干旱气象 ›› 2025, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (1): 11-20.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-01-0011
黄河上游主要汇流区夏季复合干热事件变化特征及其对径流的影响
杨博成1( ), 李维国1, 刘晓云2(
), 李维国1, 刘晓云2( ), 董胜虎3, 贵强1, 甘泽良1, 郑琼4
), 董胜虎3, 贵强1, 甘泽良1, 郑琼4
- 1.甘肃省白银市气象局,甘肃 白银 730090
2.中国气象局兰州干旱气象研究所,甘肃省干旱气候变化与减灾重点实验室,中国气象局干旱气候变化与减灾重点实验室,甘肃 兰州 730020
3.黄河水利委员会上游水文水资源局,甘肃 兰州 730030
4.甘肃省会宁县气象局,甘肃 会宁 730700
-
收稿日期:2024-09-05修回日期:2024-10-30出版日期:2025-02-28发布日期:2025-03-14 -
通讯作者:刘晓云(1980—),女,陕西宝鸡人,高级工程师,主要从事气候变化研究工作。E-mail:jqliuxy@126.com。 -
作者简介:杨博成(2000—),男,甘肃定西人,主要从事天气气候业务及科研工作。E-mail:Ybc000904@163.com。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(42375039);国家自然科学基金项目(42230611);第二次青藏高原综合科学考察研究项目(2019QZKK0105);甘肃省自然科学基金项目(23JRRA1324);甘肃省自然科学基金项目(24JRRA725);中国气象局创新发展专项(CXFZ2022J049)
Characteristics of summer compound dry hot events in the main confluence area of the upper Yellow River and their impact on runoff
YANG Bocheng1( ), LI Weiguo1, LIU Xiaoyun2(
), LI Weiguo1, LIU Xiaoyun2( ), DONG Shenghu3, GUI Qiang1, GAN Zeliang1, ZHENG Qiong4
), DONG Shenghu3, GUI Qiang1, GAN Zeliang1, ZHENG Qiong4
- 1. Baiying Meteorological Bureau of Gansu Province,Baiying 730090,Gansu,China
2. Lanzhou Institute of Arid Meteorology,CMA,Key Laboratory of Arid Climate Change and Reducing Disaster of Gansu Province,Key Laboratory of Arid Climate Change and Reducing Disaster,CMA,Lanzhou 730020,China
3. Bureau of Upper Reach Hydrology and Water Resource,YRCC,Lanzhou 730030,China
4. Huining County Meteorological Bureau of Gansu Province,Huining 730700,Gansu,China
-
Received:2024-09-05Revised:2024-10-30Online:2025-02-28Published:2025-03-14
摘要:
基于气象、水文观测及NCEP/NCAR(National Center for Environmental Prediction/National Center for Atmospheric Research)再分析数据对黄河上游主要汇流区夏季复合干热事件变化特征及其成因以及对径流的影响进行了分析与探讨。结果表明,在平均空间分布上,黄河上游主要汇流区夏季高温日数从西南到东北逐渐增多,而夏季降水量正好相反;从时空分布看,1961年以来黄河上游主要汇流区夏季高温日数呈一致增多趋势;夏季降水从长期趋势看呈一致波动变化,但2000年以后呈一致增加趋势;复合干热事件本世纪以来显著增多。在多时间尺度变化上,黄河上游主要汇流区夏季复合干热事件主要以年际和趋势变化为主。环流影响因子方面,黄河上游主要汇流区夏季复合干热事件变化受多环流因子共同影响,但在不同时间尺度上影响因子差异较大,年际尺度上西风环流、东亚夏季风、南亚夏季风、高原夏季风及北风环流的影响程度均较弱,年代际尺度上主要受高原夏季风环流影响,多年代际尺度上同时受西风环流、东亚夏季风、南亚夏季风、高原夏季风及北风环流共同影响。大尺度环流背景场上,西太平洋副热带高压偏西偏强、缺少异常的西南水汽输送及垂直场上异常的下沉运动是本世纪以来黄河上游主要汇流区夏季复合干热事件增多的主要原因。黄河上游主要汇流区夏季复合干热事件的增加会使得流域兰州站的径流量减少,而1998年以来黄河兰州段径流量的增加主要原因是降水增加。
中图分类号:
引用本文
杨博成, 李维国, 刘晓云, 董胜虎, 贵强, 甘泽良, 郑琼. 黄河上游主要汇流区夏季复合干热事件变化特征及其对径流的影响[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(1): 11-20.
YANG Bocheng, LI Weiguo, LIU Xiaoyun, DONG Shenghu, GUI Qiang, GAN Zeliang, ZHENG Qiong. Characteristics of summer compound dry hot events in the main confluence area of the upper Yellow River and their impact on runoff[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(1): 11-20.

图2 黄河上游主要汇流区1961—2022年多年平均夏季高温日数(a,单位:d)和降水量(b,单位:mm)空间分布
Fig.2 The spatial distribution of summer high temperature days (a,Unit: d) and precipitation (b,Unit: mm) in the main confluence area of the upper Yellow River averaged from 1961 to 2022
| 模态 | 高温日数 | 降水量 |
|---|---|---|
| EOF1 | 77.18 | 26.73 |
| EOF2 | 5.97 | 9.78 |
| EOF3 | 3.65 | 6.72 |
| EOF4 | 3.09 | 6.18 |
| EOF5 | 1.73 | 5.72 |
| EOF6 | 1.24 | 5.12 |
| EOF7 | 1.13 | 4.81 |
| EOF8 | 0.91 | 4.05 |
| EOF9 | 0.76 | 3.71 |
| EOF10 | 0.67 | 3.37 |
表1 The variance contribution of the top ten modes of EOF decomposition of high temperature days and precipitation in the main confluence area of the upper Yellow River in summer from 1961 to 2022 单位:%
Tab.1
| 模态 | 高温日数 | 降水量 |
|---|---|---|
| EOF1 | 77.18 | 26.73 |
| EOF2 | 5.97 | 9.78 |
| EOF3 | 3.65 | 6.72 |
| EOF4 | 3.09 | 6.18 |
| EOF5 | 1.73 | 5.72 |
| EOF6 | 1.24 | 5.12 |
| EOF7 | 1.13 | 4.81 |
| EOF8 | 0.91 | 4.05 |
| EOF9 | 0.76 | 3.71 |
| EOF10 | 0.67 | 3.37 |
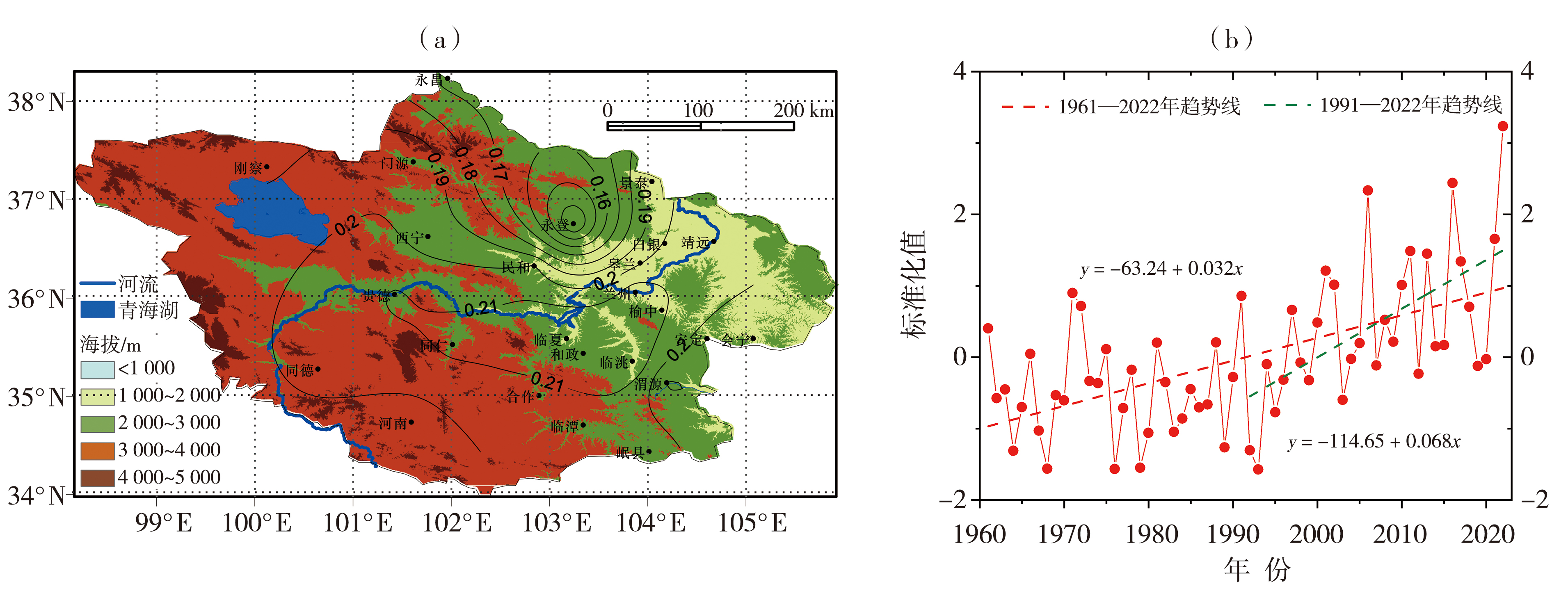
图3 1961—2022年夏季黄河上游主要汇流区高温日数EOF分解的第一模态空间分布(a)及其时间系数(b)
Fig.3 The first model spatial distribution (a) and time coefficient (b) of EOF decomposition of high temperature days in the main confluence area of the upper Yellow River in summer from 1961 to 2022
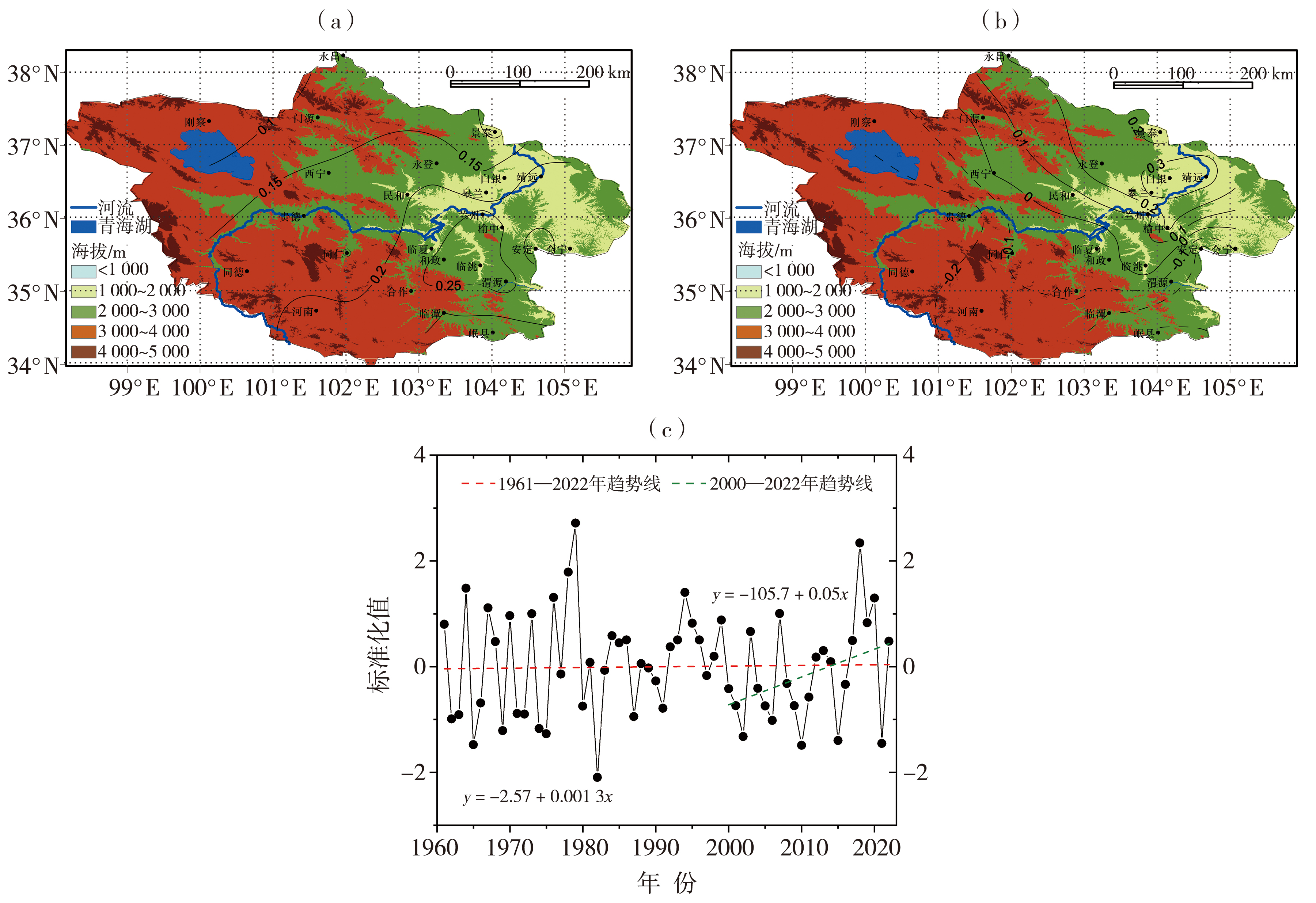
图4 1961—2022年夏季黄河上游主要汇流区降水量EOF分解的第一模态(a)、第二模态(b)空间分布及第一模态的时间系数(c)
Fig.4 The spatial distribution of the first mode (a),the second mode (b),and the time coefficient of the first mode (c) of EOF decomposition of precipitation in the main confluence area of the upper Yellow River in summer from 1961 to 2022
| 排位 | 年份 | 复合干热指数 | 高温日数PC1标准化值 | 降水量PC1标准化值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 顺序1 | 2021 | 8.59 | 1.66 | -1.45 |
| 顺序2 | 2006 | 5.18 | 2.33 | -1.02 |
| 顺序3 | 2010 | 4.72 | 1.01 | -1.49 |
| 顺序4 | 2002 | 4.56 | 1.02 | -1.32 |
| 顺序5 | 1971 | 3.16 | 0.90 | -0.89 |
| 逆序5 | 1995 | -2.47 | -0.78 | 0.82 |
| 逆序4 | 1967 | -4.36 | -1.03 | 1.11 |
| 逆序3 | 1964 | -7.07 | -1.31 | 1.49 |
| 逆序2 | 1976 | -7.10 | -1.57 | 1.31 |
| 逆序1 | 1979 | -9.16 | -1.55 | 2.71 |
表2 1961—2022年黄河上游主要汇流区夏季复合干热指数顺序和逆序前5位对应年份的高温日数和降水量标准化值
Tab.2 The high temperature days and precipitation standardized values of the top 5 corresponding years in the order and reverse order of summer compound dry-hot index in the main confluence area of the upper Yellow River from 1961 to 2022
| 排位 | 年份 | 复合干热指数 | 高温日数PC1标准化值 | 降水量PC1标准化值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 顺序1 | 2021 | 8.59 | 1.66 | -1.45 |
| 顺序2 | 2006 | 5.18 | 2.33 | -1.02 |
| 顺序3 | 2010 | 4.72 | 1.01 | -1.49 |
| 顺序4 | 2002 | 4.56 | 1.02 | -1.32 |
| 顺序5 | 1971 | 3.16 | 0.90 | -0.89 |
| 逆序5 | 1995 | -2.47 | -0.78 | 0.82 |
| 逆序4 | 1967 | -4.36 | -1.03 | 1.11 |
| 逆序3 | 1964 | -7.07 | -1.31 | 1.49 |
| 逆序2 | 1976 | -7.10 | -1.57 | 1.31 |
| 逆序1 | 1979 | -9.16 | -1.55 | 2.71 |

图5 1961—2022年黄河上游主要汇流区夏季复合干热指数年际变化
Fig.5 The inter-annual variation of summer compound dry-hot index in the main confluence area of the upper Yellow River from 1961 to 2022
| 分量 | 贡献率C/% | 周期T/a | 与原序列相关系数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| IMF1 | 53.17 | 3.3 | 0.59*** |
| IMF2 | 11.71 | 8.2 | 0.568*** |
| IMF3 | 7.47 | 17.7 | 0.340** |
| IMF4 | 1.22 | 20.7 | 0.212 |
| 趋势项 | 26.43 | 0.395** |
表3 基于EEMD分解的1961—2022年黄河上游主要汇流区夏季复合干热指数不同时间尺度分量贡献率
Tab.3 Contribution rates of different time scale components of sumer compound dry-hot index based on EEMD decomposition in the main confluence area of the upper Yellow River from 1961 to 2022
| 分量 | 贡献率C/% | 周期T/a | 与原序列相关系数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| IMF1 | 53.17 | 3.3 | 0.59*** |
| IMF2 | 11.71 | 8.2 | 0.568*** |
| IMF3 | 7.47 | 17.7 | 0.340** |
| IMF4 | 1.22 | 20.7 | 0.212 |
| 趋势项 | 26.43 | 0.395** |
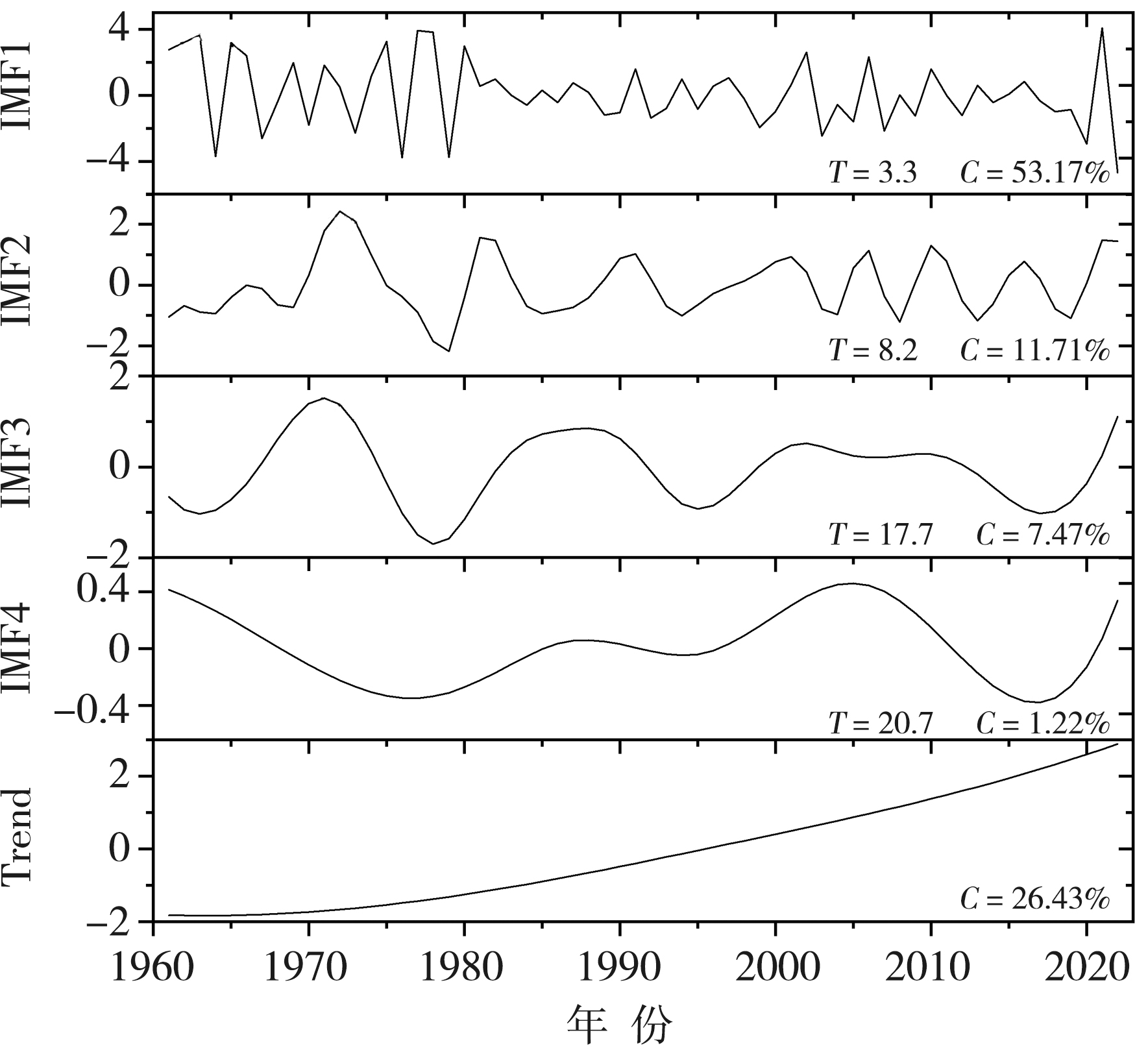
图6 基于EEMD分解的1961—2022年黄河上游主要汇流区夏季复合干热指数不同时间尺度分量变化
Fig.6 The variation of different time scales components of summer compound dry-hot index based on EEMD decomposition in the main confluence area of the upper Yellow River from 1961 to 2022
| 项目 | 时间尺度 | 西风指数 | 东亚夏季风指数 | 南亚夏季风指数 | 高原夏季风指数 | 北风指数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EEMD分解前 | -0.09 | 0.01 | -0.24* | 0.06 | 0.05 | |
| EEMD分解后 | 年际 | -0.01 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.02 | -0.02 |
| 年代际 | 0.19 | -0.09 | 0.03 | 0.65*** | 0.09 | |
| 多年代际 | -0.52*** | -0.49*** | -0.88*** | -0.28* | 0.51*** |
表4 EEMD分解前后的黄河上游主要汇流区夏季复合干热指数与环流指数的相关系数
Tab.4 Correlation coefficients between summer compound dry-hot index in the main confluence area of the upper Yellow River and circulation indices before and after EEMD decomposition
| 项目 | 时间尺度 | 西风指数 | 东亚夏季风指数 | 南亚夏季风指数 | 高原夏季风指数 | 北风指数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EEMD分解前 | -0.09 | 0.01 | -0.24* | 0.06 | 0.05 | |
| EEMD分解后 | 年际 | -0.01 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.02 | -0.02 |
| 年代际 | 0.19 | -0.09 | 0.03 | 0.65*** | 0.09 | |
| 多年代际 | -0.52*** | -0.49*** | -0.88*** | -0.28* | 0.51*** |

图7 夏季气候态500 hPa位势高度场(a),复合干热年份的500 hPa位势高度场(b)及其距平场(c)(单位:dagpm) (黑点区为通过α=0.05的显著性检验,红色闭合区域为研究区,下同)
Fig.7 The summer climate state of 500 hPa geopotential height field (a),and 500 hPa geopotential height field (b) and its anomaly field (c) in compound dry-hot years (Unit: dagpm) (The black dotted areas passed the significant test at 0.05,the red closed area is the research area,the same as below)
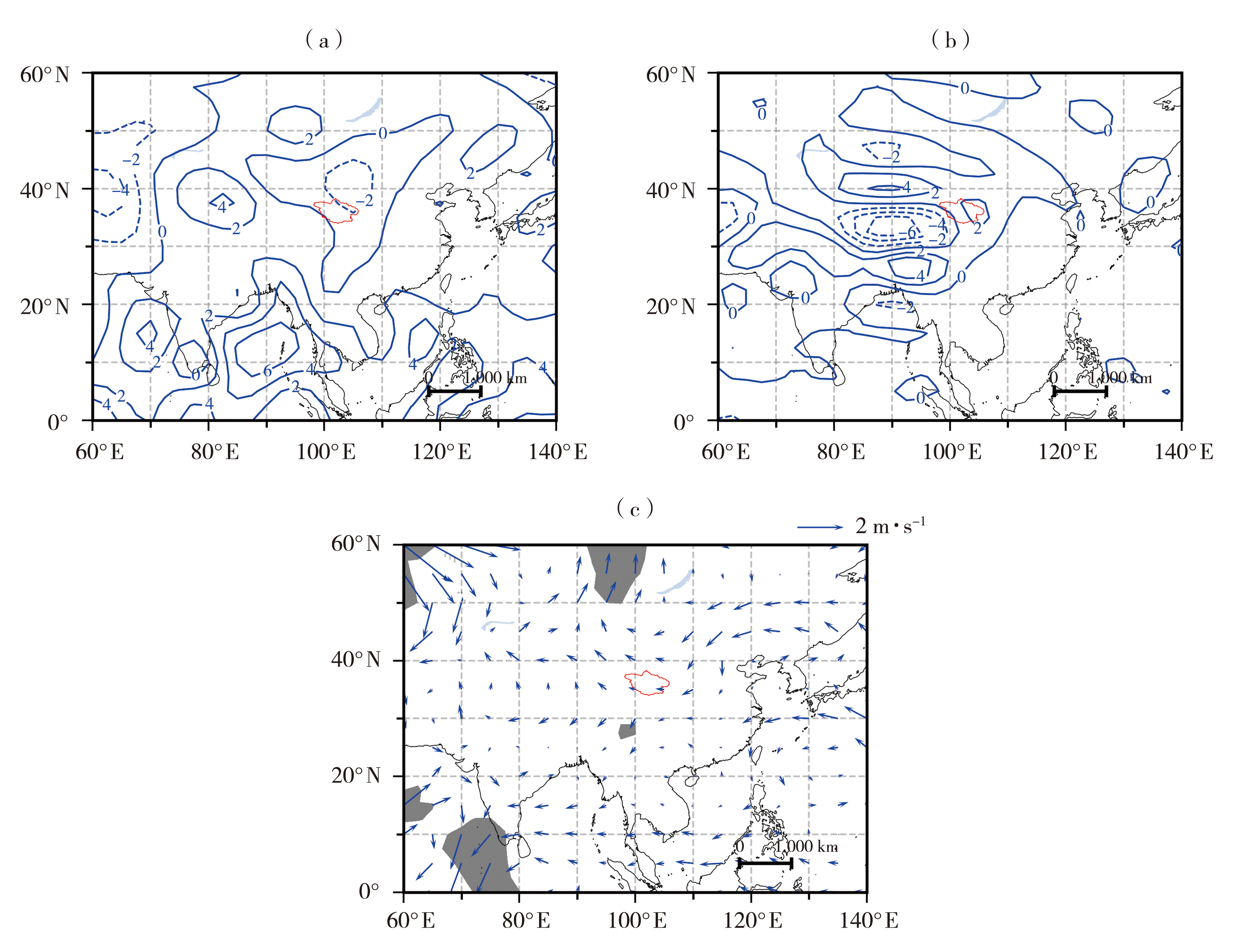
图8 夏季复合干热年份200 hPa(a)、600 hPa(b)散度场(单位:10-6s)及600 hPa风场距平(c,单位:m·s-1) (灰色阴影表示通过α=0.05的显著性检验)
Fig.8 The 200 hPa (a),600 hPa (b) divergence fields (Unit: 10-6s) and 600 hPa anomalous wind fields (c,Unit: m·s-1) in summer compound dry-hot years (The gray shaded areas passed the significant test at 0.05)
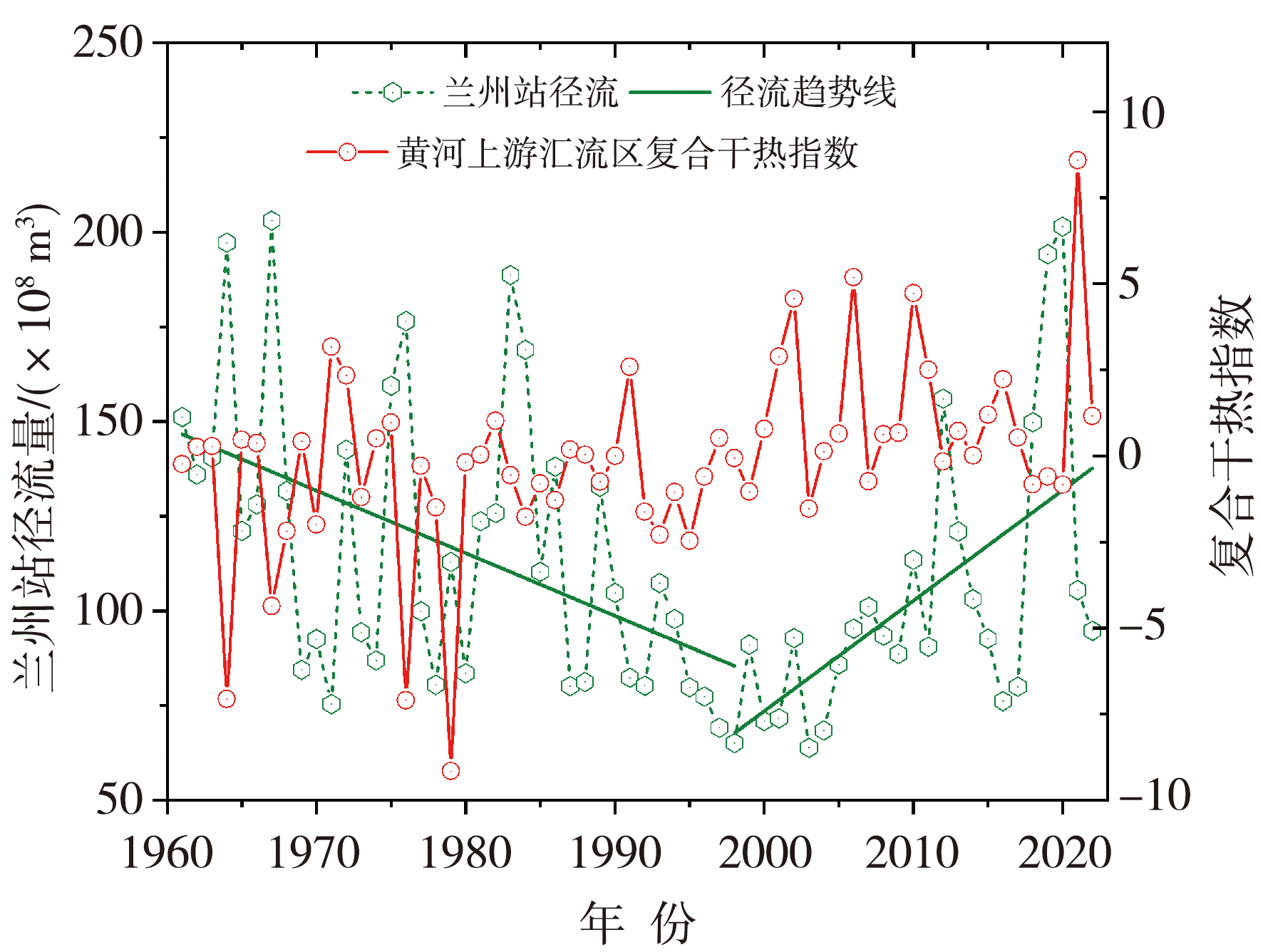
图9 1961—2022年黄河兰州段夏季径流量与黄河上游主要汇流区夏季复合干热指数年际变化
Fig.9 The inter-annual variation of summer runoff in the Lanzhou section of the Yellow River and the summer compound dry-hot index in the main confluence area of the upper Yellow River from 1961 to 2022
| 时段 | 高温 | 降水 | 复合干热指数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1961—1997年 | -0.33* | 0.14 | -0.41** |
| 1998—2022年 | -0.18 | 0.48** | -0.32* |
表5 黄河上游主要汇流区不同时段夏季高温、降水及复合干热指数与黄河兰州段夏季径流量相关系数
Tab.5 Correlation coefficients between summer high temperature,precipitation,and compound dry-hot index in the main confluence area of the upper Yellow River and summer runoff in the Lanzhou section of the Yellow River during different time periods
| 时段 | 高温 | 降水 | 复合干热指数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1961—1997年 | -0.33* | 0.14 | -0.41** |
| 1998—2022年 | -0.18 | 0.48** | -0.32* |
| [1] | 白肇烨, 徐国昌, 1988. 中国西北天气[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [2] | 毕硕本, 孙力, 李兴宇, 等, 2018. 基于EEMD的1470—1911年黄河中下游地区旱涝灾害多时间尺度特征分析[J]. 自然灾害学报, 27(1):137-147. |
| [3] |
陈少勇, 王劲松, 郭俊庭, 等, 2012. 中国西北地区1961—2009年极端高温事件的演变特征[J]. 自然资源学报, 27(5): 832-844.
DOI |
| [4] | 程捷, 张绪教, 田明中, 等, 2006. 黄河源区冰楔假型群的发育及其古气候意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 26(1):92-98. |
| [5] | 李万莉, 王可丽, 傅慎明, 等, 2008. 区域西风指数对西北地区水汽输送及收支的指示性[J]. 冰川冻土, 30(1):28-34. |
| [6] |
林纾, 李红英, 黄鹏程, 等, 2022. 2022年夏季我国高温干旱特征及其环流形势分析[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5): 748-763.
DOI |
| [7] | 马浩, 刘昌杰, 钱奇峰, 等, 2020. 2018年5月浙江省极端高温气候特征及环流背景[J]. 干旱气象, 38(6): 909-919. |
| [8] | 梅梅, 高歌, 李莹, 等, 2023. 1961—2022年长江流域高温干旱复合极端事件变化特征[J]. 人民长江, 54(2): 12-20. |
| [9] |
