干旱气象 ›› 2021, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (06): 995-1005.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2021)-06-0995
气象条件对深圳市罗湖区上呼吸道感染就诊人数的影响
黄开龙1,4( ), 林锦春2, 马盼1, 黄文静2, 陆俊翔2, 唐小新3, 王式功1(
), 林锦春2, 马盼1, 黄文静2, 陆俊翔2, 唐小新3, 王式功1( )
)
- 1.成都信息工程大学大气科学学院,高原大气与环境四川省重点实验室,四川 成都 610225
2.深圳大学第三附属医院,广东 深圳 518000
3.广东省深圳市气象服务中心,广东 深圳 518000
4.广东省汕头市气象局,广东 汕头 515041
-
收稿日期:2020-04-25修回日期:2021-01-05出版日期:2021-12-30发布日期:2021-12-31 -
通讯作者:王式功 -
作者简介:黄开龙(1995— ),男,广东汕头人,硕士研究生,研究方向为气象环境与健康. E-mail: huangkl123@126.com。 -
基金资助:“医学气象学服务于全民大健康的应用研究”(2019ZDIANXM09);国家自然科学基金共同资助(41775147)
Influence of meteorological factors on number of upper respiratory tract infection visits in Luohu of Shenzhen
HUANG Kailong1,4( ), LIN Jinchun2, MA Pan1, HUANG Wenjing2, LU Junxiang2, TANG Xiaoxin3, WANG Shigong1(
), LIN Jinchun2, MA Pan1, HUANG Wenjing2, LU Junxiang2, TANG Xiaoxin3, WANG Shigong1( )
)
- 1. College of Atmospheric Sciences, Chengdu University of Information Technology, Chengdu 610225, China
2. The Third Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518000, Guangdong, China
3. Shenzhen Meteorological Service Center of Guangdong Province, Shenzhen 518000, Guangdong, China
4. Shantou Meteorological Bureau of Guangdong Province, Shantou 515041, Guangdong, China
-
Received:2020-04-25Revised:2021-01-05Online:2021-12-30Published:2021-12-31 -
Contact:WANG Shigong
摘要:
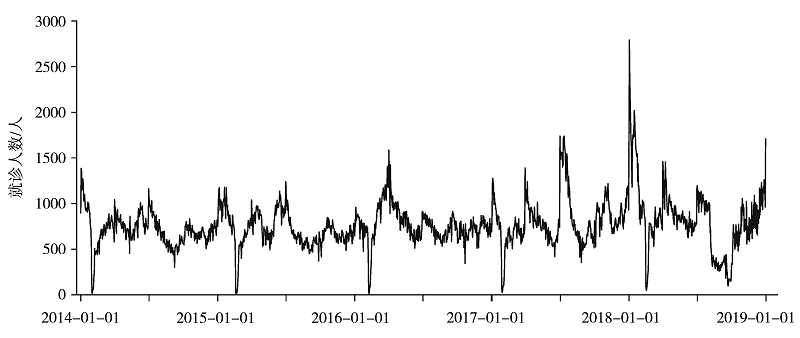
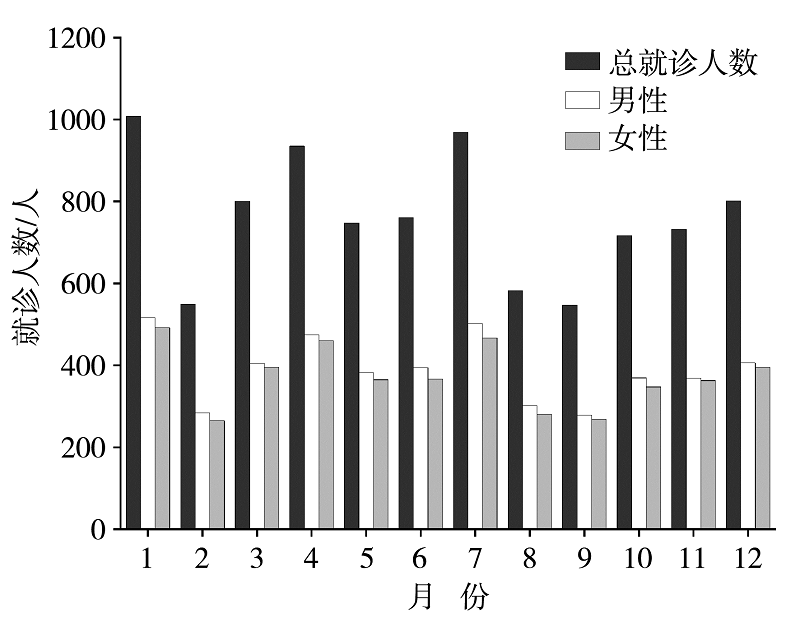
基于2014—2018年深圳市罗湖区49家社区健康服务中心上呼吸道感染(简称“上感”)的逐日就诊人数和同期气象要素资料,利用不同时间尺度分析上感就诊人数的变化特征,并采用分布滞后非线性模型(DLNM)、广义线性模型(GLM)等研究不同气象要素与深圳地区上感就诊人数的关系。结果表明:深圳市罗湖区上感就诊人数存在明显的季节性变化,春季3—4月、夏季7月和冬季12月至次年1月为发病高峰时段,分别对应24节气中的清明、小暑、小寒节气。DLNM反映气温为主控因素,它对上感就诊人数的影响以冷效应为主,相对风险(RR)在滞后4 d达到峰值(RR为1.041,95%置信区间为1.022~1.060),且女性较男性、中老年人较少儿更易受冷效应的影响;其次是暑期的热效应和春季温度多变的影响。湿度影响主要表现为低湿效应,其相对风险在当天达到峰值(RR为1.058,95%置信区间为1.049~1.068)。气压和风速影响则表现为高压效应和大风效应,RR在滞后1 d达最高。总之,深圳市冬、春季冷空气活动及其所反映的低温、低湿、大风等产生的冷效应是诱发上呼吸道感染的关键因素,其次是夏季持续高温的影响,两者都应予以重点及时防范。
中图分类号:
引用本文
黄开龙, 林锦春, 马盼, 黄文静, 陆俊翔, 唐小新, 王式功. 气象条件对深圳市罗湖区上呼吸道感染就诊人数的影响[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(06): 995-1005.
HUANG Kailong, LIN Jinchun, MA Pan, HUANG Wenjing, LU Junxiang, TANG Xiaoxin, WANG Shigong. Influence of meteorological factors on number of upper respiratory tract infection visits in Luohu of Shenzhen[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(06): 995-1005.
| 日平均 气温/ ℃ | 日最高 气温/ ℃ | 日最低 气温/ ℃ | 日平均 相对 湿度/% | 日平均 气压/ hPa | 日平均 风速/ (m·s-1) | 日降水量/ mm | 气温 日较差/ ℃ | 日均 水汽压/ hPa | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X±s | 23.5±5.5 | 27.1±5.6 | 21.1±5.6 | 75.4±12.6 | 1005.6±6.6 | 1.9±0.8 | 5.3±17.0 | 6.0±2.0 | 23.2±8.3 |
| Pmin | 3.5 | 6.5 | 1.7 | 19 | 983.1 | 0.4 | 0 | 0.9 | 2.7 |
| P25 | 19.4 | 23.2 | 16.8 | 70 | 1000.8 | 1.4 | 0 | 4.6 | 16.4 |
| P50 | 24.8 | 28.4 | 22.5 | 77 | 1005.6 | 1.8 | 0 | 5.9 | 24 |
| P75 | 28.2 | 31.7 | 25.9 | 84 | 1010.4 | 2.3 | 1.2 | 7.3 | 31 |
| Pmax | 33 | 37 | 29.9 | 100 | 1027.3 | 6.1 | 187.8 | 14 | 38 |
表1 2014—2018年深圳市不同气象要素统计特征
Tab.1 The statistical characteristics of meteorological elements in Shenzhen from 2014 to 2018
| 日平均 气温/ ℃ | 日最高 气温/ ℃ | 日最低 气温/ ℃ | 日平均 相对 湿度/% | 日平均 气压/ hPa | 日平均 风速/ (m·s-1) | 日降水量/ mm | 气温 日较差/ ℃ | 日均 水汽压/ hPa | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X±s | 23.5±5.5 | 27.1±5.6 | 21.1±5.6 | 75.4±12.6 | 1005.6±6.6 | 1.9±0.8 | 5.3±17.0 | 6.0±2.0 | 23.2±8.3 |
| Pmin | 3.5 | 6.5 | 1.7 | 19 | 983.1 | 0.4 | 0 | 0.9 | 2.7 |
| P25 | 19.4 | 23.2 | 16.8 | 70 | 1000.8 | 1.4 | 0 | 4.6 | 16.4 |
| P50 | 24.8 | 28.4 | 22.5 | 77 | 1005.6 | 1.8 | 0 | 5.9 | 24 |
| P75 | 28.2 | 31.7 | 25.9 | 84 | 1010.4 | 2.3 | 1.2 | 7.3 | 31 |
| Pmax | 33 | 37 | 29.9 | 100 | 1027.3 | 6.1 | 187.8 | 14 | 38 |
| 人群 | X±s | Pmin | P25 | P50 | P75 | Pmax |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总人群 | 764.3±258.5 | 6 | 629 | 741 | 875 | 2792 |
| 男性 | 391.2±131.9 | 2 | 321 | 379 | 450 | 1384 |
| 女性 | 373.0±128.8 | 1 | 305 | 361 | 430 | 1408 |
| 0~18岁 | 231.9±106.2 | 1 | 172 | 219 | 280 | 1047 |
| 19~59岁 | 470.1±153.7 | 4 | 392 | 455 | 539 | 1546 |
| 大于60岁 | 62.3±23.0 | 0 | 48 | 60 | 75 | 199 |
表2 2014—2018年深圳市罗湖区上感就诊人数统计 单位:人
Tab.2 Summary statistics of the number of upper respiratory tract infections (URI) visits in Luohu district of Shenzhen from 2014 to 2018
| 人群 | X±s | Pmin | P25 | P50 | P75 | Pmax |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总人群 | 764.3±258.5 | 6 | 629 | 741 | 875 | 2792 |
| 男性 | 391.2±131.9 | 2 | 321 | 379 | 450 | 1384 |
| 女性 | 373.0±128.8 | 1 | 305 | 361 | 430 | 1408 |
| 0~18岁 | 231.9±106.2 | 1 | 172 | 219 | 280 | 1047 |
| 19~59岁 | 470.1±153.7 | 4 | 392 | 455 | 539 | 1546 |
| 大于60岁 | 62.3±23.0 | 0 | 48 | 60 | 75 | 199 |
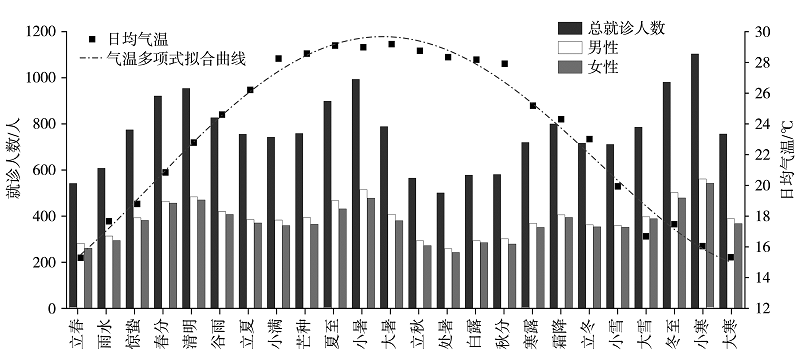
图3 2014—2018年深圳市罗湖区不同节气的日平均气温及日上感就诊人数分布
Fig.3 The distribution of daily average temperature and the number of daily URI visits in Luohu district of Shenzhen during different solar terms from 2014 to 2018
| 气象要素 | 人 群 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全人群 | 男性 | 女性 | 0~18岁 | 19~59岁 | ≥60岁 | |
| 日均气温 | -0.120** | -0.101** | -0.135** | 0.025 | -0.179** | -0.187** |
| 日最高气温 | -0.117** | -0.098** | -0.132** | 0.024 | -0.175** | -0.182** |
| 日最低气温 | -0.137** | -0.119** | -0.151** | 0.013 | -0.197** | -0.203** |
| 日均相对湿度 | -0.131** | -0.129** | -0.131** | -0.032 | -0.158** | -0.159** |
| 气压 | 0.126** | 0.107** | 0.142** | 0.010 | 0.167** | 0.182** |
| 日均风速 | -0.020 | -0.021 | -0.018 | -0.067** | 0.010 | 0.013 |
| 日累计降水 | -0.155** | -0.150** | -0.156** | -0.124** | -0.136** | -0.111** |
| 日较差 | 0.098** | 0.100** | 0.093** | 0.055* | 0.101** | 0.094** |
| 水汽压 | -0.147** | -0.128** | -0.161** | 0.009 | -0.205** | -0.212** |
表3 2014—2018年深圳市罗湖区上感就诊人数与气象要素的Spearman相关系数
Tab.3 Spearman correlation coefficients between the number of URI visits and major meteorological elements in Luohu district of Shenzhen from 2014 to 2018
| 气象要素 | 人 群 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全人群 | 男性 | 女性 | 0~18岁 | 19~59岁 | ≥60岁 | |
| 日均气温 | -0.120** | -0.101** | -0.135** | 0.025 | -0.179** | -0.187** |
| 日最高气温 | -0.117** | -0.098** | -0.132** | 0.024 | -0.175** | -0.182** |
| 日最低气温 | -0.137** | -0.119** | -0.151** | 0.013 | -0.197** | -0.203** |
| 日均相对湿度 | -0.131** | -0.129** | -0.131** | -0.032 | -0.158** | -0.159** |
| 气压 | 0.126** | 0.107** | 0.142** | 0.010 | 0.167** | 0.182** |
| 日均风速 | -0.020 | -0.021 | -0.018 | -0.067** | 0.010 | 0.013 |
| 日累计降水 | -0.155** | -0.150** | -0.156** | -0.124** | -0.136** | -0.111** |
| 日较差 | 0.098** | 0.100** | 0.093** | 0.055* | 0.101** | 0.094** |
| 水汽压 | -0.147** | -0.128** | -0.161** | 0.009 | -0.205** | -0.212** |
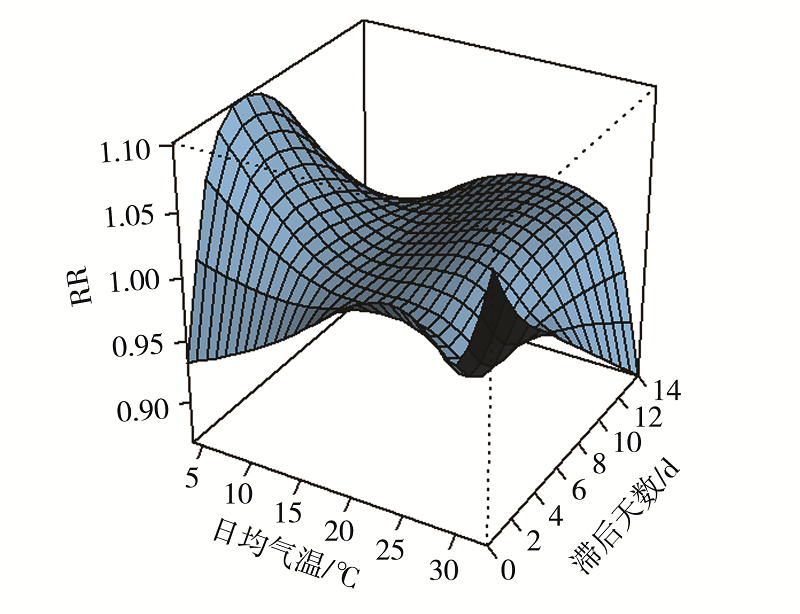
图4 2014—2018年深圳市罗湖区气温与上感就诊人数的暴露-反应关系三维图
Fig.4 Three-dimensional map of exposure-response relationship between temperature and number of URI visits in Luohu district of Shenzhen from 2014 to 2018
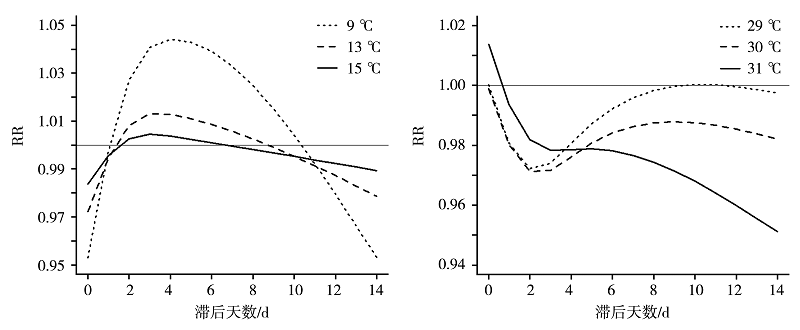
图5 2014—2018年深圳市罗湖区气温关键表征值的相对风险剖面
Fig.5 Relative risk (RR) profile of temperature key characteristic value in Luohu district of Shenzhen from 2014 to 2018
| 不同人群 | RR及其95%置信区间 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 冷效应(9 ℃) | 热效应(31 ℃) | ||||
| 累积期4 d | 累积期10 d | 累积期0 d | 累积期4 d | ||
| 全人群 | 1.06 (0.967~1.162) | 1.239* (1.088~1.411) | 1.014 (0.939~1.095) | 0.947 (0.833~1.076) | |
| 男性 | 1.057 (0.963~1.16) | 1.241* (1.088~1.415) | 1.007 (0.931~1.088) | 0.946 (0.831~1.077) | |
| 女性 | 1.063 (0.968~1.167) | 1.238* (1.084~1.413) | 1.022 (0.945~1.104) | 0.948 (0.832~1.079) | |
| 0~18岁 | 0.883 (0.786~0.993) | 0.801 (0.676~0.949) | 1.076 (0.984~1.176) | 1.014 (0.873~1.177) | |
| 19~59岁 | 1.130* (1.033~1.235) | 1.409* (1.243~1.598) | 0.986 (0.913~1.065) | 0.915 (0.806~1.04) | |
| ≥60岁 | 1.115* (1.001~1.242) | 1.597* (1.376~1.854) | 1.000 (0.91~1.098) | 0.938 (0.802~1.097) | |
表4 2014—2018年深圳市罗湖区温度效应对不同人群上感就诊人数的影响
Tab.4 The effects of temperature on the number of URI visits in Luohu district of Shenzhen from 2014 to 2018
| 不同人群 | RR及其95%置信区间 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 冷效应(9 ℃) | 热效应(31 ℃) | ||||
| 累积期4 d | 累积期10 d | 累积期0 d | 累积期4 d | ||
| 全人群 | 1.06 (0.967~1.162) | 1.239* (1.088~1.411) | 1.014 (0.939~1.095) | 0.947 (0.833~1.076) | |
| 男性 | 1.057 (0.963~1.16) | 1.241* (1.088~1.415) | 1.007 (0.931~1.088) | 0.946 (0.831~1.077) | |
| 女性 | 1.063 (0.968~1.167) | 1.238* (1.084~1.413) | 1.022 (0.945~1.104) | 0.948 (0.832~1.079) | |
| 0~18岁 | 0.883 (0.786~0.993) | 0.801 (0.676~0.949) | 1.076 (0.984~1.176) | 1.014 (0.873~1.177) | |
| 19~59岁 | 1.130* (1.033~1.235) | 1.409* (1.243~1.598) | 0.986 (0.913~1.065) | 0.915 (0.806~1.04) | |
| ≥60岁 | 1.115* (1.001~1.242) | 1.597* (1.376~1.854) | 1.000 (0.91~1.098) | 0.938 (0.802~1.097) | |
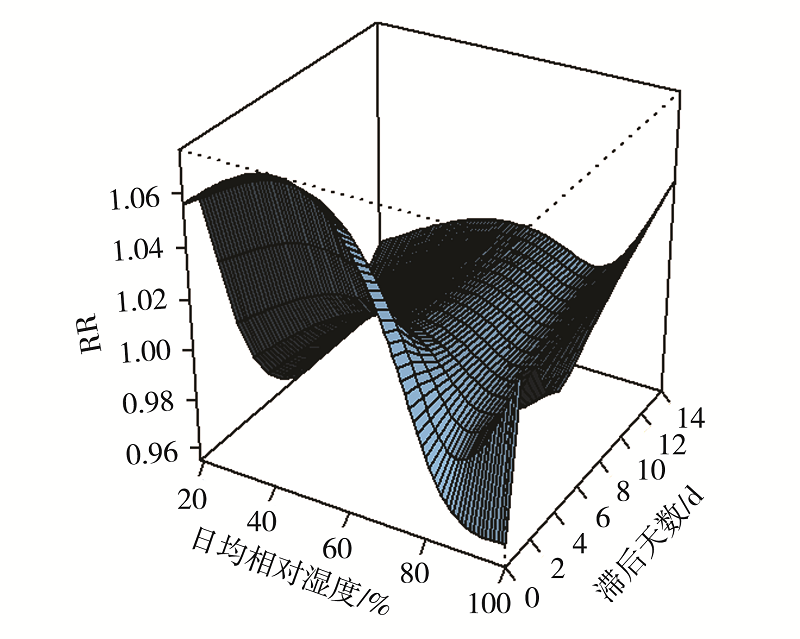
图6 2014—2018年深圳市罗湖区湿度与上感就诊人数的暴露-反应关系三维图
Fig.6 Three-dimensional map of exposure-response relationship between humidity and number of URI visits in Luohu district of Shenzhen from 2014 to 2018
| 人群 | RR及其95%置信区间 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低湿效应(RH=36%) | 高湿效应(RH=96%) | ||||
| 滞后0 d | 滞后3 d | 滞后2 d | 滞后14 d | ||
| 全人群 | 1.072* (1.061~1.085) | 1.014* (1.010~1.018) | 1.010* (1.005~1.014) | 1.029* (1.024~1.033) | |
| 男性 | 1.064* (1.047~1.081) | 1.013* (1.008~1.019) | 1.008* (1.002~1.016) | 1.027* (1.020~1.033) | |
| 女性 | 1.082* (1.065~1.100) | 1.015* (1.010~1.020) | 1.012* (1.005~1.018) | 1.031* (1.024~1.037) | |
| 0~18岁 | 1.063* (1.041~1.086) | 0.998 (0.991~1.005) | 1.019* (1.011~1.027) | 1.044* (1.036~1.052) | |
| 19~60岁 | 1.077* (1.061~1.092) | 1.020* (1.015~1.025) | 1.003 (0.997~1.009) | 1.024* (1.018~1.030) | |
| >60岁 | 1.070* (1.029~1.113) | 1.028* (1.014~1.042) | 1.035* (1.018~1.051) | 1.013 (0.997~1.029) | |
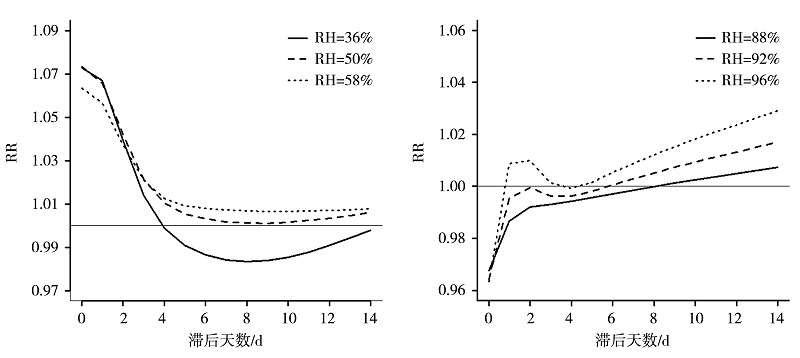
表5 2014—2018年深圳市罗湖区湿度效应对上感就诊人数的影响
Tab.5 The effect of humidity on the number of URI visits in Luohu district of Shenzhen from 2014 to 2018
| 人群 | RR及其95%置信区间 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低湿效应(RH=36%) | 高湿效应(RH=96%) | ||||
| 滞后0 d | 滞后3 d | 滞后2 d | 滞后14 d | ||
| 全人群 | 1.072* (1.061~1.085) | 1.014* (1.010~1.018) | 1.010* (1.005~1.014) | 1.029* (1.024~1.033) | |
| 男性 | 1.064* (1.047~1.081) | 1.013* (1.008~1.019) | 1.008* (1.002~1.016) | 1.027* (1.020~1.033) | |
| 女性 | 1.082* (1.065~1.100) | 1.015* (1.010~1.020) | 1.012* (1.005~1.018) | 1.031* (1.024~1.037) | |
| 0~18岁 | 1.063* (1.041~1.086) | 0.998 (0.991~1.005) | 1.019* (1.011~1.027) | 1.044* (1.036~1.052) | |
| 19~60岁 | 1.077* (1.061~1.092) | 1.020* (1.015~1.025) | 1.003 (0.997~1.009) | 1.024* (1.018~1.030) | |
| >60岁 | 1.070* (1.029~1.113) | 1.028* (1.014~1.042) | 1.035* (1.018~1.051) | 1.013 (0.997~1.029) | |
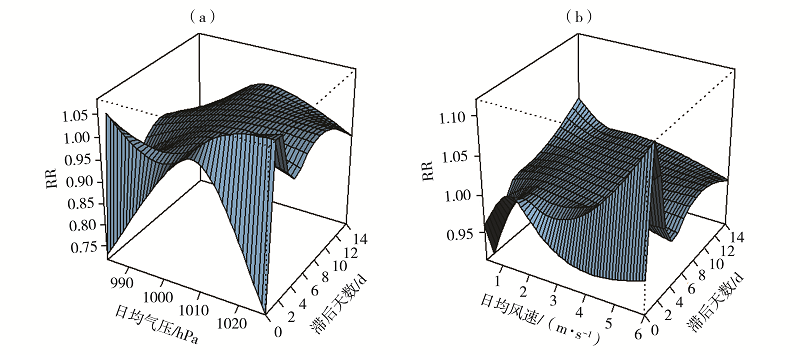
图8 2014—2018年深圳市罗湖区气压(a)、风速(b)与上感就诊人数的暴露-反应关系三维图
Fig.8 Three-dimensional map of exposure-response relationship between air pressure (a), wind speed (b) and the number of URI visits in Luohu district of Shenzhen from 2014 to 2018
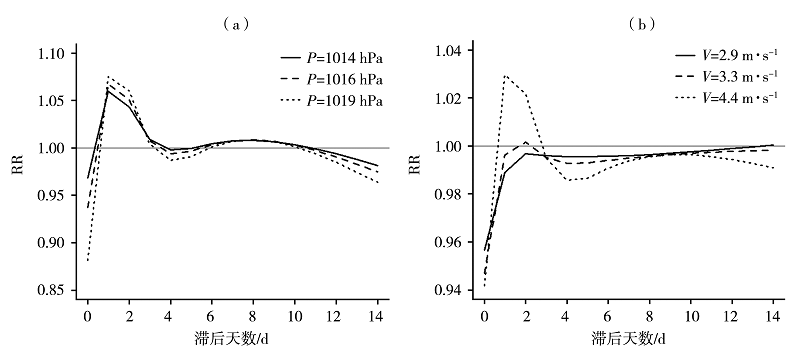
图9 2014—2018年深圳市罗湖区高压(a)、大风(b)效应对上感就诊人数的相对风险剖面图
Fig.9 Relative risk profile of high-pressure (a) and strong wind (b) conditions to the number of URI visits in Luohu district of Shenzhen from 2014 to 2018
| [1] | THOMAS F. Climate change and health[J]. Encyclopedia of the Anthropocene, 2018, 2:429-434. |
| [2] | MCMICHAEL A J, LINDGREN E. Climate change: present and future risks to health, and necessary responses[J]. Journal of Internal Medicine, 2011, 270(5):410-413. |
| [3] | CHRISTOPHER B F, VICENTE R B, MICHAEL D M, el al. Climate change 2014: impacts, adaptation, and vulnerability[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2014. |
| [4] |
SUMMERSKILL W, WANG H H, HORTON R. Healthy cities: key to a healthy future in China[J]. The Lancet, 2018, 391(10135):2086-2087.
DOI URL |
| [5] | 冯录召. 急性呼吸道感染住院病例病毒性病原谱及流感季节性研究[D]. 北京: 中国疾病预防控制中心, 2014. |
| [6] | KUCHAR E, MIŚSKIEWICZ K, SZENBORN L, el al. Respiratory tract infections in children in primary healthcare in Poland[J]. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 2015, 835:53-59. |
| [7] | 王伟, 李晓光, 胥婕. 发热门诊疾病谱及流行性感冒样病例监测意义研究[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2015, 35(1):60-62. |
| [8] | 高燕. 中国大陆季节性流感活动的时空分布特征[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2009, 30(11):1097-1101. |
| [9] | 刘文宽. 广州儿童呼吸道病原体流行与气候相关性及呼吸道合胞病毒诊断技术研究[D]. 广州: 广州医科大学, 2017. |
| [10] |
SONG X, WANG S, LI T, et al. The impact of heat waves and cold spells on respiratory emergency department visits in Beijing, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 615:1499-1505.
DOI URL |
| [11] | 马盼, 黎檀实, 宁贵财, 等. 北京市上呼吸道感染与气象环境关系及其冬季天气分型初探[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 51(1):79-86. |
| [12] | 张楠, 刘继锋, 徐军昶, 等. 西安气象因素和舒适度对呼吸系统疾病死亡的影响分析[J]. 科技与创新, 2019(10):8-11. |
| [13] | 王洪新. 兰州市气象因素对居民健康影响的研究[D]. 兰州:兰州大学, 2013. |
| [14] | 乐满, 王式功, 谢佳君, 等. 环境条件对遵义市呼吸系统疾病的影响及预测研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2018, 38(11):4334-4347. |
| [15] | 张志薇, 王宏斌, 李艳, 等. 诱发南京地区呼吸系统疾病的气象条件与天气类型分析[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 52(6):813-820. |
| [16] | 赵琳, 王长科, 李旭东, 等. 海南省不同人群对高温热浪及其影响与适应的感知分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2015, 33(2):310-316. |
| [17] |
LIN Y, CHANG C, CHANG S C, et al. Temperature, nitrogen dioxide, circulating respiratory viruses and acute upper respiratory infections among children in Taipei, Taiwan: a population-based study[J]. Environmental Research, 2013, 120:109-118.
DOI URL |
| [18] | 李瑞盈, 张一博, 杨佳, 等. 秦皇岛气象因素对儿童下呼吸道疾病就诊人数影响及预测研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2019, 37(3):460-466. |
| [19] | 张立杰, 李磊. 近20年深圳城市气候环境研究的进展[J]. 广东气象, 2017, 39(1):48-52. |
| [20] | 黄智峰, 刘晓剑, 杨连朋, 等. 深圳市流行性感冒与气象因素的关联性分析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2017, 21(10):1035-1043. |
| [21] |
BAO J, GUO Y, WANG Q, et al. Effects of heat on first-ever strokes and the effect modification of atmospheric pressure: a time-series study in Shenzhen, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 654:1372-1378.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
ZHANG Y, YU C, PENG M, et al. The burden of ambient temperature on years of life lost: a multi-community analysis in Hubei, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 621:1491-1498.
DOI URL |
| [23] | KIM J, LEE J Y. Synoptic approach to evaluate the effect of temperature on pediatric respiratory disease-related hospitalization in Seoul, Korea[J]. Environmental Research, 2019, 178, DOI: 10.1016/j.envres.2019.108650. |
| [24] | 耿迪, 孙宏, 蒋薇, 等. 南京市呼吸系统疾病死亡人数与气象因子的关系[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 51(1):93-97. |
| [25] | 卫生部卫生统计信息中心. 国际疾病分类(ICD-10)应用指导手册[M]. 北京: 中国协和医科大学出版社, 2001. |
| [26] | 朱乾根, 林锦瑞, 寿绍文. 天气学原理和方法[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2007. |
| [27] |
HUANG J. A simple accurate formula for calculating saturation vapor pressure of water and ice[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 2018, 57(6):1265-1272.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
GASPARRINI A. Modeling exposure-lag-response associations with distributed lag non-linear models[J]. Statistics in Medicine, 2014, 33(5):881-899.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
GUO Y, GASPARRINI A, ARMSTRONG B, et al. Global variation in the effects of ambient temperature on mortality: a systematic evaluation[J]. Epidemiology, 2014, 25(6):781-789.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
GASPARRINI A, GUO Y, HASHIZUME M, et al. Mortality risk attributable to high and low ambient temperature: a multicountry observational study[J]. Lancet, 2015, 386:369-375.
DOI URL |
| [31] | 乐满, 李海飞, 王式功, 等. 北京市主要天气敏感性疾病发病与流行的24节气特征分析和预报模型构建[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 53(3):394-400. |
| [32] | 王敏珍. 中国三个代表城市呼吸系统疾病对主要气象要素的响应及预测研究[D]. 兰州:兰州大学, 2013. |
| [33] | 杨高, 周春山, 王少剑. 快速移民城市深圳人口增长的时空特征及模式[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 58(2):77-87. |
| [34] | 罗小莉, 姚才, 谭金凯. 登陆华南台风的频数及强度变化特征分析[J]. 海洋预报, 2018, 35(4):58-67. |
| [35] | 李佳蔚, 魏然, 张安然, 等. 热带气旋与医院门诊呼吸系统疾病日就诊量的病例交叉研究[J]. 山东大学学报(医学版), 2018, 56(8):43-49. |
| [36] |
YANG Y, GENG X, LIU X, et al. Association between the incidence of varicella and meteorological conditions in Jinan, Eastern China, 2012-2014[J]. BMC Infectious Diseases, 2016, 16(1):1-8.
DOI URL |
| [37] | RIZMIE D, MIRALDO M, ATUN R, et al. The effect of extreme temperature on emergency admissions across vulnerable populations in England: an observational study[J]. The Lancet, 2019, 394(supplement2), DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32804-1. |
| [38] |
GUO Y, MA Y, JI J, et al. The relationship between extreme temperature and emergency incidences: a time series analysis in Shenzhen, China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25(36):36 239-36 255.
DOI URL |
| [39] | 杨军, 欧春泉, 丁研, 等. 广州市逐日死亡人数与气温关系的时间序列研究[J]. 环境与健康杂志, 2012, 29(2):136-138. |
| [40] | 马盼, 王式功, 尚可政, 等. 气象舒适条件对呼吸系统疾病的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 2018, 38(1):374-382. |
| [41] | 王敏珍, 郑山, 王式功, 等. 气温与湿度的交互作用对呼吸系统疾病的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 2016, 36(2):581-588. |
| [42] | 曾洁, 张学海, 林爱华, 等. 2010—2013年浙江省相对湿度对呼吸系统疾病死亡的影响[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2018, 22(5):455-458. |
| [43] |
LI Y, XIAO C, LI J, et al. Association between air pollution and upper respiratory tract infection in hospital outpatients aged 0-14 years in Hefei, China: a time series study[J]. Public Health, 2018, 156:92-100.
DOI URL |
| [44] | 谷少华, 贾红英, 李萌萌, 等. 济南市空气污染对呼吸系统疾病门诊量的影响[J]. 环境与健康杂志, 2015, 32(2):95-98. |
| [1] | 杨婧, 朱海斌, 刘建军, 严晓瑜, 纳丽, 刘玉兰. 气象条件对银川市区近地面臭氧质量浓度的影响[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(2): 302-308. |
| [2] | 齐亚杰, 陈敏, 仲跻芹, 范水勇, 刘瑞婷, 郭淳薇. RMAPS-ST耦合城市冠层模式后对华北地面气象要素的短期预报评估[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(5): 859-868. |
| [3] | 王洁, 范俊红, 赵增保, 张彦恒, 杨琳晗. 冀北输电线舞动灾害特征与气象条件分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2019, 37(6): 1021-1027. |
| [4] | 谈昌蓉,郭晓宁,陈奇,李金海,尤桑杰,马学莲,马元仓,祁彩虹. 西宁近地面臭氧特征及其影响因素[J]. 干旱气象, 2019, 37(1): 31-39. |
| [5] | 闫昕旸,王小勇,达选芳,赵福年,牛喜梅. 甘肃高速公路山区段路面温度特征及其预报模型[J]. 干旱气象, 2018, 36(5): 864-872. |
| [6] | 张小军,马学谦,田建兵. 1961—2015年青海省总云量时空变化特征及影响因子[J]. 干旱气象, 2017, 35(4): 622-633. |
| [7] | 李玲萍1,胡丽莉1,刘维成2,李岩瑛1,梁红霞1. 河西走廊东部夏季沙尘暴气象要素变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2017, 35(3): 427-. |
| [8] | 张娣1,曲晓黎1,2,张金满1,赵增保1,张成伟1. 河北省高速公路秋冬季浓雾特征及预报[J]. 干旱气象, 2017, 35(1): 51-56. |
| [9] | 黄少妮1,袁媛2,井宇1,陈小婷1,刘瑞芳1. 陕西关中地区冬季一次重霾污染过程及气象条件影响分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2016, 34(6): 1037-1046. |
| [10] | 王建鹏,薛春芳,黄少妮,王丹,潘留杰,程路. 城市化及人为热对西安市气象要素影响差异敏感性分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2015, 33(3): 434-443. |
| [11] | 黄洁,金莉莉,曹兴,关小军,薛福民. 塔中气象要素变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2011, 29(3): 315-321. |
| [12] | 沙莎 ,邱新法,何永健. 基于GIS 的自动气象站数据系统的研发[J]. J4, 2011, 29(3): 372-376. |
| [13] | 马凤莲,刘园园,周士茹,朱环娟,董学友. 从对比观测资料看城镇化对气象要素的影响 ———以围场国家基本气象站为例[J]. J4, 2011, 29(2): 205-210. |
| [14] | 刘世祥, 陶健红, 张铁军, 尚大成, 伏晓红, 张静, 宋秀玲. 西北区秋季短期气象要素客观预报检验评估[J]. J4, 2010, 28(3): 346-351. |
| [15] | 李祥余, 何清, 艾力·买买提明, 李帅 , 李红军, 吴新萍. 塔中春季阴天近地层风速、温度和湿度廓线特征分析[J]. J4, 2007, 25(2): 22-28. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||