干旱气象 ›› 2022, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (5): 823-830.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-05-0823
基于GIS的鄂东南枇杷种植生态适宜性精细化区划
魏华兵1( ), 陈正洪2(
), 陈正洪2( ), 罗翔3, 肖运4, 罗昱1, 张鹏3
), 罗翔3, 肖运4, 罗昱1, 张鹏3
- 1.湖北省咸宁市气象局,湖北 咸宁 437100
2.湖北省气象局,湖北 武汉 430074
3.湖北省通山县气象局,湖北 通山 437600
4.湖北省通山县农业局,湖北 通山 437600
Refined division of ecological suitability of loquat planting in southeastern Hubei Province based on GIS
WEI Huabing1( ), CHEN Zhenghong2(
), CHEN Zhenghong2( ), LUO Xiang3, XIAO Yun4, LUO Yu1, ZHANG Peng3
), LUO Xiang3, XIAO Yun4, LUO Yu1, ZHANG Peng3
- 1. Xianning Meteorological Bureau of Hubei Province, Xianning 437100, Hubei, China
2. Hubei Meteorological Administration, Wuhan 430074, China
3. Tongshan Meteorological Station of Hubei Province, Tongshan 437600, Hubei, China
4. Tongshan Agricultural Bureau of Hubei Province, Tongshan 437600, Hubei, China
摘要:
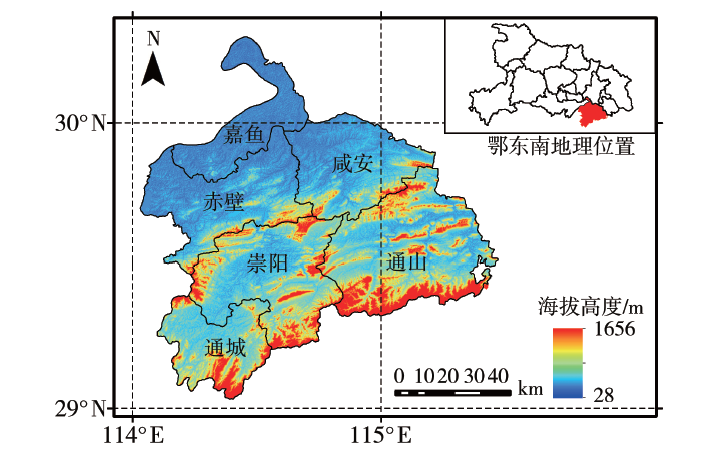
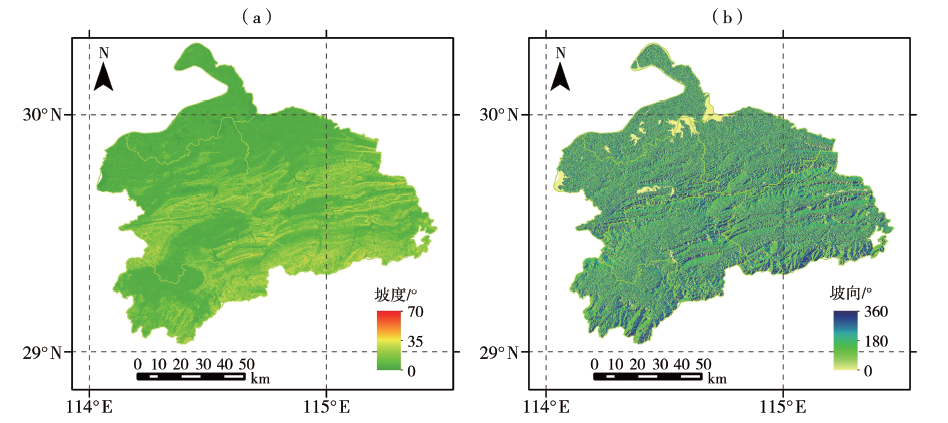
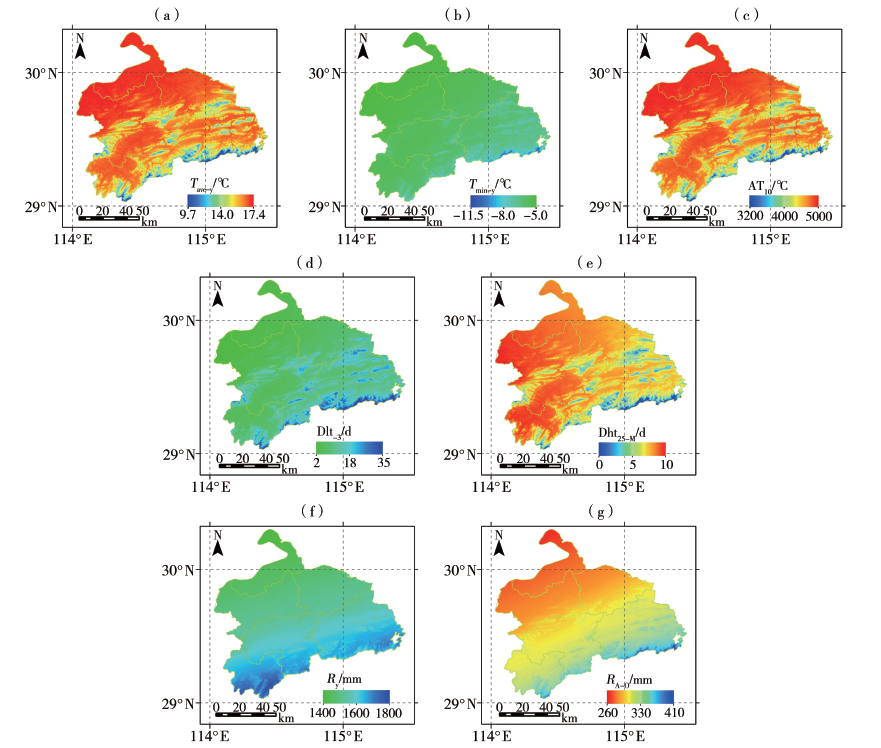
利用鄂东南6个国家气象站和135个区域气象站逐日气象观测资料和30 m分辨率的数字高程模型数据,综合考虑影响枇杷生长发育和产量品质的气候因子和地形因子,筛选出年平均气温、年最低气温、≥10.0 ℃活动积温、最低气温≤-3.0 ℃的日数、5月平均气温≥25.0 ℃的日数、年降水量、8—10月降水量以及坡向、坡度等9个适宜性指标,采用层次分析法和综合生态适宜度方法,在ArcGIS环境下对鄂东南枇杷种植生态适宜性进行精细化区划。结果表明:整体来看,影响鄂东南枇杷种植生态适宜性的主要因素是年最低气温和最低气温≤-3.0 ℃的日数。全区可分为枇杷种植生态不适宜区、次适宜区、适宜区和最适宜区。其中,西北部的沿江、沿湖区域为最适宜区,可以发展枇杷早熟品种;中部和东南部海拔高度100~250 m的区域为适宜区,适宜种植枇杷中熟品种,而海拔高度为251~450 m的坡地为次适宜区,可以发展营养和功能价值俱佳的中晚熟品种;中部和东南部海拔高度在450 m以上的山区为不适宜区。经初步验证,鄂东南枇杷规模化种植区生产实际与区划结果有很好的一致性,区划结果可为鄂东南枇杷种植产业合理布局提供参考。
中图分类号: