Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2025, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (6): 920-930.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-06-0920
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Fine-scale spatio-temporal characteristics of short-term heavy precipitation and topographic influences in Zhengzhou
CUI Huihui1,2( ), LI Rong1,2(
), LI Rong1,2( ), SUN Cunyong1,2
), SUN Cunyong1,2
1. Key Laboratory of Agrometeorological Support and Applied Technique ,CMA Zhengzhou 450003, China 2. Zhengzhou Meteorological Bureau of Henan Province Zhengzhou 450005, China
-
Received:2025-03-07Revised:2025-08-25Online:2025-12-31Published:2026-01-19
郑州短时强降水精细时空分布特征及地形影响
1.中国气象局农业气象保障与应用技术重点实验室 河南 郑州 450003 2.河南省郑州市气象局 河南 郑州 450005
-
通讯作者:李荣 -
作者简介:崔慧慧(1988—),河南郑州人,高级工程师,主要从事灾害性天气预报预警技术研究。E-mail:huihuismile2008@126.com。 -
基金资助:河南省科技厅科技攻关计划项目(242103810092);全国暴雨研究开放基金(BYKJ2025M05);河南省气象局重点实验室面上项目(KM202334);河南省气象局大城市气象预报服务创新团队共同资助
CLC Number:
Cite this article
CUI Huihui, LI Rong, SUN Cunyong. Fine-scale spatio-temporal characteristics of short-term heavy precipitation and topographic influences in Zhengzhou[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(6): 920-930.
崔慧慧, 李荣, 孙存永. 郑州短时强降水精细时空分布特征及地形影响[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(6): 920-930.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-06-0920
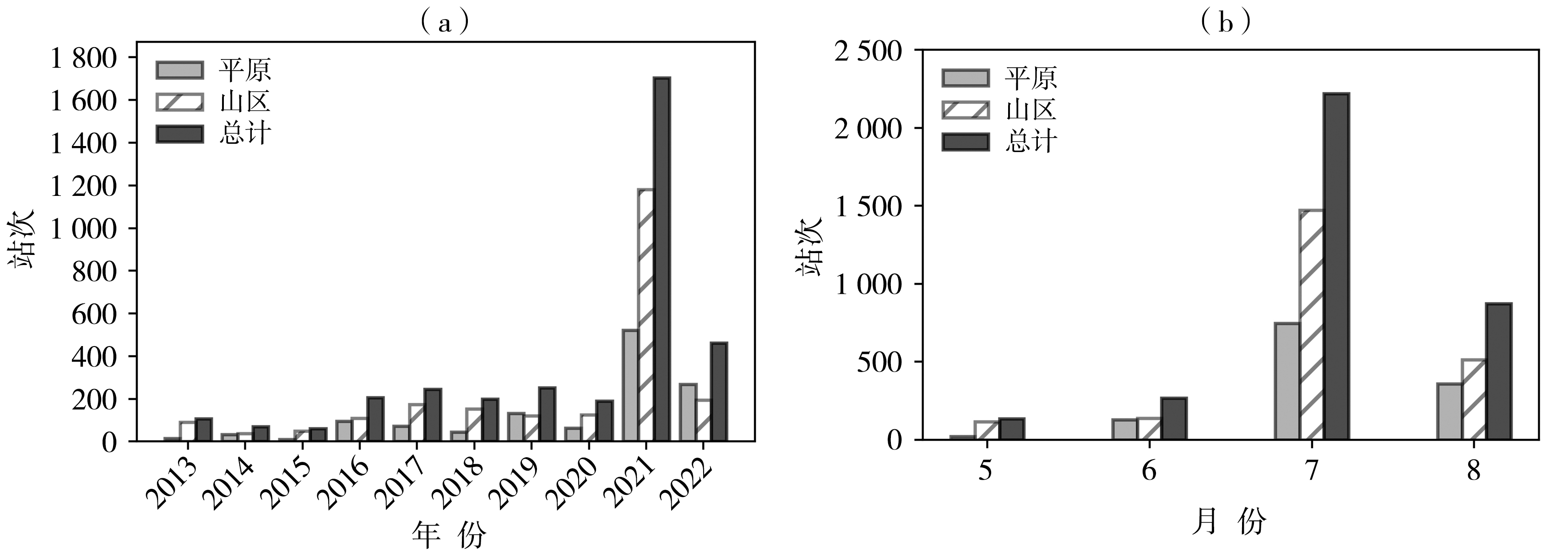
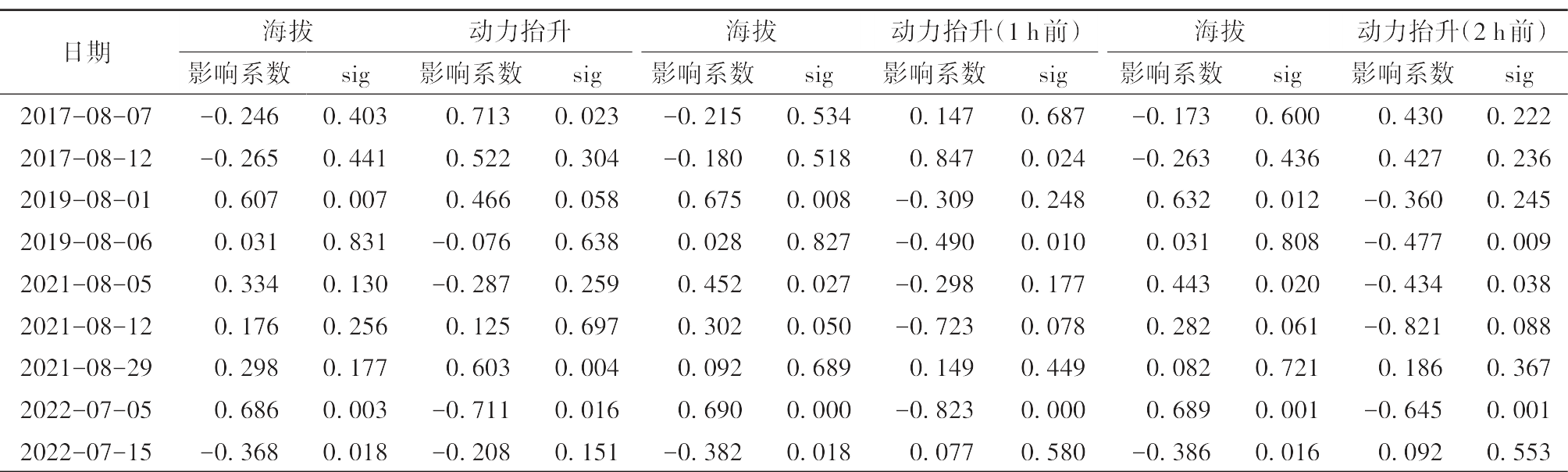
Fig.2 The yearly (a) and monthly (May to August) (b) variations of the number of stations occurring short-term heavy precipitation from 2013 to 2022 in Zhengzhou
| 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5月 | 52.3 | 72.6 | 29.3 | — | 77.8 | 68.6 | 27.7 | — | 39.2 | — |
| 6月 | 61.6 | 92.5 | — | 85.2 | 45.7 | 38.9 | 37.3 | 48.4 | 39.9 | 61.9 |
| 7月 | 121.8* | 60.9 | 41.8 | 79.2* | 58.3 | 84.7* | 64.9 | 56.1 | 201.9* | 103.7* |
| 8月 | 97.6 | 92.5* | 58.1* | 45.9 | 77.9* | 78.9 | 88.2* | 92.4* | 71.4 | 49.6 |
Tab.1 Maximums of short-term heavy precipitation intensity from May to August during the period of 2013-2022 in Zhengzhou
| 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5月 | 52.3 | 72.6 | 29.3 | — | 77.8 | 68.6 | 27.7 | — | 39.2 | — |
| 6月 | 61.6 | 92.5 | — | 85.2 | 45.7 | 38.9 | 37.3 | 48.4 | 39.9 | 61.9 |
| 7月 | 121.8* | 60.9 | 41.8 | 79.2* | 58.3 | 84.7* | 64.9 | 56.1 | 201.9* | 103.7* |
| 8月 | 97.6 | 92.5* | 58.1* | 45.9 | 77.9* | 78.9 | 88.2* | 92.4* | 71.4 | 49.6 |

Fig.3 Hourly variation of the number of stations occurring short-term heavy precipitation and maximum rainfall intensity from 2013 to 2022 in Zhengzhou

Fig.4 Spatial distributions of station numbers (a, b) and precipitation intensity (c, d) for short-term heavy precipitation events with hourly rainfall equal to or greater than 20 mm (a, c) and equal to or greater than 50 mm (b, d) from 2013 to 2022 in Zhengzhou

Fig.5 The box plots of short-term heavy precipitation intensity (a), station numbers (b) and altitude in Zhengzhou (The R represents precipitation intensity, F represents the number of stations occurring short-term strong precipitation)

Fig.6 Meteorological conceptual model of short-term heavy precipitation in Zhengzhou (a) internal type of subtropical high pressure, (b) high-altitude northwest airflow type, (c) typhoon low pressure type, (d) high altitude trough type

Fig.7 The 925 hPa horizontal wind field (arrow vectors, Unit: m·s-1) and water vapor flux (the color shaded, Unit: g·cm-1·hPa-1·s-1) at 08:00 July 19 (a) and 08:00 July 20 (b), 2021 (The ● represents the location of Zhengzhou)

Fig.9 Surface wind field at 08:00 (a) and composite radar reflectivity at 09:00 (the color shaded, Unit: dBZ) (b) over Zhengzhou on 19 July 2021 (The red rectangle in figure 9 (a) denotes a mesoscale convergence zone, and the red rectangle in figure 9 (b) indicates an area with repeatedly triggered convection over the mountainous region)
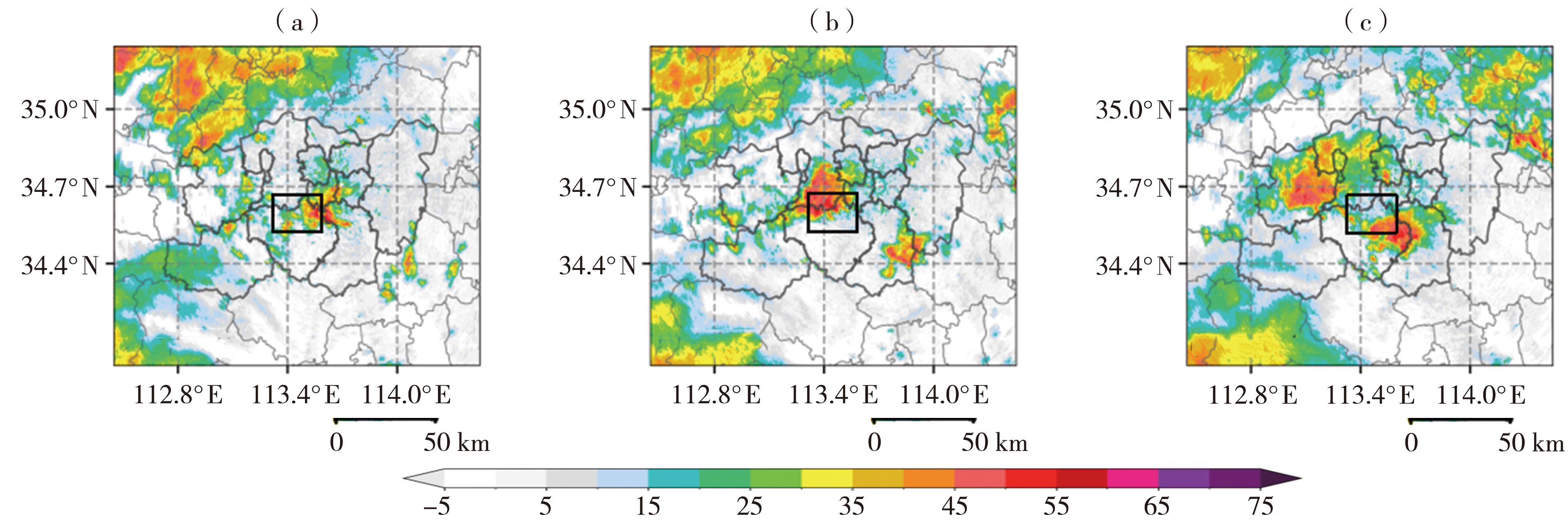
Fig.10 Radar composite reflectivity (Unit: dBZ) in Zhengzhou at 08:30 (a), 09:12 (b), and 10:00 (c) on 19 July 2021 (The black rectangle indicates the area of the windward slope in the eastern section of the Songshan Mountain)

Fig.11 Distribution of surface temperature (isolines, Unit: °C) (a) and dew point (isolines, Unit: °C) (b)overlaid on topography (the color shaded, Unit: m) in Zhengzhou at 08:00 on 19 July 2021
| [1] | 陈炯, 郑永光, 张小玲, 等, 2013. 中国暖季短时强降水分布和日变化特征及其与中尺度对流系统日变化关系分析[J]. 气象学报, 71(3): 367-382. |
| [2] | 陈敏, 陈豫英, 陈荣, 等, 2025. 贺兰山东麓暴雨天气分型及气象要素演变特征研究[J]. 干旱气象, 43(3): 413-423. |
| [3] | 崔慧慧, 李荣, 郜彦娜, 等, 2023. “7·20”郑州极端特大暴雨降水细节特征和成灾过程研究[J]. 灾害学, 38(2):114-120. |
| [4] | 付超, 谌芸, 单九生, 2017. 地形因子对降水的影响研究综述[J]. 气象与减灾研究, 40(4): 318-324. |
| [5] | 傅抱璞, 1988. 山地气候要素空间分布的模拟[J]. 气象学报, 46(3): 319-326. |
| [6] | 傅抱璞, 1992. 地形和海拔对降水的影响[J]. 地理学报, 47(4): 302-314. |
| [7] | 高洁, 漆梁波, 2015. 上海地区短时强降水特点及其影响[J]. 气象与环境科学, 38(3): 52-60. |
| [8] | 黄小彦, 孙继松, 刘文婷, 2020. 地形作用下低空急流的演变与强降水对流风暴系统的相互作用[J]. 气象学报, 78(4): 551-567. |
| [9] | 廖菲, 洪延超, 郑国光, 2007. 地形对降水的影响研究概述[J]. 气象科技, 35(3): 309-316. |
| [10] | 林慧敏, 闵锦忠, 朱利剑, 等, 2023. 太行山地形在“7·19”华北持续性低涡暴雨中的作用[J]. 气象科学, 43(1): 46-58. |
| [11] | 孟丽霞, 许东蓓, 狄潇泓, 等, 2017. 甘肃省短时强降水的时空特征[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 11(6): 34-39. |
| [12] | 乔春贵, 高牧原, 梁钰, 等, 2024. 河南省近30年分级短时强降水时空分布特征分析[J]. 气象与环境科学, 47(3): 72-81. |
| [13] | 苏爱芳, 吕晓娜, 崔丽曼, 等, 2021. 郑州“7.20”极端暴雨天气的基本观测分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 40(5): 445-454. |
| [14] | 苏爱芳, 席乐, 吕晓娜, 等, 2022. 豫北“21·7”极端暴雨过程特征及成因分析[J]. 气象, 48(5): 556-570. |
| [15] | 孙继松, 2005. 气流的垂直分布对地形雨落区的影响[J]. 高原气象, 24(1): 62-69. |
| [16] | 唐永兰, 徐桂荣, 王晓芳, 等, 2023. 1992—2021年三峡库区夏季小时强降水时空分布特征[J]. 干旱气象, 41(4): 589-598. |
| [17] | 王国荣, 王令, 2013. 北京地区夏季短时强降水时空分布特征[J]. 暴雨灾害, 32(3): 276-279. |
| [18] | 汪小康, 崔春光, 王婧羽, 等, 2022. “21·7”河南特大暴雨水汽和急流特征诊断分析[J]. 气象, 48(5): 533-544. |
| [19] | 魏晓雯, 梁萍, 何金海, 2016. 上海地区不同类型短时强降水的大尺度环流背景特征分析[J]. 气象与环境科学, 39(2): 69-75. |
| [20] | 肖安, 尹小飞, 刘献耀, 2022. 江西省降水日变化时空分布特征[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5): 840-848. |
| [21] | 杨浩, 周文, 汪小康, 等, 2022. “21·7”河南特大暴雨降水特征及极端性分析[J]. 气象, 48(5): 571-579. |
| [22] | 杨丽杰, 曹彦超, 刘维成, 等, 2022. 陇东黄土高原旱区短时强降水的时空分布特征及地形影响研究[J]. 干旱气象, 40(6): 945-953. |
| [23] | 杨舒楠, 张芳华, 胡艺, 等, 2023. “23·7”华北特大暴雨过程的基本特征与成因初探[J]. 暴雨灾害, 42(5): 508-520. |
| [24] | 姚莉, 李小泉, 张立梅, 2009. 我国1小时雨量的时空分布特征[J]. 气象, 35(2): 80-87. |
| [25] | 俞小鼎, 2013. 短时强降水临近预报的思路与方法[J]. 暴雨灾害, 32(3): 202-209. |
| [26] | 张宁, 刘科男, 王遂缠, 等, 2020. 兰州市短时强降水的时空分布特征及地形因素[J]. 干旱气象, 38(2): 242-248. |
| [27] | 赵煜飞, 张强, 鞠晓慧, 等, 2024. 中国近30年短时极端降水特征分析[J]. 大气科学, 48(3): 1 144-1 156. |
| [28] | 郑祚芳, 王在文, 高华, 2013. 北京地区夏季极端降水变化特征及城市化的影响[J]. 气象, 39(12): 1 635-1 641. |
| [29] | 钟水新, 2020. 地形对降水的影响机理及预报方法研究进展[J]. 高原气象, 3 9(5): 1 122-1 132. |
| [30] | 周学云, 高文良, 吴亚平, 等, 2019. 定量研究雅安地形坡向坡度对降水分布的影响[J]. 气象科学, 39(3): 322-335. |
| [31] | LI Z H, LUO Y L, DU Y, et al, 2020. Statistical characteristics of pre-summer rainfall over South China and associated synoptic conditions[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan, Series II, 98: 213-233. |
| [32] | LUO Y L, JI H, ZHANG M Y, et al, 2023. On the influences of urbanization on the extreme rainfall over Zhengzhou on 20 July 2021: A convection-permitting ensemble modeling study[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 40: 393-409. |
| [33] | LUO Y L, WU M, REN F, et al, 2016. Synoptic situations of extreme hourly precipitation over China[J]. Journal of Climate, 29: 8 703-8 719. |
| [34] | RAO X N, ZHAO K, CHEN X C, et al, 2019. Influence of synoptic pattern and low-level wind speed on intensity and diurnal variations of orographic convection in summer over Pearl River Delta, South China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 124: 6 157-6 179. |
| [35] | ZHUO H, ZHAO P, ZHOU T J, 2014. Diurnal cycle of summer rainfall in Shandong of eastern China[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 34: 742-750. |
| [36] | ZHANG X H, YANG X M, WANG L, et al, 2021. Analysis on characteristic and abnormality of atmospheric circulations of the July 2021 extreme precipitation in Henan[J]. Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences, 44: 672-687. |
| [1] | REN Zhihan, NI Changjian, SHI Qiaoyu, CHEN Ning. Analysis of drought characteristics in Chengdu over the past 63 years based on the optimal probability distribution function [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(6): 844-853. |
| [2] | TANG Yonglan, XU Guirong, WANG Xiaofang, XIAO Yanjiao, QI Haixia, LENG Liang. Spatio-temporal distribution characteristics of summer hourly heavy rainfall in the Three Gorges Reservoir area from 1992 to 2021 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(4): 589-598. |
| [3] | YANG Lijie, CAO Yanchao, LIU Weicheng, XU Lili, ZHANG Hongfen, SUN Zizhu. Research on spatio-temporal distribution characteristics of short-term heavy rainfall and terrain influence in the Loess Plateau arid region of eastern Gansu [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(6): 945-953. |
| [4] | LIN Chunying, WANG Qihua, LI Hongmei, GUO Qiang, HOU Yonghui, ZHOU Wanfu, ZHANG Liyan. Characteristics and disaster risk analysis of hail in agricultural area of eastern Qinghai Province in recent 60 years [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(3): 436-443. |
| [5] | GUO Guangfen, DU Liangmin, XIAO Ying, GAO Yaqi, WU Yao. Spatio-temporal Distribution Characteristics of Summer Extreme Precipitation in the Yangtze River Basin [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(2): 235-243. |
| [6] | DONG Junling, LIU Chao, SU Aifang. Impact of Urbanization on a Torrential Rain Process in Zhengzhou Region [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(6): 922-932. |
| [7] | YANG Wei, FENG Wen, CHEN Youlong. Numerical Experiments of Impact of Topography on Winter Rainstorm over the Hainan Island [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(5): 781-789. |
| [8] | LI Jian,WANG Chenghai. Variation Characteristics of Visibility at Zhengzhou Airport During 2004 - 2012 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2014, 32(5): 733-737. |
| [9] | LIU Yuanyuan,ZHOU Shunwu,WU Peipei,MA Siqi. Precipitable Water and the Precipitation Conversion Efficiency in Summer During the Recent 45 Years in Zhengzhou [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2013, 31(3): 486-490. |
| [10] | . Impacts of Soil Temperature on Developmental Stage and Yield of Winter Wheat in Zhengzhou of Henan Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2012, 30(1): 66-70. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||