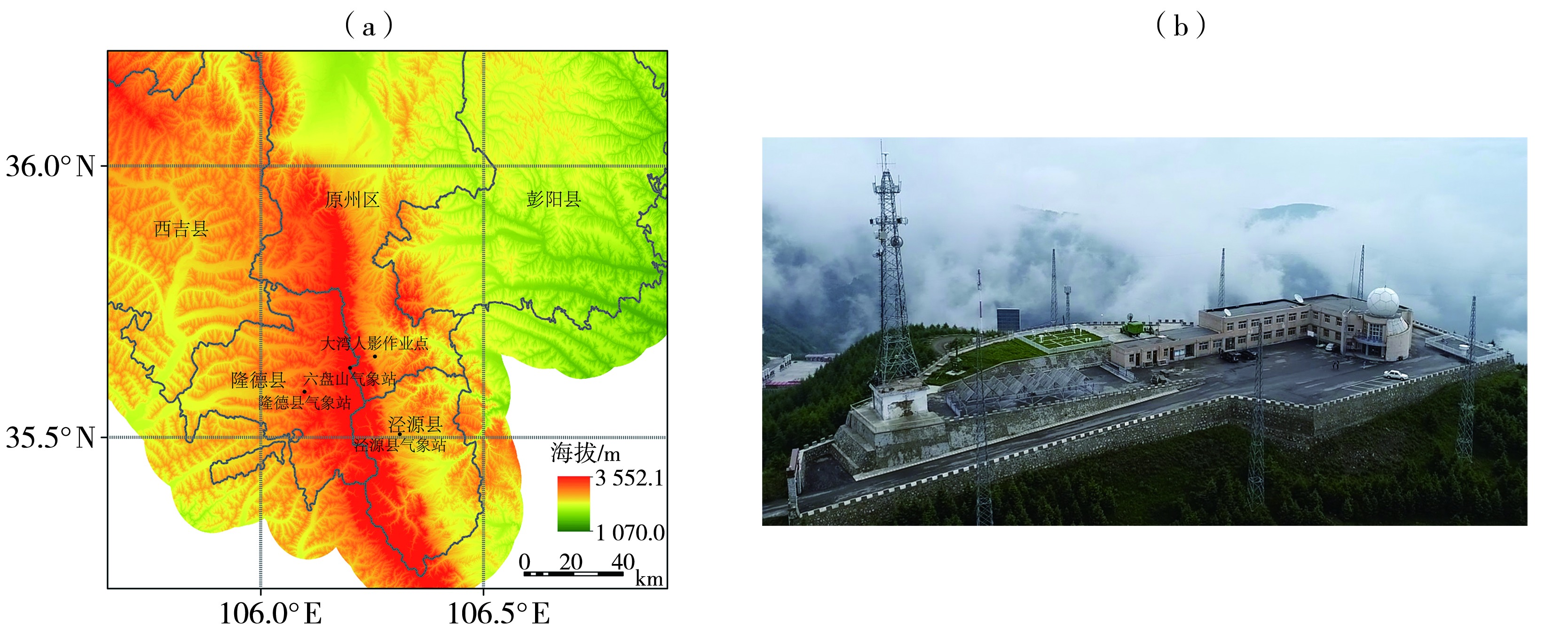
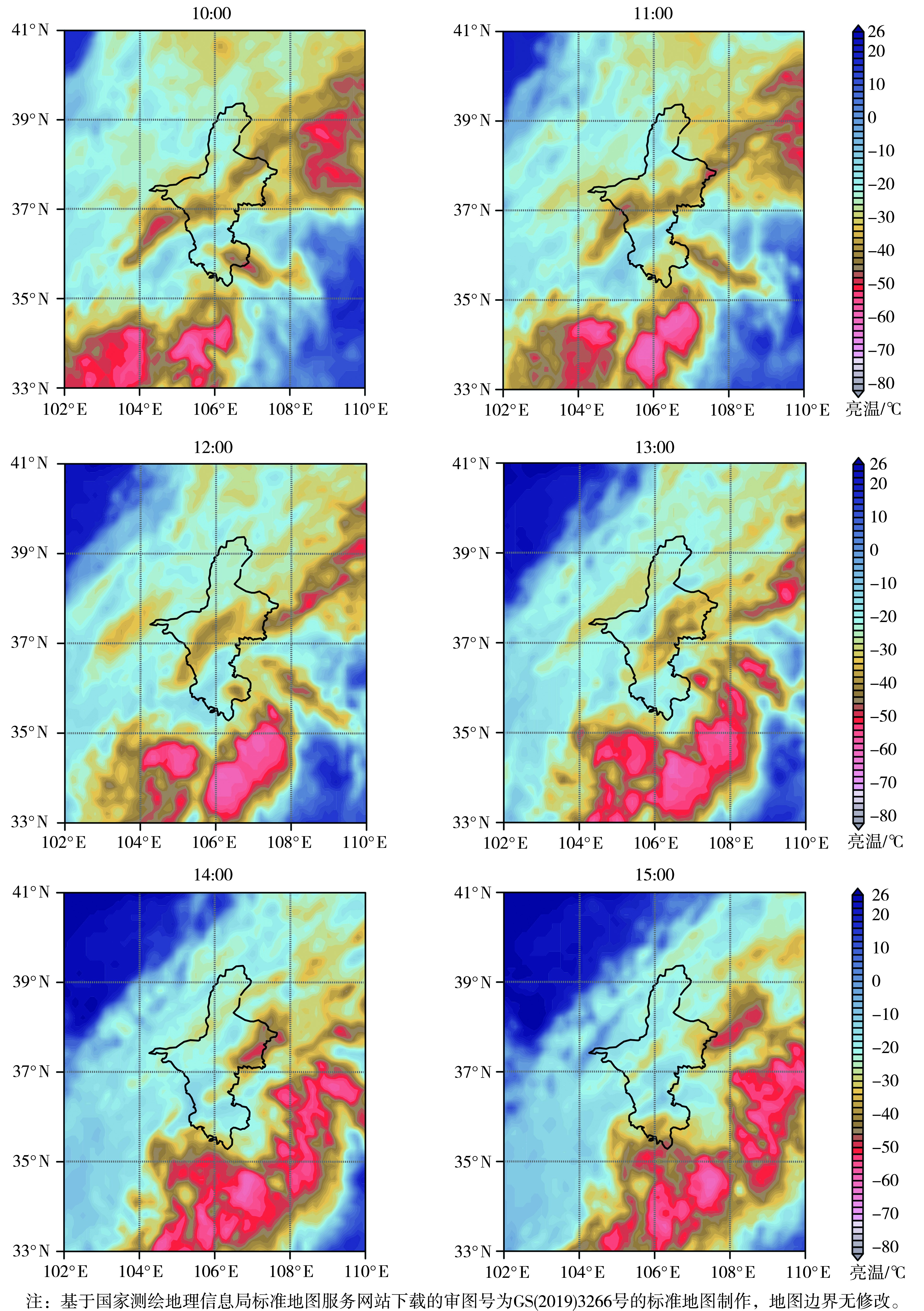
