干旱气象 ›› 2022, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (5): 791-803.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-05-0791
中国北方蒸散-降水耦合度时空变化与水热因子的关系
- 成都信息工程大学大气科学学院,高原大气与环境四川省重点实验室,四川 成都 610225
-
收稿日期:2022-09-23修回日期:2022-10-03出版日期:2022-10-31发布日期:2022-11-10 -
通讯作者:杨泽粟 -
作者简介:李梁(2001—),男,学士,主要从事陆面过程研究. E-mail:3011974904@qq.com。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(42205071);国家自然科学基金重点项目(42230611);第二次青藏高原综合科学考察研究项目(2019QZKK0102)
Evapotranspiration-precipitation coupling strength response to hydrothermal factors over northern China
LI Liang( ), YANG Zesu(
), YANG Zesu( ), HE Hang
), HE Hang
- College of Atmospheric Sciences, Chengdu University of Information Technology, Plateau Atmospheric and Environment Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Chengdu 610225, China
-
Received:2022-09-23Revised:2022-10-03Online:2022-10-31Published:2022-11-10 -
Contact:YANG Zesu
摘要:
中国北方气候过渡区作为陆-气耦合“热点”区域,水热条件空间梯度大,当前研究较少关注水分和热力因子对蒸散-降水耦合度时空变化的影响,尤其对水热协同影响考虑不足。基于多源融合蒸散、降水、气温和卫星遥感土壤湿度数据,分析中国北方地区蒸散-降水耦合度时空变化特征分别与水、热单因子及两者协同作用的关系。结果表明,中国北方地区蒸散-降水耦合度由西北区域的强正耦合逐渐过渡为东南角和东北角的负耦合。蒸散-降水耦合度随平均土壤湿度降低逐渐增大,随气温变率增大而增强。考虑水热协同作用时,平均土壤湿度和平均气温协同较土壤湿度和气温变率协同对蒸散-降水耦合度空间分布影响更大,起主导作用。时间变化上,耦合度呈春、夏、秋、冬季依次减弱的年内变化,且具有明显的年际波动特征。土壤湿度变率和平均气温是主导中国北方地区蒸散-降水耦合度年内变化的主要因素,平均土壤湿度和土壤湿度变率对蒸散-降水耦合度年际变化的影响突出。考虑协同作用时,平均土壤湿度和气温的年内循环共同决定了蒸散-降水耦合度年内变化,对蒸散-降水耦合度年际变化的影响仅在耦合度最大的半干旱地区显著。研究结果可加深认识陆-气耦合度对陆面状态时空变化的响应特征,为提高陆气耦合数值模拟提供参考。
中图分类号:
引用本文
李梁, 杨泽粟, 何杭. 中国北方蒸散-降水耦合度时空变化与水热因子的关系[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(5): 791-803.
LI Liang, YANG Zesu, HE Hang. Evapotranspiration-precipitation coupling strength response to hydrothermal factors over northern China[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(5): 791-803.

图2 中国北方年降水量(a、b)和蒸散量(c、d)的气候态(a、c)及标准差(b、 d)空间分布(单位:mm)
Fig.2 Spatial distribution of climate state (a, c) and standard deviation (b, d) of annual precipitation (a, b) and evapotranspiration (c, d) in northern China (Unit: mm)

图3 中国北方总蒸散-降水耦合度空间分布 (圆点区通过α=0.05的显著性检验。下同)
Fig.3 Spatial distribution of total evapotranspiration-precipitation coupling strength in northern China (the circle dot areas passing α=0.05 significance test. the same as below)