汤懋苍, 沈志宝, 陈有虞, 1979. 高原季风的平均气候特征[J]. 地理学报, 34(1): 33-42.
DOI |
| [10] |
唐懿, 蔡雯悦, 翟建青, 等, 2022. 2021年夏季中国气候异常特征及主要气象灾害[J]. 干旱气象, 40(2): 179-186.
DOI |
| [11] | 王可丽, 江灏, 吴虹, 2001. 南亚夏季风年际变化特征分析[J]. 高原气象, 20(3): 318-324. |
| [12] | 魏凤英, 2007. 现代气候统计诊断与预测技术[M]. 2版. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [13] | 魏明华, 2021. 中国北方季风边缘区1960—2010年夏季气候干湿变化的时空特征及影响因素[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学. |
| [14] | 武新英, 郝增超, 张璇, 等, 2021. 中国夏季复合高温干旱分布及变异趋势[J]. 水利水电技术:中英文, 52(12): 90-98. |
| [15] | 杨金虎, 张强, 杨博成, 等, 2023. 黄河上游暖湿化的多时间尺度特征及对生态植被的影响[J]. 高原气象, 42(4): 1 018-1 030. |
| [16] | 余荣, 翟盘茂, 2021. 关于复合型极端事件的新认识和启示[J]. 大气科学学报, 44(5): 645-649. |
| [17] | 郑本兴, 王苏民, 1996. 黄河源区的古冰川与古环境探讨[J]. 冰川冻土, 18(3): 210-218. |
| [18] | HAO Z C, 2022. Compound events and associated impacts in China[J]. iScience, 25(8): 104689. DOI:10.1016/j.isci.2022.104689. |
| [19] | HUANG N E, SHEN S P, 2005. Hibert-Huang transform and its applications[M]. Singapore: World Scientific Publishing Co Pte Ltd: 56-62. |
| [20] | IPCC, 2021. Climate Change: The Physical Science Basis[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. |
| [21] | LYU X M, ZHOU G S, ZHOU M Z, et al, 2019. Projection of heat injury to single-cropping rice in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, China under future global warming scenarios[J]. Journal of Meteorological Research, 33(2): 363-374. |
| [22] | MUKHERJEE S, ASHFAQ M, MISHRA A K, 2020. Compound drought and heatwaves at a global scale: The role of natural climate variability‐associated synoptic patterns and land‐surface energy budget anomalies[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 125(11): e2019JD031943.DOI:10.1029/2019JD031943. |
| [23] | WANG B, FAN Z, 1999. Choice of south Asian summer monsoon indices[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 80: 629-638. |
| [24] | WU Z H, HUANG N E, 2009. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A noise-assisted data analysis method[J]. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis, 1(1): 1-41. |
| [25] | XUN X Y, HU Z Y, MA Y M, 2012. The dynamic plateau monsoon index and its association with general circulation anomalies[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 29(6): 1 249-1 263. DOI:10.1007/s00376-012-1125-9. |
| [26] | YANG J H, ZHANG Q, YUE P, et al, 2023. Characteristics of warming and humidification in the Yellow River's upper reaches and their impact on surface water resources[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 43: 7 667-7 681. |
| [27] | YANG J H, ZHANG Q, LU G Y, et al, 2021. Climate transition from warm-dry to warm-wet in eastern northwest China[J]. Atmosphere, 12(5): 548.DOI:10.3390/atmos12050548. |
| [28] | YU R, ZHAI P M, 2020a. More frequent and widespread persistent compound drought and heat event observed in China[J]. Scientific Reports, 10(1): 14576.DOI:10.1038/s41598-020-71312-3. |
| [29] | YU R, ZHAI P M, 2020b. Changes in compound drought and hot extreme events in summer over populated Eastern China[J]. Weather and Climate Extremes, 30: 100295. DOI:10.1016/j.wace.2020.100295. |
| [30] | ZHANG Q, YANG J H, DUAN X Y, et al, 2022. The eastward expansion of the climate humidification trend in northwest China and the synergistic influences on the circulation mechanism[J]. Climate Dynamics, 59(7): 2 481-2 497. |
| [31] | ZSCHEISCHLER J, WESTRA S, VAN DEN HURK B J J M, et al, 2018. Future climate risk from compound events[J]. Nature Climate Change, 8(6): 469-477. |
| [1] | 谢 娜, 叶帮苹, 杨康权, 陈 军, 康 岚, 范江琳, 徐 洋.
四川盆地西部复杂地形小流域山洪径流模拟及其灾害成因分析
[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(2): 231-241. |
| [2] | 周建琴, 李蒙, 陶云, 窦小东, 王玉尤婷. 云南农业干旱灾害演变特征及其与气候因子的关系研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(1): 21-31. |
| [3] | 旦增维色, 杜军, 黄志诚, 巴桑. 1981—2023年珠穆朗玛峰地区大气饱和水汽差的时空分布特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(6): 878-888. |
| [4] | 王雅君, 罗菊英, 程烈海, 李伟. 基于机器学习的湖北省夏季干旱预测模型构建与检验[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(5): 661-670. |
| [5] | 杨静坤, 李谢辉, 雷沁雅, 龚光泽. 四川省极端气温事件与城镇化发展的关联影响[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(5): 744-754. |
| [6] | 邓佩云, 常倬林, 何佳, 杨萌, 陈得圆, 林彤, 穆建华, 戴言博. 六盘山地区大气水汽的时空差异与驱动因子分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(3): 376-384. |
| [7] | 鲍丽丽, 王小勇, 段秀兰, 程鹏, 谭丹, 闫昕旸, 何金梅. 2022年陇南“4·19”强对流天气成因及其对配电线路故障的影响分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(3): 437-446. |
| [8] | 郭立平, 刘姝, 李敬海, 曾妍婧. 毫米波云雷达在高影响天气中的预警应用[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(3): 465-472. |
| [9] | 朱占云, 张露萱, 李福刚, 张珏, 张玮玮, 李强. 新安江流域气象干旱和水文干旱特征及两者之间的关系研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(2): 157-165. |
| [10] | 郝立生, 何丽烨, 马宁, 郝钰茜. 厄尔尼诺事件年际变化与我国华北夏季干旱的关系[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(6): 829-840. |
| [11] | 魏森涛, 王澄海, 张飞民, 杨凯. 基于土壤温、湿度记忆性的土壤湿度预测方法研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(5): 783-791. |
| [12] | 张良, 张强, 王润元, 岳平, 王胜, 曾剑, 杨泽粟, 李宏宇, 乔梁, 王文玉, 张红丽, 杨司琪, 赵福年. 我国夏季风过渡区陆-气相互作用研究的新进展[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(4): 519-530. |
| [13] | 孙树娇, 曹晓云, 肖建设, 孙玮婕, 祝存兄. 基于NDVI-Albedo特征空间的柴达木盆地荒漠化监测研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(4): 560-569. |
| [14] | 张强, 杨金虎, 马鹏里, 岳平, 于海鹏, 杨泽粟, 王朋岭, 段欣妤, 刘晓云, 朱飙, 张红丽, 卢国阳, 王有恒, 刘卫平, 林婧婧, 刘丽伟, 闫昕旸. 西北地区气候暖湿化增强东扩特征及其形成机制与重要环境影响[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(3): 351-358. |
| [15] | 赵鸿, 蔡迪花, 王鹤龄, 杨阳, 王润元, 张凯, 齐月, 赵福年, 陈斐, 岳平, 王兴, 姚玉璧, 雷俊, 魏星星. 干旱灾害对粮食安全的影响及其应对技术研究进展与展望[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(2): 187-206. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||

