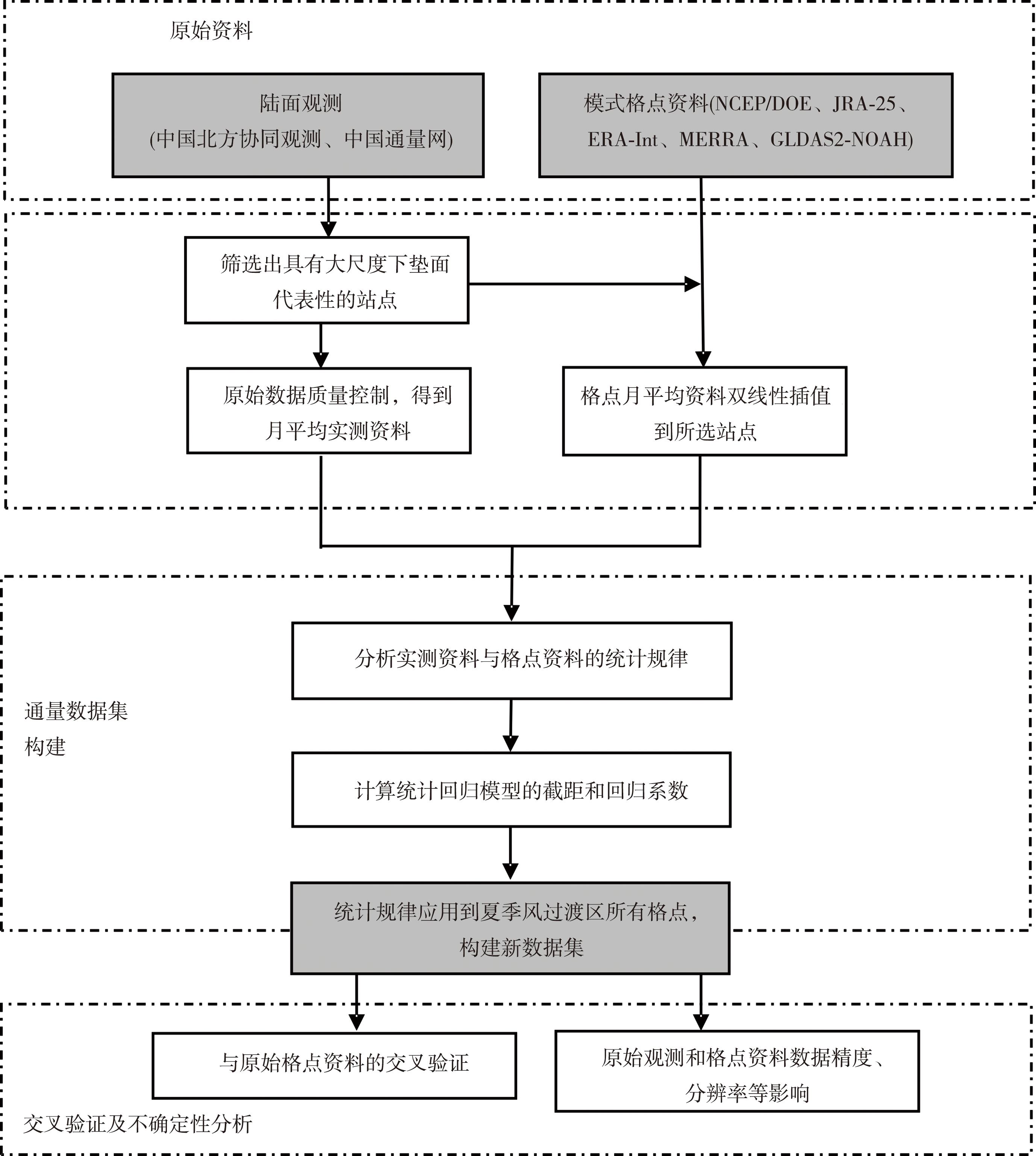
干旱气象 ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (4): 519-530.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-04-0519
我国夏季风过渡区陆-气相互作用研究的新进展
张良1( ), 张强1(
), 张强1( ), 王润元1, 岳平1, 王胜1, 曾剑2, 杨泽粟2, 李宏宇3, 乔梁4, 王文玉5, 张红丽6, 杨司琪1, 赵福年1
), 王润元1, 岳平1, 王胜1, 曾剑2, 杨泽粟2, 李宏宇3, 乔梁4, 王文玉5, 张红丽6, 杨司琪1, 赵福年1
- 1.中国气象局兰州干旱气象研究所,甘肃省干旱气候变化与减灾重点实验室/中国气象局干旱气候变化与减灾重点实验室,甘肃 兰州 730020
2.成都信息工程大学大气科学学院,四川 成都 610225
3.河北地质大学,河北 石家庄 050031
4.复旦大学大气与海洋科学系,上海 200433
5.中国气象局气象干部培训学院湖北分院,湖北 武汉 430074
6.天水师范学院资源与环境工程学院,甘肃 天水 741001
-
收稿日期:2023-07-10修回日期:2023-07-25出版日期:2023-08-31发布日期:2023-08-29 -
通讯作者:张强(1965—),男,研究员,博士生导师,主要从事陆-气相互作用、边界层与干旱研究。E-mail:zhangqiang@cma.gov.cn。 -
作者简介:张良(1980—),男,副研究员,主要从事陆-气相互作用与干旱研究。E-mail:lzhangmet@163.com。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金重点项目(42230611);国家自然科学基金重点项目(41630426);国家自然科学基金面上与青年项目(41875020);国家自然科学基金面上与青年项目(42005097)
New progresses in the study of land-atmosphere interaction in summer monsoon transition zone in China
ZHANG Liang1( ), ZHANG Qiang1(
), ZHANG Qiang1( ), WANG Runyuan1, YUE Ping1, WANG Sheng1, ZENG Jian2, YANG Zesu2, LI Hongyu3, QIAO Liang4, WANG Wenyu5, ZHANG Hongli6, YANG Siqi1, ZHAO Funian1
), WANG Runyuan1, YUE Ping1, WANG Sheng1, ZENG Jian2, YANG Zesu2, LI Hongyu3, QIAO Liang4, WANG Wenyu5, ZHANG Hongli6, YANG Siqi1, ZHAO Funian1
- 1. Institute of Arid Meteorology, Key Laboratory of Arid Climatic Change and Reducing Disaster of Gansu Province/Key Laboratory of Arid Climatic Change and Disaster Reduction, China Meteorological Administration, Lanzhou 730020, China
2. College of Atmospheric Sciences, Chengdu University of Information Technology, Chengdu 610225, China
3. Hebei GEO University, Shijiazhuang 050031, China
4. Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China
5. Hubei Meteorology Training Centre, China Meteorological Administration, Wuhan 430074, China
6. College of Resources and Environmental Engineering, Tianshui Normal University, Tianshui 741001, Gansu, China
-
Received:2023-07-10Revised:2023-07-25Online:2023-08-31Published:2023-08-29
摘要:
中国夏季风过渡区是全球陆-气相互作用强盛区域之一,也是极端天气灾害频发且易造成严重经济损失的区域,对过渡区陆-气相互作用的进一步认识将有助于提升该区域防灾减灾能力。以近年来中国气象局干旱气候变化与减灾重点实验室为平台开展的夏季风过渡区相关项目群取得的研究成果为基础,对过渡区陆-气相互作用时空分布规律、陆面水分收支对夏季风响应新特征、边界层时空变化特征及发展机制、季风与陆-气相互作用对区域气候影响、陆-气相互作用对作物产量影响以及多因子和多尺度动力学粗糙度参数化方案等方面的新进展进行系统总结,并根据夏季风过渡区陆-气作用研究的发展趋势,提出今后应在侧重加强陆-气交换多循环过程对夏季风年循环响应规律研究基础上,探讨陆-气相互作用对夏季风的多尺度动态响应,建立地表过程和大气边界层关键物理量的气候动力学关系,以改进和提升区域气候模式模拟水平。该工作对推动我国陆-气耦合过程的研究具有重要意义。
中图分类号:
引用本文
张良, 张强, 王润元, 岳平, 王胜, 曾剑, 杨泽粟, 李宏宇, 乔梁, 王文玉, 张红丽, 杨司琪, 赵福年. 我国夏季风过渡区陆-气相互作用研究的新进展[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(4): 519-530.
ZHANG Liang, ZHANG Qiang, WANG Runyuan, YUE Ping, WANG Sheng, ZENG Jian, YANG Zesu, LI Hongyu, QIAO Liang, WANG Wenyu, ZHANG Hongli, YANG Siqi, ZHAO Funian. New progresses in the study of land-atmosphere interaction in summer monsoon transition zone in China[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(4): 519-530.
| 数据类型 | 名称 | 机构名称 | 空间分辨率 | 时间分辨率 | 时间长度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 再分析资料 | NCEP/DOE | NCEP/DOE | T62 (200 km) | 6 h | 1979年1月至今 |
| JRA-25 | JMA | T106 (110 km) | 3 h | 1979年1月至2014年2月 | |
| ERA-Int | ECMWF | 1.5°×1.5° | 6 h | 1979年1月至今 | |
| MERRA | NASA | 0.5°×0.67° | 1 h | 1979年1月至今 | |
| 离线陆面模式数据集 陆面观测 | GLDAS2-NOAH | NASA | 1°×1° | 3 h | 1979年1月至2010年12月 |
| 中国北方陆面过程观测 | 中国科学院大气物理研究所/地理科学与资源研究所 | 16个站点 | 30 min | 2003年1月至2009年9月 |
表1 资料信息(李宏宇等, 2020)
Tab.1 Information of Dataset (Liet al., 2020)
| 数据类型 | 名称 | 机构名称 | 空间分辨率 | 时间分辨率 | 时间长度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 再分析资料 | NCEP/DOE | NCEP/DOE | T62 (200 km) | 6 h | 1979年1月至今 |
| JRA-25 | JMA | T106 (110 km) | 3 h | 1979年1月至2014年2月 | |
| ERA-Int | ECMWF | 1.5°×1.5° | 6 h | 1979年1月至今 | |
| MERRA | NASA | 0.5°×0.67° | 1 h | 1979年1月至今 | |
| 离线陆面模式数据集 陆面观测 | GLDAS2-NOAH | NASA | 1°×1° | 3 h | 1979年1月至2010年12月 |
| 中国北方陆面过程观测 | 中国科学院大气物理研究所/地理科学与资源研究所 | 16个站点 | 30 min | 2003年1月至2009年9月 |

图2 陆面能量平衡各分量随经度(a)、纬度(b)和海拔高度(c)的变化(曾剑等,2016)
Fig.2 Variations of each component of land surface energy balance with longitude(a), latitude(b) and altitude(c)(Zeng et al., 2016)

图3 夏季风过渡区西部(a、c)和东部(b、d)陆面热通量、夏季风持续时间指数年际变化(a、b)及陆面热通量和夏季风持续时间指数关系(c、d)(Li et al.,2021)
Fig.3 Inter-annual variations of land-surface heat fluxes and duration index of summer monsoon (a, b) and relation between land-surface heat fluxes and duration index of summer monsoon in west (a, c) and east (b, d) regions of the summer monsoon transition zone (Li et al., 2021)

图4 1961—2013年夏季风过渡区西部季风持续时间指数和夏季平均感热通量基于集合经验模态分解的5个主要时间尺度变化(Li et al.,2021) (a)约3 a尺度,(b)5~7 a尺度,(c)年代际尺度,(d)多年代际尺度,(e)自适应非线性趋势
Fig.4 Five major time scales variations of summer monsoon duration index and summer mean sensible heat flux from 1961 to 2013 decomposed by the ensemble empirical mode decomposition in west region of the summer monsoon transition zone(Li et al., 2021) (a) about 3 a time scale, (b) 5-7 a time scale, (c) inter-decadal time scale, (d) multi-decadal time scale, (e) the adaptive nonlinear trend
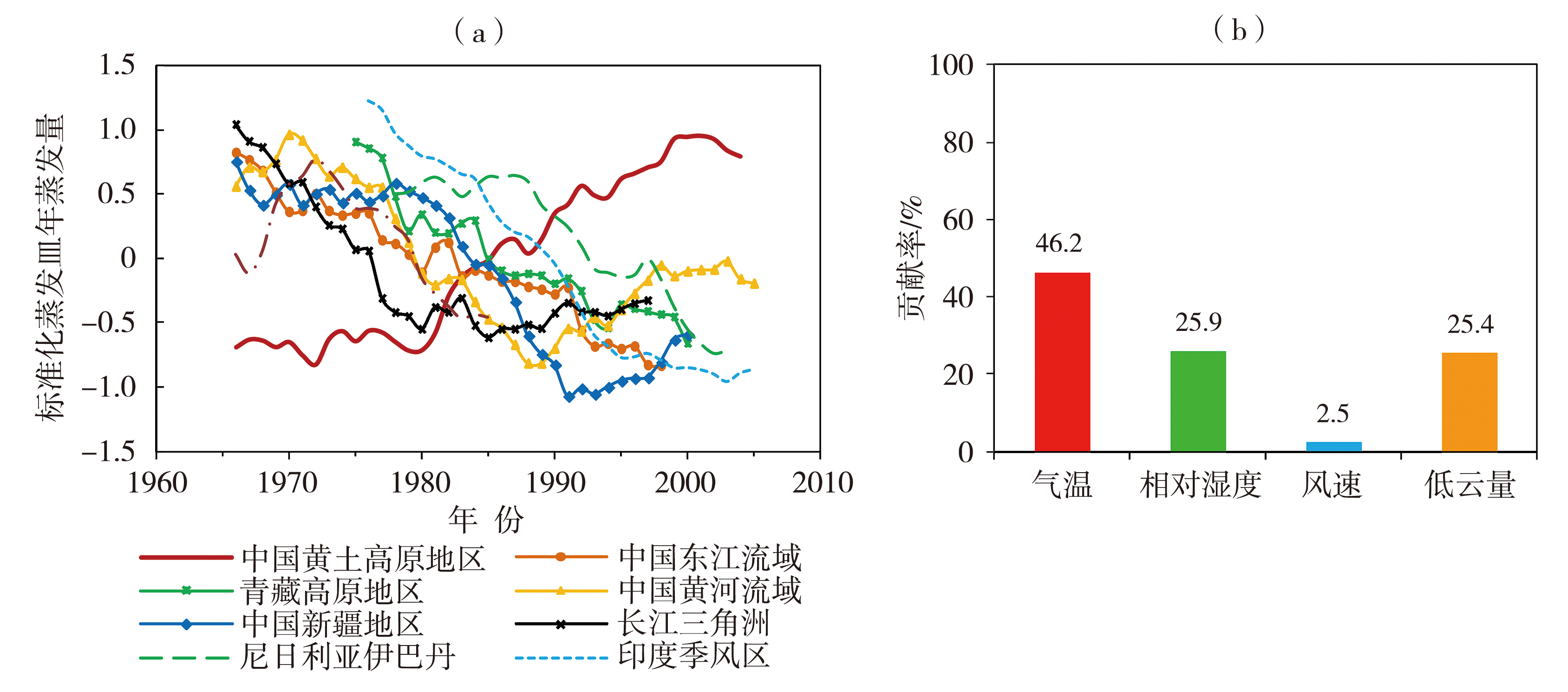
图5 中国夏季风过渡区与世界其他地区蒸发皿蒸发量趋势对比(a) (Zhang et al.,2016a)及其主要影响因素贡献率(b) (杨司琪等,2019)
Fig.5 Comparison of change trend of pan evaporation in the summer monsoon transition zone in China with other parts of the world (a) (Zhang et al., 2016a) and the contribution rate of its main influence factors (b) (Yang et al., 2019)
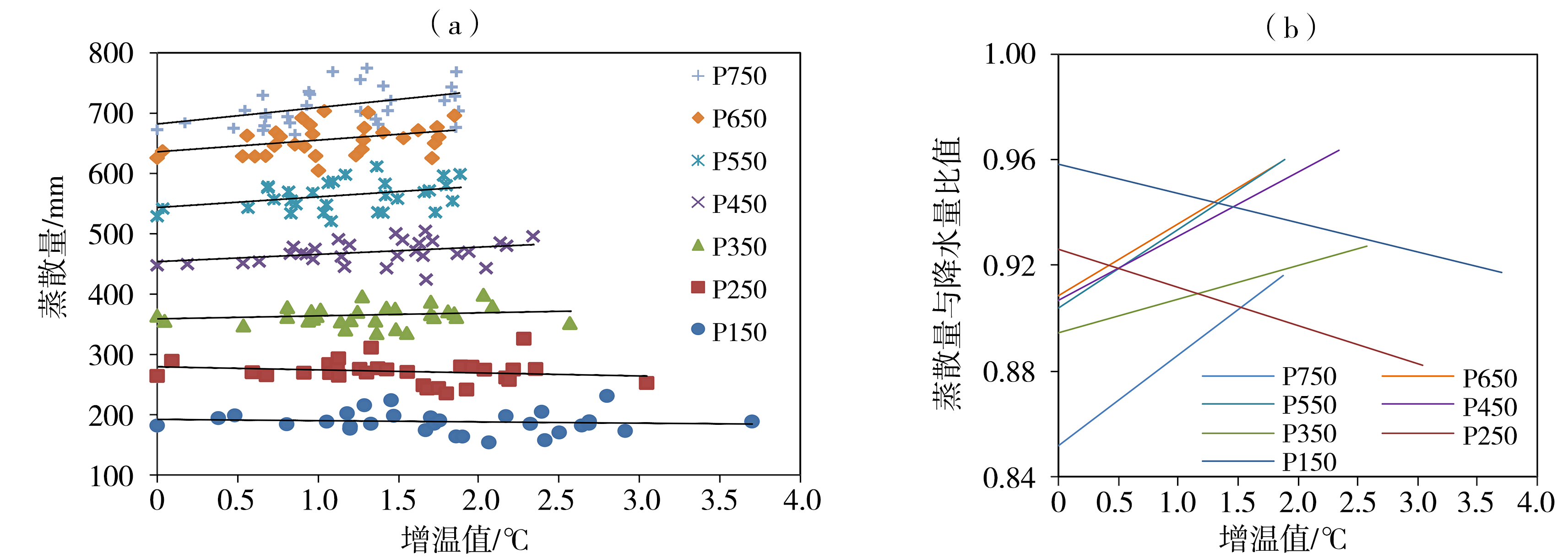
图6 不同降水量气候类型年平均蒸散量(a)及其基于降水量的归一化值(b)随气温增幅的变化趋势(Zhang et al.,2019) (Pxxx表示降水气候空间类型)
Fig.6 Variation trend of annual mean evapotranspiration (a) and normalized evapotranspiration by annual precipitation (b) with temperature increase under different precipitation-based climate types (Zhang et al., 2019) (Pxxx denotes precipitation-based climate type)
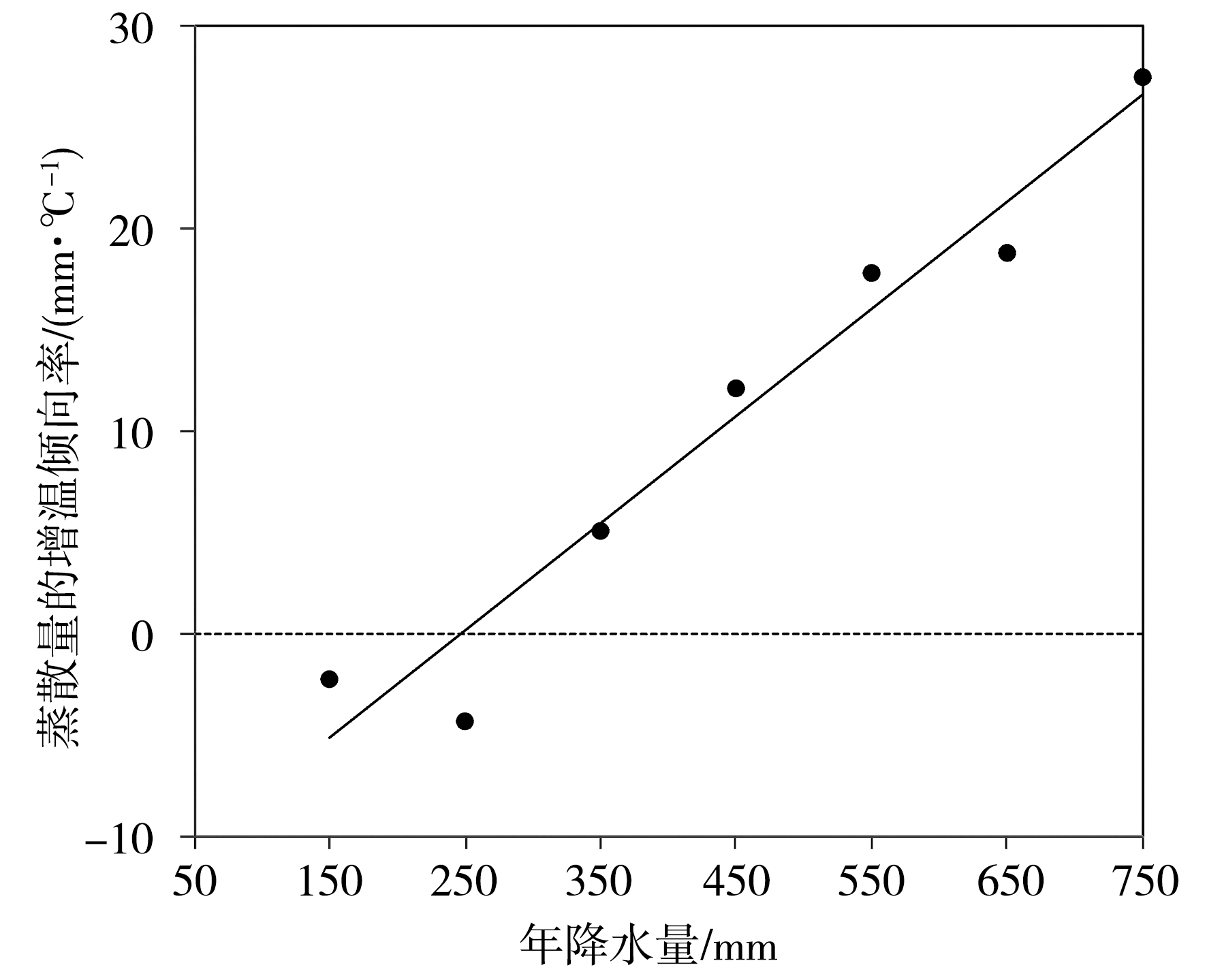
图7 年平均地表蒸散量的增温倾向率随年降水量的变化(Zhang et al.,2019)
Fig.7 Variation of warming tendency of annual mean surface evapotranspiration with annual precipitation (Zhang et al., 2019)

图8 气候环境要素对地表蒸散量的影响机制示意图(Zhang et al.,2019)
Fig.8 Schematic diagram of influence mechanism of climate and environmental elements on surface evapotranspiration (Zhang et al., 2019)
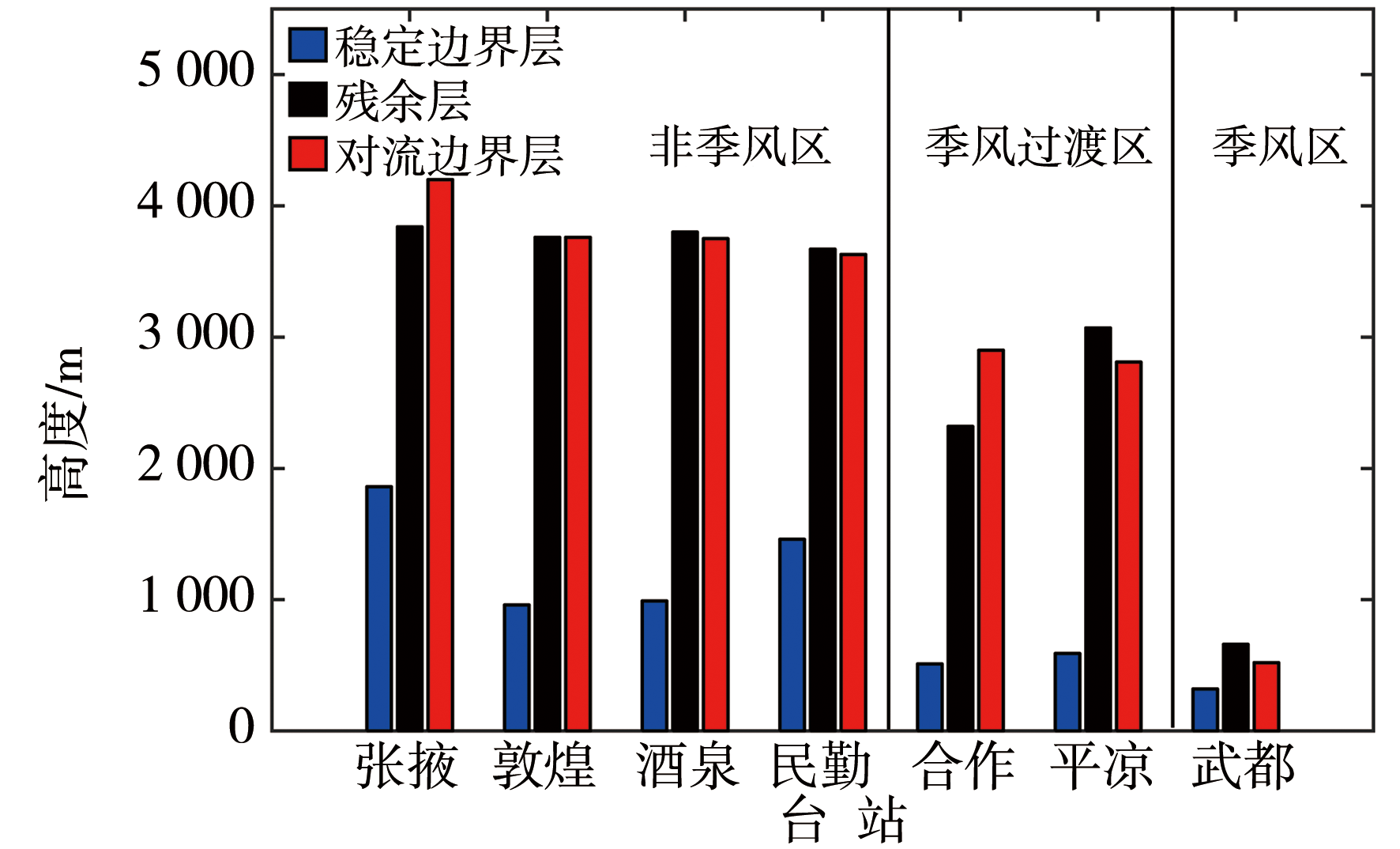
图9 典型非季风区、夏季风过渡区和季风区夏季晴天边界层高度对比(乔梁等,2019)
Fig.9 Comparison of atmospheric boundary layer height on sunny summer days in typical non-monsoon zone, summer monsoon transition zone and monsoon zone (Qiao et al., 2019)
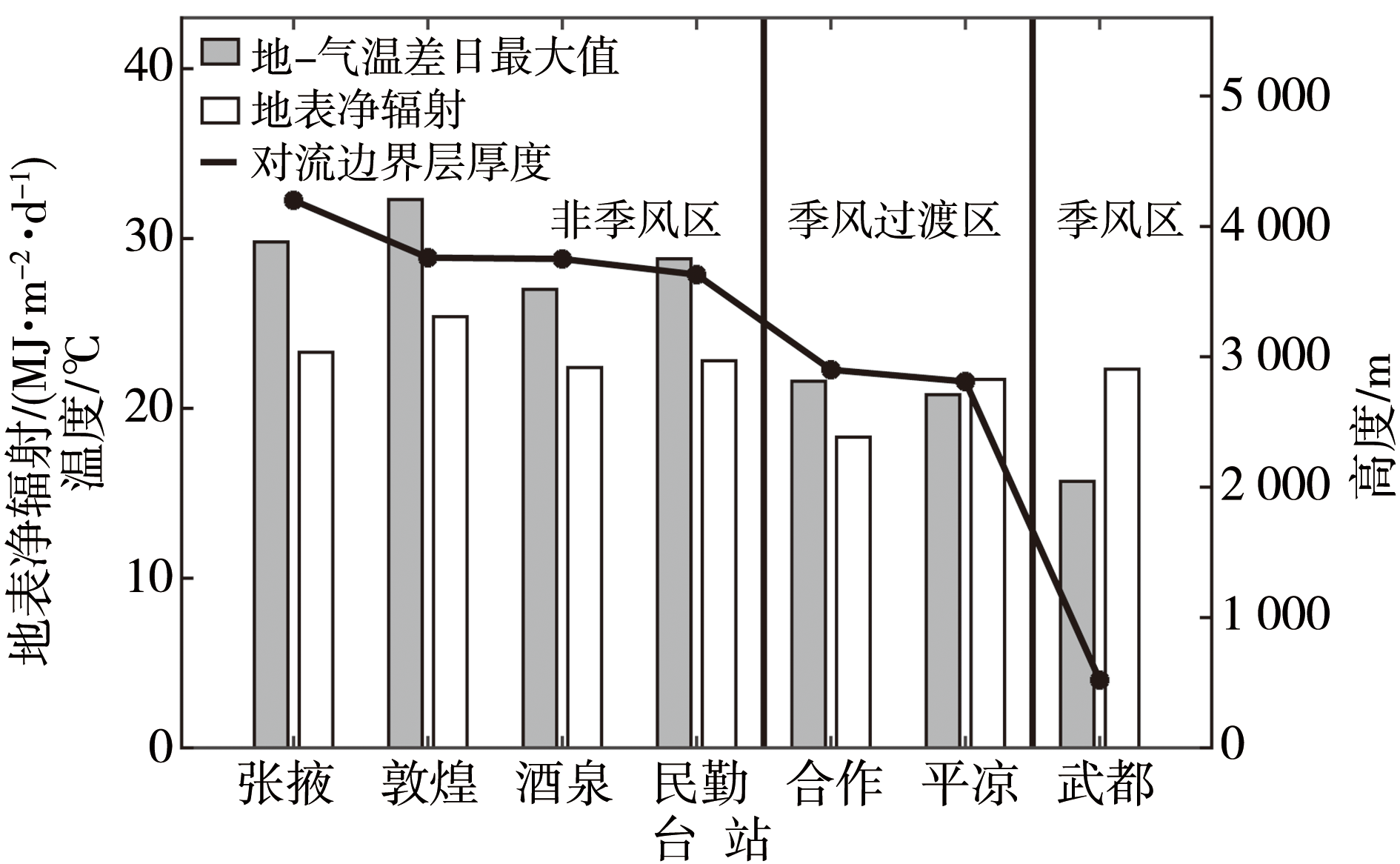
图10 典型非季风区、夏季风过渡区、季风区夏季晴天地表净辐射、地-气温差日最大值与对流边界层厚度对比(乔梁等,2019)
Fig.10 Comparison of surface net radiation, maximum of daily difference between ground and air temperature and convective boundary layer thickness on sunny summer days in typical non-monsoon zone, summer monsoon transition zone and monsoon zone (Qiao et al., 2019)

图11 过渡区3个气候子区夏季风北边缘指数的时间演变(Zhang et al.,2016)
Fig.11 The temporal evolution of the northern edge index of summer monsoon in three climatic sub-regions of the summer monsoon transition zone (Zhang et al., 2016)
| 相关系数 | 气候倾向率/[(°)·(10a)-1] | 年平均夏季风北边缘指数 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A区 | B区 | C区 | |||
| A区 | 1 | 0.61** | 0.06 | -0.22* | 34.87°N |
| B区 | 1 | 0.21 | -0.18* | 41.98°N | |
| C区 | 1 | -0.01 | 44.64°N | ||
表2 各子区夏季风北边缘指数的相关系数及气候倾向率(Zhang et al.,2016)
