干旱气象 ›› 2021, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (5): 857-863.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2021)-05-0857
西安市供暖期日燃气负荷预测方法
- 1.陕西省气象服务中心,陕西 西安 710014
2.秦岭和黄土高原生态环境气象重点实验室,陕西 西安 710016
3.西安市秦华天然气公司,陕西 西安 710075
Forecast Method of Daily Gas Load During Heating Period in Xi’an of Shaanxi Province
GAO Hongyan1,2( ),YANG Yanchao1,ZHANG Xi1,WANG Dan1,CUI Yu3,XIE Feng3
),YANG Yanchao1,ZHANG Xi1,WANG Dan1,CUI Yu3,XIE Feng3
- 1. Shaanxi Meteorological Service Center, Xi’an 710014, China
2. Key Laboratory of Eco-environment and Meteorology for the Qinling Mountains and Loess Plateau, Xi’an 710016, China
3. Xi’an Qinhua Natural Gas Company, Xi’an 710075, China
摘要:
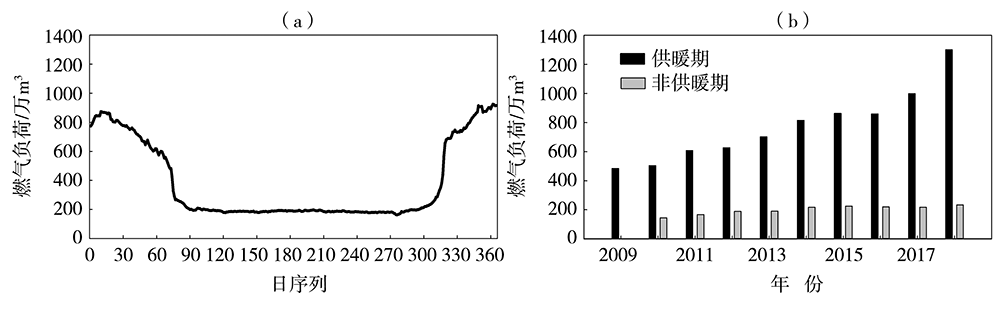
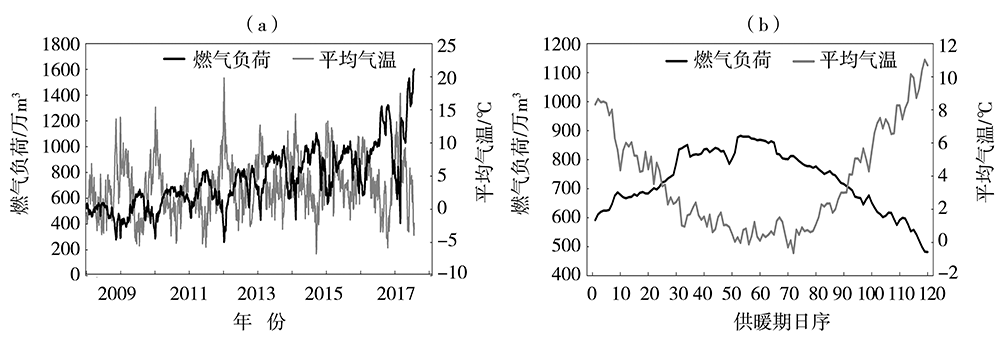
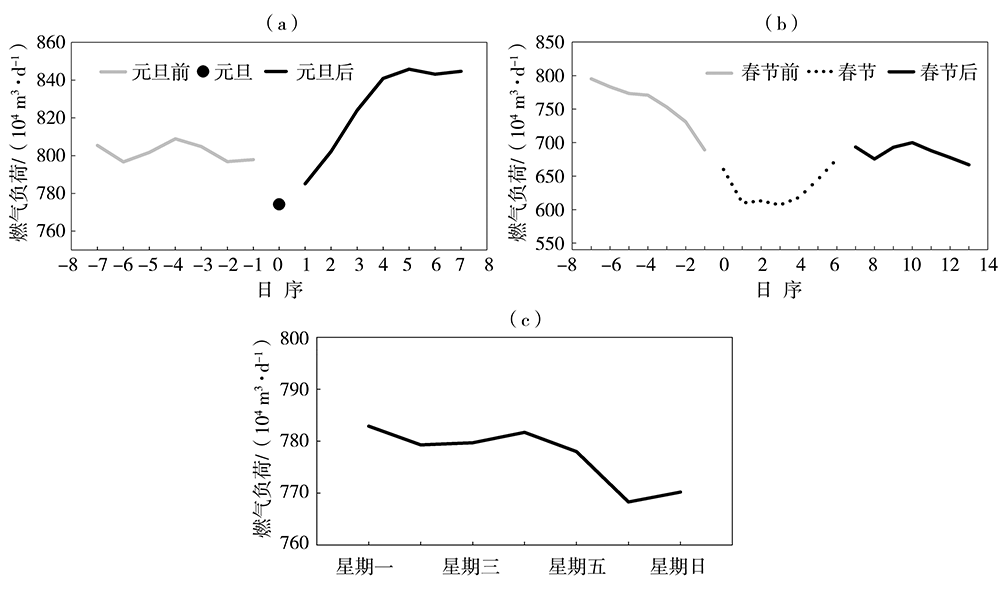
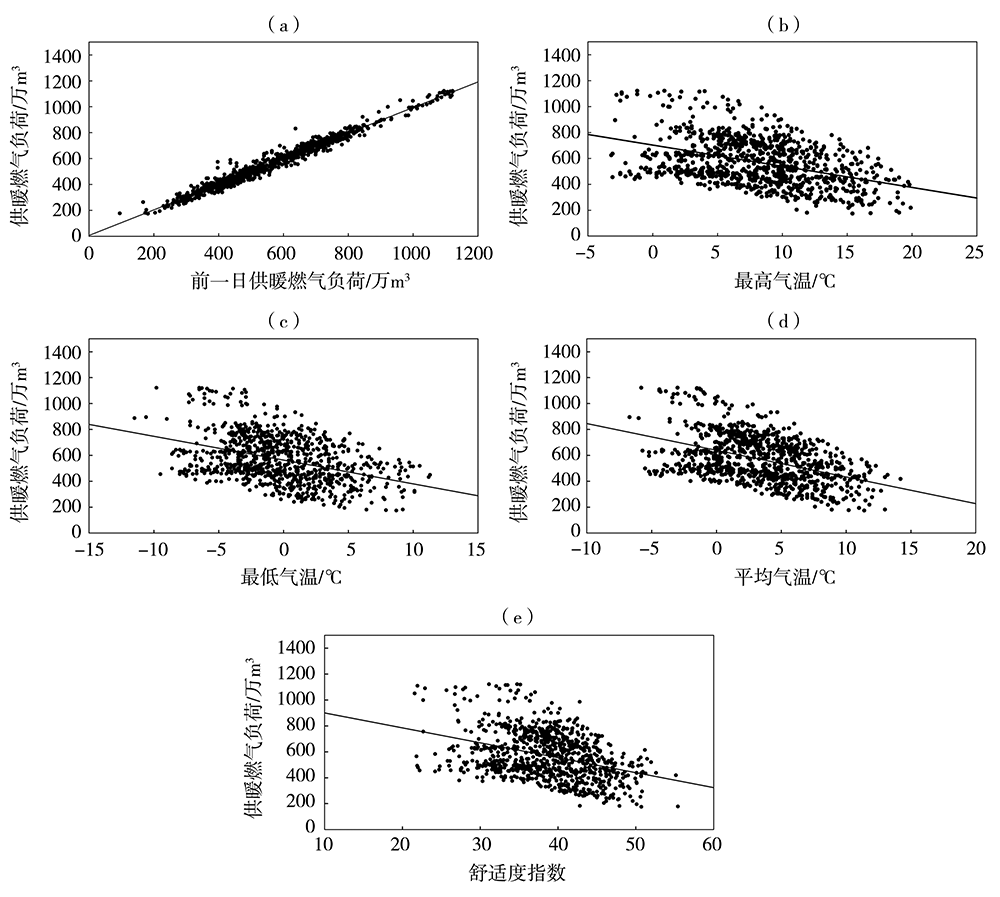
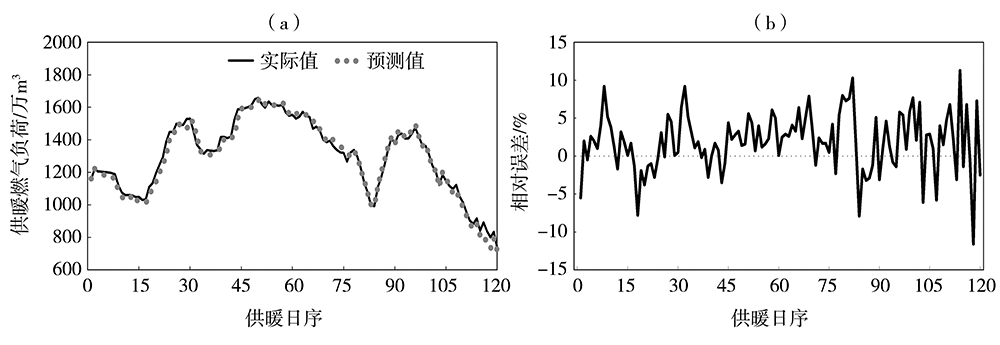
利用西安市2009年11月15日至2019年3月14日供暖期燃气负荷及气象观测逐日资料,分析西安市供暖期、节假日、双休日燃气负荷的变化规律,采用相关分析方法,筛选相关性显著的因子作为燃气负荷影响因子。在此基础上,采用多元线性回归分析方法,构建供暖期日燃气负荷预测模型,并对模型进行检验评估。结果表明:近10 a西安市供暖期燃气用量逐年增加,且日燃气负荷呈单峰型波动变化,峰值出现在1月。供暖期燃气负荷具有双休日、节假日效应,其燃气负荷明显低于工作日,且节假日越长影响越明显。供暖期燃气负荷与前一日燃气负荷呈显著正相关,而与最高气温、最低气温、平均气温及人体舒适度等气象因子呈显著负相关,分离基础燃气负荷后的供暖燃气负荷与上述气象因子的相关性明显提高。基于上述5个影响因子构建的供暖期日燃气负荷动态预测模型,经检验,平均相对误差为3.4%,且用气高峰期模型预测更稳定,相对误差为2.77%,能够满足天然气公司供暖期燃气调度需求。
中图分类号: