Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (2): 293-304.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2024)-02-0293
• Test and Correction of New Meteorological Data • Previous Articles Next Articles
Correction of ECMWF ensemble average precipitation forecast using two objective precipitation statistical methods
JIAO Yang( ), ZHENG Lina(
), ZHENG Lina( ), ZHANG Yongjing, SU Yi
), ZHANG Yongjing, SU Yi
- Ji’nan Meteorological Bureau of Shandong Province, Ji’nan 250102, China
-
Received:2023-05-08Revised:2023-12-05Online:2024-04-30Published:2024-05-12
两种降水客观统计方法对ECMWF集合平均降水预报的订正研究
- 山东省济南市气象局,山东 济南 250102
-
通讯作者:郑丽娜(1971—),女,山东东营人,博士,正高级工程师,从事天气预报和气候变化研究。E-mail:dongyingzln@163.com 。 -
作者简介:焦洋(1989—),女,山东济南人,硕士,工程师,从事预报方法和极端天气研究。E-mail: jiaoyang0621@foxmail.com。 -
基金资助:中国气象局气象软科学重点项目(2023ZDIANXM03);山东省自然科学基金项目(ZR2021MD012);山东省气象局青年基金项目(2020SDQN11);中国气象局决策服务专项“特大城市内涝风险预估技术研究”共同资助
CLC Number:
Cite this article
JIAO Yang, ZHENG Lina, ZHANG Yongjing, SU Yi. Correction of ECMWF ensemble average precipitation forecast using two objective precipitation statistical methods[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(2): 293-304.
焦洋, 郑丽娜, 张永婧, 苏轶. 两种降水客观统计方法对ECMWF集合平均降水预报的订正研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(2): 293-304.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2024)-02-0293
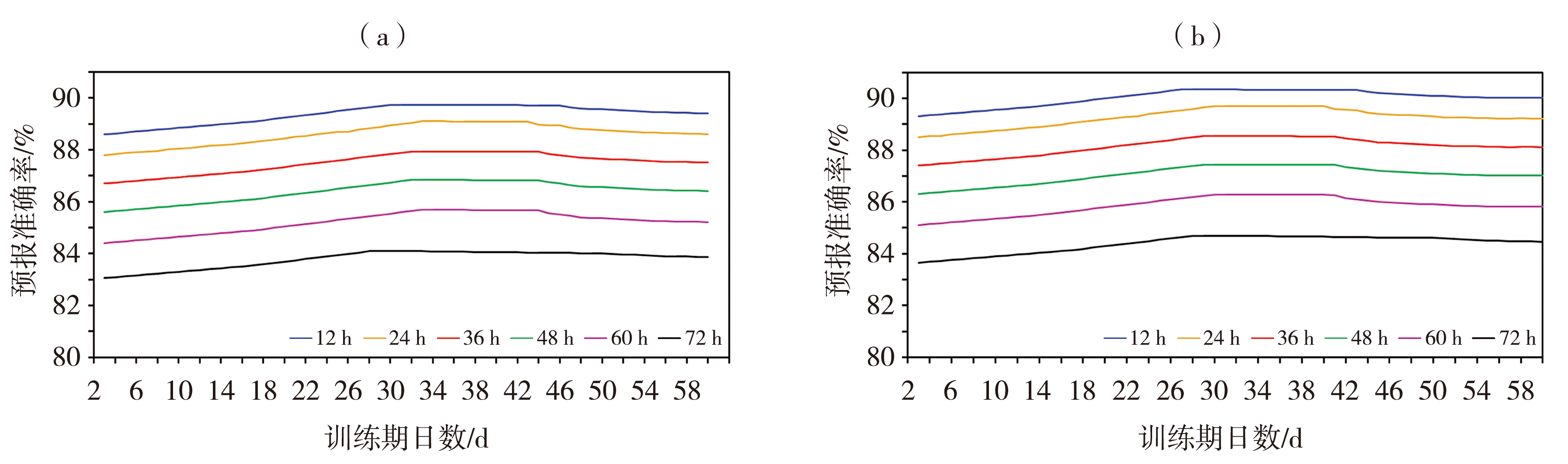
Fig.1 Variation of accuracy of precipitation forecast in 12 hours interval with the change of running training period for prediction period of 12 to 72 hours for two correction algorithms (a) EC_EPEM_MOS, (b) EC_EPEM_OTS
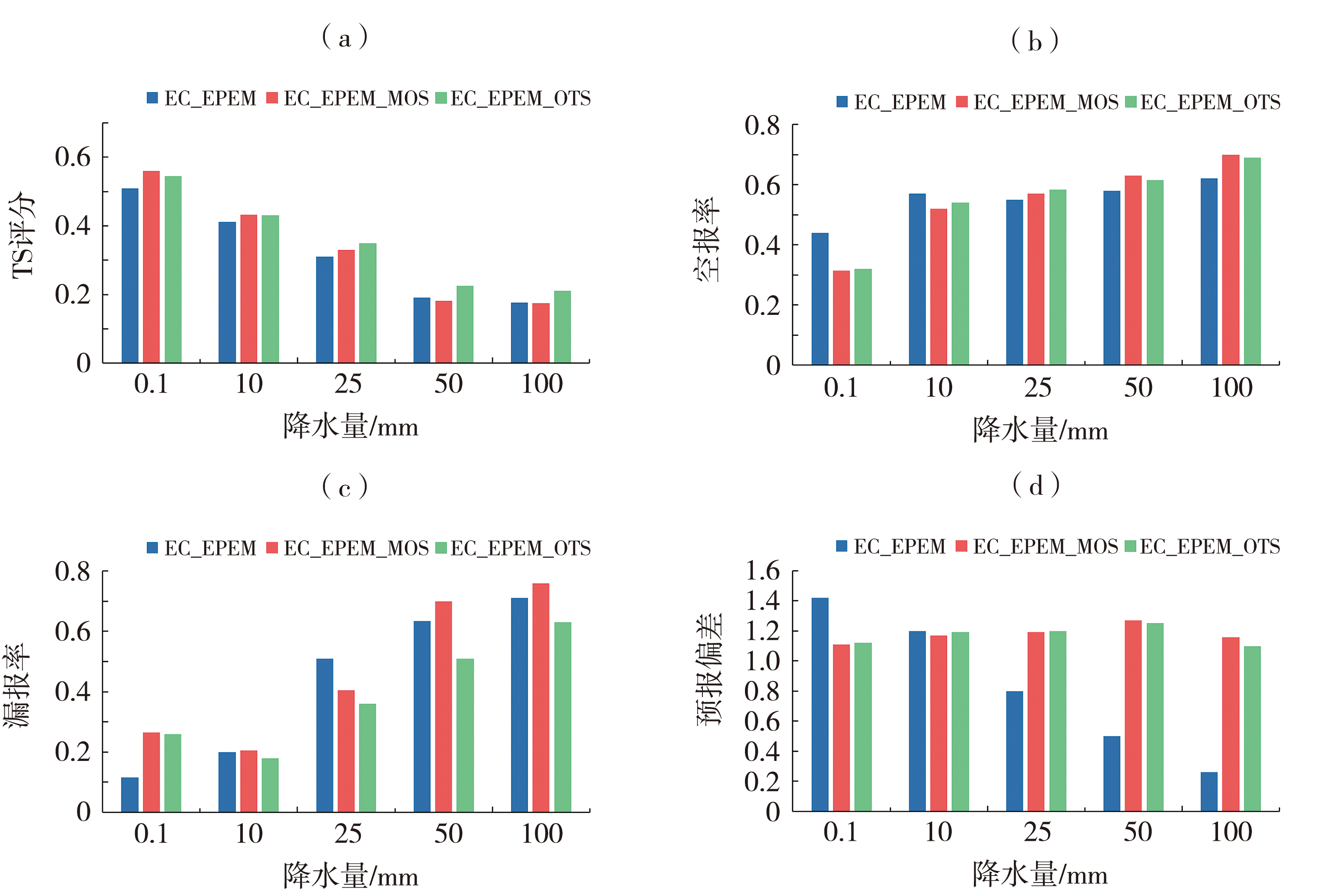
Fig.2 The threat score (a), empty report rate (b), missing report rate (c) and forecast deviation (d) of 12 h cumulative precipitation prediction of EC_EPEM,EC_EPEM_MOS and EC_EPEM_OTS for 12 h prediction period during 2019-2020

Fig.3 The variation of threat score of prediction with the time interval of 12 h for precipitation with different grades of EC_EPEM,EC_EPEM_MOS and EC_EPEM_OTS for prediction period of 12 to 72 h during 2019-2020 (a) 0.1 mm,(b) 10 mm,(c) 25 mm, (d) 50 mm, (e) 100 mm
| 降水量级/mm | 预报时效/h | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | 24 | 36 | 48 | 60 | 72 | ||
| 0.1~9.9 | EC_EPEM | 0.282 | 0.265 | 0.248 | 0.231 | 0.214 | 0.190 |
| EC_EPEM_MOS | 0.303 | 0.285 | 0.268 | 0.246 | 0.229 | 0.198 | |
| EC_EPEM_OTS | 0.301 | 0.284 | 0.267 | 0.250 | 0.233 | 0.205 | |
| 10.0~24.9 | EC_EPEM | 0.200 | 0.192 | 0.177 | 0.166 | 0.154 | 0.139 |
| EC_EPEM_MOS | 0.205 | 0.193 | 0.183 | 0.175 | 0.167 | 0.159 | |
| EC_EPEM_OTS | 0.206 | 0.197 | 0.188 | 0.180 | 0.172 | 0.155 | |
| 25.0~49.9 | EC_EPEM | 0.141 | 0.130 | 0.119 | 0.108 | 0.093 | 0.076 |
| EC_EPEM_MOS | 0.132 | 0.119 | 0.105 | 0.092 | 0.080 | 0.058 | |
| EC_EPEM_OTS | 0.166 | 0.161 | 0.150 | 0.137 | 0.128 | 0.118 | |
| 50.0~99.9 | EC_EPEM | 0.157 | 0.145 | 0.137 | 0.121 | 0.112 | 0.094 |
| EC_EPEM_MOS | 0.140 | 0.127 | 0.113 | 0.100 | 0.087 | 0.066 | |
| EC_EPEM_OTS | 0.168 | 0.156 | 0.145 | 0.133 | 0.120 | 0.108 | |
Tab.1 The threat scores of EC_EPEM, EC_EPEM_MOS and EC_EPEM_OTS for prediction period of 12 to 72 h with the time interval of 12 h from June to September during 2019-2020
| 降水量级/mm | 预报时效/h | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | 24 | 36 | 48 | 60 | 72 | ||
| 0.1~9.9 | EC_EPEM | 0.282 | 0.265 | 0.248 | 0.231 | 0.214 | 0.190 |
| EC_EPEM_MOS | 0.303 | 0.285 | 0.268 | 0.246 | 0.229 | 0.198 | |
| EC_EPEM_OTS | 0.301 | 0.284 | 0.267 | 0.250 | 0.233 | 0.205 | |
| 10.0~24.9 | EC_EPEM | 0.200 | 0.192 | 0.177 | 0.166 | 0.154 | 0.139 |