图4 中国北方冬季(a)、春季(b)、夏季(c)和秋季(d)蒸散-降水耦合度空间分布
Fig.4 Spatial distribution of evapotranspiration-precipitation coupling strength in northern China in winter (a), spring (b), summer (c) and autumn (d)

图6 中国北方地区土壤湿度(a、b)和气温(c、d,单位:℃)气候态(a、 c)及变率(b、d)空间分布
Fig.6 The spatial distribution of climate state (a, c) and standard deviation (b, d) of soil moisture (a,b) and air temperature (c, d) (Unit: ℃) in northern China
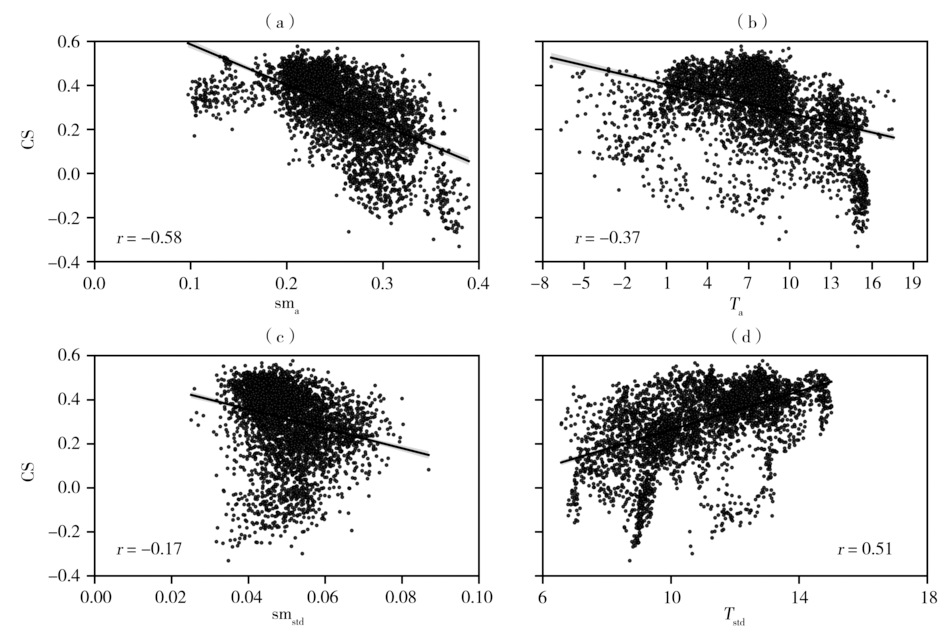
图7 蒸散-降水耦合度与平均土壤湿度(a)、平均气温(b)、土壤湿度变率(c)和气温变率(d)的散点图
Fig.7 The scatter plots of evapotranspiration-precipitation coupling strength with average soil moisture (a), average temperature (b), soil moisture standard deviation (c) and temperature standard deviation (d)

图8 蒸散-降水耦合度与平均土壤湿度和平均气温(a)及土壤湿度和气温变率(b)的多元线性回归
Fig.8 Multiple linear regression of evapotranspiration-precipitation coupling strength with average soil moisture and average temperature (a), and soil moisture standard deviation and temperature standard deviation (b)

图9 不同干湿气候背景区蒸散-降水耦合度年内(a)和年际(b)变化
Fig.9 Intra-annual (a) and inter-annual (b) fluctuations of evapotranspiration-precipitation coupling strength in different dry and wet climate background regions
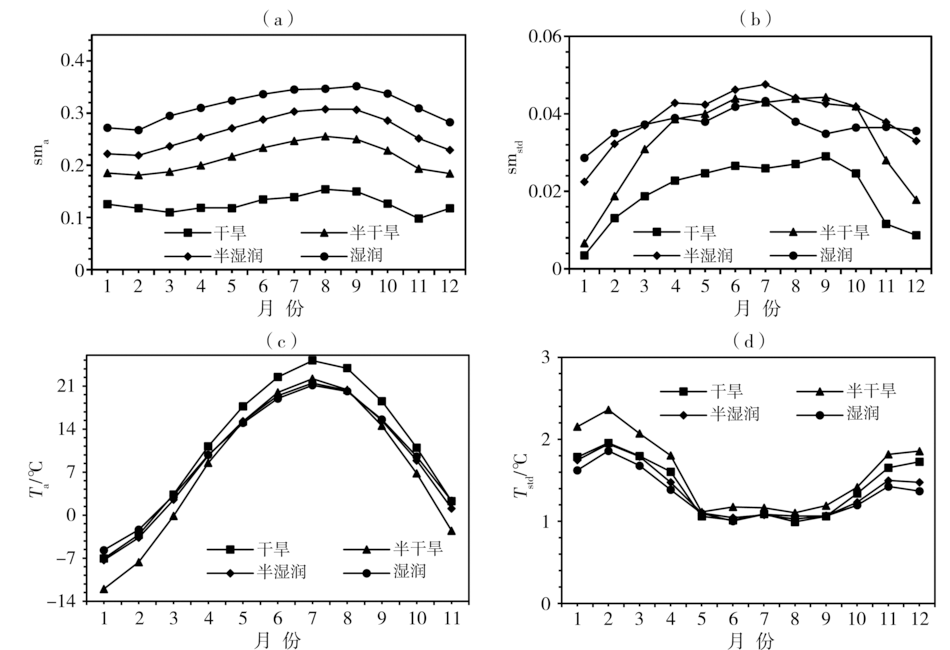
图10 不同干湿气候背景区逐月土壤湿度(a、b)、气温(c、d)的气候态(a、c)及标准差(b、d)变化
Fig.10 Monthly change of climate state (a, c) and standard deviation (b, d) of soil moisture (a, b), temperature (c, d)in different dry and wet climate background regions
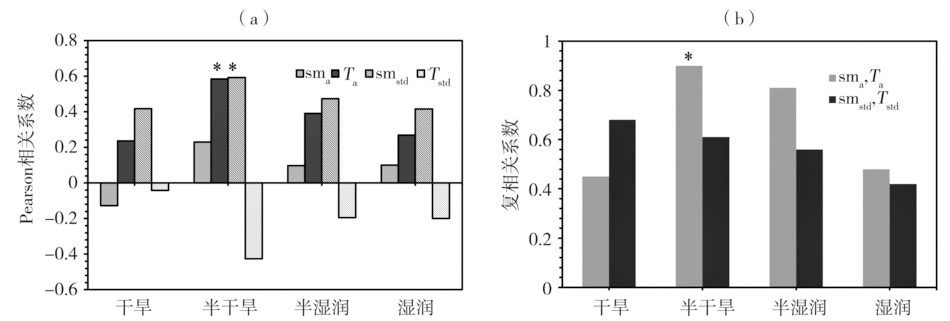
图11 不同干湿气候背景区蒸散-降水耦合度与平均土壤湿度、平均气温、土壤湿度变率和气温变率的Pearson相关系数(a),蒸散-降水耦合度与平均土壤湿度和平均气温、土壤湿度变率和气温变率的复相关系数(b)(*表示相关系数/复相关系数通过α=0.05显著性检验。下同)
Fig.11 Pearson correlation coefficients of evapotranspiration-precipitation coupling strength with average soil moisture, average temperature, soil moisture standard deviation, temperature standard deviation (a), and complex correlation coefficients of evapotranspiration-precipitation coupling strength with average soil moisture and average temperature, and with soil moisture standard deviation, temperature standard deviation (b)in different dry and wet climate background regions (the asterisk indicates correlation coefficient or multiple correlation coefficient passing α=0.05 significance test. the same as below)

图12 中国北方不同干湿气候背景区平均土壤湿度(a)、土壤湿度标准差(b)、平均气温(c)、气温标准差(d)年际变化
Fig.12 Inter-annual variation of average soil moisture (a) and soil moisture standard deviation (b), average temperature (c) and temperature standard deviation (d) in different dry and wet climate background regions in the northern China

图13 不同干湿气候背景区蒸散-降水耦合度分别与平均土壤湿度、平均气温、土壤湿度变率和气温变率的Pearson相关系数(a),蒸散-降水耦合度与平均土壤湿度和平均气温、土壤湿度变率和气温变率的复相关系数(b)
Fig.13 Pearson correlation coefficients of evapotranspiration-precipitation coupling strength with average soil moisture, average temperature, soil moisture standard deviation, temperature standard deviation (a), and complex correlation coefficients of evapotranspiration-precipitation coupling strength with average soil moisture and average temperature, and with soil moisture standard deviation, temperature standard deviation (b) in different dry and wet climate background regions
| [1] |
黄荣辉. 我国重大气候灾害的形成机理和预测理论研究[J]. 地球科学进展, 2006, 21(6): 564-575.
DOI |
| [2] |
SENEVIRATNE S I, LüTHI D, LITSCHI M, et al. Land-atmosphere coupling and climate change in Europe[J]. Nature, 2006, 443(7108): 205-209.
DOI URL |
| [3] | 张井勇, 吴凌云. 陆-气耦合增加中国的高温热浪[J]. 科学通报, 2011, 56(23): 1905-1909. |
| [4] | ZHOU S, WILLIAMS A P, BERG A M, et al. Land-atmosphere feedbacks exacerbate concurrent soil drought and atmospheric aridity[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2019, 116(38): 18 848-18 853. |
| [5] |
KOSTER R D. Regions of strong coupling between soil moisture and precipitation[J]. Science, 2004, 305(5687): 1138-1140.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
ZENG X, BARLAGE M, CASTRO C, et al. Comparison of land-precipitation coupling strength using observations and models[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2010, 11(4): 979-994.
DOI URL |
| [7] | DIRMEYER P A. The terrestrial segment of soil moisture-climate coupling[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2011, 38(16): L16702. |
| [8] |
KOSTER R D, SUAREZ M J, LIU P, et al. Realistic Initialization of land surface states: impacts on subseasonal forecast skill[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2004, 5(6): 1049-1063.
DOI URL |
| [9] | 陈海山, 周晶. 土壤湿度年际变化对中国区域极端气候事件模拟的影响研究Ⅱ.敏感性试验分析[J]. 大气科学, 2013, 37(1): 1-13. |
| [10] | 单机坤, 沈学顺, 李维京. 陆气相互作用对中尺度对流系统影响的研究进展[J]. 气象, 2013, 39(11): 1413-1421. |
| [11] | 岳平, 张强, 赵文, 等. 黄土高原半干旱草地生长季干湿时段环境因子对陆面水、热交换的影响[J]. 中国科学:D辑地球科学, 2015, 45(8): 1229-1242. |
| [12] | 郭维栋, 马柱国, 姚永红. 近50年中国北方土壤湿度的区域演变特征[J]. 地理学报, 2003, 58(增刊1): 83-90. |
| [13] |
WILLIAMS I N, TORN M S. Vegetation controls on surface heat flux partitioning, and land-atmosphere coupling[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2015, 42(21): 9416-9424.
DOI URL |
| [14] | 曾毓金, 谢正辉. 基于CMIP5模拟的中国区域陆气耦合强度评估及未来情景预估[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2015, 20(3): 337-346. |
| [15] | 张述文, 刘源, 曹帮军, 等. GLDAS和CMIP5产品的中国土壤湿度-降水耦合分析及变化趋势[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2016, 21(2): 188-196. |
| [16] |
SENEVIRATNE S I, CORTI T, DAVIN E L, et al. Investigating soil moisture-climate interactions in a changing climate: a review[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2010, 99(3): 125-161.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
ELTAHIR E A B, BRAS R L. Precipitation recycling[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 1996, 34(3): 367-378.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
WEI J, DIRMEYER P A. Toward understanding the large-scale land-atmosphere coupling in the models: roles of different processes[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2010, 37, L19707. DOI:10.1029/2010GL044769.
DOI |
| [19] |
GOESSLING H F, REICK C H. What do moisture recycling estimates tell us? Exploring the extreme case of non-evaporating continents[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 2011, 15(10): 3217-3235.
DOI URL |
| [20] | 左志燕, 张人禾. 中国东部夏季降水与春季土壤湿度的联系[J]. 科学通报, 2007, 54(14): 1722-1724. |
| [21] |
GAO C, CHEN H, LI G, et al. Land-atmosphere interaction over the Indo-China Peninsula during spring and its effect on the following summer climate over the Yangtze River basin[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2019, 53(9/10): 6181-6198.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
FINDELL K L, ELTAHIR E A B. Atmospheric controls on soil moisture-boundary layerinteractions. part I: framework development[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2003, 4(3): 552-569.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
BERG A, FINDELL K, LINTNER B R, et al. Precipitation sensitivity to surface heat fluxes over North America in reanalysis and model data[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2013, 14(3): 722-743.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
SANTANELLO J A, DIRMEYER P A, FERGUSON C R, et al. Land-atmosphere interactions: the LoCo perspective[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2018, 99(6): 1253-1272.
DOI URL |
| [25] | 张宏升, 刘新建, 朱好, 等. 北京北郊冬季大风过程湍流通量演变特征的分析研究[J]. 大气科学, 2010, 34(3): 661-668. |
| [26] |
DIRMEYER P A, CHEN L, WU J, et al. Verification of land-atmosphere coupling in forecast models, reanalyses and land surface models using flux site observations[J]. Journal of hydrometeorology, 2018, 19(2): 375-392.
DOI URL |
| [27] | WEI J, DIRMEYER P A. Dissecting soil moisture-precipitation coupling[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2012, 39(19): 1-6. |
| [28] |
GUO Z, DIRMEYER P A. Interannual variability of land-atmosphere coupling strength[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2013, 14(5): 1636-1646.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
PHILLIPS T J, KLEIN S A. Land-atmosphere coupling manifested in warm-season observations on the U.S. southern great plains[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2014, 119(2): 509-528.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
RUSCICA R C, SöRENSSON A A, MENéNDEZ C G. Pathways between soil moisture and precipitation in southeastern South America[J]. Atmospheric Science Letters, 2015, 16(3): 267-272.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
RUSCICA R C, MENéNDEZ C G, SöRENSSON A A. Land surface-atmosphere interaction in future South American climate using a multi-model ensemble[J]. Atmospheric Science Letters, 2016, 17(2): 141-147.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
PETROVA I Y, VAN HEERWAARDEN C C, HOHENE-GGER C, et al. Regional co-variability of spatial and temporal soil moisture-precipitation coupling in North Africa: an observational perspective[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 2018, 22(6): 3275-3294.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
LI M, MA Z, GU H, et al. Production of a combined land surface data set and its use to assess land-atmosphere coupling in China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2017, 122(2): 948-965.
DOI URL |
| [34] | 杨扬, 杨启东, 王芝兰, 等. 中国区域陆气耦合强度的时空分布特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(3): 374-385. |
| [35] |
GAO C, CHEN H, SUN S, et al. Regional features and seasonality of land-atmosphere coupling over eastern China[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2018, 35(6): 689-701.
DOI URL |
| [36] | 赵靖川, 刘树华. 植被变化对西北地区陆气耦合强度的影响[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015, 58(1): 47-62. |
| [37] | 张强, 杨泽粟, 郝小翠, 等. 北方蒸散对气候变暖响应随降水类型转换特征[J]. 科学通报, 2018, 63(11): 1035-1049. |
| [38] | HOBEICHI S, ABRAMOWITZ G, EVANS J, et al. Derived Optimal Linear Combination Evapotranspiration (DOLCE): a global gridded synthesis ET estimate[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences (Online), 2018, 22(2): 1317-1336 |
| [39] |
HE J, YANG K, TANG w, et al. The first high-resolution meteorological forcing dataset for land process studies over China[J]. Scientific Data, 2020, 7(5): 1-15.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
GRUBER A, SCANLON T, VAN DER SCHALIE R, et al. Evolution of the ESA CCI Soil Moisture climate data records and their underlying merging methodology[J]. Earth System Science Data, 2019, 11(2): 717-739.
DOI URL |
| [41] | ALLEN R, PEREIRA L, RAES D, et al. Crop evapotranspiration, Guidelines for computing crop water requirements-FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56[R]. Rome: FAO, 1998. |
| [1] | 王晓晨, 马雪晴, 和骅芸, 任思琪, 唐书玥, 赵金媛, 潘志华, 王靖, 潘学标, 胡琦, . 1961—2020年中国北方向日葵种植区干湿变化特征及其成因分析 [J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(6): 1033-1041. |
| [2] | 陈燕丽, 唐梅蓉, 张会, 莫建飞, 钱拴. 广西喀斯特地区植被覆盖度和净初级生产力对SPEI干旱指数的响应差异 [J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(6): 1042-1050. |
| [3] | 安琳莉, 黄建平, 任钰, 张国龙. 中国北方旱区陆地水储量变化特征及其归因分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(2): 169-178. |
| [4] | 于静,王莺,高亚敏,齐佳慧,付铭. 基于MOD16产品的科尔沁草原地表蒸散时空变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(5): 831-837. |
| [5] | 张亚春, 马耀明, 马伟强, 王宾宾, 王玉阳, . 青藏高原不同下垫面蒸散量及其与气象因子的相关性[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(3): 366-373. |
| [6] | 檀艳静, 胡程达, 史桂芬. 黄淮海区域参考作物蒸散量的时空变化特征及影响因素#br#[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(5): 794-803. |
| [7] | 黄珊, 杨扬, 王含嘉, 杨启东. 中国西南地区地表感热和潜热通量时空变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(4): 601-611. |
| [8] | 陈燕丽, 蒙良莉, 黄肖寒, 莫建飞, 王莹, 莫伟华. 基于SPEI的广西喀斯特地区1971—2017年干旱时空演变[J]. 干旱气象, 2019, 37(3): 353-. |
| [9] | 孙夏, 范广洲, 张永莉, 赖欣. 夏季青藏高原不同层次土壤湿度时空变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2019, 37(2): 252-261. |
| [10] | 刘丽伟, 魏栋, 王小巍, 程善俊. 多种土壤湿度资料在中国地区的对比分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2019, 37(1): 40-47. |
| [11] | 邓明珊,孟宪红,马英赛,安颖颖. 基于GLDAS产品的青藏高原土壤湿度特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2018, 36(4): 595-602. |
| [12] | 迪丽努尔·托列吾别克,李栋梁. 近115 a中亚干湿气候变化研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2018, 36(2): 185-195. |
| [13] | 杨艳娟1,曹经福1,熊明明1,赵玉娟2. 影响海河流域参考作物蒸散量的气象因子定量分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2017, 35(3): 367-. |
| [14] | 代海燕1,都瓦拉1,王晓江2,李丹1,安丽娟3. 基于GIS的内蒙古林业气候区划[J]. 干旱气象, 2017, 35(2): 337-341. |
| [15] | 沙比提,买买提,欢乐希,哈布拉哈提,木拉提,耿燕,冯丽晔,陈亮. 1961—2014年乌鲁木齐地区气候特征及干湿区变化[J]. 干旱气象, 2016, 34(3): 448-455. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||