Tab.2 Correlation coefficient and climate tendency rate of the northern edge index of summer monsoon in each sub-region (Zhang et al., 2016)
| 相关系数 | 气候倾向率/[(°)·(10a)-1] | 年平均夏季风北边缘指数 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A区 | B区 | C区 | |||
| A区 | 1 | 0.61** | 0.06 | -0.22* | 34.87°N |
| B区 | 1 | 0.21 | -0.18* | 41.98°N | |
| C区 | 1 | -0.01 | 44.64°N | ||

图12 大气干湿条件分类(a)和未分类(b)的春小麦产量与播前土壤水分关系及生育期大气干湿状况分类(c)(Zhao et al.,2022)
Fig.12 The relationship between spring wheat yield and soil moisture before sowing considering (a) and no considering (b) the atmospheric dry and wet conditions and classification of atmospheric dry and wet conditions during the growth period (Zhao et al., 2022)
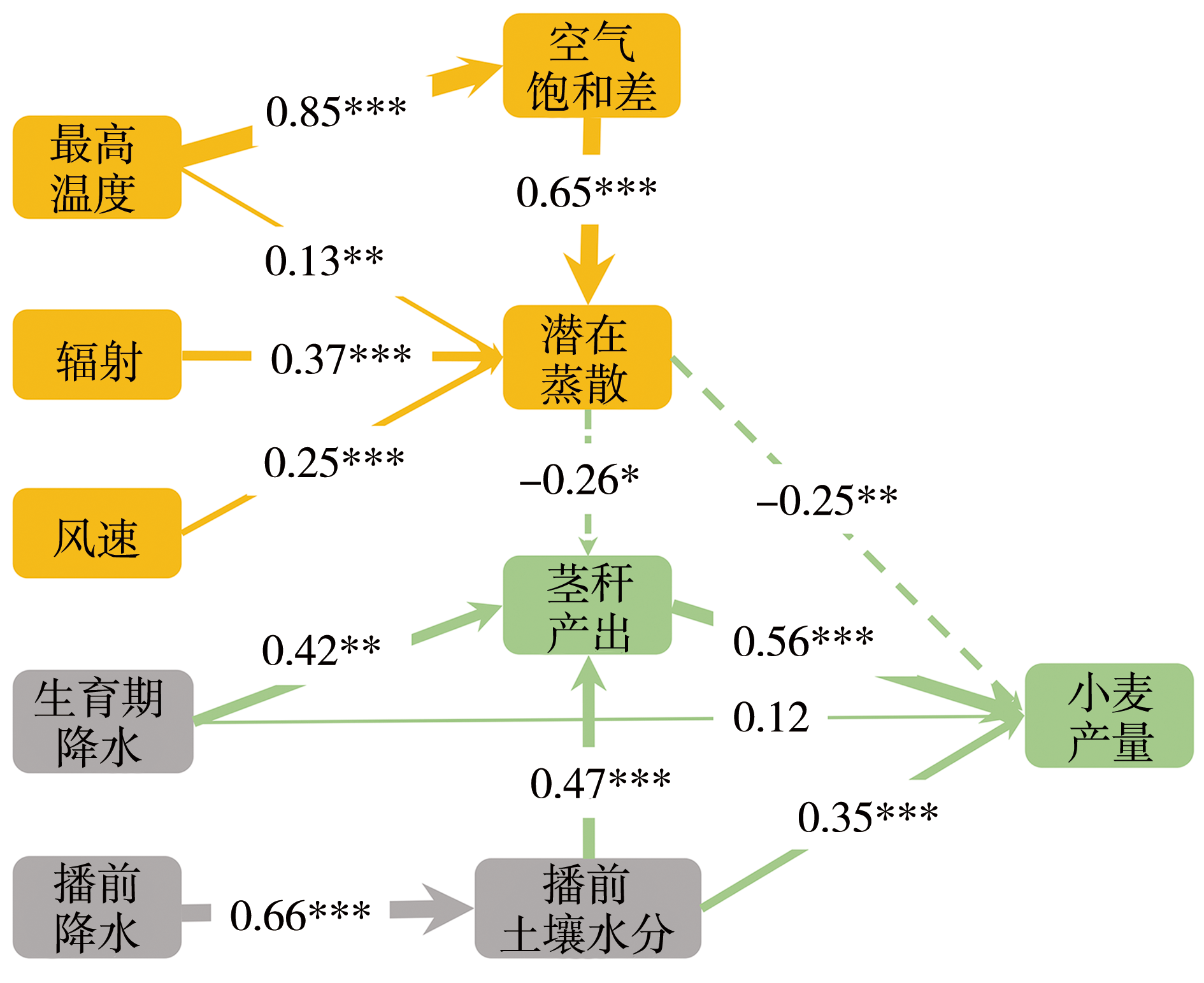
图13 春小麦产量形成的环境因素(Zhao et al.,2022) (***、**和*分别表示通过α=0.001,α=0.01,α=0.05的显著性检验)
Fig.13 Environmental factors in the formation of spring wheat yield (Zhao et al., 2022) (***, ** and * passing the significance tests at α=0.001, α=0.01, α=0.05, respectively)
| [1] | 丁一汇, 孙颖, 刘芸芸, 等, 2013. 亚洲夏季风的年际和年代际变化及其未来预测[J]. 大气科学, 37(2): 253-280. |
| [2] | 符淙斌, 安芷生, 郭维栋, 2005. 我国生存环境演变和北方干旱化趋势预测研究(Ⅱ): 研究成果的创新性及项目实施效果[J]. 地球科学进展, 20(11): 1 168-1 175. |
| [3] | 胡豪然, 钱维宏, 2007. 东亚夏季风北边缘的确认[J]. 自然科学进展, 17(1): 57-65. |
| [4] | 黄荣辉, 周德刚, 陈文, 等, 2013. 关于中国西北干旱区陆-气相互作用及其对气候影响研究的最近进展[J]. 大气科学, 37(2): 189-210. |
| [5] | 李宏宇, 张强, 王春玲, 等, 2020. 基于多源陆面通量数据相融合的新资料及其在中国夏季风影响过渡区的应用[J]. 大气科学, 44(6): 1 224-1 242. |
