干旱气象 ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (6): 976-986.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2024-06-0976
基于CRA空间检验技术的甘肃河东汛期降水智能网格预报偏差特征分析
韩晶1( ), 焦美玲1, 曹彦超1(
), 焦美玲1, 曹彦超1( ), 王娟1, 贺涛1, 徐耕1, 周忠文1, 金满慧2
), 王娟1, 贺涛1, 徐耕1, 周忠文1, 金满慧2
- 1.甘肃省庆阳市气象局,甘肃 庆阳 745000
2.甘南藏族自治州气象局,甘肃 甘南 747000
-
收稿日期:2024-03-18修回日期:2024-07-22出版日期:2024-12-31发布日期:2025-01-15 -
通讯作者:曹彦超(1985—),男,甘肃庆阳人,高级工程师,主要从事气候变化及灾害性天气研究。E-mail:646891024@qq.com。 -
作者简介:韩晶(1988—),女,甘肃庆阳人,工程师,主要从事气候变化及灾害性天气研究。E-mail:446843809@qq.com。 -
基金资助:甘肃省自然科学基金项目(22JRRM1045);甘肃省自然科学基金项目(24JRRM008);庆阳市科技计划项目(QY-STK-2022A-129);甘肃省气象局科研项目(ZcMs2022-33)
Deviation characteristics in intelligent grid forecast of flood season precipitation in Hedong area of Gansu based on CRA spatial forecast verification
HAN Jing1( ), JIAO Meiling1, CAO Yanchao1(
), JIAO Meiling1, CAO Yanchao1( ), WANG Juan1, HE Tao1, XU Geng1, ZHOU Zhongwen1, JIN Manhui2
), WANG Juan1, HE Tao1, XU Geng1, ZHOU Zhongwen1, JIN Manhui2
- 1. Qingyang Meteorological Bureau of Gansu Province, Qingyang 745000, Gansu, China
2. Gannan Meteorological Bureau of Gansu Province, Gannan 747000, Gansu, China
-
Received:2024-03-18Revised:2024-07-22Online:2024-12-31Published:2025-01-15
摘要:
研究甘肃河东地区汛期降水智能网格预报偏差特征,对提升区域降水预报预警的精准化水平和防灾减灾服务能力具有重要意义。利用甘肃河东1 766个自动气象观测站的汛期降水资料,筛选出2018—2020年264个降水个例,基于中央气象台发布的3 h智能网格降水预报数据,对预报场和实况场的连续雨区(Contiguous Rain Area,CRA)进行识别和配对,并按照命中、假警报和未命中3种情况分类分析,进一步对预报命中的CRA偏差特征进行研究。结果表明:对于预报命中的降水个例,智能网格降水预报的落区偏差以暖强迫类最大,斜压锋生类和冷强迫类次之;强度偏差以冷强迫类最大,暖强迫类和斜压锋生类次之;形态偏差以斜压锋生类最大,冷强迫类和暖强迫类次之。暖强迫类和斜压锋生类降水的落区预报偏东偏北,冷强迫类偏东偏南。3类降水预报均表现为对β及以下尺度的降水落区面积偏大,而对α尺度降水落区面积偏小。基于CRA空间检验结果,预报员可建立本地化的模式订正方案,提高智能网格降水预报的服务能力。
中图分类号:
引用本文
韩晶, 焦美玲, 曹彦超, 王娟, 贺涛, 徐耕, 周忠文, 金满慧. 基于CRA空间检验技术的甘肃河东汛期降水智能网格预报偏差特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(6): 976-986.
HAN Jing, JIAO Meiling, CAO Yanchao, WANG Juan, HE Tao, XU Geng, ZHOU Zhongwen, JIN Manhui. Deviation characteristics in intelligent grid forecast of flood season precipitation in Hedong area of Gansu based on CRA spatial forecast verification[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(6): 976-986.
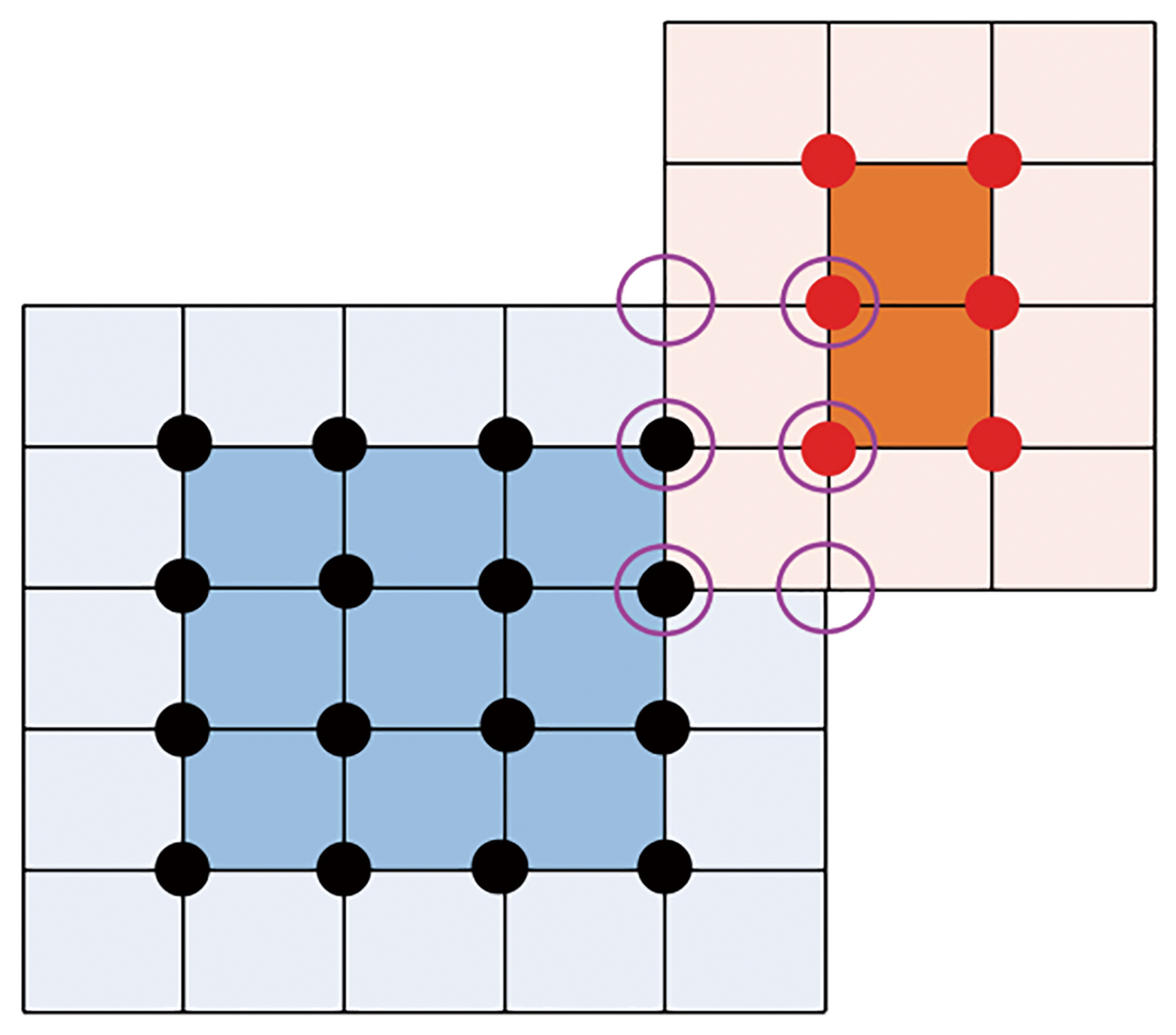
图2 预报场与实况场CRA匹配图 (蓝色区域为预报CRA,其外围浅蓝色区域为预报扩展区,橙色区域为实况CRA,其外围浅橙色为实况扩展区,紫色圆圈为扩展区域交集)
Fig.2 The CRA matching between forecast field and actual field (The blue area represents the forecast CRA, the surrounding light blue area represents the forecast extension area, the orange area represents the actual CRA, the surrounding light orange area represents the actual extension area, and the purple circle represents the intersection of the extension areas)
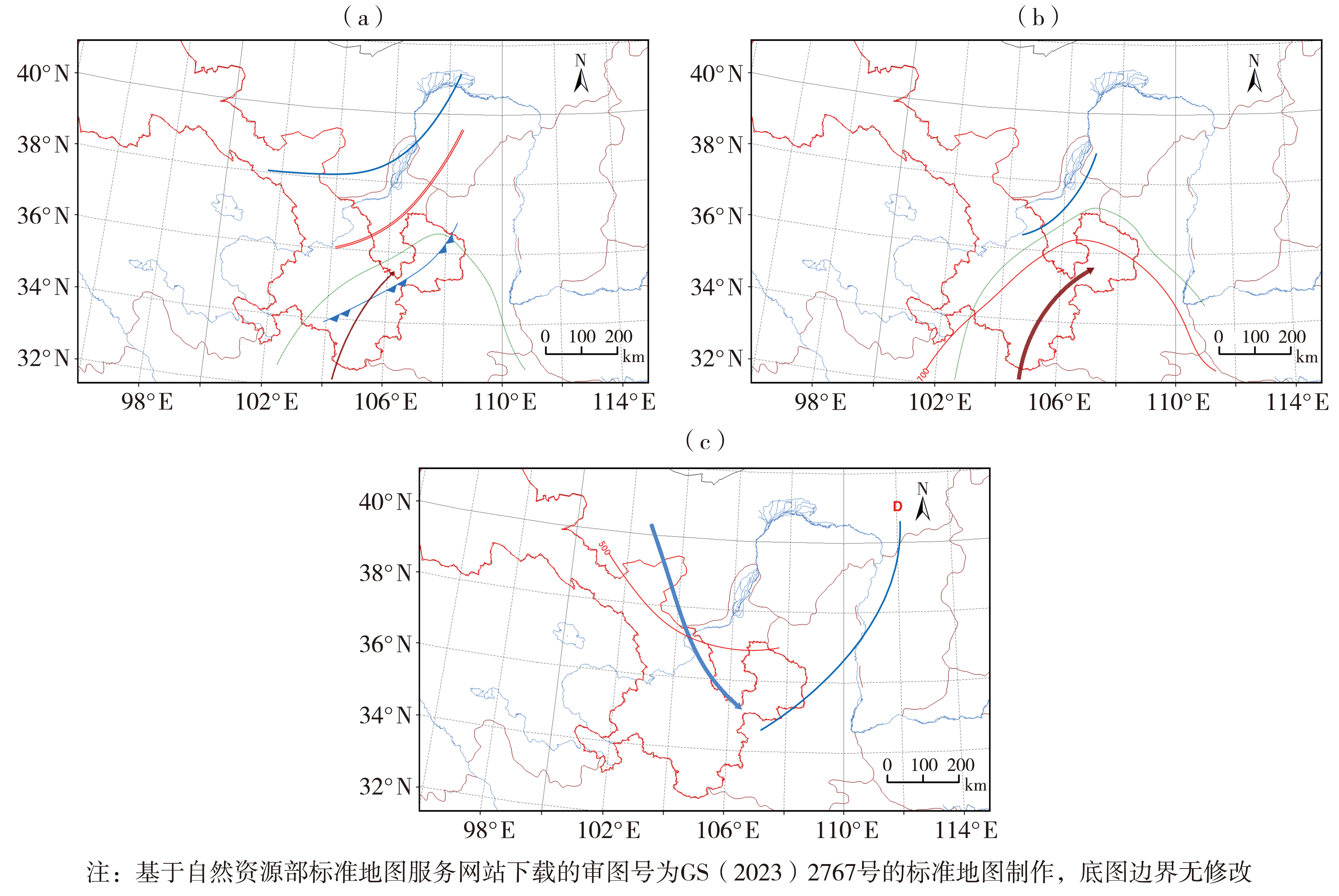
图3 河东斜压锋生类(a)、暖强迫类(b)及冷强迫类(c)降水的天气系统配置 (绿色虚线为700 hPa等比湿线,单位:g·kg-1;棕色细箭头为700 hPa显著流线;棕色粗箭头为700 hPa低空急流;红色双实线为700 hPa切变线;红色单实线为500、700 hPa等温度线,单位:℃;蓝色单实线为500 hPa槽线;蓝色粗箭头为200 hPa高空急流;蓝色锯齿线为冷锋;D为低压系统)
Fig.3 Weather system configuration for oblique frontal (a), warm forcing (b) and cold forcing (c) precipitation in Hedong area of Gansu Province (The green dashed lines indicate the 700 hPa isobaric humidity line, Unit: g·kg-1; the brown thin arrow represents a significant streamline at 700 hPa; the brown thick arrow represents the 700 hPa low-level jet stream; the red double solid line represents the 700 hPa shear line; the red solid lines represent temperature lines at 500 and 700 hPa, Unit: ℃; the blue solid line represents the 500 hPa trough line; the blue thick arrow represents the 200 hPa high-altitude jet stream; the blue sawtooth line represents a cold front; D represents a low-pressure system)

图4 2018—2020年5—9月河东地区智能网格降水预报CRA平均命中率、未命中率和假警报率的变化
Fig.4 Changes in the average hit rate, miss rate, and false alarm rate of CRA of intelligent grid precipitation forecasts in Hedong area of Gansu Province from May to September during 2018-2020

图5 2018—2020年河东地区智能网格降水预报命中率及假警报率随预报场(a)、命中率及未命中率随实况场(b)CRA格点数的变化
Fig.5 Changes of the hit rate and false alarm rate with the number of CRA grid points in the forecast field (a), and hit rate and miss rate with the number of CRA grid points in the actual field (b) of intelligent grid precipitation forecast in Hedong area of Gansu Province during 2018-2020
| 天气形势类型 | 西部平均格点数 | 东部平均格点数 |
|---|---|---|
| 暖强迫 | 766 | 1 143 |
| 冷强迫 | 136 | 898 |
| 斜压锋生 | 490 | 1 243 |
表1 不同天气形势类型降水河东东、西部CRA格点分布特征
Tab.1 The CRA grid distribution characteristics of precipitation in eastern and western parts of Hedong area of Gansu Province under different weather patterns 单位:个
| 天气形势类型 | 西部平均格点数 | 东部平均格点数 |
|---|---|---|
| 暖强迫 | 766 | 1 143 |
| 冷强迫 | 136 | 898 |
| 斜压锋生 | 490 | 1 243 |
| 天气形势类型 | 平均值 | 中位数 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 落区偏差 占比/% | 强度偏差 占比/% | 形态偏差 占比/% | 平均纬向 偏差/(°) | 平均经向 偏差/(°) | 平均面积 偏差/% | 平均强度 偏差/% | 最大降水量 偏差/% | |
| 暖强迫 | 19.9 | 23.5 | 56.6 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 18.6 | 64.1 | -24.0 |
| 冷强迫 | 8.1 | 33.3 | 58.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 62.3 | 0.0 | -50.0 |
| 斜压锋生 | 15.7 | 21.2 | 63.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 12.8 | 63.9 | -29.9 |
表2 降水预报总体偏差
Tab.2 Overall deviation of precipitation forecast
| 天气形势类型 | 平均值 | 中位数 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 落区偏差 占比/% | 强度偏差 占比/% | 形态偏差 占比/% | 平均纬向 偏差/(°) | 平均经向 偏差/(°) | 平均面积 偏差/% | 平均强度 偏差/% | 最大降水量 偏差/% | |
| 暖强迫 | 19.9 | 23.5 | 56.6 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 18.6 | 64.1 | -24.0 |
| 冷强迫 | 8.1 | 33.3 | 58.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 62.3 | 0.0 | -50.0 |
| 斜压锋生 | 15.7 | 21.2 | 63.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 12.8 | 63.9 | -29.9 |
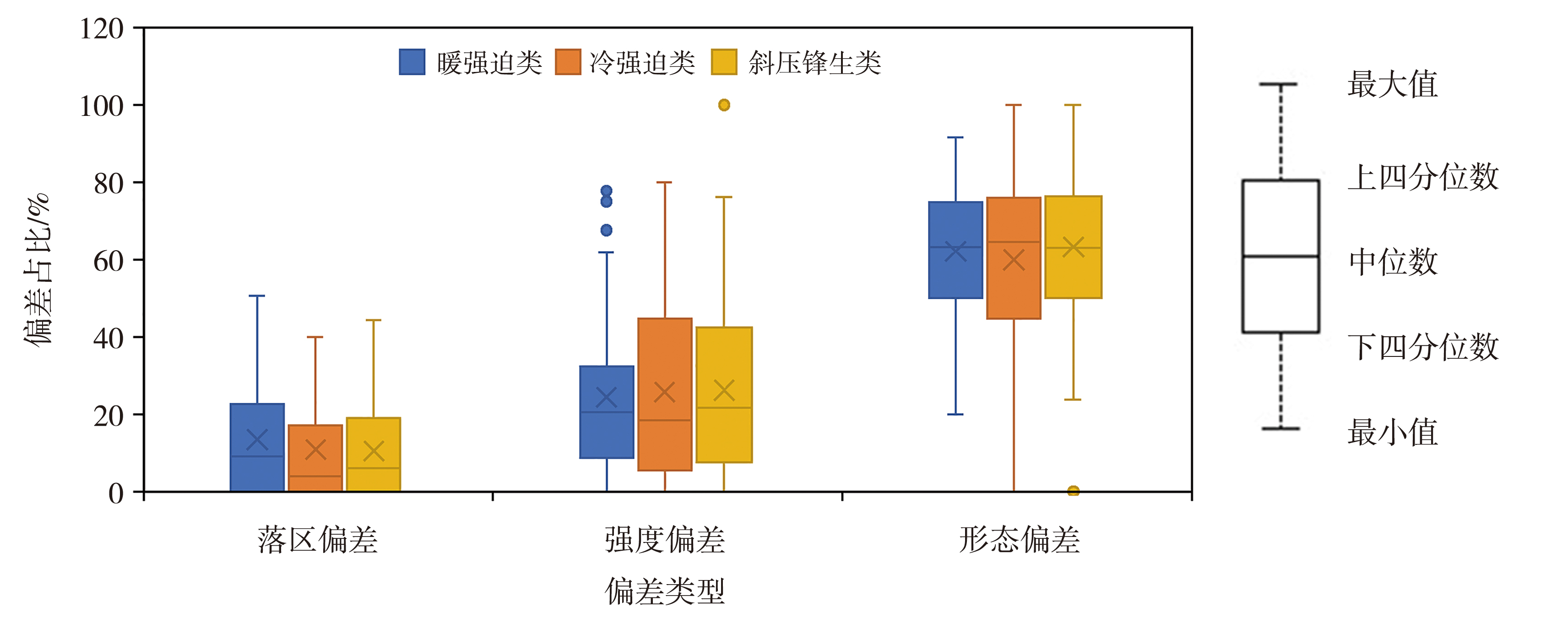
图6 不同类型降水的落区、强度和形态偏差占比箱线图
Fig.6 Box plots of proportion of precipitation zones, intensities, and morphological deviations for different types of precipitation

图8 暖强迫类(a、b)、冷强迫类(c、d)及斜压锋生类(e、f)降水预报与实况降水格点数的散点图(a、c、e)及实况雨区格点数分布(b、d、f)
Fig.8 Scatter plot of precipitation forecast and actual precipitation grid points (a, c, e) and actual precipitotion grid distribution (b, d, f) of warm forcing type (a, b), cold forcing type (c, d) and oblique pressure frontogenesis type (e, f)
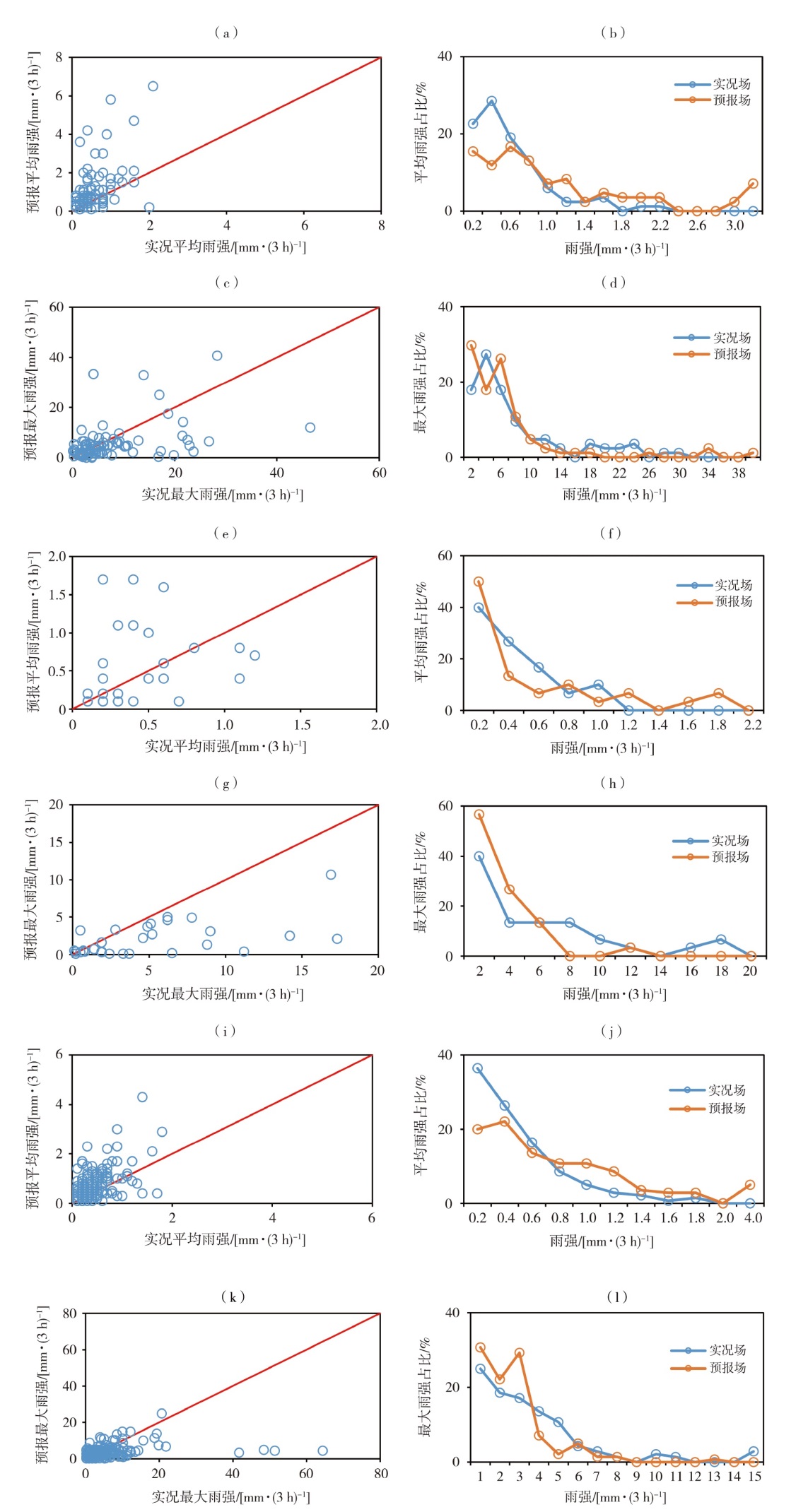
图9 暖强迫类(a、b、c、d)、冷强迫类(e、f、g、h)及斜压锋生类(i、j、k、l)平均降水实况与预报雨强散点图(a、e、i)及占比(b、f、j)和最大降水实况与预报雨强散点图(c、g、k)及占比(d、h、l)
Fig.9 The scatter plots of average precipitation and forecasted rainfall intensity (a, e, i) and their proportions (b, f, j), and the scatter plots of maximum precipitation and forecasted rainfall intensity (c, g, k) and their proportions (d, h, l) of warm forcing type (a, b, c, d), cold forcing type (e, f, g, h), and oblique pressure frontogenesis type (i, j, k, l)
| [1] |
蔡怡, 徐枝芳, 龚玺, 等, 2023. 2021年夏季CMA-MESO模式降水预报评估[J]. 干旱气象, 41(3): 503-515.
DOI |
| [2] |
陈晓燕, 孔祥伟, 彭筱, 等, 2022. 全球和区域数值模式在甘肃2020年汛期降水预报中的检验评估[J]. 干旱气象, 40(3): 524-535.