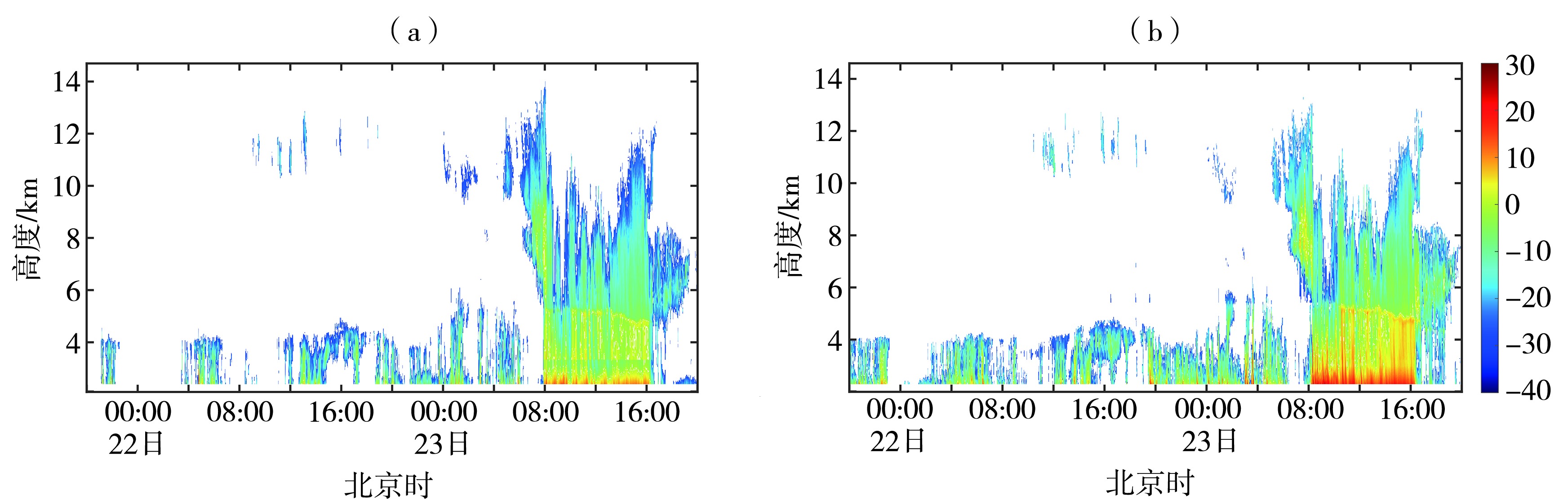
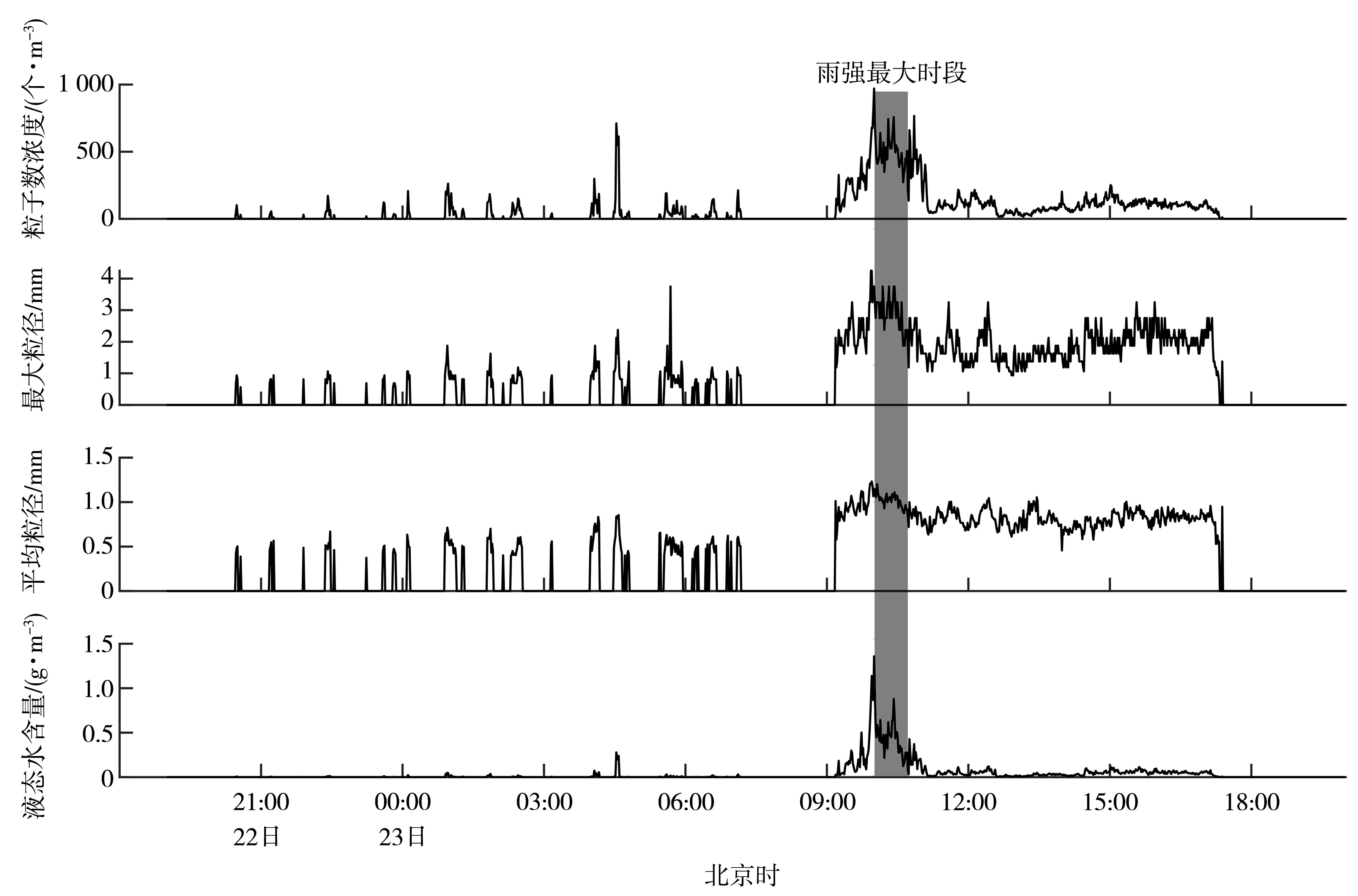
| [1] |
把黎, 奚立宗, 蔡迪花, 等, 2023. 基于微波辐射计资料的祁连山东段大气水汽和液态水时空变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 41(1):64-72.
