Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2025, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 616-626.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-04-0616
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Correction of regional rainstorm forecasts in summer in Zhejiang based on synoptic classification and frequency matching
MAO Chengyan1( ), LI Haowen1(
), LI Haowen1( ), WANG Jianjiang1, HAN Chao1, ZHENG Qian1, TONG Jianping2
), WANG Jianjiang1, HAN Chao1, ZHENG Qian1, TONG Jianping2
- 1. Quzhou Meteorological Bureau of Zhejiang Province, Quzhou 324000, Zhejiang, China
2. Changshan County Meteorological Bureau of Zhejiang Province, Changshan 324200, Zhejiang, China
-
Received:2024-07-01Revised:2025-04-23Online:2025-08-31Published:2025-09-08
基于频率匹配法的浙江夏季区域性暴雨分类订正研究
毛程燕1( ), 李浩文1(
), 李浩文1( ), 王健疆1, 韩超1, 郑倩1, 童监萍2
), 王健疆1, 韩超1, 郑倩1, 童监萍2
- 1.浙江省衢州市气象局,浙江 衢州 324000
2.浙江省衢州市常山县气象局,浙江 常山 324200
-
通讯作者:李浩文 -
作者简介:毛程燕(1988—),女,浙江衢州人,高级工程师,主要从事暴雨、强对流天气预报研究。E-mail: mcy_yxt@163.com。 -
基金资助:浙江省自然科学基金重大项目(ZJMD24D050002);浙江省自然科学基金联合基金项目(LZJMD23D050001);衢州市科技局攻关项目(2024K069);广州市科技局项目(202201011093)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
MAO Chengyan, LI Haowen, WANG Jianjiang, HAN Chao, ZHENG Qian, TONG Jianping. Correction of regional rainstorm forecasts in summer in Zhejiang based on synoptic classification and frequency matching[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(4): 616-626.
毛程燕, 李浩文, 王健疆, 韩超, 郑倩, 童监萍. 基于频率匹配法的浙江夏季区域性暴雨分类订正研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(4): 616-626.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-04-0616

Fig.1 Cumulative frequency (a) and correction coefficients (b) of precipitation with different intensity thresholds, the probability density distribution of correction coefficients for all precipitation events (c) and rainstorm events (≥50 mm) (d)
| 评分 | 小雨以上 | 中雨以上 | 大雨以上 | 暴雨以上 | 大暴雨以上 | 特大暴雨以上 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TS | 订正前 | 0.884 | 0.705 | 0.539 | 0.300 | 0.117 | 0 |
| 订正后 | 0.902 | 0.707 | 0.555 | 0.342 | 0.195 | 0.133 | |
| ETS | 订正前 | 0.151 | 0.420 | 0.375 | 0.245 | 0.112 | 0 |
| 订正后 | 0.362 | 0.418 | 0.362 | 0.269 | 0.189 | 0.133 | |
| BIAS | 订正前 | 1.128 | 1.267 | 1.099 | 0.600 | 0.218 | 0 |
| 订正后 | 1.061 | 1.286 | 1.486 | 1.008 | 1.045 | 0.410 | |
| FPR | 订正前 | 0.115 | 0.260 | 0.331 | 0.385 | 0.413 | 0 |
| 订正后 | 0.079 | 0.264 | 0.403 | 0.492 | 0.680 | 0.597 | |
| FNR | 订正前 | 0.001 | 0.062 | 0.264 | 0.631 | 0.872 | 1.000 |
| 订正后 | 0.023 | 0.053 | 0.112 | 0.488 | 0.666 | 0.835 | |
| POD | 订正前 | 0.999 | 0.938 | 0.736 | 0.369 | 0.128 | 0 |
| 订正后 | 0.977 | 0.947 | 0.888 | 0.512 | 0.334 | 0.166 |
Tab.1 Verification scores before and after correction for precipitations with different levels during 2020-2023
| 评分 | 小雨以上 | 中雨以上 | 大雨以上 | 暴雨以上 | 大暴雨以上 | 特大暴雨以上 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TS | 订正前 | 0.884 | 0.705 | 0.539 | 0.300 | 0.117 | 0 |
| 订正后 | 0.902 | 0.707 | 0.555 | 0.342 | 0.195 | 0.133 | |
| ETS | 订正前 | 0.151 | 0.420 | 0.375 | 0.245 | 0.112 | 0 |
| 订正后 | 0.362 | 0.418 | 0.362 | 0.269 | 0.189 | 0.133 | |
| BIAS | 订正前 | 1.128 | 1.267 | 1.099 | 0.600 | 0.218 | 0 |
| 订正后 | 1.061 | 1.286 | 1.486 | 1.008 | 1.045 | 0.410 | |
| FPR | 订正前 | 0.115 | 0.260 | 0.331 | 0.385 | 0.413 | 0 |
| 订正后 | 0.079 | 0.264 | 0.403 | 0.492 | 0.680 | 0.597 | |
| FNR | 订正前 | 0.001 | 0.062 | 0.264 | 0.631 | 0.872 | 1.000 |
| 订正后 | 0.023 | 0.053 | 0.112 | 0.488 | 0.666 | 0.835 | |
| POD | 订正前 | 0.999 | 0.938 | 0.736 | 0.369 | 0.128 | 0 |
| 订正后 | 0.977 | 0.947 | 0.888 | 0.512 | 0.334 | 0.166 |

Fig.2 Mean geopotential height field at 500 hPa (solid lines, Unit: dagpm), mean wind field (arrow vectors, Unit: m·s-1) and mean water vapor flux (the color shaded, Unit: g·cm-1·hPa-1·s-1) at 850 hPa on rainstorm days over Zhejiang in summer during 2010-2023 (a) stationary front rainband type, (b) warm shear type, (c) subtropical high type, (d) cold trough type, (e) typhoon type, (f) typhoon inverted trough type
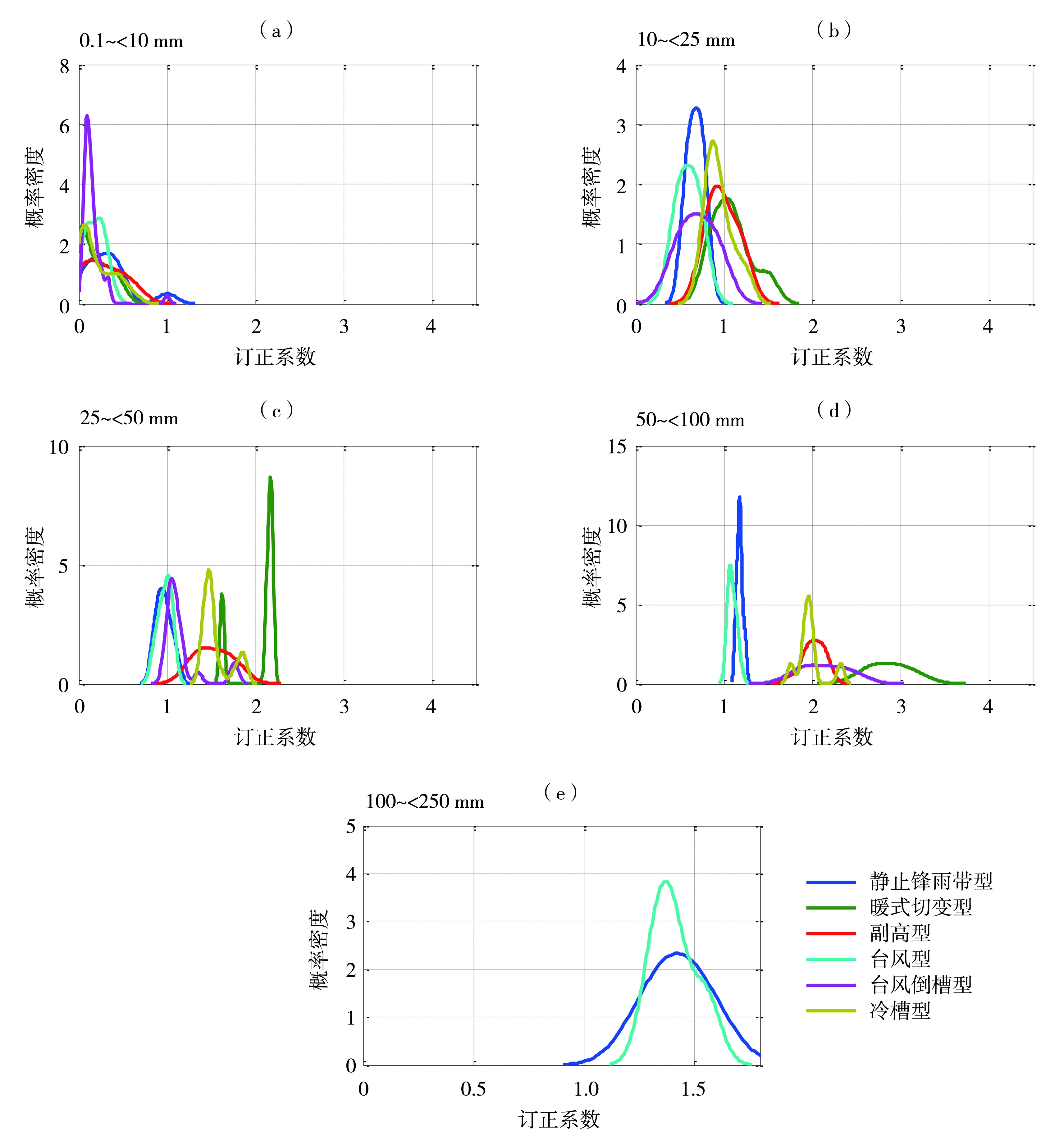
Fig.3 Probability density distributions of correction coefficients for precipitation with different types in summer from 2020 to 2023 (a) light rain, (b) moderate rain, (c) heavy rain, (d) rainstorm, (e) torrential rain
| 静止锋雨带型 | 暖式切变型 | 副高型 | 台风型 | 台风倒槽型 | 冷槽型 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TS | 订正前 | 0.335 | 0 | 0.023 | 0.433 | 0 | 0 |
| 订正后 | 0.368 | 0.118 | 0.128 | 0.456 | 0.391 | 0.154 | |
| ETS | 订正前 | 0.274 | 0 | 0.010 | 0.312 | 0 | 0.044 |
| 订正后 | 0.297 | 0.053 | 0.054 | 0.332 | 0.343 | 0.103 | |
| BIAS | 订正前 | 0.726 | 0 | 0.114 | 0.940 | 0 | 0 |
| 订正后 | 1.015 | 0.900 | 1.127 | 1.009 | 1.133 | 0.957 | |
| FPR | 订正前 | 0.404 | 0 | 0.778 | 0.376 | 0 | 1.000 |
| 订正后 | 0.466 | 0.778 | 0.787 | 0.376 | 0.471 | 0.727 | |
| FNR | 订正前 | 0.567 | 1.000 | 0.975 | 0.414 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| 订正后 | 0.458 | 0.800 | 0.760 | 0.371 | 0.400 | 0.739 | |
| POD | 订正前 | 0.433 | 0 | 0.025 | 0.586 | 0 | 0 |
| 订正后 | 0.542 | 0.200 | 0.241 | 0.629 | 0.600 | 0.261 | |
| RMSE | 订正前 | 20.351 | 24.562 | 23.542 | 29.136 | 19.072 | 22.944 |
| 订正后 | 22.347 | 32.600 | 28.560 | 32.786 | 20.434 | 28.846 | |
Tab.2 Forecast skill scores of rainstorms for different types from 2020 to 2023 using the frequency matching method
| 静止锋雨带型 | 暖式切变型 | 副高型 | 台风型 | 台风倒槽型 | 冷槽型 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TS | 订正前 | 0.335 | 0 | 0.023 | 0.433 | 0 | 0 |
| 订正后 | 0.368 | 0.118 | 0.128 | 0.456 | 0.391 | 0.154 | |
| ETS | 订正前 | 0.274 | 0 | 0.010 | 0.312 | 0 | 0.044 |
| 订正后 | 0.297 | 0.053 | 0.054 | 0.332 | 0.343 | 0.103 | |
| BIAS | 订正前 | 0.726 | 0 | 0.114 | 0.940 | 0 | 0 |
| 订正后 | 1.015 | 0.900 | 1.127 | 1.009 | 1.133 | 0.957 | |
| FPR | 订正前 | 0.404 | 0 | 0.778 | 0.376 | 0 | 1.000 |
| 订正后 | 0.466 | 0.778 | 0.787 | 0.376 | 0.471 | 0.727 | |
| FNR | 订正前 | 0.567 | 1.000 | 0.975 | 0.414 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| 订正后 | 0.458 | 0.800 | 0.760 | 0.371 | 0.400 | 0.739 | |
| POD | 订正前 | 0.433 | 0 | 0.025 | 0.586 | 0 | 0 |
| 订正后 | 0.542 | 0.200 | 0.241 | 0.629 | 0.600 | 0.261 | |
| RMSE | 订正前 | 20.351 | 24.562 | 23.542 | 29.136 | 19.072 | 22.944 |
| 订正后 | 22.347 | 32.600 | 28.560 | 32.786 | 20.434 | 28.846 | |
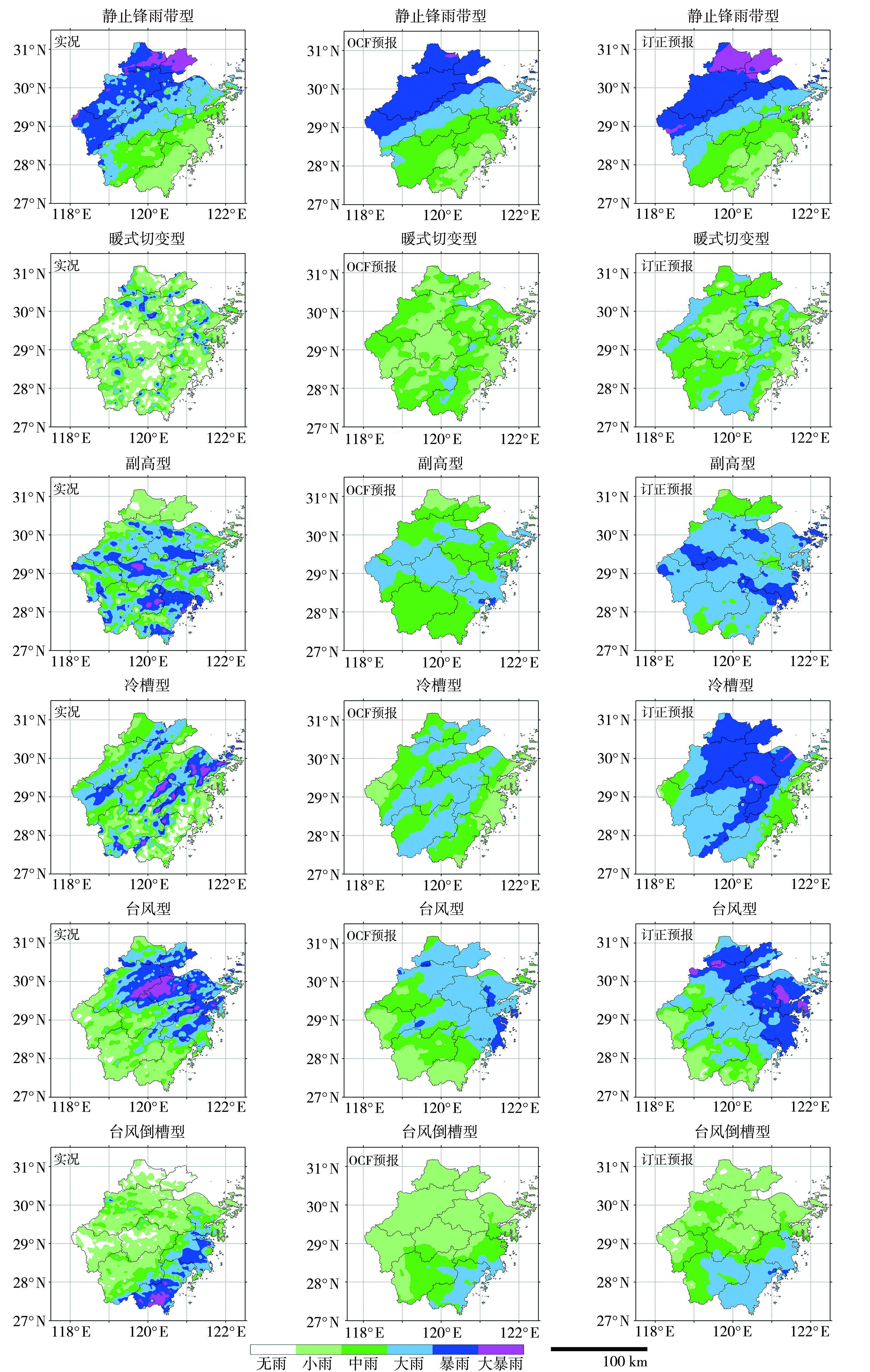
Fig.4 Comparison of actual, predicted by the OCF model and corrected precipitation for the stationary front rain belt type process on June 23, 2023, the warm shear type process on July 20, 2023, the subtropical high type process on August 16, 2021, the cold trough type on August 28, 2023, the typhoon type on July 23, 2021 and the typhoon inverted trough type process on August 3, 2021
| [1] |
蔡怡, 徐枝芳, 龚玺, 等, 2023. 2021年夏季CMA-MESO模式降水预报评估[J]. 干旱气象, 41(3): 503-515.
DOI |
| [2] | 陈静静, 叶成志, 吴贤云, 2016. 湖南汛期暴雨天气过程环流客观分型技术研究[J]. 暴雨灾害, 35(2): 119-125. |
| [3] | 陈永仁, 2024. 四川极端性暴雨的研究进展及新认识[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 44(1):1-9. |
| [4] | 陈贝, 董楚惠, 高文良, 等, 2024. 四川盆地西部2020年8月14—18日致洪强降水过程的地形影响分析[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 44(4):41-53. |
| [5] | 从靖, 吴振玲, 田笑, 等, 2021. 海河流域东北冷涡背景下的降水预报订正研究[J]. 气候与环境研究, 26(5): 556-568. |
| [6] |
戴泽军, 蔡荣辉, 彭莉莉, 等, 2019. 湖南持续性区域暴雨气候特征及暴雨落区分型[J]. 高原气象, 38(3): 573-582.
DOI |
| [7] | 冯志刚, 程兴无, 陈星, 等, 2013. 淮河流域暴雨强降水的环流分型和气候特征[J]. 热带气象学报, 29(5): 824-832. |
| [8] | 符娇兰, 宗志平, 代刊, 等, 2014. 一种定量降水预报误差检验技术及其应用[J]. 气象, 40(7): 796-805. |
| [9] | 高守亭, 周玉淑, 冉令坤, 2018. 我国暴雨形成机理及预报方法研究进展[J]. 大气科学, 42(4): 833-846. |
| [10] | 黄文彦, 雷正翠, 俞剑蔚, 等, 2021. 2017年6月上旬江苏南部一次极端暴雨过程分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 15(1):9-18. |
| [11] | 黄思先, 王保, 翟红楠, 等, 2021. 2019年5月湖北东部一次大暴雨过程诊断分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 15(3):38-45. |
| [12] |
焦洋, 郑丽娜, 张永婧, 等, 2024. 两种降水客观统计方法对ECMWF集合平均降水预报的订正研究[J]. 干旱气象, 42(2): 293-304.
DOI |
| [13] | 季晓东, 漆梁波, 2018. ECMWF模式降水预报与极端天气预报指数在暴雨预报中的评估与应用[J]. 暴雨灾害, 37(6): 566-573. |
| [14] | 井高飞, 罗丽, 肖辉, 等, 2020. 双偏振雷达在地面自动雨量观测资料质量控制中的应用研究[J]. 气象, 46(9): 1 189-1 198. |
| [15] | 江姣, 田凤国, 徐元照, 等, 2024. 重庆市长寿区暴雨特征分析及基于“酙料法”的暴雨预报模型研究[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 18(3):56-62. |
| [16] | 兰明才, 周莉, 蒋帅, 等, 2022. 副热带高压控制下湖南两次短时暴雨发生及系统维持机制对比分析[J]. 气象科技, 50(4): 512-525. |
| [17] | 梁钰, 王君, 吴璐, 2019. 淮河流域(河南段)连续性暴雨天气分型及环流背景[J]. 气象与环境科学, 42(2): 48-54. |
| [18] | 李俊, 杜钧, 陈超君, 2014. 降水偏差订正的频率(或面积)匹配方法介绍和分析[J]. 气象, 40(5): 580-588. |
| [19] | 李俊, 杜钧, 陈超君, 2015. “频率匹配法”在集合降水预报中的应用研究[J]. 气象, 41(6): 674-684. |
| [20] | 李莉, 李应林, 田华, 等, 2011. T213全球集合预报系统性误差订正研究[J]. 气象, 37(1): 31-38. |
| [21] |
李晓容, 张雪蓉, 濮梅娟, 2014. 梅汛期江淮切变线暴雨与非暴雨演变过程的合成对比分析研究[J]. 高原气象, 33(1): 199-209.
DOI |
| [22] | 刘佳, 陈艳, 王曼, 等, 2023. ERA-Interim及ERA5在中国西南复杂地形区的适用性对比分析[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 43(1): 95-103. |
| [23] | 毛程燕, 马依依, 顾振海, 等, 2021. 2020年春末夏初浙江省三次暖区暴雨过程诊断分析[J]. 气象科技, 49(6): 903-912. |
| [24] | 潘欣, 马依依, 毛程燕, 等, 2023. 基于聚类分析的浙江省汛期OCF降水预报分区订正试验[J]. 暴雨灾害, 42(6): 716-723. |
| [25] | 彭莉莉, 谢傲, 罗伯良, 等, 2018. 湖南汛期区域持续性暴雨环流型与暴雨落区关系[J]. 中国科学技术大学学报, 48(7): 580-593. |
| [26] | 邵立瑛, 郑淋淋, 朱红芳, 等, 2024. 潜热对江淮地区一次特大暴雨过程维持机制研究[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 18(3):56-62. |
| [27] | 田莹, 叶成志, 姚蓉, 2022. 2008—2018年江南暖区暴雨特征[J]. 大气科学学报, 45(1): 51-64. |
| [28] |
王彬雁, 王佳津, 肖递祥, 等, 2024. 四个数值预报模式对四川强降水过程预报能力评估[J]. 干旱气象, 42(2): 315-323.
DOI |
| [29] | 王丽芳, 漆梁波, 周伟, 等, 2021. 频率匹配技术在暴雨预报中的应用及改进分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 40(4):352-361. |
| [30] | 王雪, 何晓凤, 孙逸涵, 等, 2021. 基于数值预报和多方法集成的精细化站点预报技术研究[J]. 气象与环境科学, 44(5): 87-95. |
| [31] | 吴乃庚, 温之平, 邓文剑, 等, 2020. 华南前汛期暖区暴雨研究新进展[J]. 气象科学, 40(5): 605-616. |
| [32] | 吴启树, 韩美, 刘铭, 等, 2017. 基于评分最优化的模式降水预报订正算法对比[J]. 应用气象学报, 28(3): 306-317. |
| [33] | 辛辰, 漆梁波, 2018. ECMWF模式对南方春雨期降水预报的检验和分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 37(4): 383-391. |
| [34] | 俞燎霓, 胡波, 曹美兰, 等, 2010. 浙江梅雨气候特征及其梅汛期暴雨的形势分析[J]. 科技通报, 26(5): 782-786. |
| [35] | 张端禹, 郑彬, 汪小康, 等, 2015. 华南前汛期持续暴雨环流分型初步研究[J]. 大气科学学报, 38(3): 310-320. |
| [36] | 张富龙, 陈长胜, 李楠, 等, 2021. 基于EC数据通过“配料法”构建吉林省暴雨预报模型[J]. 气象灾害防御, 28(3): 18-23. |
| [37] | 张萍萍, 龙利民, 张宁, 等, 2012. “分型配料法” 在湖北省暴雨预报中的应用研究[J]. 热带气象学报, 28(5): 771-776. |
| [38] | 赵瑞霞, 代刊, 金荣花, 等, 2020. OTS、MOS和OMOS方法及其优化组合应用于72 h内逐3 h降水预报的试验分析研究[J]. 气象, 46(3): 420-428. |
| [39] | 赵娴婷, 闵爱荣, 廖移山, 等, 2021. 2020年4—10月我国主要暴雨天气过程简述[J]. 暴雨灾害, 40(6): 675-686. |
| [40] | 智协飞, 吕游, 2019. 基于频率匹配法的中国降水多模式预报订正研究[J]. 大气科学学报, 42(6): 814-823. |
| [41] | 周迪, 陈静, 陈朝平, 等, 2015. 暴雨集合预报-观测概率匹配订正法在四川盆地的应用研究[J]. 暴雨灾害, 34(2): 97-104. |
| [42] | 周胜男, 王东勇, 冯颖, 等, 2024. 安徽省2021年梅雨期降水预报检验分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 18(1):165-173. |
| [43] | 朱佳蓉, 漆梁波, 2013. 上海地区近12年暴雨个例分型及预报要点[J]. 大气科学研究与应用(1): 13-24. |
| [44] | 朱占云, 陈光宇, 姜瑜君, 等, 2016. 浙江省六大水库流域面雨量模式预报效果检验[J]. 气象与环境学报, 32(3): 28-33. |
| [45] | 朱占云, 潘娅英, 骆月珍, 等, 2017. 浙江省水库流域面雨量的多模式预报效果分析与检验[J]. 气象与环境科学, 40(3): 93-100. |
| [46] | DANG J T, ZHENG J W, CAI H K, et al, 2024. Research on frequency matching correction techniques for South China precipitation ensemble forecast based on the GRAPES model[J]. Atmosphere, 15(4): 466. DOI: 10.3390/atmos 15040466. |
| [47] | DING Y H, LIU Y Y, HU Z Z, 2021. The record-breaking Mei-yu in 2020 and associated atmospheric circulation and tropical SST anomalies[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 38(12): 1 980-1 993. |
| [48] | FENG S, LIU Q, FU Y F, 2009. Precipitation under subtropical high conditions: Evidence and implications[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 2(4): 244-249. |
| [49] | HERSBACH H, BELL B, BERRISFORD P, et al, 2020. The ERA5 global reanalysis[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 146(730): 1 999-2 049. |
| [50] | LAVERS D A, HERSBACH H, RODWELL M J, et al, 2024. An improved estimate of daily precipitation from the ERA5 reanalysis[J]. Atmospheric Science Letters, 25(3): e1200. DOI:10.1002/asl.1200. |
| [51] | WANG S S, YU L, ZHU S P, 2020. Precipitation forecast on the township scale using the frequency matching method[J]. IOP Conference Series Earth and Environmental Science, 467(1): 012050. DOI: 10.1088/1755-1315/467/1/012050. |
| [52] | WU H, LI X M, SCHUMANN G J, et al, 2021. From China’s heavy precipitation in 2020 to a “Glocal” hydrometeorological solution for flood risk prediction[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 38(1): 1-7. |
| [1] | XIAO Yiqing, MA Yongyong, CHEN Xiaoting, AN Dawei, HUANG Shaoni. A short-time heavy precipitation process triggered by a cold front in the Hanjiang Basin of southern Shaanxi and its precipitation forecast verification [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(6): 972-983. |
| [2] | PAN Liujie, LIANG Mian, QI Chunjuan, LI Peirong, ZHU Qingliang. Characteristics of meteorological elements and objective forecast verification at the key venues of “the 14th National Games” [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(3): 491-502. |
| [3] | QIAO Jinrong, YUAN Xinpeng, LIANG Xudong, XIE Yanxin. Application of agglomerative hierarchical clustering method in precipitation forecast assessment [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(4): 690-699. |
| [4] | TIAN Xiao, YU Wentao, CONG Jing, ZHOU Hongmei. Fine prediction of hourly precipitation and air temperature of Tianjin based on statistical downscaling in ECMWF model [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(1): 135-145. |
| [5] | MIAO Qing, BAI Zibin, WANG Hongxia, GONG Yuanfa, DONG Chunqing. Abnormal characteristics of an extreme rainstorm process in autumn in Shanxi Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(06): 984-994. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||