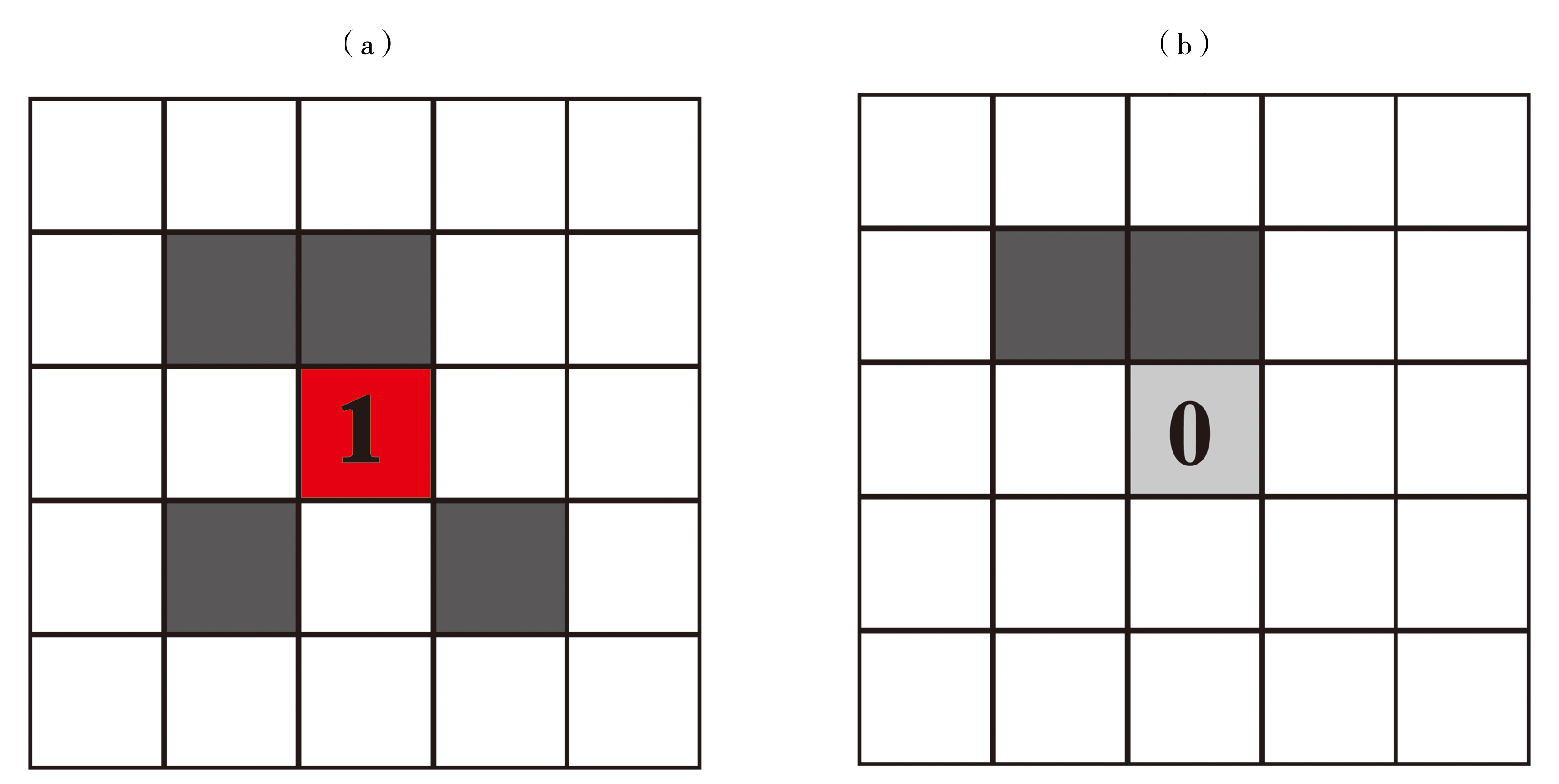
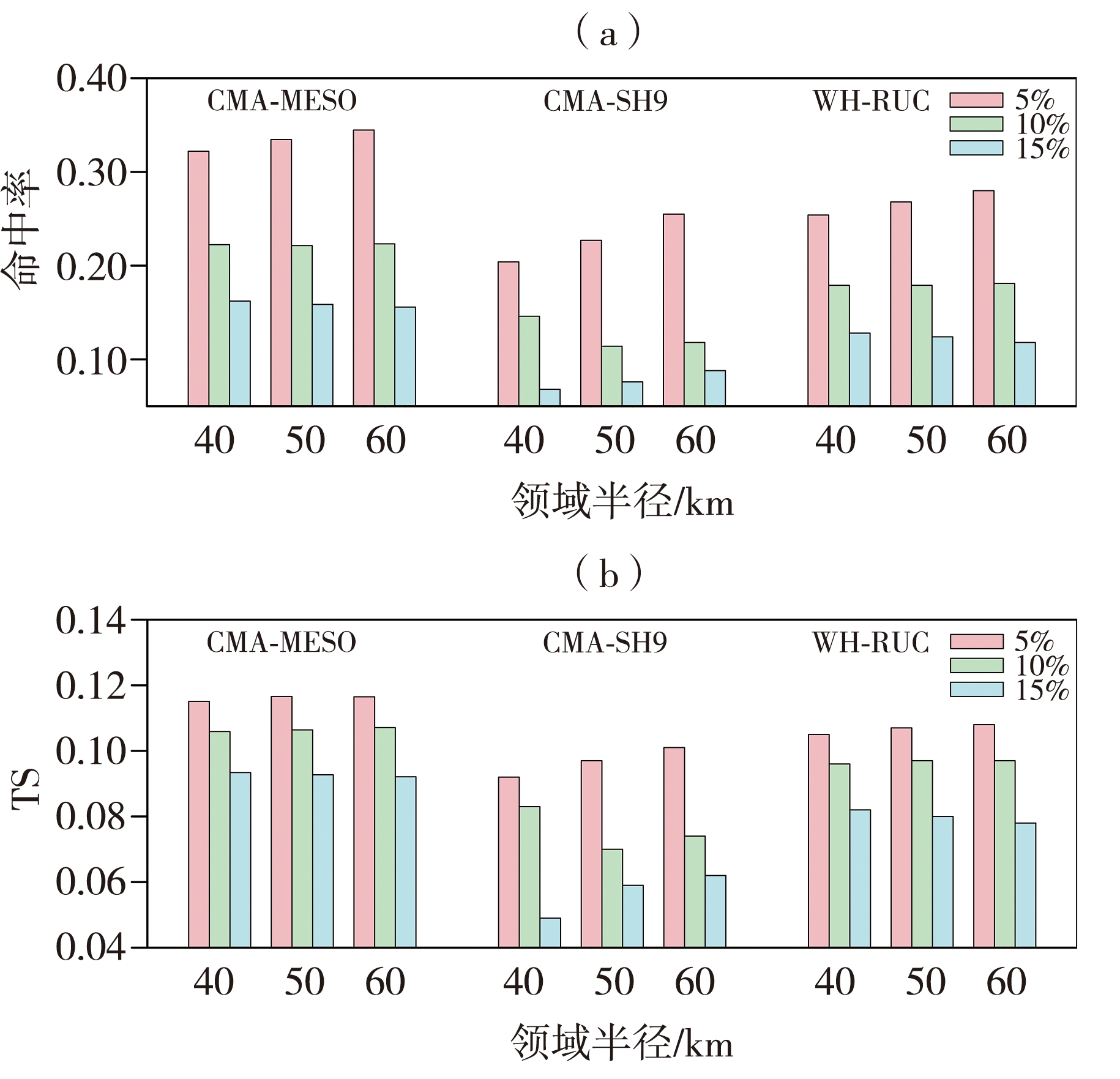
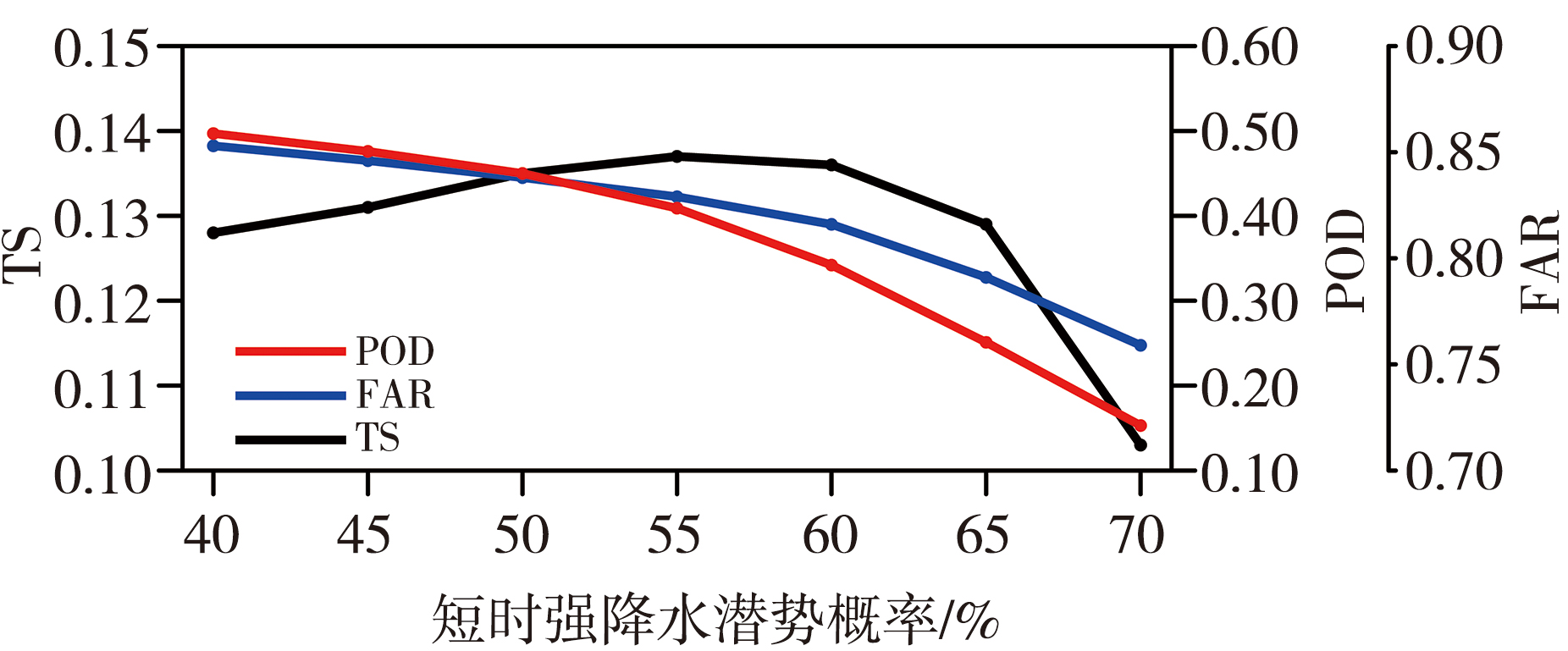
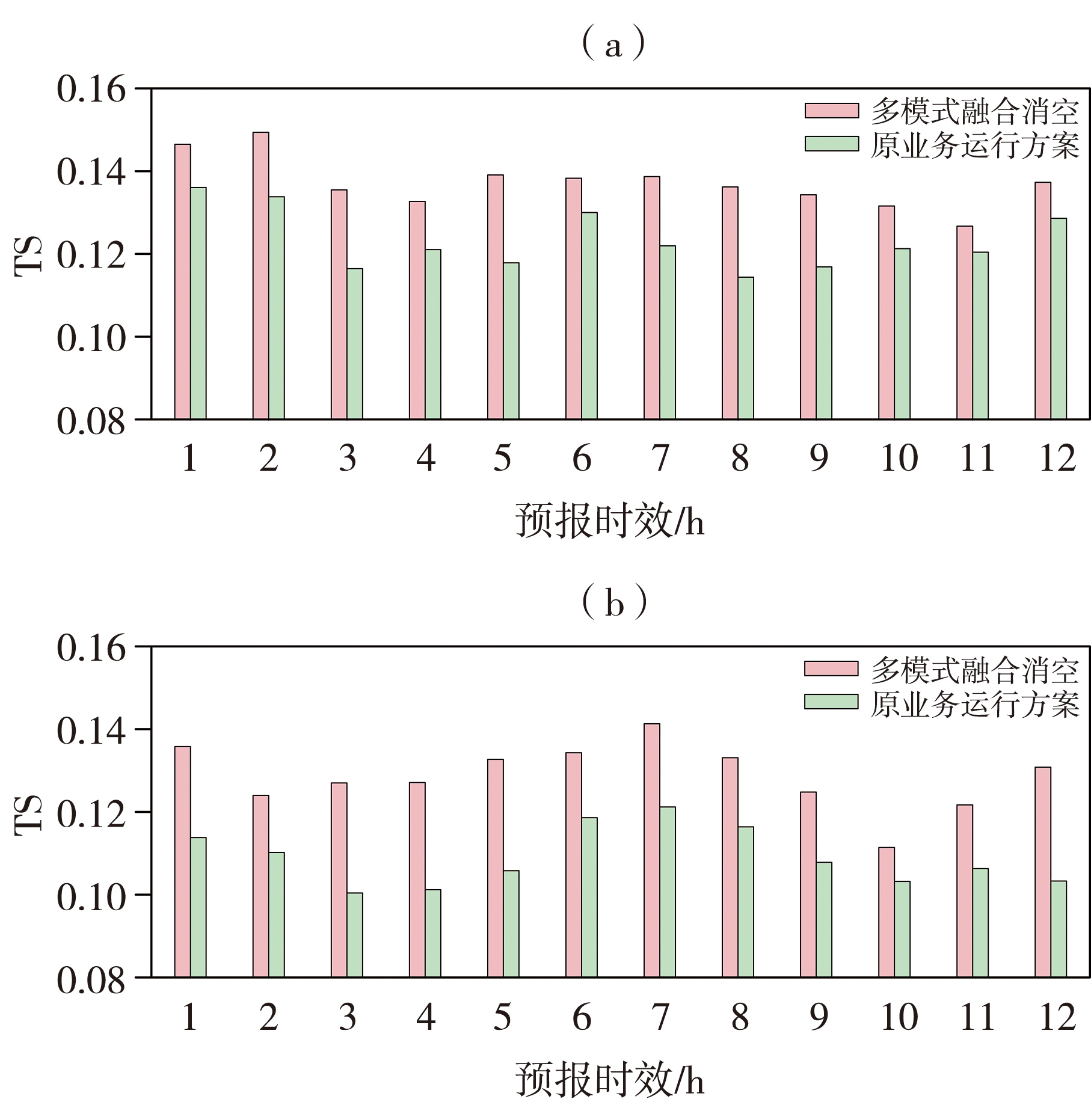
| [1] |
蔡怡, 徐枝芳, 龚玺, 等, 2023. 2021年夏季CMA-MESO模式降水预报评估[J]. 干旱气象, 41(3):503-515.
DOI
|
| [2] |
曹彦超, 焦美玲, 秦拓, 2023. 多次取样的网格化暴雨预报“配料法”研究[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 17(4):24-29.
|
| [3] |
郝莹, 姚叶青, 郑媛媛, 等, 2012. 短时强降水的多尺度分析及临近预警[J]. 气象, 38(8):903-912.
|
| [4] |
江洁, 周天军, 张文霞, 2022. 近60年来中国主要流域极端降水演变特征[J]. 大气科学, 46(3):707-724.
|
| [5] |
林晓霞, 冯业荣, 陈子通, 等, 2021. 华南区域高分辨率数值模式前汛期预报初步评估[J]. 热带气象学报, 37(4):656-668.
|
| [6] |
刘雪晴, 陈静, 陈法敬, 等, 2020. 降水邻域集合概率方法尺度敏感性试验[J]. 大气科学, 44(2):282-296.
|
| [7] |
刘松涛, 高梦竹, 齐铎, 等, 2023. 基于CMA-MESO模式的黑龙江省强对流天气分类预报方法研究[J]. 气象与环境学报, 39(4):38-46.
|
| [8] |
罗聪, 时洋, 吴乃庚, 等, 2021. 基于邻域最优概率的GRAPES快速更新循环同化预报系统逐时降水订正方法[J]. 热带气象学报, 37(4):569-578.
|
| [9] |
马申佳, 陈超辉, 智协飞, 等, 2018. 基于时空不确定性的对流尺度集合预报效果评估检验[J]. 气象学报, 76(4):578-589.
|
| [10] |
牛淑贞, 张一平, 王迪, 等, 2021. 河南省分类强对流天气概率预报方法研究与应用[J]. 气象与环境科学, 44(1):1-12.
|
| [11] |
潘留杰, 张宏芳, 陈小婷, 等, 2015. 基于邻域法的高分辨率模式降水的预报能力分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 31(5):632-642.
|
| [12] |
漆梁波, 2015. 高分辨率数值模式在强对流天气预警中的业务应用进展[J]. 气象, 41(6):661-673.
|
| [13] |
王俊超, 王志斌, 赖安伟, 等, 2022. 基于数值预报与雷达外推预报融合方法的降水回波短临预报试验研究[J]. 干旱气象, 40(3):485-499.
DOI
|
| [14] |
吴翠红, 王晓玲, 龙利民, 等, 2013. 近10 a湖北省强降水时空分布特征与主要天气概念模型[J]. 暴雨灾害, 32(2):113-119.
|
| [15] |
肖云, 熊志文, 李欢欢, 等, 2020. 江西省强对流分类潜势预报方法研究[J]. 气象水文海洋仪器, 37(3):6-11.
|
| [16] |
许冠宇, 黄龙飞, 吴涛, 等, 2022. 华中地区春季一次强对流触发的多尺度影响机制分析[J]. 气象, 48(8):979-992.
|
| [17] |
徐双柱, 吴涛, 王艳, 2012. 2010年7月7—15日湖北省持续性暴雨分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 31(1):35-43.
|
| [18] |
俞小鼎, 2013. 短时强降水临近预报的思路与方法[J]. 暴雨灾害, 32(3):202-209.
|
| [19] |
俞小鼎, 王秀明, 李万莉, 等, 2020. 雷暴与强对流临近预报[M]. 北京: 气象出版社.
|
| [20] |
曾明剑, 王桂臣, 吴海英, 等, 2015. 基于中尺度数值模式的分类强对流天气预报方法研究[J]. 气象学报, 73(5):868-882.
|
| [21] |
谌伟, 刘佩廷, 徐枝芳, 等, 2022. 湖北强降水频次时空特征及基于GWR模型的地形关系分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 38(2):216-226.
|
| [22] |
钟敏, 肖安, 许冠宇, 2022. 基于CMA-MESO的分级短时强降水概率预报方法研究[J]. 干旱气象, 40(4):700-709.
DOI
|
| [23] |
邹磊, 夏军, 张印, 2021. 长江中下游极端降水时空演变特征研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 30(5):1264-1 274.
|
| [24] |
BAI L Q, CHEN G X, HUANG L, 2020. Image processing of radar mosaics for the climatology of convection initiation in South China[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 59(1): 65-81.
|
| [25] |
CHAKRABORTY A, 2010. The skill of ECMWF medium-range forecasts during the year of tropical convection 2008[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 138(10): 3 787-3 805.
|
 ), XU Guanyu(
), XU Guanyu( ), ZHONG Min, LIU Ruixue, LIU Wenting
), ZHONG Min, LIU Ruixue, LIU Wenting