DOI |
| [3] | 符娇兰, 代刊, 2016. 基于CRA空间检验技术的西南地区东部强降水EC模式预报误差分析[J]. 气象, 42(12): 1 456-1 464 |
| [4] | 郭旭晖, 石文伯, 张曦丹, 2023. 河北省智能网格预报在张家口最高、最低气温中的检验[J]. 科技创新与应用, 13(35): 89-92. |
| [5] | 韩晶, 路亚奇, 曹彦超, 等, 2023. 基于空间检验技术的甘肃河东地区短时暴雨预报产品误差分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 17(1): 83-89. |
| [6] | 胡争光, 薛峰, 金荣花, 等, 2020. 智能网格预报应用分析平台设计与实现[J]. 气象, 46(10): 1 340-1 350 |
| [7] | 孔荣, 王建捷, 梁丰, 等, 2010. 尺度分解技术在定量降水临近预报检验中的应用[J]. 应用气象学报, 21(5): 535-544. |
| [8] | 孔祥伟, 2022. 甘肃河东短时强降水天气分类特征及模式预报评估研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学. |
| [9] | 孔祥伟, 张君霞, 杨晓军, 等, 2022. 西北地区东部强降水大尺度数值模式预报空间偏差分析[J]. 高原气象, 41(5): 1 109-1 123 |
| [10] | 李晓兰, 符娇兰, 2021. 基于CRA技术的华南前汛期强降水EC模式预报误差分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 37(2): 194-206. |
| [11] | 刘凑华, 牛若芸, 2013. 基于目标的降水检验方法及应用[J]. 气象, 39(6): 681-690. |
| [12] | 卢秀丽, 2008. 甘肃河东地区暴雨极值空间格局及地形影响分析[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学. |
| [13] | 潘留杰, 薛春芳, 梁绵, 等, 2022. 网格降水预报客观检验订正方法研究进展[J]. 气象科技进展, 12(3): 15-24. |
| [14] | 潘留杰, 张宏芳, 刘静, 等, 2023. 智能网格SCMOC及多模式降水预报对比[J]. 大气科学学报, 46(2): 217-229. |
| [15] | 钱磊, 邱学兴, 郑淋淋, 等, 2022. 基于降水空间分布相似的最优集成降水预报及其检验[J]. 暴雨灾害, 41(3): 324-335. |
| [16] | 邱雨楠, 2023. 基于深度学习的短临降水预报方法研究[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学. |
| [17] | 谌芸, 曹勇, 孙健, 等, 2021. 中央气象台精细化网格降水预报技术的发展和思考[J]. 气象, 47(6): 655-670. |
| [18] | 屠妮妮, 衡志炜, 何光碧, 等, 2022. 多数值模式对2021年7月两次大暴雨过程预报能力检验评估[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 42(2): 46-55. |
| [19] | 王新敏, 栗晗, 2020. 多数值模式对台风暴雨过程预报的空间检验评估[J]. 气象, 46(6): 753-764. |
| [20] |
王雅琦, 冯娟, 李建平, 等, 2020. 西北地区东部夏季降水年际变化特征及其与环流的关系[J]. 高原气象, 39(2): 290-300.
DOI |
| [21] |
王奕丹, 胡泽勇, 孙根厚, 等, 2019. 高原季风特征及其与东亚夏季风关系的研究[J]. 高原气象, 38(3): 518-527.
DOI |
| [22] | 韦惠红, 许冠宇, 刘希文, 等, 2022. 湖北省不同类型雷暴大风的时空分布及环境参数特征[J]. 暴雨灾害, 41(1): 66-75. |
| [23] | 韦青, 李伟, 彭颂, 等, 2019. 国家级天气预报检验分析系统建设与应用[J]. 应用气象学报, 30(2): 245-256. |
| [24] | 殷菲, 韩兰英, 王鑫, 等, 2022. 甘肃省2022年度十大天气气候事件[J]. 干旱气象, 40(6): 1 099. |
| [25] | 张博, 张芳华, 李晓兰, 等, 2024. “23·7”华北特大暴雨数值预报检验评估[J]. 应用气象学报, 35(1): 17-32. |
| [26] |
张君霞, 孔祥伟, 刘新伟, 等, 2022. 青藏高原东北侧暴雨数值模式预报空间误差特征[J]. 干旱区研究, 39(1): 64-74.
DOI |
| [27] | 赵一飞, 2013. 近50年来甘肃河东地区农业气候资源变化及其对农牧业的影响[D]. 兰州: 西北师范大学. |
| [28] | 朱国光, 陈鹤, 2022. 酉水流域智能网格降水预报产品及检验[J]. 科技创新与应用, 12(3): 30-35. |
| [29] | EBERT E E, MCBRIDE J L, 2000. Verification of precipitation in weather systems: Determination of systematic errors[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 239(1/2/3/4): 179-202. |
| [30] | MASS C F., OVENS D, WESTRICK K, et al, 2002. Does increasing horizontal resolution produce more skillful forecasts?[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 83(3): 407-430. |
| [31] | SHARMA K, ASHRIT R, EBERT E, et al, 2018. Assessment of Met Office Unified Model (UM) quantitative precipitation forecasts during the Indian summer monsoon: Contiguous Rain Area (CRA) approach[J]. Journal of Earth System Science, 128(4). DOI: 10.1007/s12040-018-1023-3. |
| [32] | WERNLI H, HOFMANN C, ZIMMER M, 2009. Spatial forecast verification methods intercomparison project: Application of the SAL technique[J]. Weather and Forecasting, 24(6): 1 472-1 484 |
| [1] | 焦洋, 郑丽娜, 张永婧, 苏轶. 两种降水客观统计方法对ECMWF集合平均降水预报的订正研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(2): 293-304. |
| [2] | 朱文刚, 盛春岩, 范苏丹, 荣艳敏, 曲美慧. 基于前馈神经网络的多模式集成降水预报研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(1): 117-128. |
| [3] | 曹萍萍, 肖递祥, 龙柯吉, 王佳津, 杨康权. 基于分位数映射法的四川省ECMWF模式降水预报误差订正分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(4): 666-675. |
| [4] | 裴坤宁, 王雁, 闫世明, 蒋云盛, 郭伟. 地形和天气形势对临汾市大气污染的影响[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(5): 879-887. |
| [5] | 乔锦荣, 原新鹏, 梁旭东, 谢衍新. 凝聚层次聚类方法在降水预报评估中的应用[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(4): 690-699. |
| [6] | 陈晓燕, 孔祥伟, 彭筱, 刘新伟, 吴晶, 任淑媛. 全球和区域数值模式在甘肃2020年汛期降水预报中的检验评估[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(3): 524-535. |
| [7] | 吴丹,李美琪,郭蕊,贾小卫,刘浩,柳泉. 2014—2017年石家庄正定国际机场低空风切变特征及天气形势分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(5): 775-784. |
| [8] | 任绪伟, 陈晓燕, 蔡迪花, 李兰倩, 邵爱梅. GRAPES_Meso模式及其云分析系统在中国西北地区降水预报中的应用评估[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(2): 333-344. |
| [9] | 王彬雁, 陈朝平, 黄楚惠, . SAL方法在四川降水预报检验中的应用[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(03): 472-479. |
| [10] | 彭舒龄,周树道,王 敏,任尚书,沈 奥. 南京市一次雾霾天气过程的阶段性特征与成因[J]. 干旱气象, 2018, 36(2): 282-289. |
| [11] | 于丽娟,尹承美,何建军,张永婧,李 瑞. 济南雾和霾特征及其影响因素分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2017, 35(4): 581-589. |
| [12] | 王海燕1,田刚1,徐卫立2,金琪3,陈良华2,陈璇1. ECMWF模式在长江上游流域调度关键期的预报检验评估[J]. 干旱气象, 2017, 35(1): 142-147. |
| [13] | 白 慧1,2,吴战平1,李忠燕1,周 涛1. DERF产品在贵州降水主分量逐步回归预报模型中的释用[J]. 干旱气象, 2015, 33(2): 344-348. |
| [14] | 倪江波,尚可政,王式功,李德帅. 华北区域性低能见度天气的自动识别及预报[J]. 干旱气象, 2015, 33(1): 174-179. |
| [15] | 吴哲红,陈贞宏,白慧. 2011 年与 2008 年贵州低温雨雪冰冻天气锋区特征对比[J]. 干旱气象, 2013, 31(4): 763-770. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||