| [6] | 李振山, 陈广庭, 1997. 粗糙度研究的现状及展望[J]. 中国沙漠, 17(1):99-102. |
| [7] | 乔梁, 张强, 岳平, 等, 2019. 由非季风区向季风区过渡过程中大气边界层结构的变化分析[J]. 大气科学, 43(2): 251-265. |
| [8] | 汤绪, 钱维宏, 梁萍, 2006. 东亚夏季风边缘带的气候特征[J]. 高原气象, 25(3): 375-381. |
| [9] | 王蓉, 黄倩, 张强, 2020. 覆盖逆温强度对干旱区超厚对流边界层影响的大涡模拟[J]. 干旱区研究, 37(4): 925-935. |
| [10] | 杨司琪, 张强, 奚小霞, 等, 2018. 夏季风影响过渡区与非夏季风影响过渡区蒸发皿蒸发趋势的对比分析[J]. 高原气象, 37(4): 1 017-1 024. |
| [11] | 杨司琪, 张强, 奚小霞, 等, 2019. 中国夏季风影响过渡区与其他地区蒸发皿蒸发量趋势相反的原因[J]. 大气科学, 43(6): 1 441-1 450. |
| [12] | 姚彤, 张强, 2014. 我国北方不同类型下垫面地表反照率特征[J]. 物理学报, 63(8): 460-468. |
| [13] | 曾剑, 张强, 王春玲, 2016. 东亚夏季风边缘摆动区陆面能量时空分布规律及其与气候环境的关系[J]. 气象学报, 74(6): 876-888. |
| [14] | 张强, 曾剑, 姚桐, 2012. 植被下垫面近地层大气动力状态与动力学粗糙度长度的相互作用及其参数化关系[J]. 科学通报, 57(8): 647-655. |
| [15] | 张强, 李宏宇, 张立阳, 等, 2013. 陇中黄土高原自然植被下垫面陆面过程及其参数对降水波动的气候响应[J]. 物理学报, 62(1): 522-532. |
| [16] | 张强, 岳平, 张良, 等, 2019. 夏季风过渡区的陆气相互作用: 述评与展望[J]. 气象学报, 77(4): 758-773. |
| [17] |
AMINZADEH M, OR D, 2017. The complementary relationship between actual and potential evaporation for spatially heterogeneous surfaces[J]. Water Resources Research, 53(1): 580-601.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
HUANG J P, YU H P, DAI A G, et al, 2017. Drylands face potential threat under 2 ℃ global warming target[J]. Nature Climate Change, 7: 417-422.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
HUANG J P, YU H P, GUAN X D, et al, 2016. Accelerated dryland expansion under climate change[J]. Nature Climate Change, 6(1): 166-171.
DOI |
| [20] |
KANAMITSU M, EBISUZAKI W, WOOLLEN J, et al, 2002. NCEP-DOEAMIP-II reanalysis (R-2)[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 83(11): 1 631-1 643.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
KONDO J, YAMAZAWA H, 1986. Aerodynamic roughness over an inhomogeneous ground surface[J]. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 35(1): 331-348.
DOI URL |
| [22] | LI H Y, ZHANG Q, YUE P, et al, 2021. Temporal duration of the East Asian summer monsoon substantially affects surface energy exchange over the summer monsoon transition zone of China[J]. Journal of Climate, 34(11): 4 643-4 660. |
| [23] | ONOGI K, TSUTSUI J, KOIDE H, et al, 2007. The JRA-25 reanalysis[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan, 85(3): 369-432. |
| [24] |
QI Y, ZHANG Q, HU S J, et al, 2022. Effects of high temperature and drought stresses on growth and yield of summer maize during grain filling in North China[J]. Agriculture, 12(11), 1948. DOI: 10.3390/agriculture12111948.
DOI |
| [25] |
ROBERTS J B, ROBERTSON F R, CLAYSON C A, et al, 2012. Characterization of turbulent latent and sensible heat flux exchange between the atmosphere and ocean in MERRA[J]. Journal of Climate, 25(3): 821-838.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
ROCHA H R, GOULDEN M L, MILLER S D, et al, 2004. Seasonality of water and heat fluxes over a tropical forest in eastern Amazonia[J]. Ecological Applications, 14(sp4): 22-32.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
RODELL M, HOUSER P R, JAMBOR U, et al, 2004. The global land data assimilation system[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 85(3): 381-394.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
RODERICK M L, FARQUHAR G D, 2002. The cause of decreased pan evaporation over the past 50 years[J]. Science, 298(5597): 1 410-1 411.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
SENEVIRATNE S I, LÜTHI D, LITSCHI M, et al, 2006. Land-atmosphere coupling and climate change in Europe[J]. Nature, 443: 205-209.
DOI |
| [30] | SIMMONS A, UPPALA S S, DEE D, et al, 2007. ERA-Interim: new ECMWF reanalysis products from 1989 onwards[J]. ECMWF Newsletter, 110(1): 25-35. |
| [31] | STULL R, 1988. An introduction to boundary layer meteorology[M]. Dordrecht: Springer: 115-149. |
| [32] |
TWINE T E, KUSTAS W P, NORMAN J M, et al, 2000. Correcting eddy-covariance flux underestimates over a grassland[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 103(3): 279-300.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
WANG R Y, ZHAO H, QI Y, et al, 2023. Onset and severity thresholds of drought impacts on wheat[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 281, 108259. DOI: 10.1016/j.agwat.2023.108259.
DOI |
| [34] |
YUE P, ZHANG Q, REN X Y, et al, 2022. Environmental and biophysical effects of evapotranspiration in semiarid grassland and maize cropland ecosystems over the summer monsoon transition zone of China[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 264, 107462. DOI: 10.1016/j.agwat.2022.107462.
DOI |
| [35] |
ZHANG H L, ZHANG Q, YUE P, et al, 2016. Aridity over a semiarid zone in northern China and responses to the East Asian summer monsoon[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 121(23): 13 901-13 918.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
ZHANG L, ZHANG Q, ZHANG H L, et al, 2022. Environmental factors driving evapotranspiration over a grassland in a transitional climate zone in China[J]. Meteorological Applications, 29(3), e2066. DOI: 10.1002/met.2066.
DOI |
| [37] |
ZHANG Q, YAO T, YUE P, et al, 2013. The influences of thermodynamic characteristics on aerodynamic roughness length over land surface[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 27(2): 249-262.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
ZHANG Q, WANG W Y, WANG S, et al, 2016a. Increasing trend of pan evaporation over the semiarid loess plateau under a warming climate[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 55(9): 2 007-2 020.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
ZHANG Q, YAO T, YUE P, 2016b. Development and test of a multi-factorial parameterization scheme of land surface aerodynamic roughness length for flat land surfaces with short vegetation[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 59(2): 281-295.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
ZHANG Q, YANG Z S, HAO X C, et al, 2019. Conversion features of evapotranspiration responding to climate warming in transitional climate regions in Northern China[J]. Climate Dynamics, 52(7): 3 891-3 903.
DOI |
| [41] |
ZHANG Q, ZENG J, YUE P, et al, 2020. On the land-atmosphere interaction in the summer monsoon transition zone in East Asia[J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 141(3): 1 165-1 180.
DOI |
| [42] |
ZHAO F N, LEI J, WANG R Y, et al, 2022. Environmental determination of spring wheat yield in a climatic transition zone under global warming[J]. International Journal of Biometeorology, 66(3): 481-491.
DOI |
| [43] |
ZUO J Q, HUANG J P, WANG J M, et al, 2009. Surface turbulent flux measurements over the Loess Plateau for a semi-arid climate change study[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 26(4): 679-691.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 杜昊霖, 王胜, 乔梁, 孙旭映. 半干旱区陆面过程观测试验的仪器精度和观测误差分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(3): 364-374. |
| [2] | 任余龙, 张铁军, 柳媛普, 吴晶. 夏季风过渡区下垫面非均匀性对一次暴雨影响的数值模拟[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(5): 755-763. |
| [3] | 吕 晶,李跃清,邹槟骏,江 南,李雪枫,王会兵. 1959—2016年峨眉山和周边地区不同量级降水变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2018, 36(2): 243-255. |
| [4] | 姚洁,赵桂香,金磊. 山西陆面过程对 A1B 排放情景下全球变化趋势的响应[J]. 干旱气象, 2014, 32(3): 346-353. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||