Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2025, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (1): 64-75.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-01-0064
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
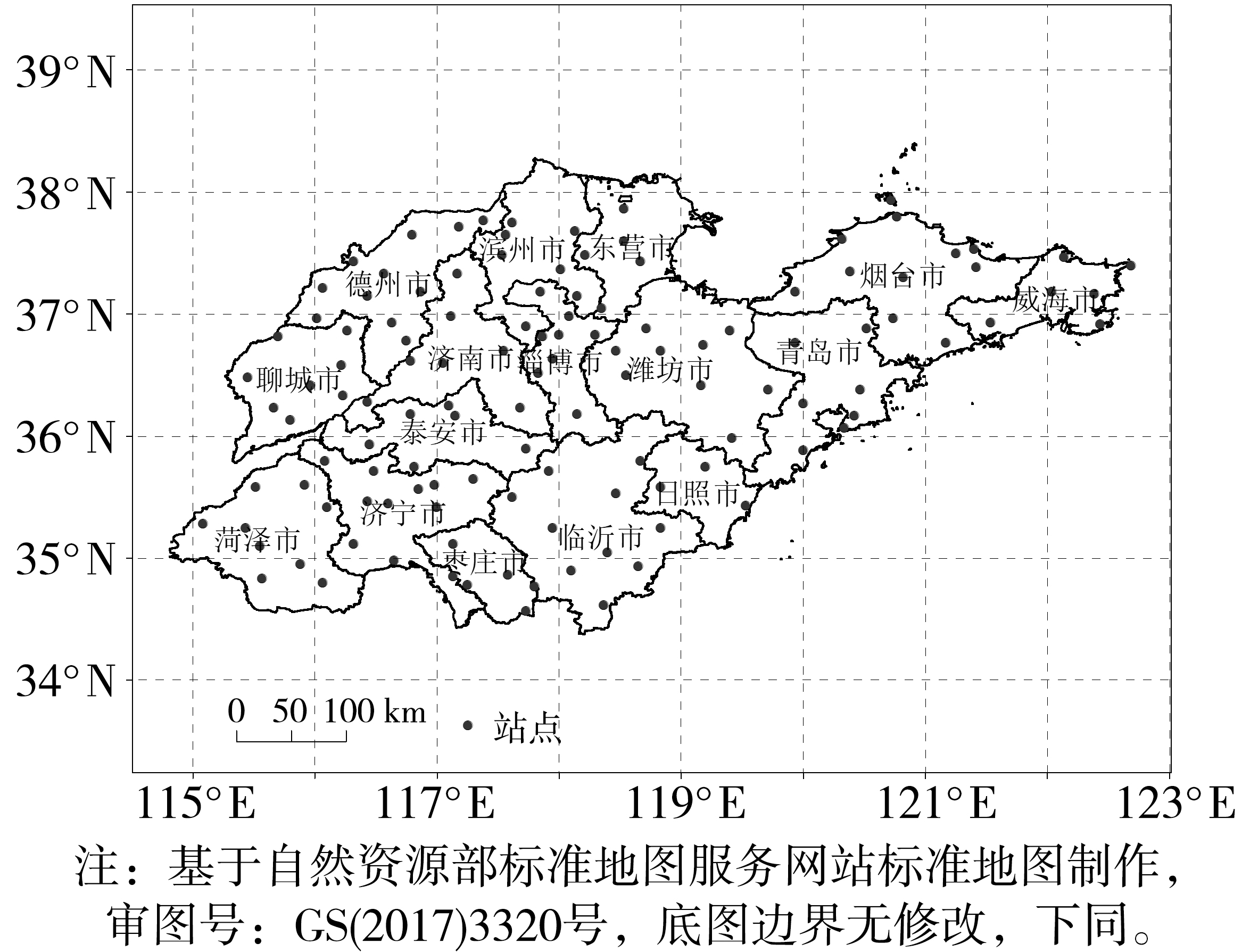
Distribution and variation characteristics of high temperature weather in Shandong
HUAN Haijun1( ), XU Weiping2, LIU Yan1, GE Ruiting1, CONG Jingcheng3, DONG Xuguang2(
), XU Weiping2, LIU Yan1, GE Ruiting1, CONG Jingcheng3, DONG Xuguang2( )
)
- 1. Zibo Meteorological Bureau of Shandong Province,Zibo 255048,Shandong,China
2. Shandong Provincial Climate Center,Ji’nan 250031,China
3. East China Air Traffic Management Bureau CAAC,Shanghai 200335,China
-
Received:2023-12-14Revised:2024-03-21Online:2025-02-28Published:2025-03-14
山东高温天气分布及变化特征
环海军1( ), 徐玮平2, 刘岩1, 葛瑞婷1, 丛菁成3, 董旭光2(
), 徐玮平2, 刘岩1, 葛瑞婷1, 丛菁成3, 董旭光2( )
)
- 1.山东省淄博市气象局,山东 淄博 255048
2.山东省气候中心,山东 济南 250031
3.中国民用航空华东地区空中交通管理局,上海 200335
-
通讯作者:董旭光(1979—),男,正高级工程师,主要从事气候应用和应用气象方面研究。E-mail:dongxugg@sina.com。 -
作者简介:环海军(1987—),男,高级工程师,主要从事气候应用和应用气象方面研究。E-mail:zbqxjhhj@163.com。 -
基金资助:山东省自然科学基金项目“山东夏季极端高温成因及其延伸期动力降尺度预测方法研究”(ZR2023QD086);山东省气象局气象科学技术研究项目“区域性高温过程风险识别与预评估技术研究”(2021SDQXZ04);山东省气象局气象科学技术研究项目“山东夏季复合型极端高温变化趋势及物理机制研究”(2022SDYD03);山东省气象局科学技术研究项目“风速数据一致性处理技术和应用研究”(2023SDBD02)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
HUAN Haijun, XU Weiping, LIU Yan, GE Ruiting, CONG Jingcheng, DONG Xuguang. Distribution and variation characteristics of high temperature weather in Shandong[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(1): 64-75.
环海军, 徐玮平, 刘岩, 葛瑞婷, 丛菁成, 董旭光. 山东高温天气分布及变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(1): 64-75.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-01-0064
| 等级 | 指标 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 轻度热浪(Ⅲ级) | 2.8≤IH<6.5 | 轻度(闷)热天气过程,对公众健康和社会生产造成一定影响 |
| 中度热浪(Ⅱ级) | 6.5≤IH<10.5 | 中度(闷)热天气过程,对公众健康和社会生产造成较为严重影响 |
| 重度热浪(Ⅰ级) | IH≥10.5 | 极度(闷)热天气过程,对公众健康和社会生产造成严重不利影响 |
Tab.1 High temperature heat wave grade division and explanation terms
| 等级 | 指标 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 轻度热浪(Ⅲ级) | 2.8≤IH<6.5 | 轻度(闷)热天气过程,对公众健康和社会生产造成一定影响 |
| 中度热浪(Ⅱ级) | 6.5≤IH<10.5 | 中度(闷)热天气过程,对公众健康和社会生产造成较为严重影响 |
| 重度热浪(Ⅰ级) | IH≥10.5 | 极度(闷)热天气过程,对公众健康和社会生产造成严重不利影响 |

Fig.2 Spatial distribution of annual mean daily maximum temperature (a) and annual maximum daily temperature (b) during 1981-2022 in Shandong Province (Unit: ℃)

Fig.3 Spatial distribution of annual mean high temperature days (a) and annual extreme high temperature days (b) during 1981-2022 in Shandong Province (Unit: d)

Fig.4 Spatial distribution of annual average days of warm nights (a) and annual extreme days of warm nights (b) during 1981-2022 in Shandong Province (Unit: d)

Fig.5 Spatial distribution of annual average mild (a, b), moderate (c, d) and severe (e, f) heat wave days (a, c, e) and extreme values (b, d, f) during 1981-2022 in Shandong Province (Unit: d)
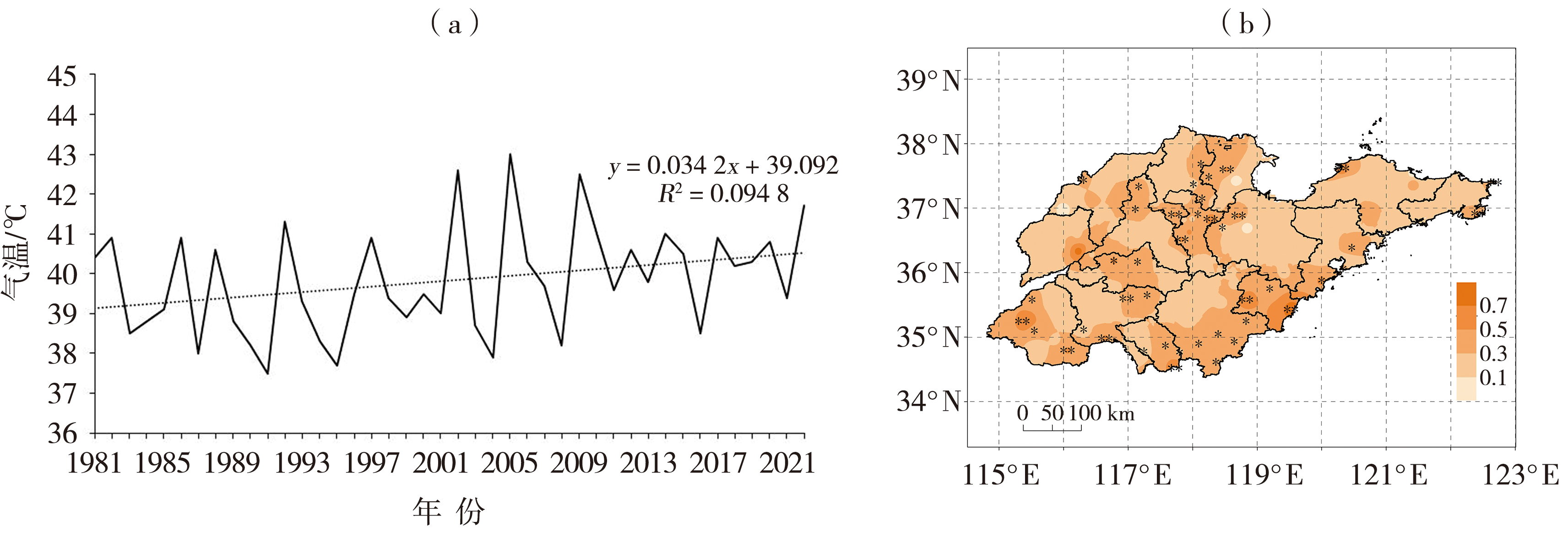
Fig.6 Variation trend of annual mean maximum temperature (a) and spatial distribution of annual maximum temperature climate tendency rate (Unit: ℃·(10 a)-1) (b) during 1981-2022 in Shandong Province (the “*”,“**” passing the significance test at 0.05 and 0.01,respectively,the same as below)
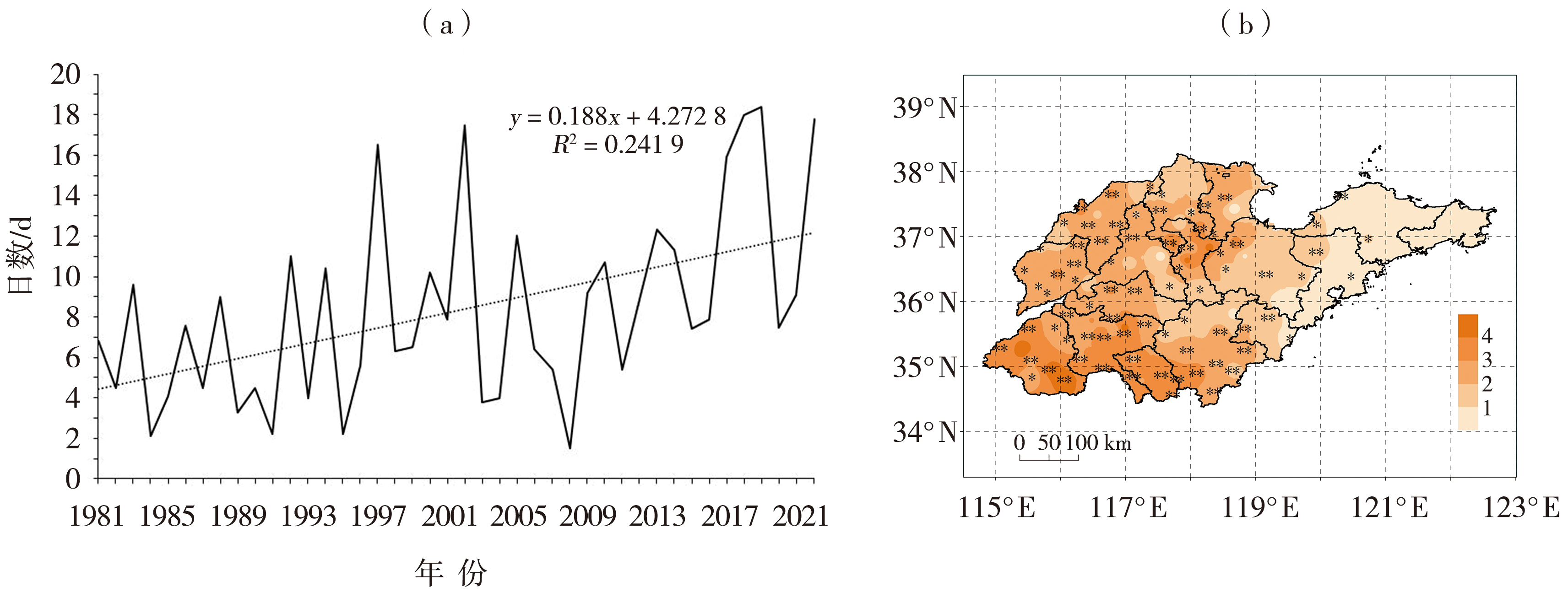
Fig.7 The variation trend of average annual high temperature days (a) and spatial distribution of climate tendency rate of annual high temperature days (Unit: d·(10 a)-1) (b) during 1981-2022 in Shandong Province
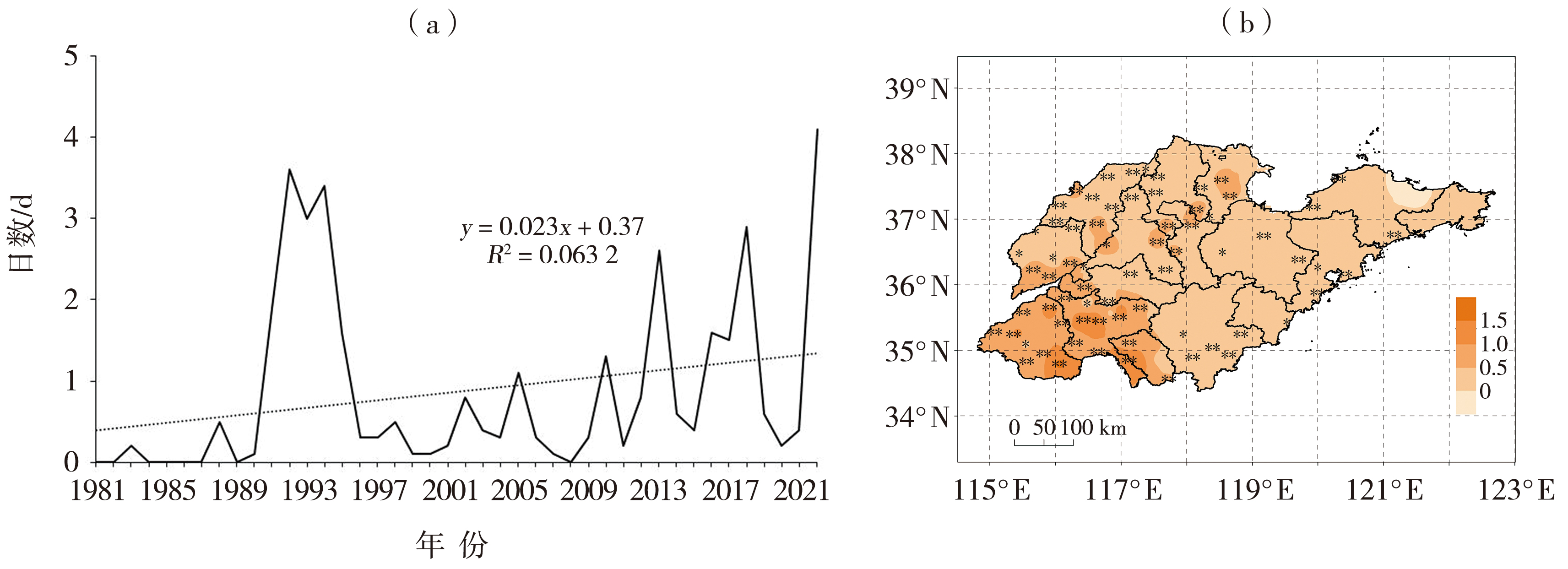
Fig.8 The variation trend of average annual warm night days (a) and spatial distribution of climate tendency rate of annual warm night days (Unit: d·(10 a)-1) (b) during 1981-2022 in Shandong Province

Fig.9 The variation of high temperature heat wave days (a, c, e) and spatial distribution of climate tendency rate (b, d, f) (Unit: d·(10 a)-1) of high temperature heat wave days with mild (a, b), moderate (c, d) and severe (e, f) grades during 1981-2022 in Shandong Province

Fig.10 The variation of high temperature heat wave days of dry type (a, c, e) and wet type (b, d, f) with mild (a, b), moderate (c, d) and severe (e, f) grades during 1981-2022 in Shandong Province
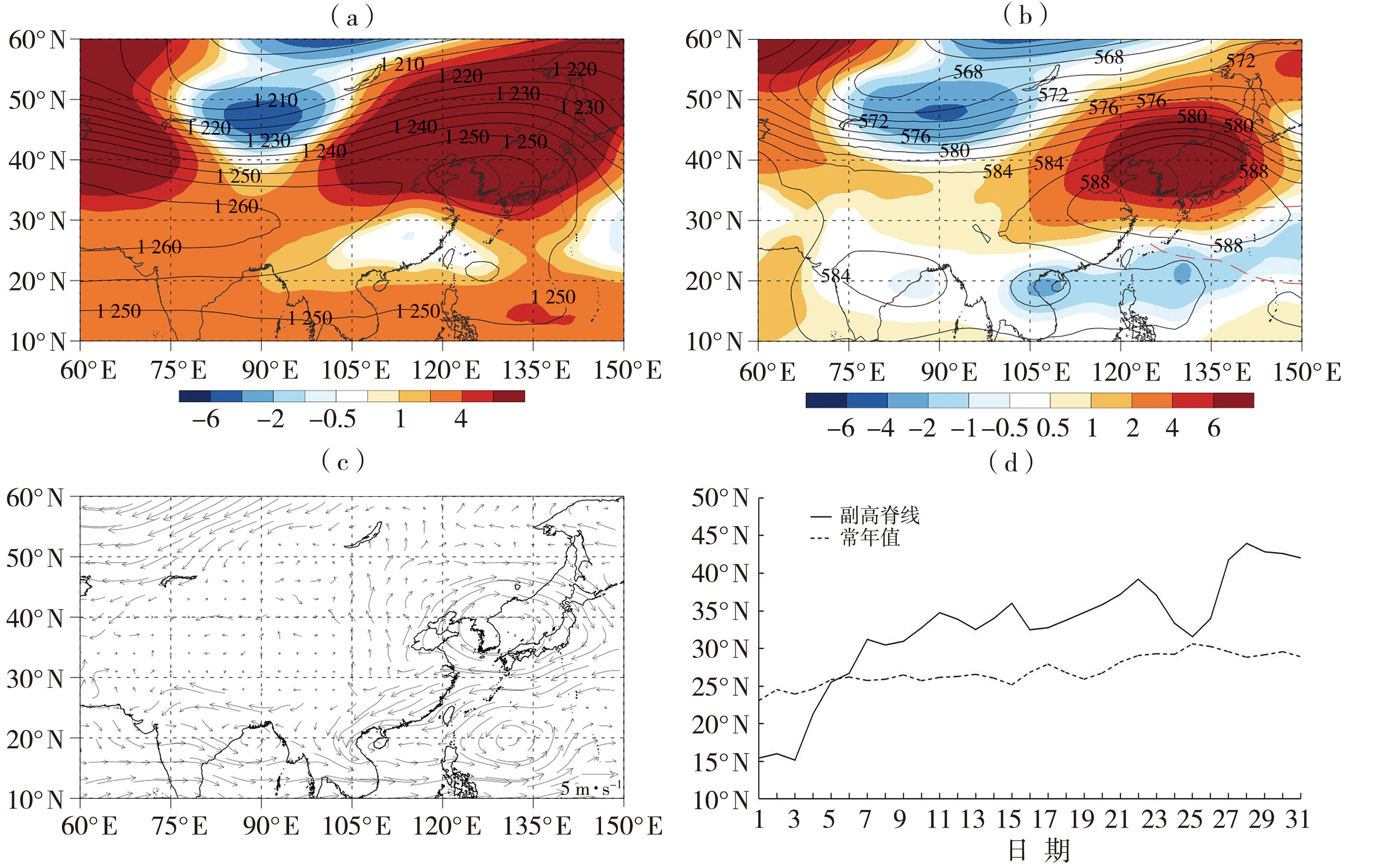
Fig.11 The 200 hPa (a), 500 hPa (b) mean geopotential height (contours) and anomaly fields (the color shaded) (Unit: dagpm), and 850 hPa wind anomaly field (arrow vectors, Unit: m·s-1) (c) on July 13-26, 2018, and daily variation of position of subtropical high ridge line on July 2018 (d)
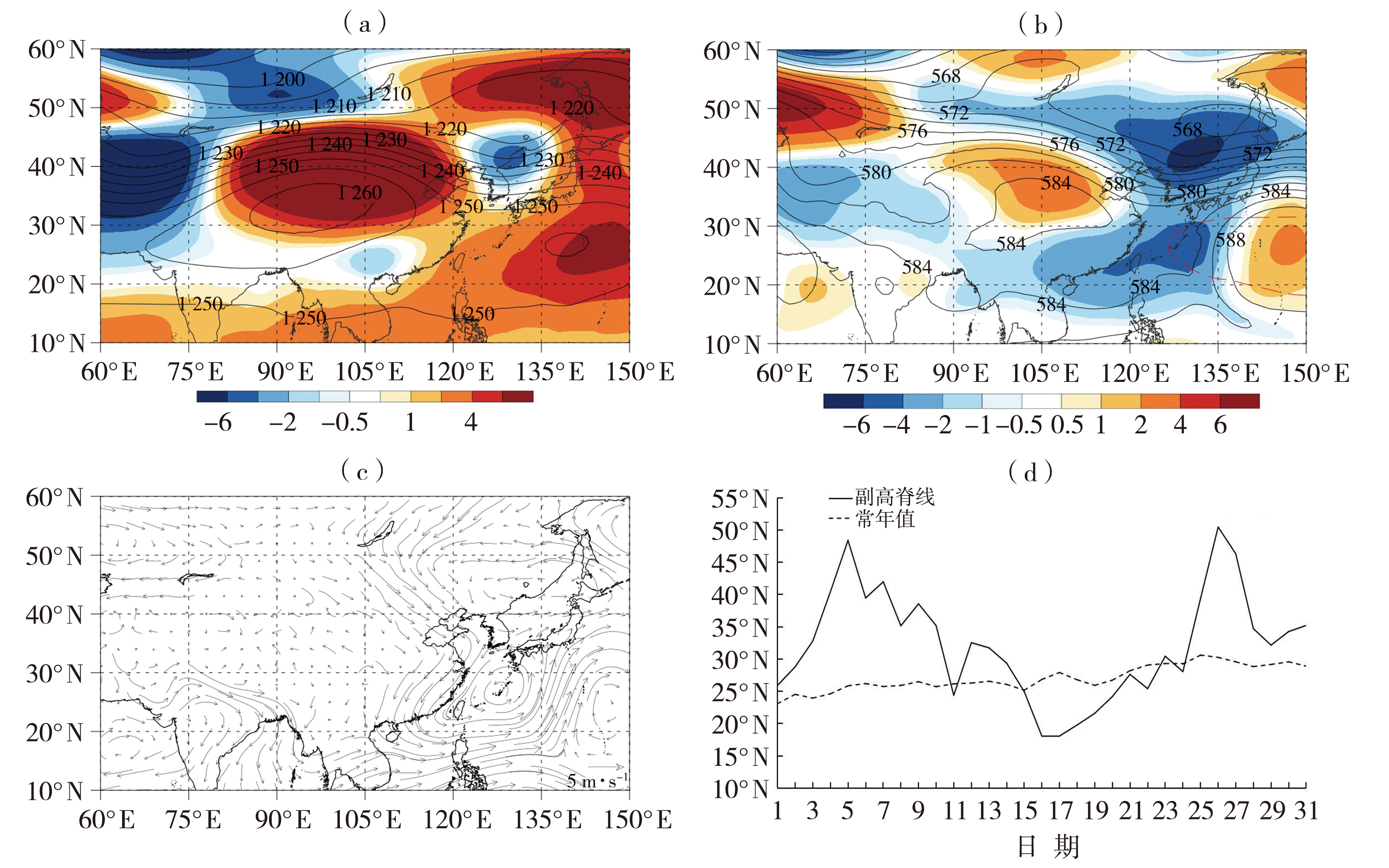
Fig.12 The 200 hPa (a), 500 hPa (b) mean geopotential height (contours) and its anomaly fields (the color shaded) (Unit: dagpm), and 850 hPa wind anomaly field (arrow vectors, Unit: m·s-1) (c) on July 8-15, 2002, and daily variation of position of subtropical high ridge line on July 2002 (d)
| [1] | 敖雪, 翟晴飞, 崔妍, 等, 2020. 不同升温情景下中国东北地区平均气候和极端气候事件变化预估[J]. 气象与环境学报, 36(5):40-51. |
| [2] | 董旭光, 周强, 刘焕彬, 等, 2020. 山东夏季极端热事件变化特征分析[J]. 海洋气象学报, 40(3):60-76. |
| [3] | 何慧根, 张驰, 吴遥, 等, 2023. 重庆夏季高温干旱特征及其对拉尼娜事件的响应[J]. 干旱气象, 41(6): 873-883. |
| [4] | 韩雪云, 赵丽, 姚俊强, 等, 2019. 西北干旱区极端高温时空变化特征分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 13(4):17-23. |
| [5] | 环海军, 张继波, 刘岩, 等, 2019. 鲁中地区极端高温变化特征分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 13(6):88-95. |
| [6] | 黄小梅, 仕仁睿, 刘思佳, 等, 2020. 西南地区夏季高温热浪时空分布特征及其成因[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 40(3):59-65. |
| [7] | 金红梅, 颜鹏程, 柏庆顺, 等, 2019. 近70 a来中亚极端高温事件时空分布[J]. 干旱气象, 37(4):550-556. |
| [8] | 马浩, 刘昌杰, 钱奇峰, 等, 2020. 2018年5月浙江省极端高温气候特征及环流背景[J]. 干旱气象, 38(6):909-919. |
| [9] | 彭京备, 孙淑清, 林大伟, 2023. 2022年8月长江流域持续性极端高温事件成因[J]. 应用气象学报, 34(5):527-539. |
| [10] | 齐道日娜, 何立富, 2023. 2022年我国夏季极端高温阶段性特征及成因[J]. 应用气象学报, 34(4):385-399. |
| [11] | 全国气象防灾减灾标准化技术委员会, 2012. 高温热浪等级:GB/T 29457—2012[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| [12] | 孙亦, 王婷, 2022. 四川省极端危害性高温变化特征分析[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 42(2):96-103. |
| [13] | 谈建国, 陆晨, 陈正洪, 2009. 高温热浪与人体健康[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [14] | 王婧, 董林, 2022. 2022年8月大气环流和天气分析[J]. 气象, 48(11):1487-1 496. |
| [15] | 王有恒, 谭丹, 赵红岩, 2012. 近50 a来甘肃省极端高温事件变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 30(3):410-414. |
| [16] |
许婷婷, 杨霞, 周鸿奎, 2022. 1981—2019年新疆区域性高温天气过程时空特征及其环流分型[J]. 干旱气象, 40(2):212-221.
DOI |
| [17] | 于浩慧, 周长艳, 陈超, 等, 2023. 2021年7—8月四川盆地高温热浪大气环流背景及影响分析[J]. 干旱气象, 41(6):923-932. |
| [18] | 张翠翠, 蔡鹏, 詹平华, 等, 2016. 济宁地区极端气温时空变化特征分析[J]. 山东气象, 36(4):13-18. |
| [19] | 周春花, 吴薇, 2023. 2022年夏季四川盆地区域性极端高温天气特征及成因分析[J]. 中国防汛抗旱, 33(8):29-35. |
| [20] | 邹瑾, 李君, 高理, 等, 2022. 山东区域性高温的变化特征及其对增暖的响应[J]. 气象科技, 50(6):802-811. |
| [21] | IPCC, 2023. Climate Change 2021: The physical science basis: Working Group I contribution to the sixth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change[R]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press: 923-1 054. |
| [22] | LU R Y, CHEN R D, 2016. A review of recent studies on extreme heat in China[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 9(2): 114-121. |
| [23] | MEDINA-RAMÓN M, SCHWARTZ J, 2007. Temperature, temperature extremes, and mortality: A study of acclimatisation and effect modification in 50 US cities[J]. Occupational and Environmental Medicine, 64(12): 827-833. |
| [1] | JIAO Yang, ZHENG Lina, ZHANG Yongjing, SU Yi. Correction of ECMWF ensemble average precipitation forecast using two objective precipitation statistical methods [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(2): 293-304. |
| [2] | WANG Xiaoci, WANG Jizhu, MENG Yingjie, LI Shuangjun. Characteristics and causes of fog along the Yangtze River from 2016 to 2020 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(5): 734-743. |
| [3] | JIAO Yang, ZHANG Yongjing, YIN Chengmei, CHU Yingjia. Response of summer rainstorm in Shandong Province to change of spring atmospheric heat sources in southeastern Tibet Plateau and its adjacent areas [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(3): 406-414. |
| [4] | LIU Xinwei,WANG Chenghai,GUO Runxia,YANG Xiaojun,DI Xiaohong. Climate and Circulation Characteristics of Extreme Rainstorm Processes in Gansu from 1981 to 2018 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(5): 750-758. |
| [5] | FENG Yao, Ayixianmu·niyazi, Reyila·yunusi. Cause Analysis of an Extreme Heavy Rainstorm Process on July 31 of 2018 in Hami of Xinjiang [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(3): 426-435. |
| [6] | GOU Yuqing, XU Dongbei. Comprehensive Analysis of a Severe Pollution Process in Chengdu in Late December 2017 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(6): 1012-. |
| [7] | SHANG Lin, GU Weizong, TANG Zidong, MENG Xiangxin, LUO Jiali, CUI Qiang. Decadal Variation of the Relationship Between Summer Precipitation in Shandong Province and Previous Winter SST over the Equatorial Central and Eastern Pacific [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(4): 552-558. |
| [8] | GAN Lu, GUO Wenli, DENG Changju. Comparative Analysis of Two Torrential Rain Processes in Beijing [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(2): 239-249. |
| [9] | KANG Guihong1, HAN Yongqing1, SUN Xingchi1, GE Xiang2. Climatic Characteristics and Circulation Situation of the First Rainstorm in Shandong Province During 1985-2014 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(6): 955-962. |
| [10] | LI Ruiying1, REN Chongyong1, CHEN Nan1, JIANG Xiaodong2. Simulation of Spring Phenophase of Typical Plants in Southwestern Shandong Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(6): 1010-1016. |
| [11] | HU Yiqing,ZHAO Haijun, ZHUANG Zhong, GAO Anchun,CAO Zhangchi, ZHANG Pinzhu, LIU Yingjie. Mesoscale Structure and Lightning Features of a Convective Weather Process in Center of Shandong Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(5): 830-837. |
| [12] | WAN Mingbo1, DONG Xuguang2. Nonuniformity Characteristics of Precipitation in Shandong Province During 1961-2010 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(4): 566-573. |
| [13] | ZHANG Chunsong1, YANG Xiaoling2, LIU Rong1, ZHOU Hua3, HU Jinge2. Temporal and Spatial Distribution of Thunderstorm in Wuwei of Gansu Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(4): 659-665. |
| [14] | ZHAO Dongxu1,YANG Xiaoling1,ZHOU Hua2,LIU Rong3. Analysis of a Heavy Rainfall Process in Wuwei of Gansu in 2013 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(1): 149-155. |
| [15] | . Characteristics and Causes of Continuous Drought from Autumn 2010 to Winter 2011 in Shandong Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2012, 30(3): 323-326. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||