干旱气象 ›› 2022, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (5): 764-770.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-05-0764
2022年西南地区极端高温干旱特征及其主要影响
- 1.四川省气候中心/西南区域气候中心,四川 成都 610072
2.高原与盆地暴雨旱涝灾害四川省重点实验室,四川 成都 610072
3.甘肃省气象局,甘肃 兰州 730020
4.中国气象局兰州干旱气象研究所,甘肃 兰州 730020
Characteristics of the extreme high temperature and drought and their main impacts in southwestern China of 2022
SUN Zhaoxuan1,2( ), ZHANG Qiang3,4, SUN Rui1,2, DENG Biao1,2
), ZHANG Qiang3,4, SUN Rui1,2, DENG Biao1,2
- 1. Sichuan Climate Center/Southwest Regional Climate Center, Chengdu 610072, China
2. Heavy Rain and Drought-Flood Disasters in Plateau and Basin Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Chengdu 610072, China
3. Gansu Provincial Meteorological Bureau, Lanzhou 730020, China
4. Institute of Arid Meteorology, CMA, Lanzhou 730020, China
摘要:
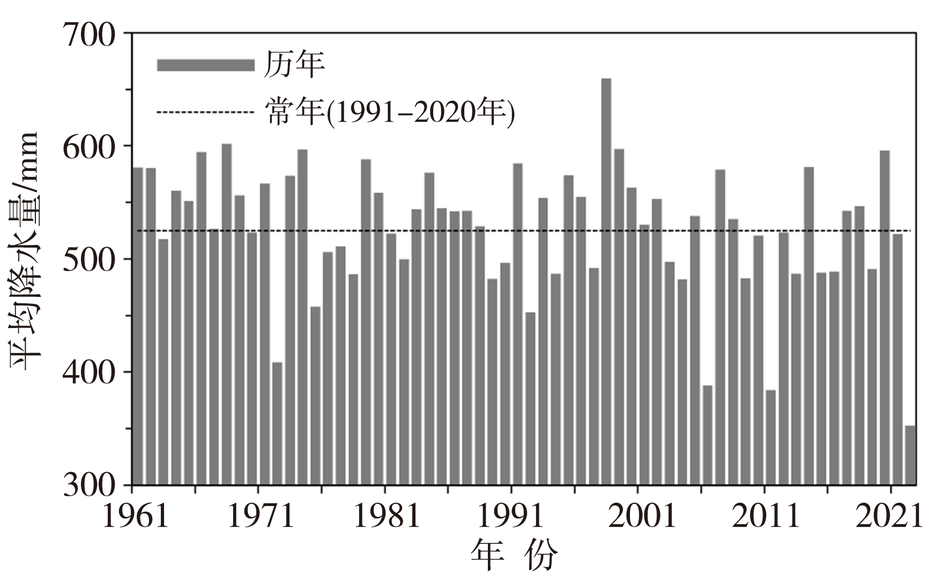
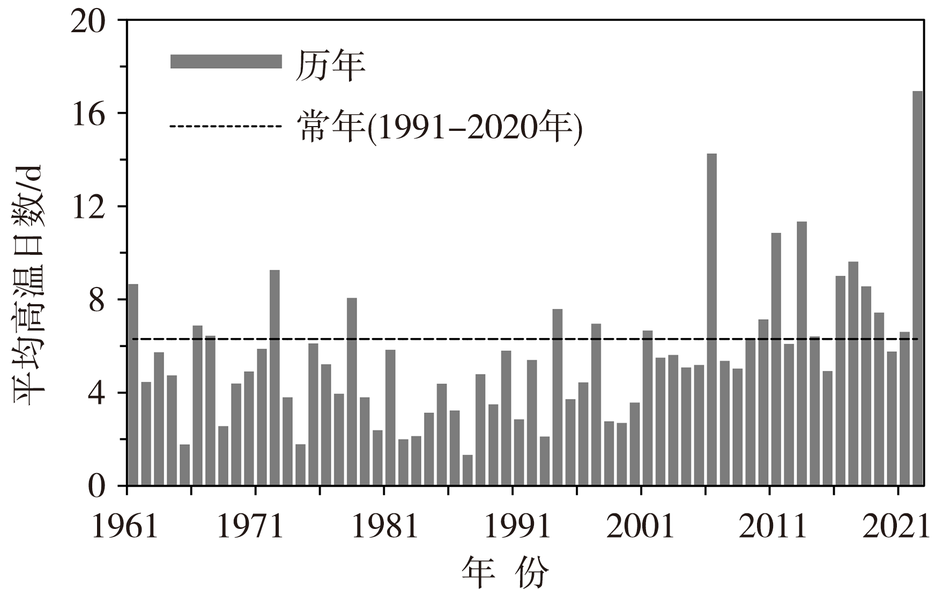
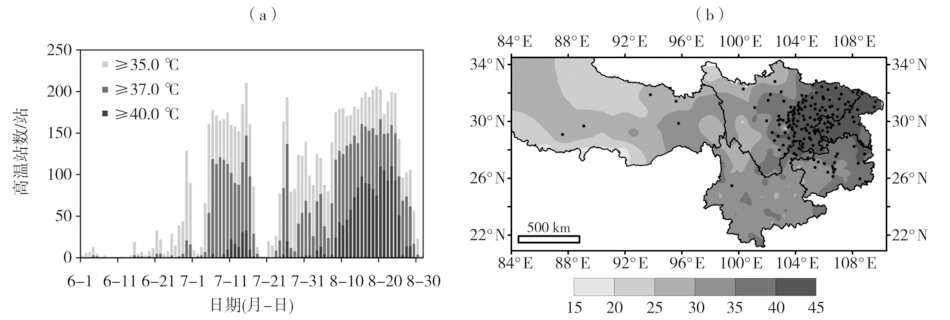
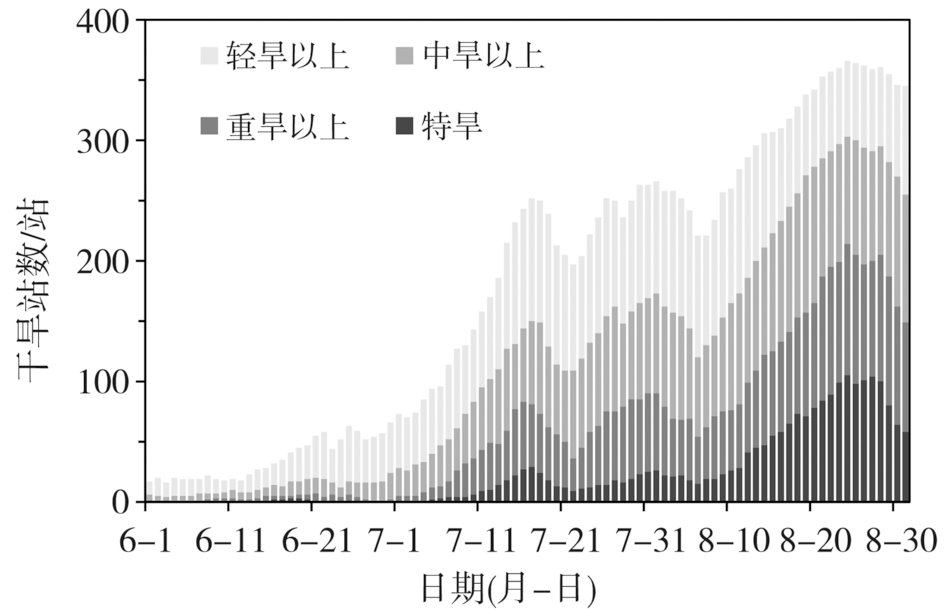
利用1961—2022年夏季(6—8月)西南地区441个国家地面气象站逐日基本气象要素观测资料,对2022年夏季西南地区的基本气候概况、高温干旱灾害的特征及其产生的主要影响进行分析。结果表明:此次极端高温干旱事件的严重程度实属历史罕见。2022年夏季西南地区平均气温历史同期最高,降水量历史同期最少,高温日数历史同期最多,极端最高气温历史同期最高。西南地区东部并发严重的气象干旱,特旱站数高达105站,主要发生在西藏中部、四川大部、重庆大部、贵州北部以及云南中部局部地区。受此极端持续的复合型高温干旱事件影响,西南地区东部部分农作物减产、甚至绝收;江河来水量出现“汛期返枯”的罕见现象;电网负荷创历史新高,加之水电发电量锐减,造成能源供应保障短缺;四川盆地东部、重庆西部发生多起森林火灾。本文力图从科学角度认识这次极端高温干旱事件,助力气象灾害风险评估业务发展,为提升防灾减灾和应对气候变化的能力提供支撑。
中图分类号: