Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2025, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (1): 76-87.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-01-0076
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Comparative analysis of characteristics and causes of summer extreme high temperatures in Zhejiang in 2022 and 2013
FU Yuan1( ), LIU Hanhua1, ZHOU Lingli1, ZHAO Junping1, MA Hao1, LU Tingting2, WEI Lei3, XUAN Zhuolin1
), LIU Hanhua1, ZHOU Lingli1, ZHAO Junping1, MA Hao1, LU Tingting2, WEI Lei3, XUAN Zhuolin1
- 1. Zhejiang Meteorological Observatory,Hangzhou 310000,China
2. Ningbo Meteorological Bureau of Zhejiang Province,Ningbo 315000,Zhejiang,China
3. China Meteorological Administration Weather Modification Centre,Beijing 100081,China
-
Received:2023-12-28Revised:2024-02-17Online:2025-02-28Published:2025-03-14
2022年与2013年浙江夏季极端高温特点和成因对比
付远1( ), 刘汉华1, 周玲丽1, 赵军平1, 马昊1, 陆婷婷2, 魏蕾3, 宣卓林1
), 刘汉华1, 周玲丽1, 赵军平1, 马昊1, 陆婷婷2, 魏蕾3, 宣卓林1
- 1.浙江省气象台,浙江 杭州 310000
2.浙江省宁波市气象局,浙江 宁波 315000
3.中国气象局人工影响天气中心,北京 100081
-
作者简介:付远(1991—),男,博士,主要从事灾害性天气预报。E-mail:1427686349@qq.com。 -
基金资助:浙江省气象科技计划项目(2021ZD05);浙江省气象科技计划项目(2022YB03)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
FU Yuan, LIU Hanhua, ZHOU Lingli, ZHAO Junping, MA Hao, LU Tingting, WEI Lei, XUAN Zhuolin. Comparative analysis of characteristics and causes of summer extreme high temperatures in Zhejiang in 2022 and 2013[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(1): 76-87.
付远, 刘汉华, 周玲丽, 赵军平, 马昊, 陆婷婷, 魏蕾, 宣卓林. 2022年与2013年浙江夏季极端高温特点和成因对比[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(1): 76-87.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-01-0076

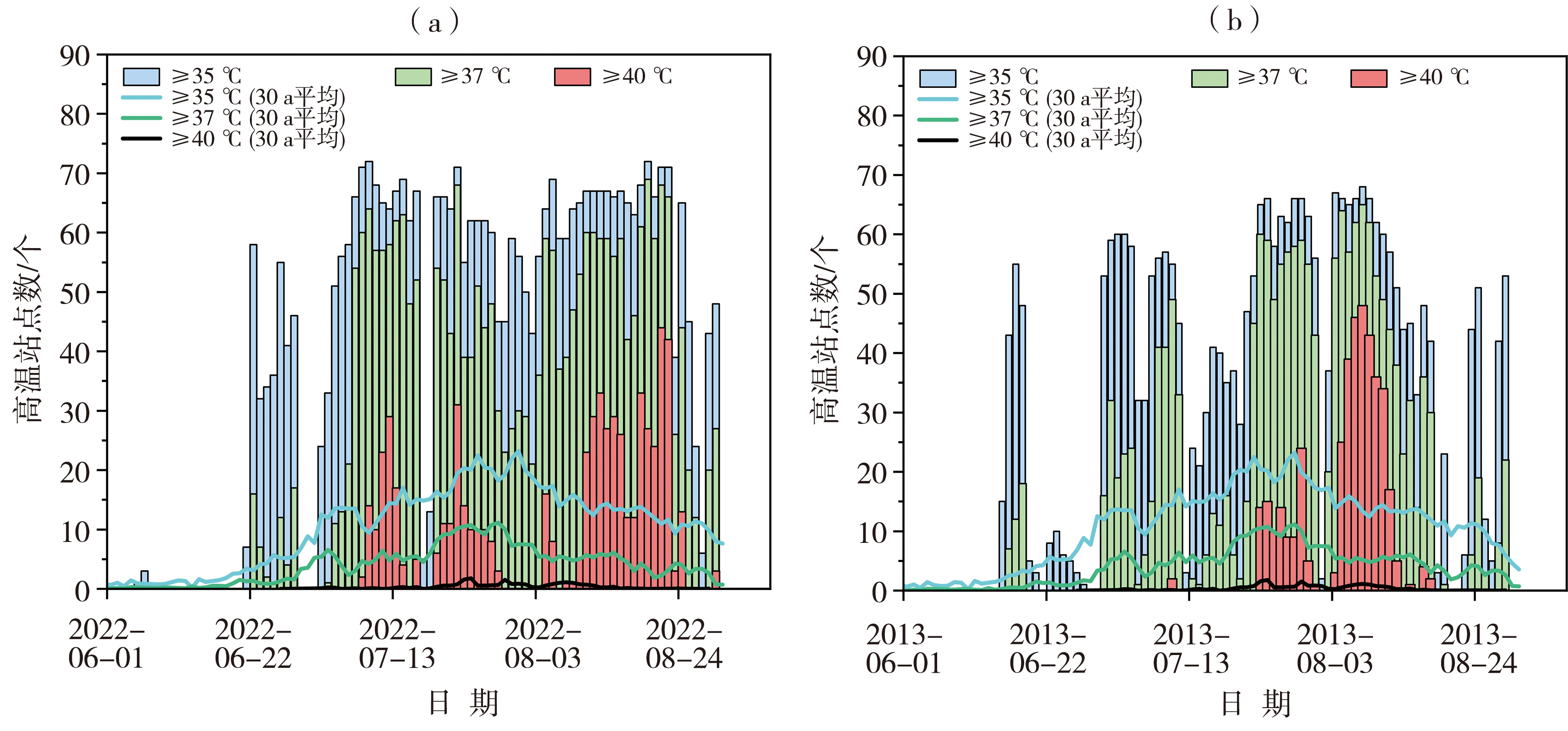
Fig.2 The spatial distribution of extreme values of high temperature (Unit: ℃)(a,e),and high temperature days (Unit: d) with daily maximum temperature equal to or more than 35 °C (b,f),37 °C (c,g),40 °C (d,h) in summers of 2022 (a,b,c,d) and 2013 (e,f,g,h) in Zhejiang Province (Interpolation is done using the inverse distance weighting method)
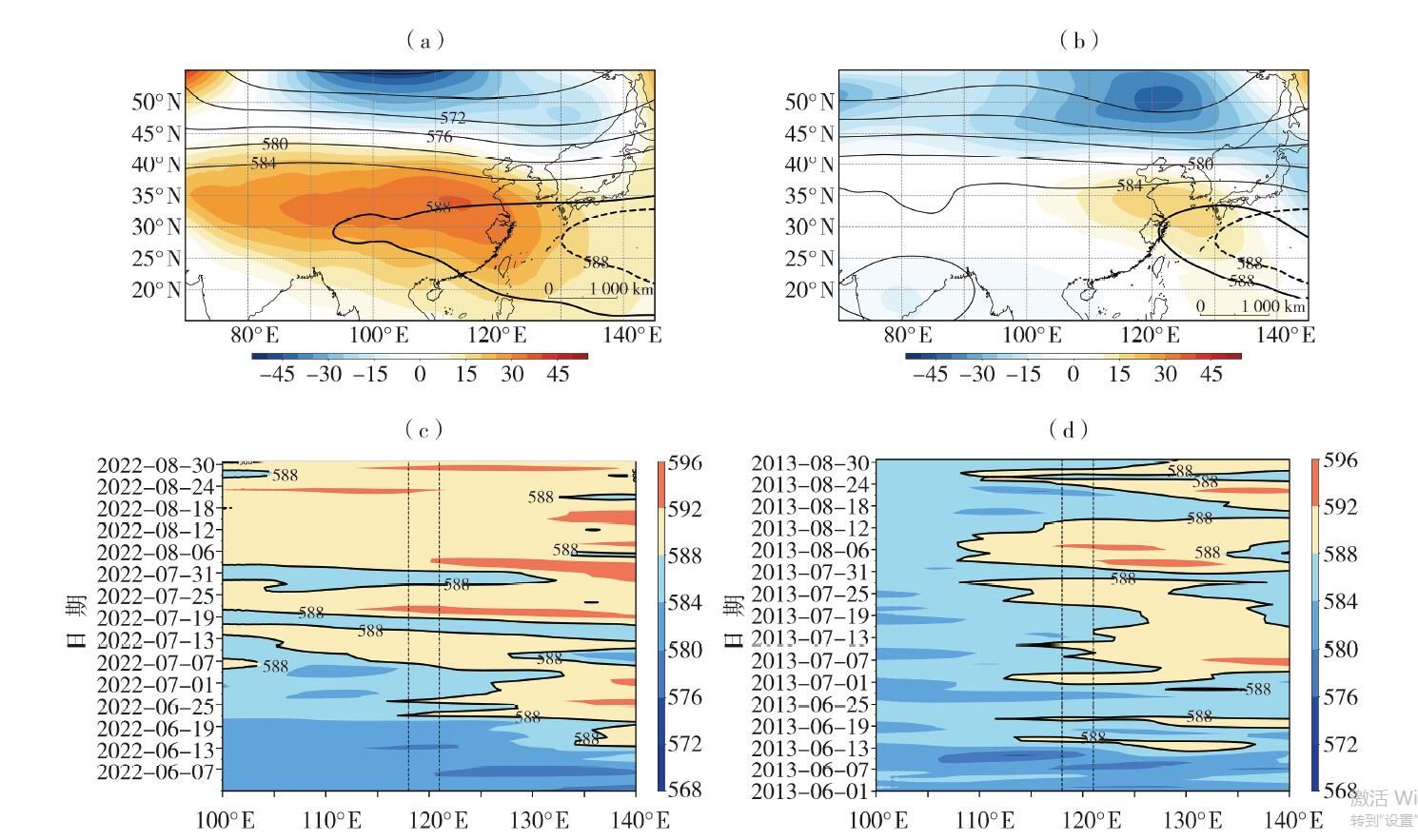
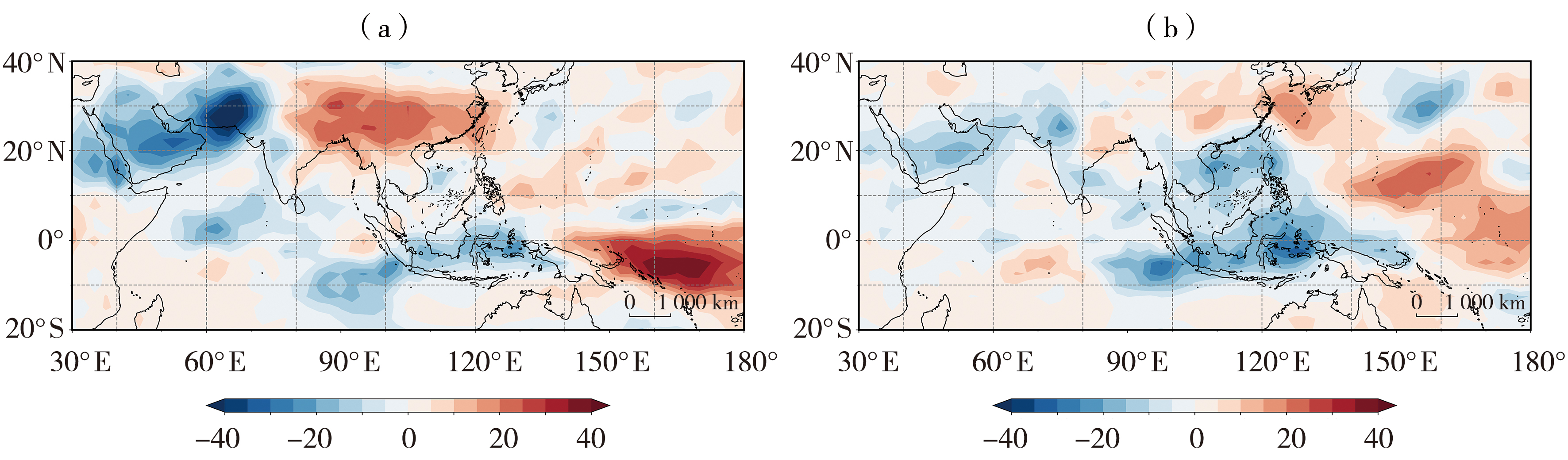
Fig.3 The 500 hPa geopotential height ( contours) and its anomalies ( the color shaded) from July to August in 2022 (a) and 2013 (b), and the longitude-time cross-sections of 500 hPa geopotential height averaged over 28° N-31°N in summers of 2022 (c) and 2013 (d) (Unit: dagpm) (The thick black solid line and thick dashed lines are the 588 dagpm lines in July-August and the climatological average,respectively. The area enclosed by the black dashed lines represents the location of Zhejiang Province (118° E-121°E), the same as below)

Fig.5 The 200 hPa geopotential height (contours) and its anomalies (the color shaded) from July to August in 2022 (a) and 2013 (b),and the longitude-time cross-sections of 200 hPa geopotential height averaged over 28°N-31°N in summers of 2022 (c) and 2013 (d)(Unit: dagpm) (The thick black solid line and thick dashed lines are the 1 252 dagpm lines in July-August and the climatological average,respectively)

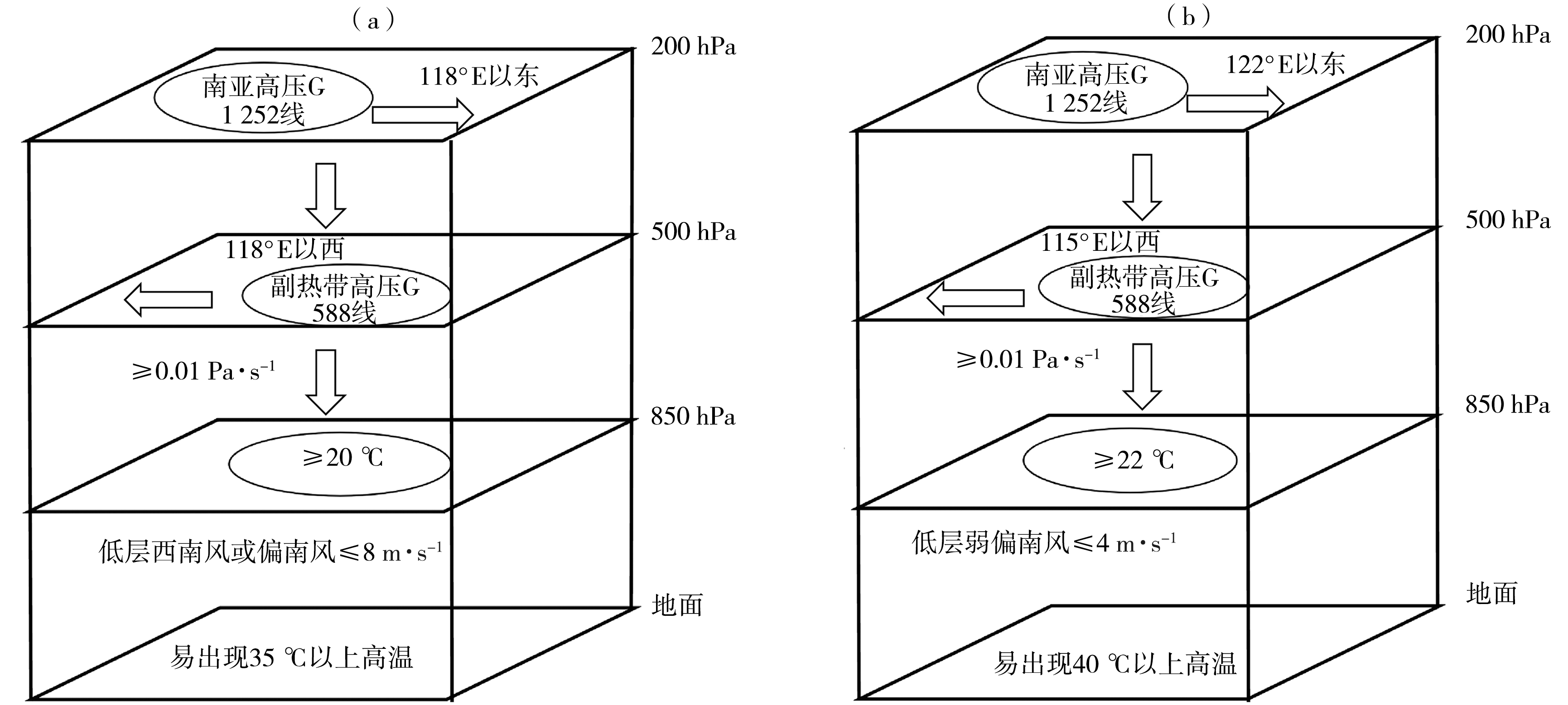
Fig.7 The time-height profiles of horizontal wind field (wind vectors,the color shaded for wind speed,Unit: m·s-1) and vertical velocity (red solid lines,Unit: Pa·s-1) averaged over the region (118°E-121°E,28°N-31°N) in summers of 2022 (a) and 2013 (b)

Fig.9 The zonal circulation (arrow vectors,Unit:m·s-1) and vertical velocity (the color shaded,Unit: Pa·s-1) anomalies within the scope of 28°N-31°N (a,b),and the meridional circulation (arrow vectors,Unit:m·s-1) and vertical velocity (the color shaded,Unit: Pa·s-1) anomalies within the scope of 118°E-121°E (c,d) in July and August in 2022 (a,c) and 2013 (b,d)
| [1] | 何慧根, 张驰, 吴遥, 等, 2023. 重庆夏季高温干旱特征及其对拉尼娜事件的响应[J]. 干旱气象, 41(6):873-883. |
| [2] | 贾子康, 郑志海, 封国林, 2020. 中国南方地区盛夏高温类型及其对应的大尺度环流和海温异常[J]. 气象学报, 78(6):928-944. |
| [3] | 靳振华, 管兆勇, 2013. 海洋性大陆区域OLR的气候低频振荡及其与中国降水的可能联系[J]. 热带气象学报, 29(5):705-716. |
| [4] | 李栋梁, 章基嘉, 吴洪宝, 1996. 青藏高原OLR的气候特征及其对北半球大气环流的影响[J]. 高原气象, 15(3):259-268. |
| [5] | 李莹, 叶殿秀, 高歌, 等, 2023. 2022年夏季中国气候特征及主要天气气候事件[J]. 大气科学学报, 46(1): 110-118. |
| [6] | 李永华, 徐海明, 刘德, 2009. 2006年夏季西南地区东部特大干旱及其大气环流异常[J]. 气象学报, 67(1):122-132. |
| [7] |
林纾, 李红英, 黄鹏程, 等, 2022. 2022年夏季我国高温干旱特征及其环流形势分析[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5):748-763.
DOI |
| [8] | 刘建军, 郑有飞, 吴荣军, 2008. 热浪灾害对人体健康的影响及其方法研究[J]. 自然灾害学报, 17(1):151-156. |
| [9] | 彭海燕, 周曾奎, 赵永玲, 等, 2005. 2003年夏季长江中下游地区异常高温的分析[J]. 气象科学, 25(4): 355-361. |
| [10] | 彭京备, 刘舸, 孙淑清, 2016. 2013年我国南方持续性高温天气及副热带高压异常维持的成因分析[J]. 大气科学, 40(5): 897-906. |
| [11] | 彭京备, 张庆云, 布和朝鲁, 2007. 2006年川渝地区高温干旱特征及其成因分析[J]. 气候与环境研究, 12(3):464-474. |
| [12] | 齐道日娜, 何立富, 2023. 2022年我国夏季极端高温阶段性特征及成因[J]. 应用气象学报, 34(4):385-399. |
| [13] | 全国气象防灾减灾标准化技术委员会, 2014. 区域性高温天气过程等级划分:QX/T 228—2014[S]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [14] | 任荣彩, 刘屹岷, 吴国雄, 2007. 1998年7月南亚高压影响西太平洋副热带高压短期变异的过程和机制[J]. 气象学报, 65(2):183-197. |
| [15] | 宋大伟, 管兆勇, 唐卫亚, 2011. 夏季海洋性大陆区域OLR年际变动与中国长江中上游旱涝的关系[J]. 热带气象学报, 27(4):560-568. |
| [16] | 孙博, 王会军, 黄艳艳, 等, 2023. 2022年夏季中国高温干旱气候特征及成因探讨[J]. 大气科学学报, 46(1):1-8. |
| [17] | 陶诗言, 朱福康, 1964. 夏季亚洲南部100毫巴流型的变化及其与西太平洋副热带高压进退的关系[J]. 气象学报, 34(4):385-396. |
| [18] | 王斌, 李跃清, 2011. 近10多年南亚高压活动特征及其影响的研究进展[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 31(2):75-80. |
| [19] | 王国复, 叶殿秀, 张颖娴, 等, 2018. 2017年我国区域性高温过程特征及异常大气环流成因分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 14(4):341-349. |
| [20] |
薛亮, 袁淑杰, 王劲松, 2023. 我国不同区域气象干旱成因研究进展与展望[J]. 干旱气象, 41(1):1-13.
DOI |
| [21] |
许婷婷, 杨霞, 周鸿奎, 2022. 1981—2019年新疆区域性高温天气过程时空特征及其环流分型[J]. 干旱气象, 40(2):212-221.
DOI |
| [22] | 周波涛, 钱进, 2021. IPCC AR6报告解读:极端天气气候事件变化[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 17(6):713-718. |
| [23] | 张礼平, 丁一汇, 陈正洪, 等, 2007. OLR与长江中游夏季降水的关联[J]. 气象学报, 65(1):75-83. |
| [24] |
张灵, 郭广芬, 熊开国, 等, 2023. 长江流域2022年夏季高温过程的成因分析[J]. 地理科学进展, 42(5): 971-981.
DOI |
| [25] | 张强, 姚玉璧, 李耀辉, 等, 2020. 中国干旱事件成因和变化规律的研究进展与展望[J]. 气象学报, 78(3): 500-521. |
| [26] | 张琼, 刘平, 吴国雄, 2003. 印度洋和南海海温与长江中下游旱涝[J]. 大气科学, 27(6):992-1 006. |
| [27] | 张琼, 吴国雄, 2001. 长江流域大范围旱滞与南亚高压的关系[J]. 气象学报, 59(5):569-577. |
| [28] | 张书余, 张夏琨, 田颖, 等, 2015. 模拟热浪天气对冠心病影响及其机理实验研究[J]. 气象, 41(6):761-770. |
| [29] | 张子涵, 楼茂园, 刘汉华, 等, 2018. 2013年7—8月浙江省异常高温特点及成因分析[J]. 科技通报, 34(4):55-61. |
| [30] | 赵军平, 刘汉华, 周春雨, 等, 2016. 2013年浙江夏季异常高温及环流特征分析[J]. 气象科技进展, 6(1):26-30. |
| [31] | ALMAZROUI M, SAEED F, SAEED S, et al, 2020. Projected change in temperature and precipitation over Africa from CMIP6[J]. Earth Systems and Environment, 4(3): 455-475. |
| [32] | BARTOLINI G, MORABITO M, CRISCI A, et al, 2008. Recent trends in Tuscany (Italy) summer temperature and indices of extremes[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 28(13): 1 751-1 760. |
| [33] | CHEN H P, SUN J Q, 2015. Assessing model performance of climate extremes in China: An intercomparison between CMIP5 and CMIP3[J]. Climatic Change, 129(1/2): 197-211. |
| [34] | DING Y H, 2007. Updated understanding of climate change sciences[J]. Advances in Climate Change Research, 3(2): 63. |
| [35] | DING Y H, SUN Y, 2006. Recent advances in climate change science[J]. Advances in Climate Change Research, 2(4): 161-167. |
| [36] | Environmental Protection Agency, 2021. Seasonality and Climate Change: A Review of Observed Evidence in the United States[R/OL]. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency:EPA430-R-21-002. https://www.epa.gov/climate-indicators/seasonality-and-climate-change. |
| [37] | IPCC, 2021. Summary for policymakers[R]//Climate change 2021:The physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge, UK and New York: Cambridge University Press. |
| [38] | KLUTSE N A B, QUAGRAINE K A, NKRUMAH F, et al, 2021. The climatic analysis of summer monsoon extreme precipitation events over west Africa in CMIP6 simulations[J]. Earth Systems and Environment, 5(1): 25-41. |
| [39] | LI Y F, LUO Y, DING Y H, 2004. The relationships between the global satellite-observed outgoing longwave radiation and the rainfall over China in summer and winter[J]. Advances in Space Research, 33(7): 1 089-1 097. |
| [40] | LIU G, WU R G, SUN S Q, et al, 2015. Synergistic contribution of precipitation anomalies over northwestern India and the South China Sea to high temperature over the Yangtze River Valley[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 32(9): 1 255-1 265. |
| [41] | LYU Z Z, GAO H, GAO R, et al, 2023. Extreme characteristics and causes of the drought event in the whole Yangtze River Basin in the midsummer of 2022[J]. Advances in Climate Change Research, 14(5): 642-650. |
| [42] | NASRALLAH H A, NIEPLOVA E, RAMADAN E, 2004. Warm season extreme temperature events in Kuwait[J]. Journal of Arid Environments, 56(2): 357-371. |
| [43] | WMO, 2018. Guide for Urban Integrated Hydro-meteorological[Z]//World Meteorological Organization. Climate and Environmental Services, Vol.1: Concepts and Methodology. Geneva. |
| [44] | ZHANG D Q, CHEN L J, YUAN Y, et al, 2023. Why was the heat wave in the Yangtze River valley abnormally intensified in late summer 2022?[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 18(3): 034014. DOI: 10.1088/1748-9326/acba30. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||