DOI
|
| [2] |
曹宁, 张立新, 桑建人, 等, 2019. 基于微雨雷达的六盘山区地形云降水宏微观特征观测分析[J]. 气象科学, 39(6):775-785.
|
| [3] |
陈添宇, 郑国光, 陈跃, 等, 2010. 祁连山夏季西南气流背景下地形云形成和演化的观测研究[J]. 高原气象, 29(1):152-163.
|
| [4] |
樊曙先, 2000. 层状云微物理结构演变特征的个例研究[J]. 宁夏大学学报:自然科学版, 21(2):179-182.
|
| [5] |
冯晋勤, 卢芸芸, 赖巧珍, 等, 2022. 福建西部山区一次中尺度对流系统触发机制分析[J]. 干旱气象, 40(1):62-72.
DOI
|
| [6] |
郭丽君, 郭学良, 楼小凤, 等, 2019. 庐山云雾及降水的日、季节变化和宏微观物理特征观测研究[J]. 气象学报, 77(5):923-937.
|
| [7] |
李军, 汪晓滨, 吴万友, 2008. 中国气象科学研究院庐山云雾试验站建站以来的工作:中国人工影响天气事业50周年纪念文集[C]. 北京: 气象出版社.
|
| [8] |
李子华, 2001. 中国近40年来雾的研究[J]. 气象学报, 59(5):616-624.
|
| [9] |
林彤, 桑建人, 姚展予, 等, 2021. 基于微波辐射计的宁夏六盘山西侧大气水汽变化特征[J]. 干旱区地理, 44(4):923-933.
DOI
|
| [10] |
马思敏, 穆建华, 舒志亮, 等, 2022. 六盘山区一次典型暴雨过程的地形敏感性模拟试验[J]. 干旱气象, 40(3):457-468.
DOI
|
| [11] |
马思敏, 舒志亮, 常倬林, 等, 2023. 宁夏六盘山区地面雨滴谱特征统计分析[J]. 干旱区研究, 40(8):1203-1 214.
|
| [12] |
庞朝云, 李宝梓, 张丰伟, 等, 2021. 祁连山北坡一次人工增雨降水过程雨滴谱特征分析[J]. 气象科技, 49(4):621-628.
|
| [13] |
石爱丽, 郑国光, 黄庚, 等, 2004. 2002年秋季河南省层状云降水的雨滴谱特征[J]. 气象, 30(8):12-17.
|
| [14] |
陶涛, 张立新, 桑建人, 等, 2020. 六盘山区一次非典型冰雹天气过程微物理量特征的分析[J]. 干旱区地理, 43(2):299-307.
|
| [15] |
汪学军, 王新来, 姚叶青, 2012. 九华山雾日时间变化特征及其形成的气象条件分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 31(3): 287-292.
|
| [16] |
郑国光, 陈跃, 陈添宇, 等, 2011. 祁连山夏季地形云综合探测试验[J]. 地球科学进展, 26(10):1057-1 070.
|
| [17] |
郑娇恒, 陈宝君, 2007. 雨滴谱分布函数的选择:M-P和Gamma分布的对比研究[J]. 气象科学, 27(1):17-25.
|
| [18] |
ATLAS D, SRIVASTAVA R C, SEKHON R S, 1973. Doppler radar characteristics of precipitation at vertical incidence[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 11(1): 1-35.
|
| [19] |
CHEN B J, HU Z Q, LIU L P, et al, 2017. Raindrop size distribution measurements at 4, 500 m on the Tibetan Plateau during TIPEX-III[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 122(20): 11 092-11 106.
|
| [20] |
HOBBS P V, 1975. The nature of winter clouds and precipitation in the Cascade Mountains and their modification by artificial seeding. Part Ⅰ: Natural conditions[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 14(5): 783-804.
|
| [21] |
JING X Q, GEERTS B, BOE B, 2016. The extra-area effect of orographic cloud seeding: Observational evidence of precipitation enhancement downwind of the target mountain[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 55(6): 1 409-1 424.
|
| [22] |
LEOPOLD L B, 1949. The interaction of trade wind and sea breeze, Hawaii[J]. Journal of Meteorology, 6(5): 312-320.
|
| [23] |
LIN Y L, REEVES H D, CHEN S Y, et al, 2005. Formation mechanisms for convection over the Ligurian Sea during MAP IOP-8[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 133(8): 2 227-2 245.
|
| [24] |
MARSHALL J S, PALMER W MCK, 1948. The distribution of raindrops with size[J]. Journal of Meteorology, 5(4): 165-166.
|
| [25] |
NIU S J, ZHOU Y, JIA R, et al, 2012. The microphysics of ice accretion on wires: Observations and simulations[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 55(3): 428-437.
|
| [26] |
POKHAREL B, GEERTS B, JING X Q, 2014. The impact of ground-based glaciogenic seeding on orographic clouds and precipitation: A multisensor case study[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 53(4): 890-909.
|
| [27] |
RASMUSSEN R M, SMOLARKIEWICZ P K, 1993. On the dynamics of Hawaiian cloud bands. Part Ⅲ: Local aspects[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 50(11): 1 560-1 572.
|
| [28] |
RASMUSSEN R M, SMOLARKIEWICZ P, WARNER J, 1989. On the dynamics of Hawaiian cloud bands: Comparison of model results with observations and island climatology[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 46(11): 1 589-1 608.
|
| [29] |
ROSENFELD D, DAI J, YU X, et al, 2007. Inverse relations between amounts of air pollution and orographic precipitation[J]. Science, 315(5817): 1 396-1 398.
|
| [30] |
ROTUNNO R, FERRETTI R, 2003. Orographic effects on rainfall in MAP cases IOP 2b and IOP 8[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 129(588): 373-390.
|
| [31] |
TOKAY A, PETERSEN W A, GATLIN P, et al, 2013. Comparison of raindrop size distribution measurements by collocated disdrometers[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 30(8): 1 672-1 690.
|
| [32] |
ULBRICH C W, 1983. Natural variations in the analytical form of the raindrop size distribution[J]. Journal of Climate and Applied Meteorology, 22(10): 1 764-1 775.
|
| [33] |
WMO, 2001. WMO statement on the status of weather modification[R]. Geneva: WMO.
|
| [34] |
XUE L L, CHU X, RASMUSSEN R, et al, 2016. A case study of radar observations and WRF LES simulations of the impact of ground-based glaciogenic seeding on orographic clouds and precipitation. Part Ⅱ: AgI dispersion and seeding signals simulated by WRF[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 55(2): 445-464.
|
 ), 舒志亮1,3,4(
), 舒志亮1,3,4( ), 邓佩云1,2,3,4, 何佳1,3,4, 巴音那木拉5, 常倬林1,3,4
), 邓佩云1,2,3,4, 何佳1,3,4, 巴音那木拉5, 常倬林1,3,4
 ), SHU Zhiliang1,3,4(
), SHU Zhiliang1,3,4( ), DENG Peiyun1,2,3,4, HE Jia1,3,4, BAYIN Namula5, CHANG Zhuolin1,3,4
), DENG Peiyun1,2,3,4, HE Jia1,3,4, BAYIN Namula5, CHANG Zhuolin1,3,4