| EC_EPEM_MOS | 0.205 | 0.193 | 0.183 | 0.175 | 0.167 | 0.159 | |
| EC_EPEM_OTS | 0.206 | 0.197 | 0.188 | 0.180 | 0.172 | 0.155 | |
| 25.0~49.9 | EC_EPEM | 0.141 | 0.130 | 0.119 | 0.108 | 0.093 | 0.076 |
| EC_EPEM_MOS | 0.132 | 0.119 | 0.105 | 0.092 | 0.080 | 0.058 | |
| EC_EPEM_OTS | 0.166 | 0.161 | 0.150 | 0.137 | 0.128 | 0.118 | |
| 50.0~99.9 | EC_EPEM | 0.157 | 0.145 | 0.137 | 0.121 | 0.112 | 0.094 |
| EC_EPEM_MOS | 0.140 | 0.127 | 0.113 | 0.100 | 0.087 | 0.066 | |
| EC_EPEM_OTS | 0.168 | 0.156 | 0.145 | 0.133 | 0.120 | 0.108 | |

Fig.4 The spatial distribution of optimal products with high threat scores for 0.1 to 9.9 mm grades precipitation prediction with the time interval of 12 h for different prediction periods from June to September during 2019-2020 (a) 12 h, (b) 24 h, (c) 36 h, (d) 48 h, (e) 60 h, (f) 72 h

Fig.5 The spatial distribution of optimal products with high threat scores for 10.0 to 24.9 mm grades precipitation prediction with the time interval of 12 h for different prediction periods from June to September during 2019-2020 (a) 12 h, (b) 24 h, (c) 36 h, (d) 48 h, (e) 60 h, (f) 72 h

Fig.6 The spatial distribution of optimal products with high threat scores for 25.0 to 49.9 mm grades precipitation prediction with the time interval of 12 h for different prediction periods from June to September during 2019-2020 (a) 12 h, (b) 24 h, (c) 36 h, (d) 48 h, (e) 60 h, (f) 72 h

Fig.7 The spatial distribution of optimal products with high threat scores for 50.0 to 99.9 mm grades precipitation prediction with the time interval of 12 h for different prediction periods from June to September during 2019-2020 (a) 12 h, (b) 24 h, (c) 36 h, (d) 48 h, (e) 60 h, (f) 72 h

Fig.8 The spatial distribution of observations (a), EC_EPEM (b), EC_EPEM_MOS (c), EC_EPEM_OTS (d) precipitation grades and optimal forecasting products (e) from 08:00 to 20:00 on July 22, 2020
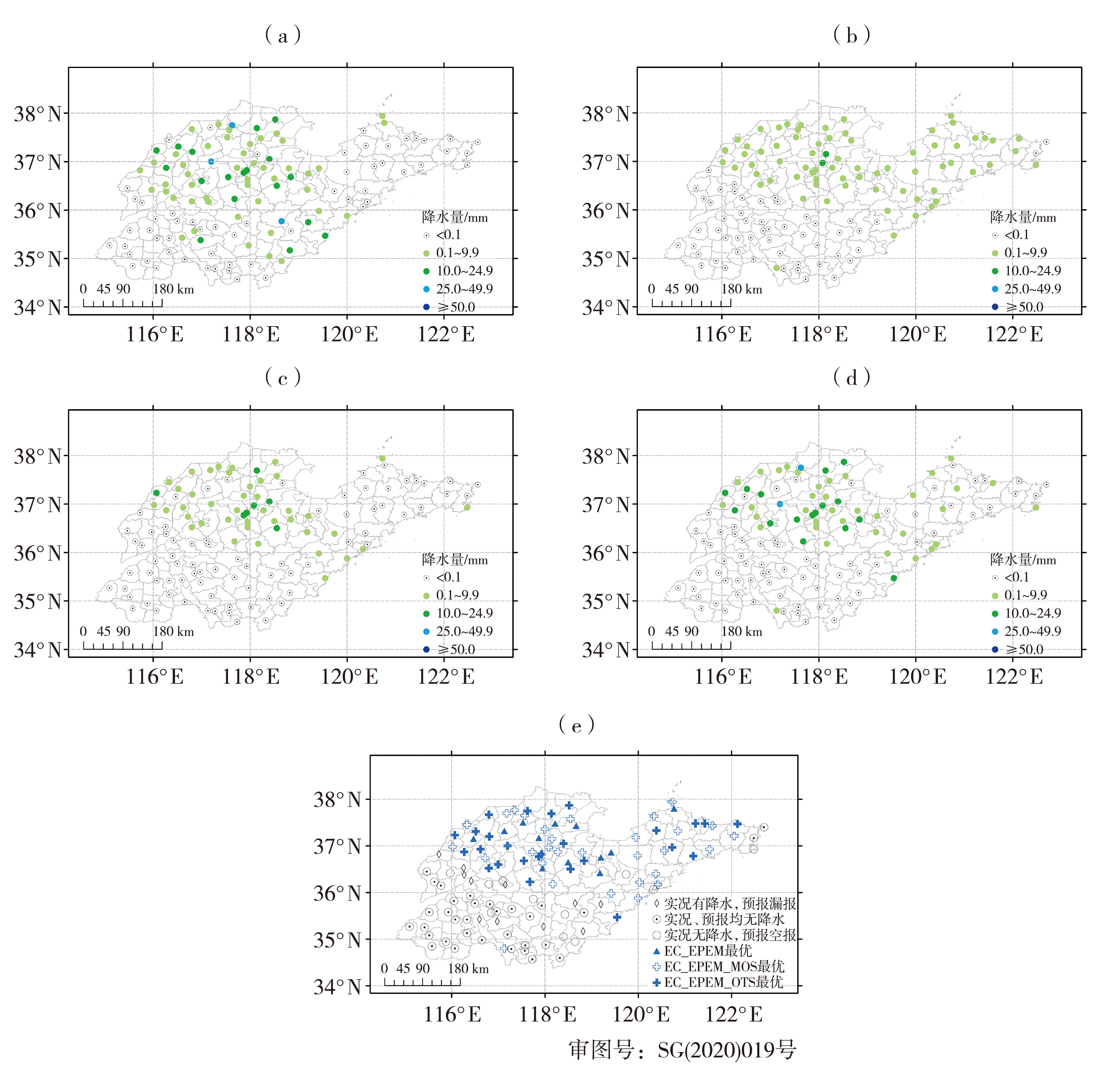
Fig.9 The spatial distribution of observations (a), EC_EPEM (b), EC_EPEM_MOS (c), EC_EPEM_OTS (d) precipitation grades and optimal forecasting products (e) from 20:00 on September 7 to 08:00 September 8, 2020
| [1] | 邓国, 龚建东, 邓莲堂, 等, 2010. 国家级区域集合预报系统研发和性能检验[J]. 应用气象学报, 21(5): 513-523. |
| [2] | 顾震潮, 1958. 作为初值问题的高空大尺度天气数值预报与由地面温压场历史演变作预报的等值性[J]. 科学通报, 3(1): 19-20. |
| [3] | 韩念霏, 杨璐, 陈明轩, 等, 2022. 京津冀站点风温湿要素的机器学习订正方法[J]. 应用气象学报, 33(4): 489-500. |
| [4] | 李佰平, 智协飞, 2012. ECMWF模式地面气温预报的四种误差订正方法的比较研究[J]. 气象, 38(8): 897-902. |
| [5] | 刘还珠, 赵声蓉, 陆志善, 等, 2004. 国家气象中心气象要素的客观预报—MOS系统[J]. 应用气象学报, 15(2): 181-191. |
| [6] | 林春泽, 智协飞, 韩艳, 等, 2009. 基于TIGGE资料的地面气温多模式超级集合预报[J]. 应用气象学报, 20(6): 706-712. |
| [7] | 麻巨慧, 朱跃建, 王盘兴, 等, 2011. NCEP、ECMWF及CMC全球集合预报业务系统发展综述[J]. 大气科学学报, 34(3): 370-380. |
| [8] | 漆梁波, 曹晓岗, 夏立, 等, 2007. 上海区域要素客观预报方法效果检验[J]. 气象, 33(9): 9-18. |
| [9] | 任宏利, 张培群, 李维京, 等, 2006. 基于多个参考态更新的动力相似预报方法及应用[J]. 物理学报, 55(8): 4 388-4 396. |
| [10] | 盛春岩, 范苏丹, 荣艳敏, 等, 2020. 几种气温客观预报方法对比及最优集成预报研究[J]. 气象, 46(10): 1 351-1 361. |
| [11] | 王雨, 闫之辉, 2007. 降水检验方案变化对降水检验评估效果的影响分析[J]. 气象, 33(12): 53-61. |
| [12] | 吴启树, 韩美, 郭弘, 等, 2016. MOS温度预报中最优训练期方案[J]. 应用气象学报, 27(4): 426-434. |
| [13] | 吴启树, 韩美, 刘铭, 等, 2017. 基于评分最优化的模式降水预报订正算法对比[J]. 应用气象学报, 28(3): 306-317. |
| [14] | 徐姝, 熊明明, 王颖, 等, 2018. 改进的ECMWF集合预报融合产品在海河流域的检验与分析[J]. 气象与环境科学, 41(4): 41-46. |
| [15] | 薛谌彬, 陈娴, 张瑛, 等, 2019. ECMWF高分辨率模式2 m温度预报误差订正方法研究[J]. 气象, 45(6): 831-842. |
| [16] | 杨杰, 龚志强, 赵俊虎, 等, 2014. 基于模式误差分布特征的中国夏季旱涝预测可信度研究[J]. 物理学报, 63(14): 427-438. |
| [17] | 杨璐, 王晓丽, 宋林烨, 等, 2023. 基于阵风系数模型的百米级阵风客观预报算法研究[J]. 气象学报, 81(1): 94-109. |
| [18] | 赵华生, 黄小燕, 黄颖, 2018. ECMWF集合预报产品在广西暴雨预报中的释用[J]. 应用气象学报, 29(3): 344-353. |
| [19] | 赵瑞霞, 代刊, 金荣花, 等, 2020. OTS、MOS和OMOS方法及其优化组合应用于72 h内逐3 h降水预报的试验分析研究[J]. 气象, 46(3): 420-428. |
| [20] | 赵声蓉, 赵翠光, 邵明轩, 2009. 事件概率回归估计与降水等级预报[J]. 应用气象学报, 20(5): 521-529. |
| [21] | 赵声蓉, 赵翠光, 赵瑞霞, 等, 2012. 我国精细化客观气象要素预报进展[J]. 气象科技进展, 2(5): 12-21. |
| [22] | 郑志海, 任宏利, 黄建平, 2009. 基于季节气候可预报分量的相似误差订正方法和数值实验[J]. 物理学报, 58(10): 7 359-7 367. |
| [23] | 智协飞, 陈雯, 2010. THORPEX国际科学研究新进展[J]. 大气科学学报, 33(4): 504-511. |
| [24] | 智协飞, 季晓东, 张璟, 等, 2013. 基于TIGGE资料的地面气温和降水的多模式集成预报[J]. 大气科学学报, 36(3): 257-266. |
| [25] | 智协飞, 赵忱, 2020. 基于集合成员订正的强降水多模式集成预报[J]. 应用气象学报, 31(3): 303-314. |
| [26] | BARNETT T P, PREISENDORFER R W, 2010. Multi-field analog prediction of short-term climate fluctuations using a climate state vector[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 35(10): 1 771-1 787. |
| [27] | CARTER G M, DALLAVALLE J P, GLAHN H R, 1989. Statistical forecasts based on the National Meteorological Center’s numerical weather prediction system[J]. Weather and Forecasting, 4(3): 401-412. |
| [28] | GLAHN H R, LOWRY D A, 1972. The use of model output statistics (MOS) in objective weather forecasting[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 11(8): 1 203-1 211. |
| [29] | HAGEDORN R, BUIZZA R, HAMILL T M, et al, 2012. Comparing TIGGE multi-model forecasts with reforecast-calibrated ECMWF ensemble forecasts[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 138(668): 1 814-1 827. |
| [30] | VISLOCKY R L, FRITSCH J M, 1995. Improved model output statistics forecasts through model consensus[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 76(7): 1 157-1 164. |
| [31] | World Meteorological Organization, 2012. Guidelines on ensemble prediction systems and forecasting[R]. WMO-No.1091, Geneva. |
| [1] | HUAN Haijun, XU Weiping, LIU Yan, GE Ruiting, CONG Jingcheng, DONG Xuguang. Distribution and variation characteristics of high temperature weather in Shandong [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(1): 64-75. |
| [2] | HAN Jing, JIAO Meiling, CAO Yanchao, WANG Juan, HE Tao, XU Geng, ZHOU Zhongwen, JIN Manhui. Deviation characteristics in intelligent grid forecast of flood season precipitation in Hedong area of Gansu based on CRA spatial forecast verification [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(6): 976-986. |
| [3] | ZHU Wengang, SHENG Chunyan, FAN Sudan, RONG Yanmin, QU Meihui. Research on multi-model integrated precipitation forecast based on feed forward neural network [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(1): 117-128. |
| [4] | CAO Pingping, XIAO Dixiang, LONG Keji, WANG Jiajin, YANG Kangquan. Deviation correction of precipitation forecast by ECMWF model based on quantile mapping method in Sichuan Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(4): 666-675. |
| [5] | QIAO Jinrong, YUAN Xinpeng, LIANG Xudong, XIE Yanxin. Application of agglomerative hierarchical clustering method in precipitation forecast assessment [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(4): 690-699. |
| [6] | JIAO Yang, ZHANG Yongjing, YIN Chengmei, CHU Yingjia. Response of summer rainstorm in Shandong Province to change of spring atmospheric heat sources in southeastern Tibet Plateau and its adjacent areas [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(3): 406-414. |
| [7] | LI Tao, CHEN Jie, WANG Fang, HAN Rui. A correction algorithm of summer precipitation prediction based on neural network in China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(2): 308-316. |
| [8] | REN Xuwei, CHEN Xiaoyan, CAI Dihua, LI Lanqian, SHAO Aimei. Evaluation of Precipitation Forecast Based on GRAPES_Meso Model and Its Cloud Analysis System in Northwest China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(2): 333-344. |
