. Chifeng Meteorological Bureau of Inner Mongolia,Chifeng 024000,Inner Mongolia,China
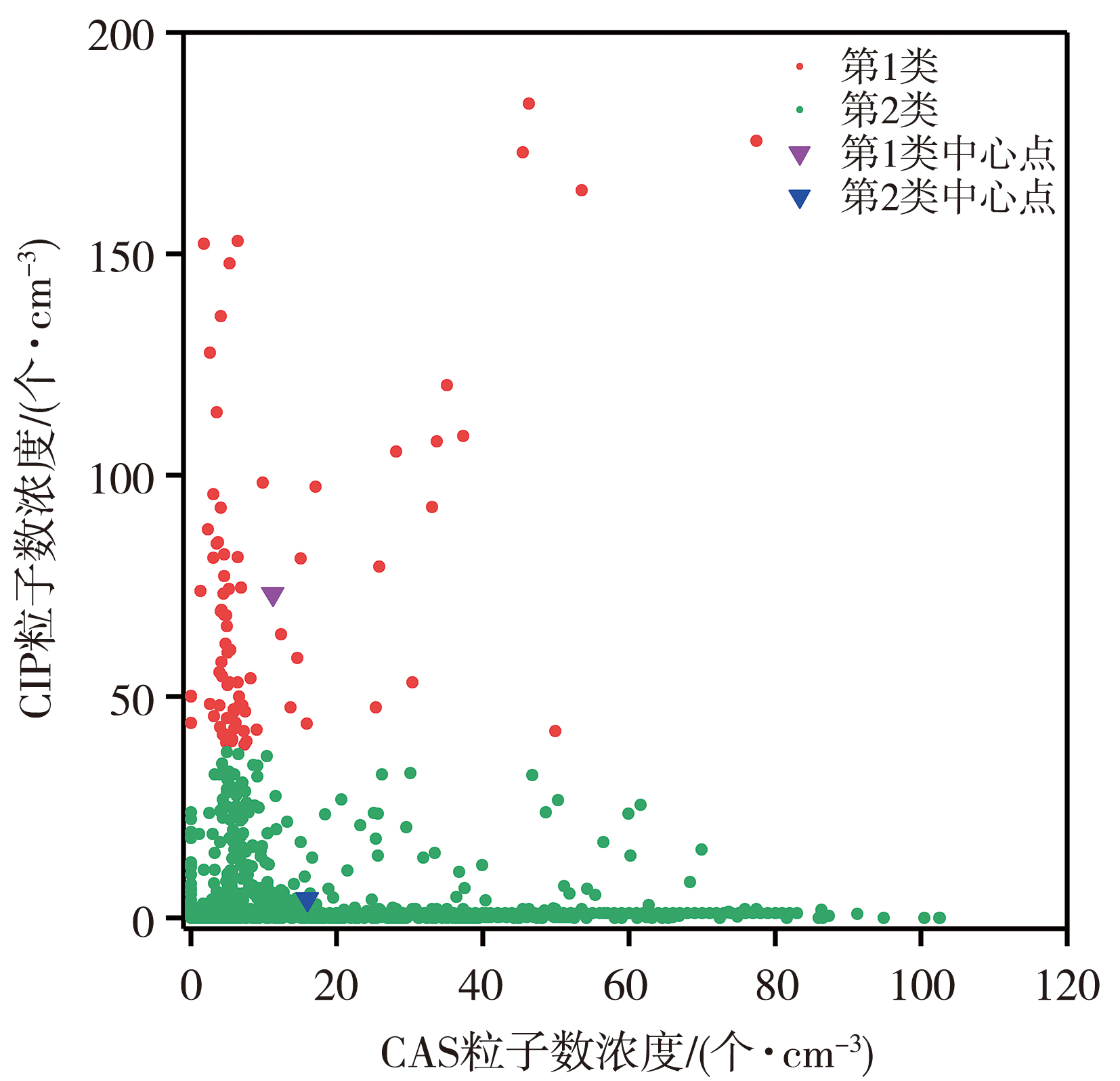
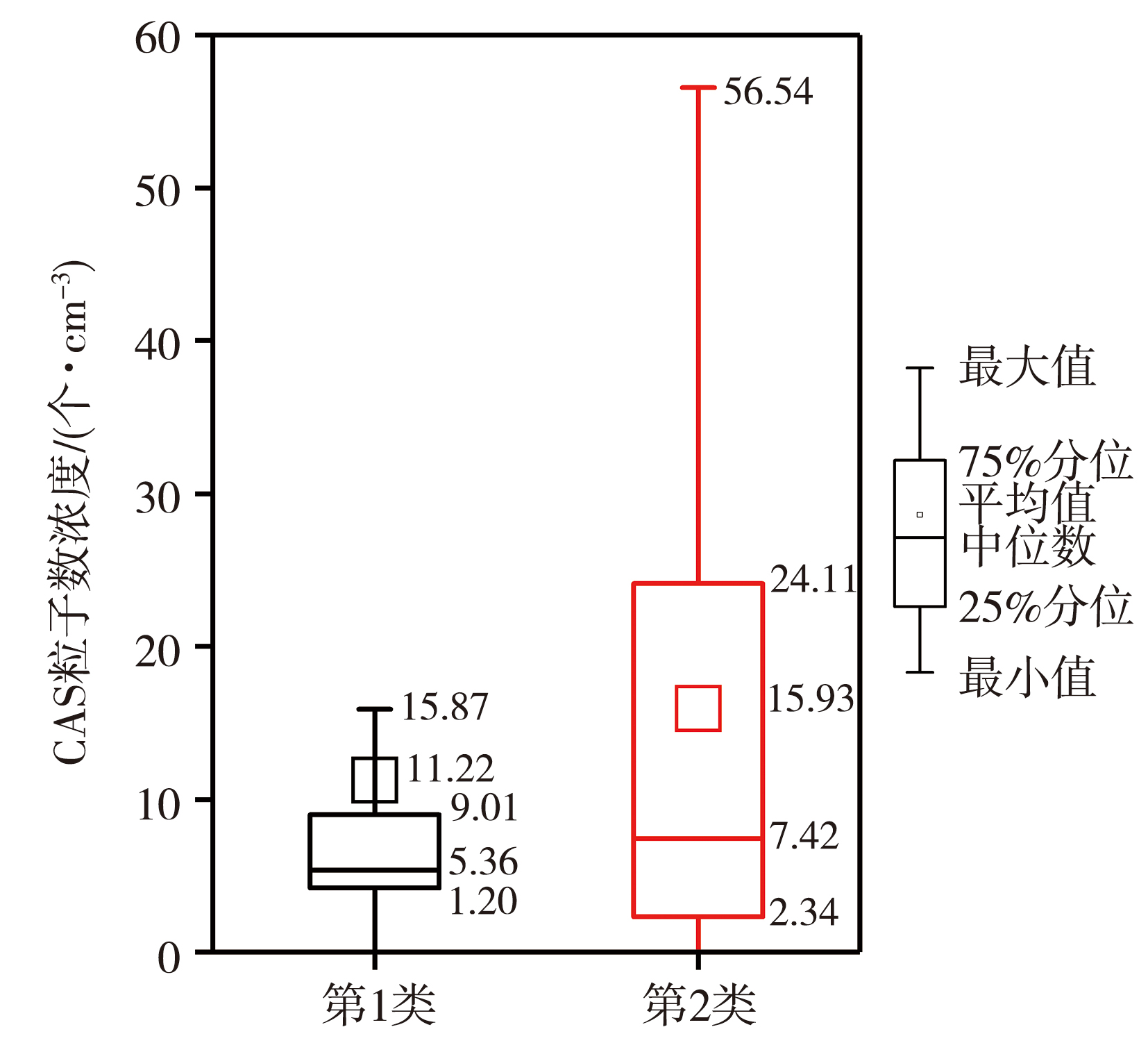
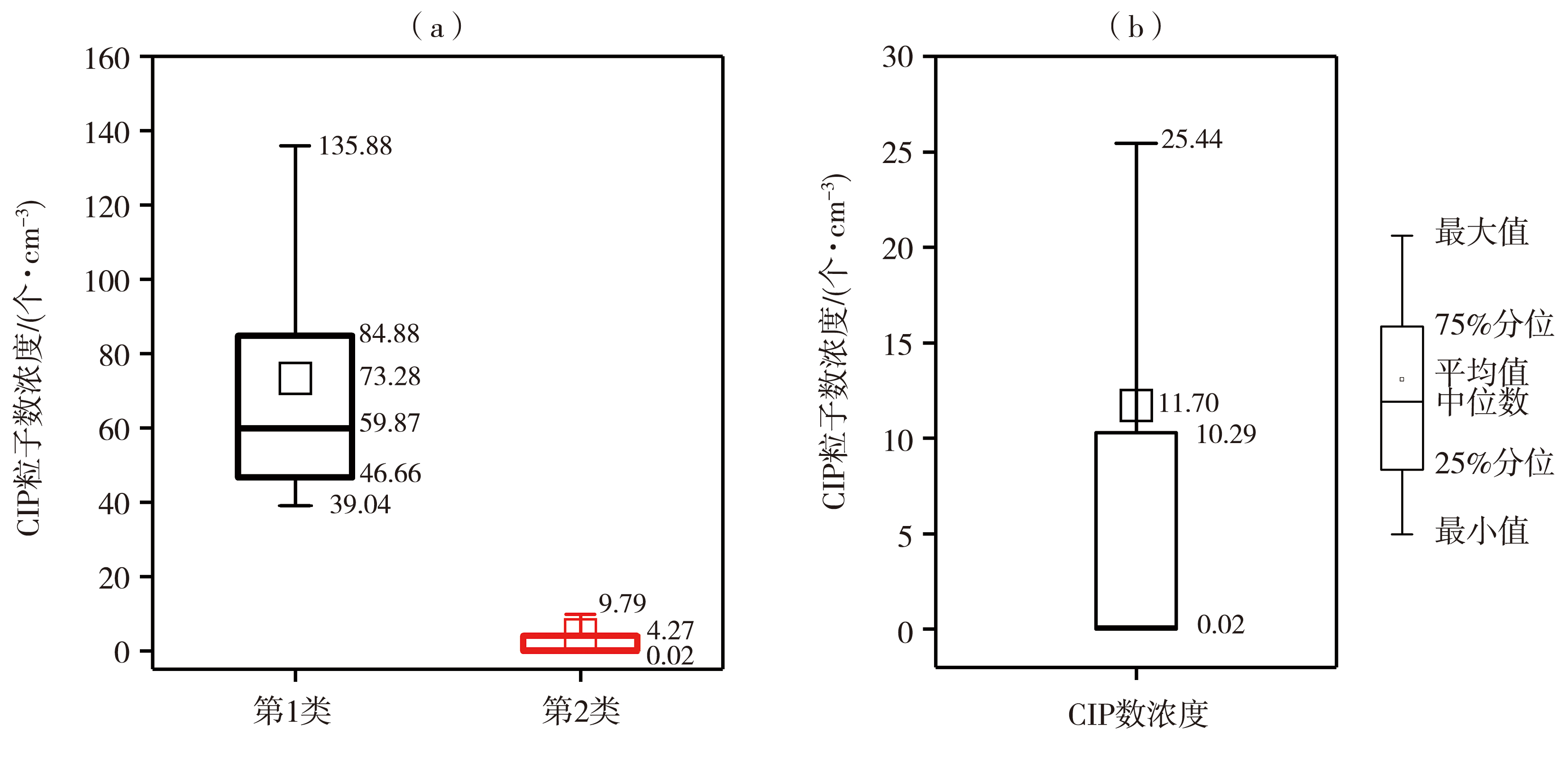
摘要: 对层状云降水云系开展云微物理特征及可播性实时识别研究,有利于提高对层状云降水云系增雨催化潜力的认识,为人工增雨作业实时识别提供技术支撑。利用内蒙古中部地区2018—2019年8架次层状云飞机作业机载探测资料,研究该地区层状云微物理特征及人工增雨可播度特征。结果表明:层状云中云水、液态水、过冷水出现频率分别为59.97%、82.99%、70.84%;液态水含量主要集中在0.001~0.100 g·m-3,过冷水含量主要分布在0.010~0.100 g·m-3,具有较好的引晶催化潜力。大云粒子数浓度平均为8个·cm-3,数浓度大于20个·cm-3的占比14.10%;小云粒子数浓度平均为20个·cm-3,数浓度大于20个·cm-3的占比28.54%。云粒子数浓度总体上较小,70%以上的云粒子位于负温区。层状云中小云粒子数浓度达到15个·cm-3时,云区具有可播度;当可播云区中大云粒子数浓度小于10个·cm-3时,云区具有强可播度。
中图分类号: