Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2025, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (3): 424-434.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-03-0424
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Comparative analysis of physical quantity characteristic of three extreme short-term heavy rainfalls with different intensities under cold vortex background during summer in Tianjin
JIN Zhenhua1( ), BU Qingjun1(
), BU Qingjun1( ), HUANG Anning2
), HUANG Anning2
- 1. Binhai New Area Meteorological Office of Tianjin, Tianjin 300457, China
2. School of Atmospheric Sciences, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210023,China
-
Received:2024-07-15Revised:2024-09-25Online:2025-06-30Published:2025-07-12
冷涡背景下天津夏季三次不同强度极端短时强降水物理量特征对比分析
- 1.天津市滨海新区气象局,天津 300457
2.南京大学大气科学学院,江苏 南京 210023
-
通讯作者:卜清军 -
作者简介:靳振华(1984—),女,天津滨海新区人,硕士,高级工程师,主要从事灾害性天气预报技术研究。E-mail:jinzhenhua2009@163.com。 -
基金资助:中国气象局复盘总结专项(FPZJ2023-007);中国气象局城市气象重点开放实验室开放基金课题(LUM-2024-12)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
JIN Zhenhua, BU Qingjun, HUANG Anning. Comparative analysis of physical quantity characteristic of three extreme short-term heavy rainfalls with different intensities under cold vortex background during summer in Tianjin[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(3): 424-434.
靳振华, 卜清军, 黄安宁. 冷涡背景下天津夏季三次不同强度极端短时强降水物理量特征对比分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(3): 424-434.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-03-0424
| 因子分类 | 物理量 | 单位 |
|---|---|---|
| 对流潜势因子 | 对流有效位能(Convective Available Potential Energy,CAPE) | J·kg-1 |
| 抬升凝结高度(Lifted Condensation Level,LCL) | km | |
| 湿层厚度(Humidity Layer Thickness,Hwet) | km | |
| 暖云层厚度(Warm Cloud Layer Thickness,Hwarm) | km | |
| 0~6 km垂直风切变(0~6 km Vertical Wind Shear,SHR6) | m·s-1 | |
| K指数 | ℃ | |
| 强天气威胁指数(Severe Weather Threat Index,SWEAT) | ||
| 动力因子 | 垂直速度(Vertical Velocity,w) | Pa·s-1 |
| 水汽因子 | 整层大气可降水量(Precipitable Water Vapor,PWV) | mm |
| 热力因子 | 假相当位温(Pseudo Equivalent Potential Temperature,θse) | K |
| 回波参数 | 组合反射率(Composite Reflectivity,CR) | dBZ |
| 回波顶高(Echo Top,ET) | km | |
| 垂直累积液态水含量(Vertical Integrated Liquid Water Content,VIL) | kg·m-2 |
Tab.1 Main physical quantity list
| 因子分类 | 物理量 | 单位 |
|---|---|---|
| 对流潜势因子 | 对流有效位能(Convective Available Potential Energy,CAPE) | J·kg-1 |
| 抬升凝结高度(Lifted Condensation Level,LCL) | km | |
| 湿层厚度(Humidity Layer Thickness,Hwet) | km | |
| 暖云层厚度(Warm Cloud Layer Thickness,Hwarm) | km | |
| 0~6 km垂直风切变(0~6 km Vertical Wind Shear,SHR6) | m·s-1 | |
| K指数 | ℃ | |
| 强天气威胁指数(Severe Weather Threat Index,SWEAT) | ||
| 动力因子 | 垂直速度(Vertical Velocity,w) | Pa·s-1 |
| 水汽因子 | 整层大气可降水量(Precipitable Water Vapor,PWV) | mm |
| 热力因子 | 假相当位温(Pseudo Equivalent Potential Temperature,θse) | K |
| 回波参数 | 组合反射率(Composite Reflectivity,CR) | dBZ |
| 回波顶高(Echo Top,ET) | km | |
| 垂直累积液态水含量(Vertical Integrated Liquid Water Content,VIL) | kg·m-2 |
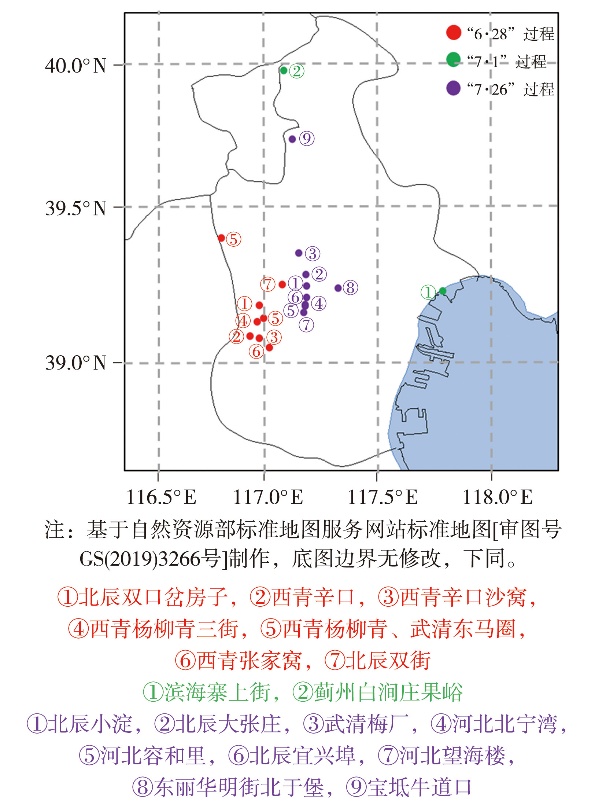
Fig.1 The extreme rainfall intensity areas of three short-term heavy rainfall processes in Tianjin in 2022(The circle digital indicates the sequence of occurrence of the extreme short-term heavy rainfalls at each station)
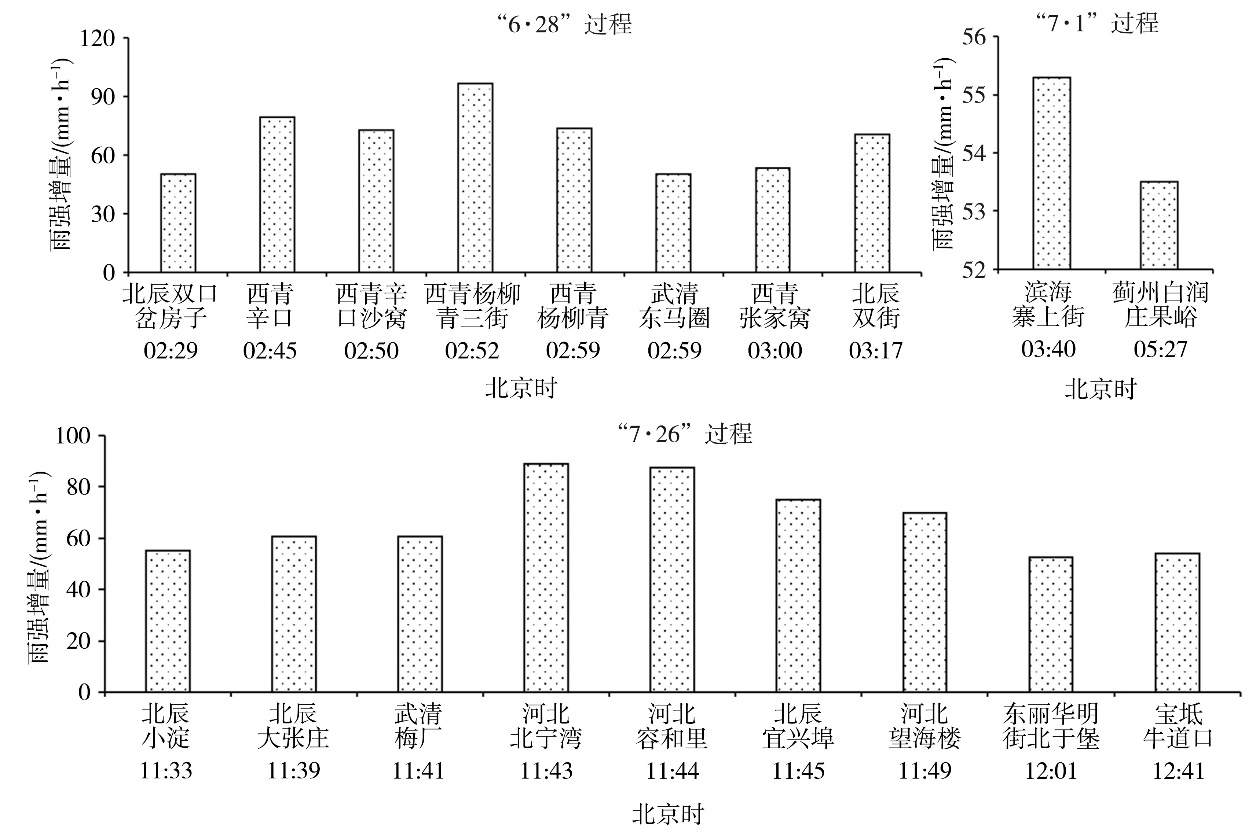
Fig.2 The increment of rainfall intensity compared to the previous hour at different stations and times during three short-term heavy rainfall processes in Tianjin in 2022

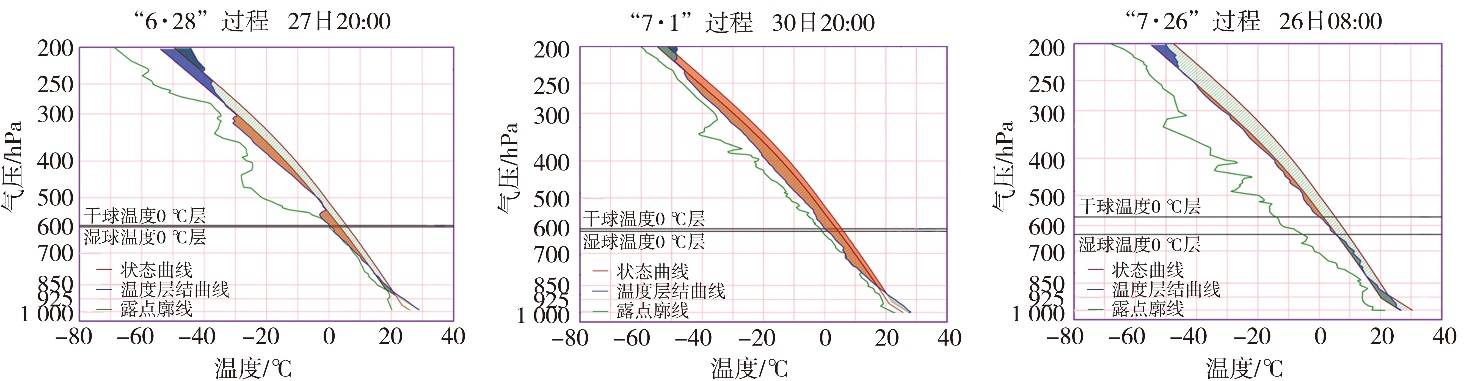
Fig.3 The circulation situation at 200 hPa, 500 hPa, 700 hPa, and 850 hPa before the occurrence of three extreme short-term heavy rainfall processes in Tianjin in 2022 (The black circle represents the cold vortex circulation, the letters A, B, C and D represent the centers of the cold vortex; wind vectors, Unit: m·s-1; the purple solid line represents trough lines, the area surrounded by the red line indicates the Tianjin area)
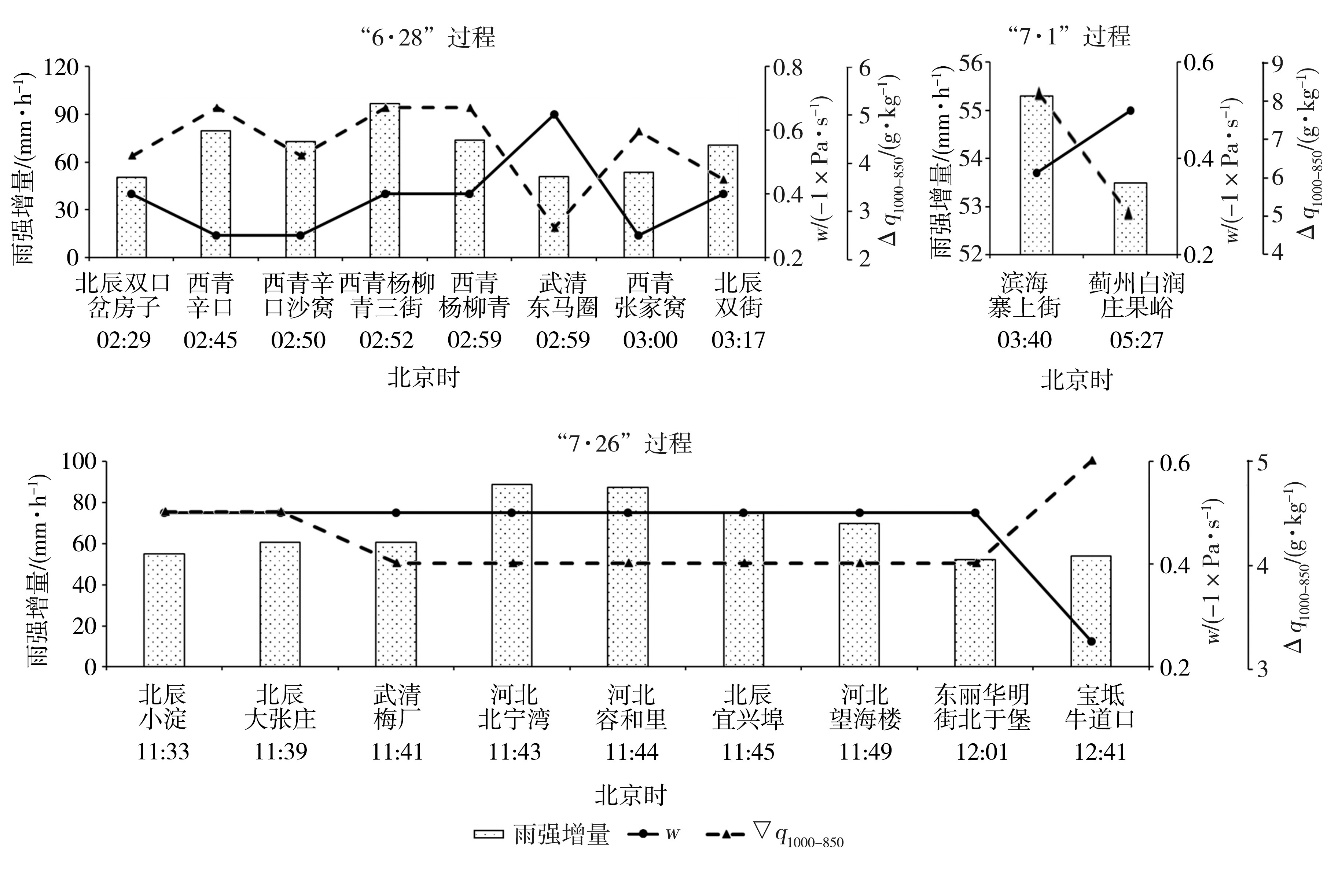
Fig.5 The increment rainfall intensity compared to the previous hour at different stations and times, as well as the maximum values of vertical velocity (w) and the specific humidity difference between 1 000 hPa and 850 hPa (?q1000-850) in the first 4 hours during three extreme short-term heavy rainfall processes in Tianjin in 2022
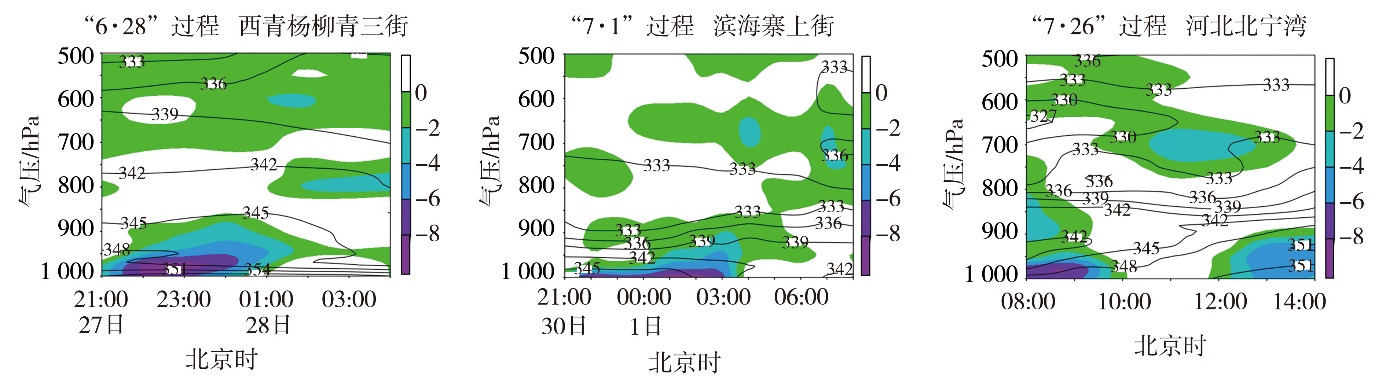
Fig.6 The time-height sections of water vapor flux divergence (the color shaded, Unit: 10-7 g·hPa-1·cm-2·s-1) and pseudo equivalent potential temperature θse (isolines, Unit: K) at different stations during three extreme short-term heavy rainfall processes in Tianjin in 2022
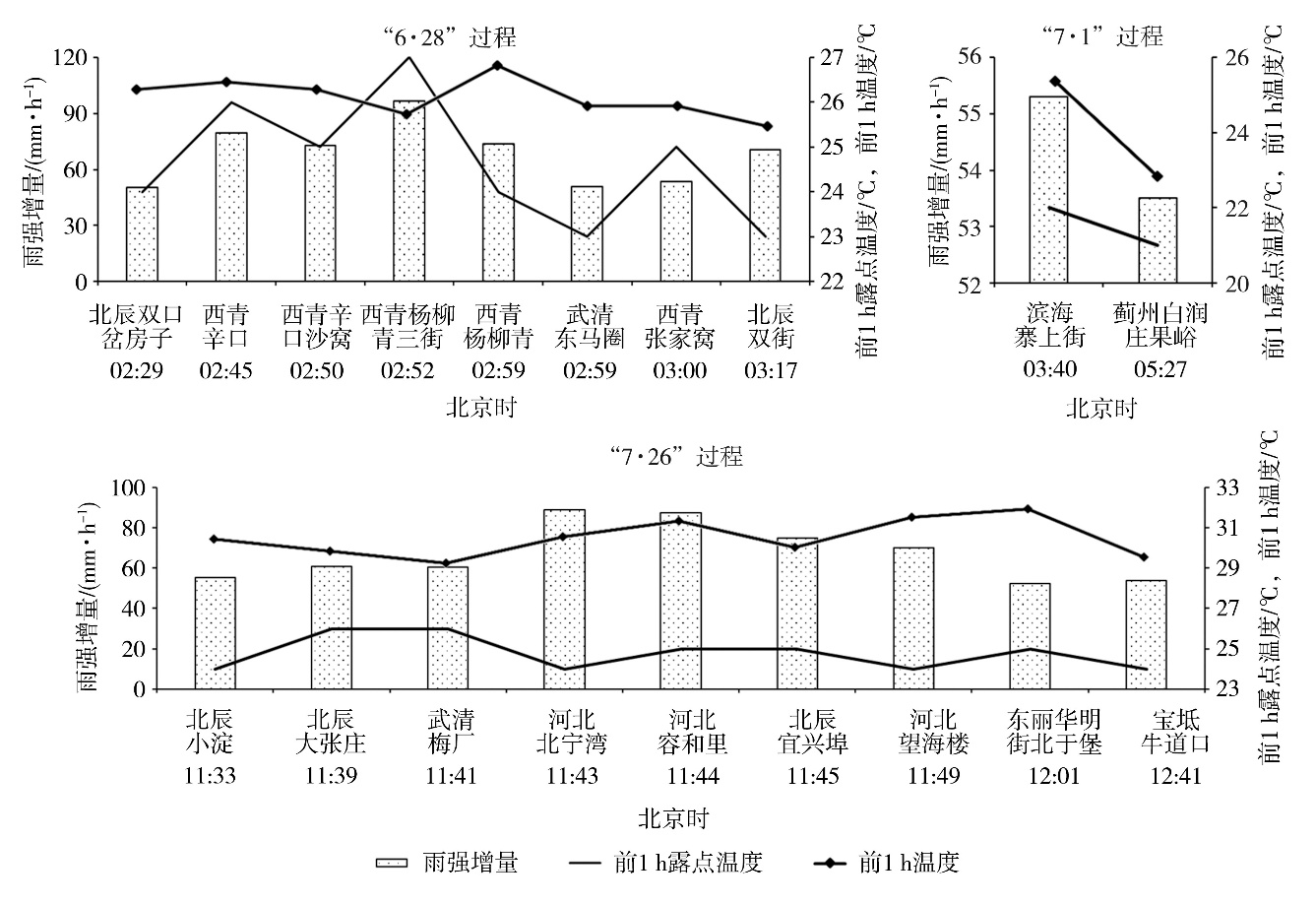
Fig.7 The increment of rainfall intensity compared to the previous hour, dew-point temperature and temperature in the previous hour of the ground at different stations and times during the three extreme short-term heavy rainfall processes in Tianjin in 2022
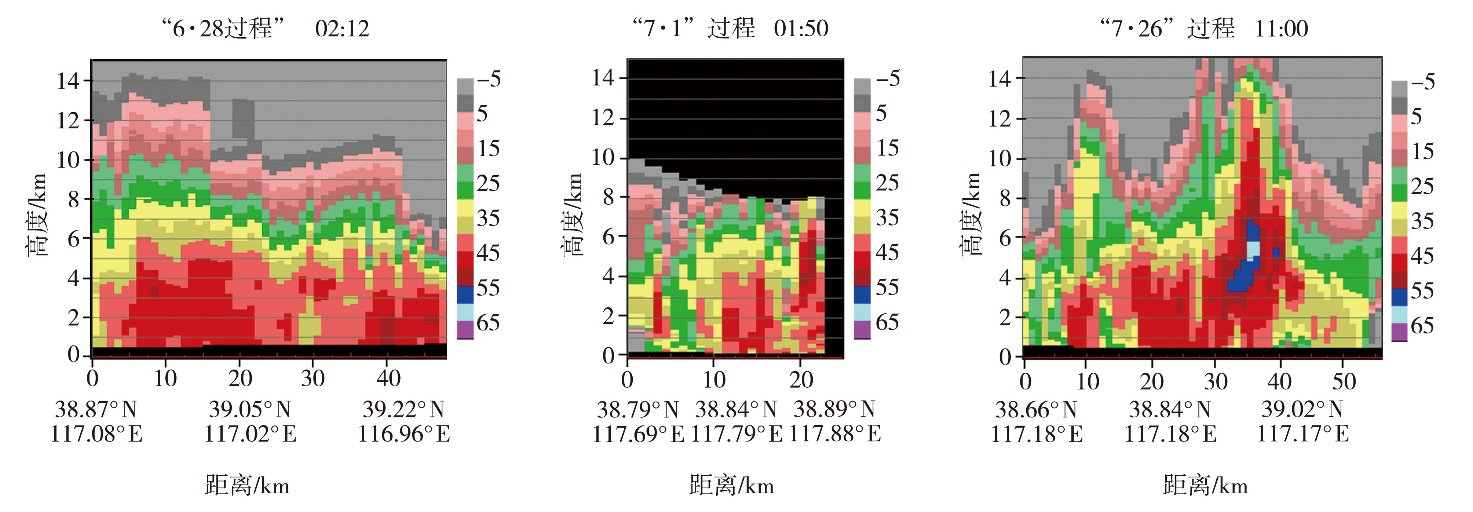
Fig.8 The vertical profile of the combinations reflectivity factor along the straight line of the strongest area of convective storm echo at Tanggu Station during three extreme short-term heavy rainfall processes in Tianjin in 2022 (Unit: dBZ)
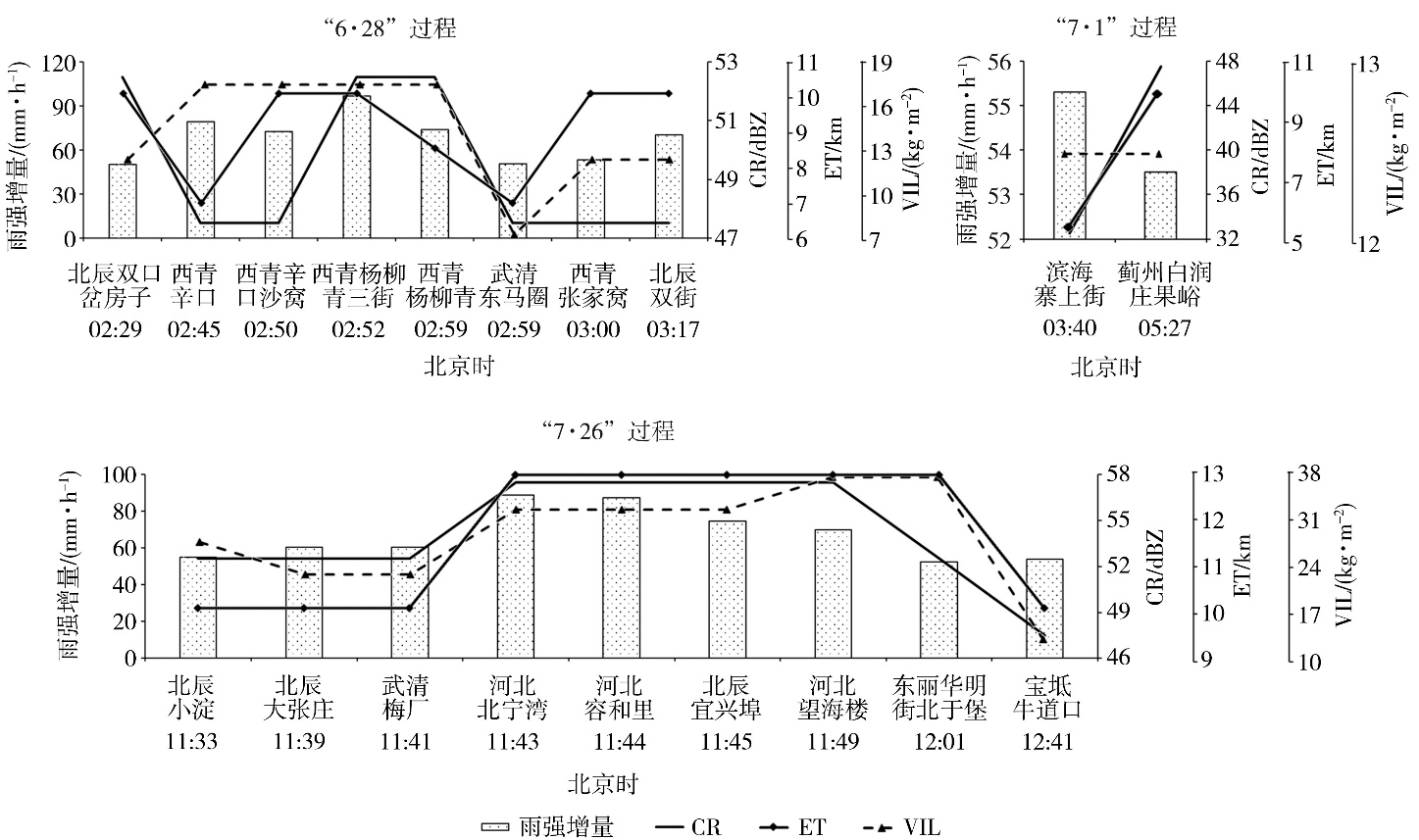
Fig.9 The increment of rainfall intensity compared to the previous hour at different stations and times, as well as the maximum values of CR, ET and VIL in the previous hour during three extreme short-term heavy rainfall processes in Tianjin in 2022
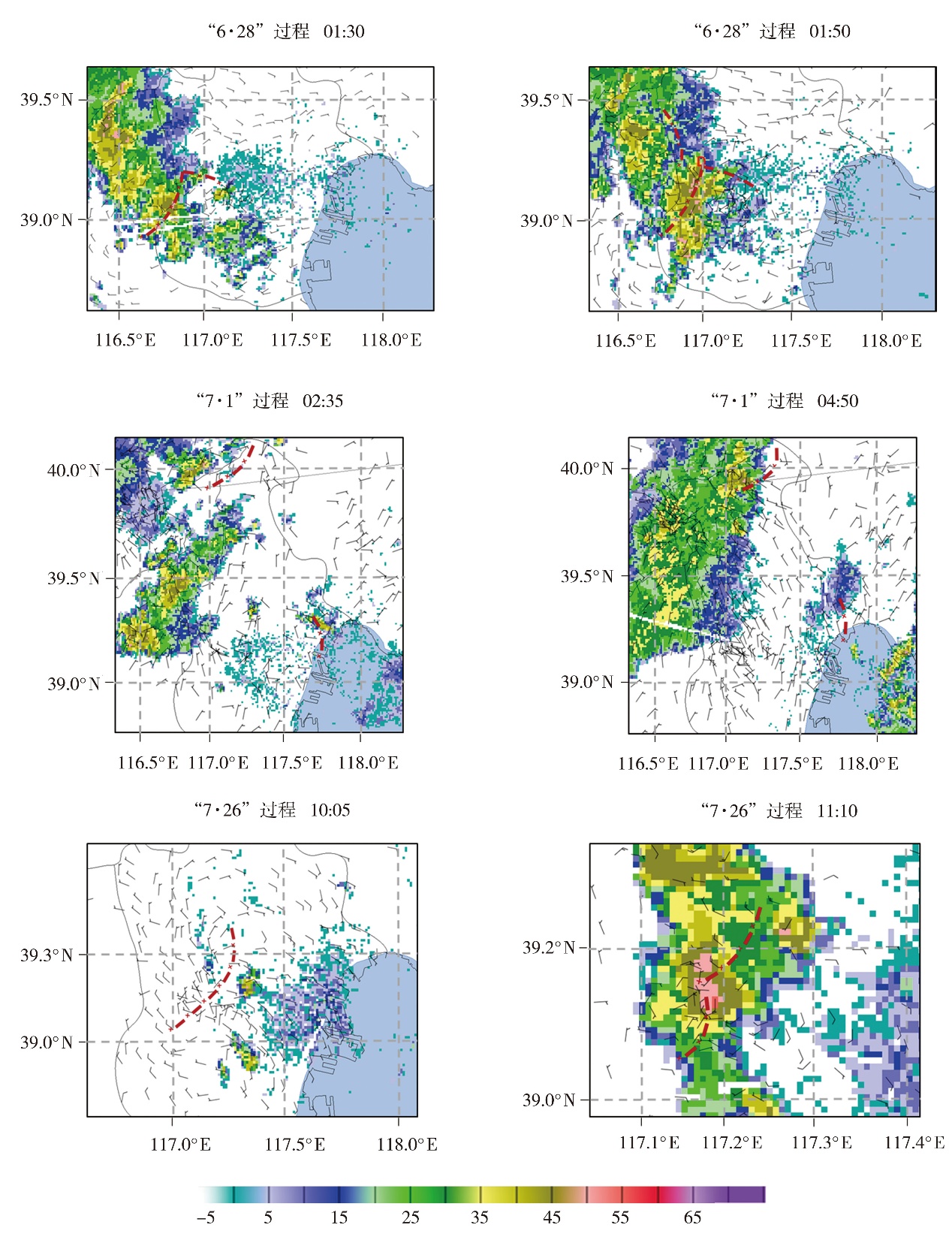
Fig.10 The ground wind fields (wind vectors, Unit: m·s?1) and basic reflectivity at 1.5° elevation angle (the color shaded, Unit: dBZ) at different times during three extreme short-term heavy rainfall processes in Tianjin in 2022 (The red dotted line represents the ground convergence line, the letter D represents the center of the vortex)
| [1] | 曹艳察, 郑永光, 孙继松, 等, 2024. 东北冷涡背景下三类区域性强对流天气过程时空分布和环境特征对比分析[J]. 气象学报, 82(1): 22-36. |
| [2] | 陈涛, 孙军, 谌芸, 等, 2019. 广州“5·7”局地突发特大暴雨过程的数值可预报性分析[J]. 气象, 45(9):1199-1 212. |
| [3] |
褚颖佳, 郭飞燕, 高帆, 等, 2023. 冷涡影响下两次不同类型强对流过程对比分析[J]. 干旱气象, 41(2):279-289.
DOI |
| [4] |
段云霞, 崔锦, 李得勤, 等, 2024. 东北冷涡背景下两次强降水干侵入特征对比分析[J]. 干旱气象, 42(3): 357-366.
DOI |
| [5] | 刘胜男, 屈丽玮, 张蔚然, 等, 2024. 陕北两次不同强度的区域性暴雨过程特征对比[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 44(3): 48-57. |
| [6] | 罗金芳, 吴君涛, 姜敏, 等, 2024. 鄂东北春季三类典型极端强降水特征分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 18(2): 44-51. |
| [7] |
齐铎, 袁美英, 周奕含, 等, 2020. 一次东北冷涡过程的结构特征与降水关系分析[J]. 高原气象, 39(4): 808-818.
DOI |
| [8] | 孙虎林, 黄焕卿, 于庆龙, 等, 2019. 2012—2017年珠江口海区短时强对流天气灾害的统计分析[J]. 海洋预报, 36(4): 35-43. |
| [9] | 孙建华, 周玉淑, 傅慎明, 等, 2024. 近十年我国涡旋系统的研究进展[J]. 大气科学, 48(1): 228-260. |
| [10] | 唐鹏, 张丽, 陈天宇, 等, 2024. 2019年6月下旬中昆仑山北坡两场强降水对比分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 18(2): 27-34. |
| [11] | 王万筠, 殷海涛, 窦策伟, 等, 2019. 天津地区三次低涡暴雨过程的诊断分析[J]. 气象与环境科学, 42(3): 42-50. |
| [12] | 王莹, 王艳春, 易笑园, 等, 2024. 天津一次夜间极端短时强降水的中尺度特征及成因探究[J]. 气象, 50(12): 1 451-1 466. |
| [13] | 王宗敏, 李江波, 王福侠, 等, 2015. 东北冷涡暴雨的特点及其非对称结构特征[J]. 高原气象, 34(6): 1 721-1 731. |
| [14] | 魏庆, 周威, 吴容, 等, 2023. 盆地西部一次极端短时强降水过程的多源资料分析[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 43(2): 19-27. |
| [15] | 徐灵芝, 许长义, 卜清军, 等, 2019. 非常规资料在天津沿海一次灾害暴雨过程中的应用[J]. 气象与环境科学, 42(3): 68-77. |
| [16] | 杨吉, 郑媛媛, 夏文梅, 等, 2020. 东北冷涡影响下江淮地区一次飑线过程的模拟分析[J]. 气象, 46(3): 357-366. |
| [17] | 易笑园, 陈宏, 张庆, 等, 2024. 渤海湾西岸一次局地极端短时强降水事件的成因分析[J]. 海洋气象学报, 44(3): 1-13. |
| [18] | 俞小鼎, 2013. 短时强降水临近预报的思路与方法[J]. 暴雨灾害, 32(3): 202-209. |
| [19] | 郁珍艳, 何立富, 范广洲, 等, 2011. 华北冷涡背景下强对流天气的基本特征分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 27(1): 89-94. |
| [20] | 张楠, 杨晓君, $\boxed{\hbox{何群英}}$, 等, 2020. 一次台风残涡引发的天津局地暴雨中尺度对流过程分析[J]. 气象与环境学报, 36(4): 1-10. |
| [21] | 张文龙, 崔晓鹏, 黄荣, 等, 2019. 北京“623”大暴雨的强降水超级单体特征和成因研究[J]. 大气科学, 43(5): 1 171-1 190. |
| [22] | 张武龙, 杨康权, 康岚, 等, 2024. 川西高原和攀西地区不同级别短时强降水环境参量特征对比分析[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 44(2): 75-82. |
| [23] | 郑永光, 宋敏敏, 2021. 冷涡影响中国对流性大风与冰雹的分布特征[J]. 热带气象学报, 37(5/6): 710-720. |
| [24] | ZHANG C, ZHANG Q, WANG Y, et al, 2008. Climatology of warm season cold vortices in East Asia:1979-2005[J]. Meteorology and Atmospheric Physics, 100(1): 291-301. |
| [1] | DUAN Yunxia, CUI Jin, LI Deqin, WANG Yue, BAN Weilong, LIU Qing. Comparative analysis of the characteristics of dry intrusions during two heavy rainfall processes under Northeast Cold Vortex background [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(3): 357-366. |
| [2] | CHU Yingjia, GUO Feiyan, GAO Fan, HU Peng, ZHENG Lina, LIU Yichen, LU Qi. Comparative analysis of two different types of severe convective processes under the influence of cold vortex [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(2): 279-289. |
| [3] | REN Li, YANG Yanmin. Dynamic and Thermal Characteristics of a Heavy Rain Caused by MCC at Bottom of Northeast Cold Vortex [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(1): 65-75. |
| [4] | . Predictability of a Cold Vortex Snowfall Process in Ningxia in the Late Autumn of 2015 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(3): 465-. |
| [5] | LI Dian, LU Yang, WU Yutong, LI Chong, CHAI Xiaoling, CUI Jinglin, ZHANG Shuai. Application of Wind Profiler Radar Data to Convective Weather Forecast Under Background of Cold Vortex in Shenyang [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2016, 34(5): 886-897. |
| [6] | LI Shuang, DING Zhiying, DAI Ping, LIU Yunhua, HAN Ying. Recent Advances in Research on Northeast China Cold Vortex [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2016, 34(1): 13-19. |
| [7] | YE Gengxin,LIU Zhuanghua,LIU Guoyu. Characteristic of a Rare Moving Left Supercell Storm [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2014, 32(3): 431-438. |
| [8] | LI Bin,SU Xiaolan,WANG Zhilong,JIANG Aihong. Analysis on a Severe Hail Weather Occurred in Western Talimu Basin of Southern Xinjiang [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2013, 31(4): 790-795. |
| [9] | . Analysis on Structure Characteristic of Two Cold Vortex Processes [J]. J4, 2012, 30(4): 555-562. |
| [10] | JI Xiao-Ling, LIU Qiang-Jun, LIU Jian-Jun, CHEN Yang. Analysis of a Severe Convection Process Influenced by Mongolia Cold Vortex [J]. J4, 2005, 23(1): 26-32. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||