| [9] | WANG Binyan, CHEN Chaoping, HUANG Chuhui, . Application of SAL Method to Verification of Precipitation Forecasts in Sichuan Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(03): 472-479. |
| [10] | SHANG Lin, GU Weizong, TANG Zidong, MENG Xiangxin, LUO Jiali, CUI Qiang. Decadal Variation of the Relationship Between Summer Precipitation in Shandong Province and Previous Winter SST over the Equatorial Central and Eastern Pacific [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(4): 552-558. |
| [11] | WANG Haiyan1, TIAN Gang1, XU Weili2, JIN Qi3, CHEN Lianghua2, CHEN Xuan1. Evaluation and Inspection of ECMWF Model Forecast Product During Dispatch Key Periods in Upper Reaches of the Yangtze River Basin [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(1): 142-147. |
| [12] | LI Ruiying1, REN Chongyong1, CHEN Nan1, JIANG Xiaodong2. Simulation of Spring Phenophase of Typical Plants in Southwestern Shandong Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(6): 1010-1016. |
| [13] | HU Yiqing,ZHAO Haijun, ZHUANG Zhong, GAO Anchun,CAO Zhangchi, ZHANG Pinzhu, LIU Yingjie. Mesoscale Structure and Lightning Features of a Convective Weather Process in Center of Shandong Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(5): 830-837. |
| [14] | WAN Mingbo1, DONG Xuguang2. Nonuniformity Characteristics of Precipitation in Shandong Province During 1961-2010 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(4): 566-573. |
| [15] | BAI Hui1,2,WU Zhanping1,LI Zhongyan1,ZHOU Tao1. Application of DERF Products to Forecast Precipitation Based on PCA Regression Forecast Model in Guizhou [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(2): 344-348. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||