Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2025, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (1): 21-31.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-01-0021
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Study on the evolutionary characteristics of agricultural drought disasters and the relationship with climatic factors in Yunnan
ZHOU Jianqin1( ), LI Meng1, TAO Yun2, DOU Xiaodong3(
), LI Meng1, TAO Yun2, DOU Xiaodong3( ), WANG Yuyouting1
), WANG Yuyouting1
- 1. Yunnan Climate Center,Kunming 650034,China
2. Yunnan Institute of Meteorology Sciences,Kunming 650034,China
3. Yunnan Meteorological Service Center,Kunming 650034,China
-
Received:2024-11-04Revised:2024-12-30Online:2025-02-28Published:2025-03-14
云南农业干旱灾害演变特征及其与气候因子的关系研究
周建琴1( ), 李蒙1, 陶云2, 窦小东3(
), 李蒙1, 陶云2, 窦小东3( ), 王玉尤婷1
), 王玉尤婷1
- 1.云南省气候中心,云南 昆明 650034
2.云南省气象科学研究所,云南 昆明 650034
3.云南省气象服务中心,云南 昆明 650034
-
通讯作者:窦小东(1979—),男,汉族,黑龙江依兰人,高级工程师,主要研究方向为气候变化对水资源与水安全的影响。E-mail:154233007@qq.com。 -
作者简介:周建琴(1982—),女,汉族,云南宾川人,高级工程师,主要研究方向为气候变化与气候预测。E-mail:24095528@qq.com。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(42165004);国家自然科学基金项目(42465004);云南省重点研发计划项目(202203AC100005);云南省重点研发计划项目(202403AC100026);中国气象局复盘总结专项(FPZJ2024-123);科技人才与平台计划项目(202405AC350093);中国气象局创新专项(CXFZ2024J045);中国气象局创新专项(CXFZ2025J046);香格里拉大气成分云南省野外科学观测研究站项目(202405AW340007)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZHOU Jianqin, LI Meng, TAO Yun, DOU Xiaodong, WANG Yuyouting. Study on the evolutionary characteristics of agricultural drought disasters and the relationship with climatic factors in Yunnan[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(1): 21-31.
周建琴, 李蒙, 陶云, 窦小东, 王玉尤婷. 云南农业干旱灾害演变特征及其与气候因子的关系研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(1): 21-31.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-01-0021
| 等级 | 类型 | MCI |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 无旱 | -0.5<MCI |
| 2 | 轻旱 | -1.0<MCI≤-0.5 |
| 3 | 中旱 | -1.5<MCI≤-1.0 |
| 4 | 重旱 | -2.0<MCI≤-1.5 |
| 5 | 特旱 | MCI≤-2.0 |
Tab.1 The classification standard of meteorological drought composite index
| 等级 | 类型 | MCI |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 无旱 | -0.5<MCI |
| 2 | 轻旱 | -1.0<MCI≤-0.5 |
| 3 | 中旱 | -1.5<MCI≤-1.0 |
| 4 | 重旱 | -2.0<MCI≤-1.5 |
| 5 | 特旱 | MCI≤-2.0 |

Fig.1 The inter-annual variation of disaster-affected rate and disaster-damaged rate of agricultural drought (a) and their 9-year moving t-test (b) in Yunnan from 1978 to 2022
| 时段 | 受灾率 | 成灾率 |
|---|---|---|
| 1978—2004年 | 11.28 | 5.02 |
| 2005—2013年 | 20.11 | 11.44 |
| 2014—2022年 | 6.10 | 2.38 |
| 1978—2022年 | 11.88 | 5.77 |
Tab.2
| 时段 | 受灾率 | 成灾率 |
|---|---|---|
| 1978—2004年 | 11.28 | 5.02 |
| 2005—2013年 | 20.11 | 11.44 |
| 2014—2022年 | 6.10 | 2.38 |
| 1978—2022年 | 11.88 | 5.77 |
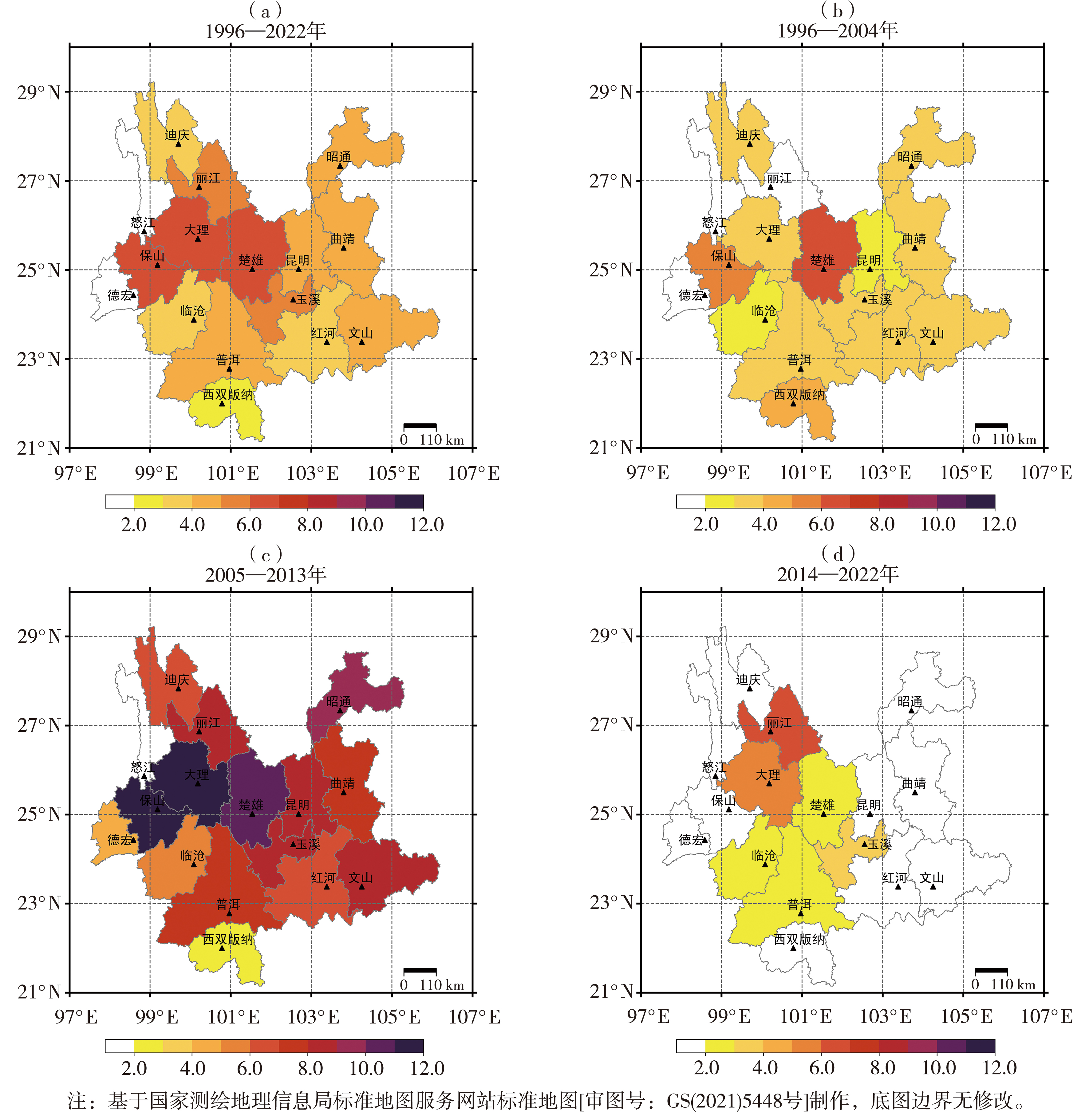
Fig.2 The spatial distribution of comprehensive loss rates of agricultural drought in 16 prefectures (cities) of Yunnan during different periods (Unit: %)
| 州(市) | 不同程度干旱灾害年数/a | 综合损失率气候倾向率/[%·(10 a)-1] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 重灾 | 中灾 | 轻灾 | ||
| 昆明 | 8 | 2 | 12 | -0.59 |
| 昭通 | 8 | 3 | 8 | -0.46 |
| 曲靖 | 6 | 3 | 12 | -0.57 |
| 玉溪 | 10 | 5 | 9 | 0.89 |
| 保山 | 8 | 7 | 8 | -1.48 |
| 楚雄 | 10 | 6 | 3 | -1.39 |
| 红河 | 6 | 7 | 7 | -1.19 |
| 文山 | 6 | 6 | 5 | -1.28 |
| 普洱 | 8 | 5 | 7 | -0.07 |
| 西双版纳 | 6 | 3 | 4 | -1.30 |
| 大理 | 12 | 5 | 3 | 0.78 |
| 德宏 | 1 | 3 | 8 | 0.11 |
| 丽江 | 9 | 3 | 8 | 2.21 |
| 怒江 | 2 | 1 | 4 | -0.01 |
| 迪庆 | 5 | 5 | 5 | -0.98 |
| 临沧 | 3 | 7 | 14 | 0.04 |
Tab.3 The number of years with different levels of agricultural drought disasters and the climate tendency rate of comprehensive loss rate in 16 prefectures (cities) of Yunnan from 1996 to 2022
| 州(市) | 不同程度干旱灾害年数/a | 综合损失率气候倾向率/[%·(10 a)-1] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 重灾 | 中灾 | 轻灾 | ||
| 昆明 | 8 | 2 | 12 | -0.59 |
| 昭通 | 8 | 3 | 8 | -0.46 |
| 曲靖 | 6 | 3 | 12 | -0.57 |
| 玉溪 | 10 | 5 | 9 | 0.89 |
| 保山 | 8 | 7 | 8 | -1.48 |
| 楚雄 | 10 | 6 | 3 | -1.39 |
| 红河 | 6 | 7 | 7 | -1.19 |
| 文山 | 6 | 6 | 5 | -1.28 |
| 普洱 | 8 | 5 | 7 | -0.07 |
| 西双版纳 | 6 | 3 | 4 | -1.30 |
| 大理 | 12 | 5 | 3 | 0.78 |
| 德宏 | 1 | 3 | 8 | 0.11 |
| 丽江 | 9 | 3 | 8 | 2.21 |
| 怒江 | 2 | 1 | 4 | -0.01 |
| 迪庆 | 5 | 5 | 5 | -0.98 |
| 临沧 | 3 | 7 | 14 | 0.04 |
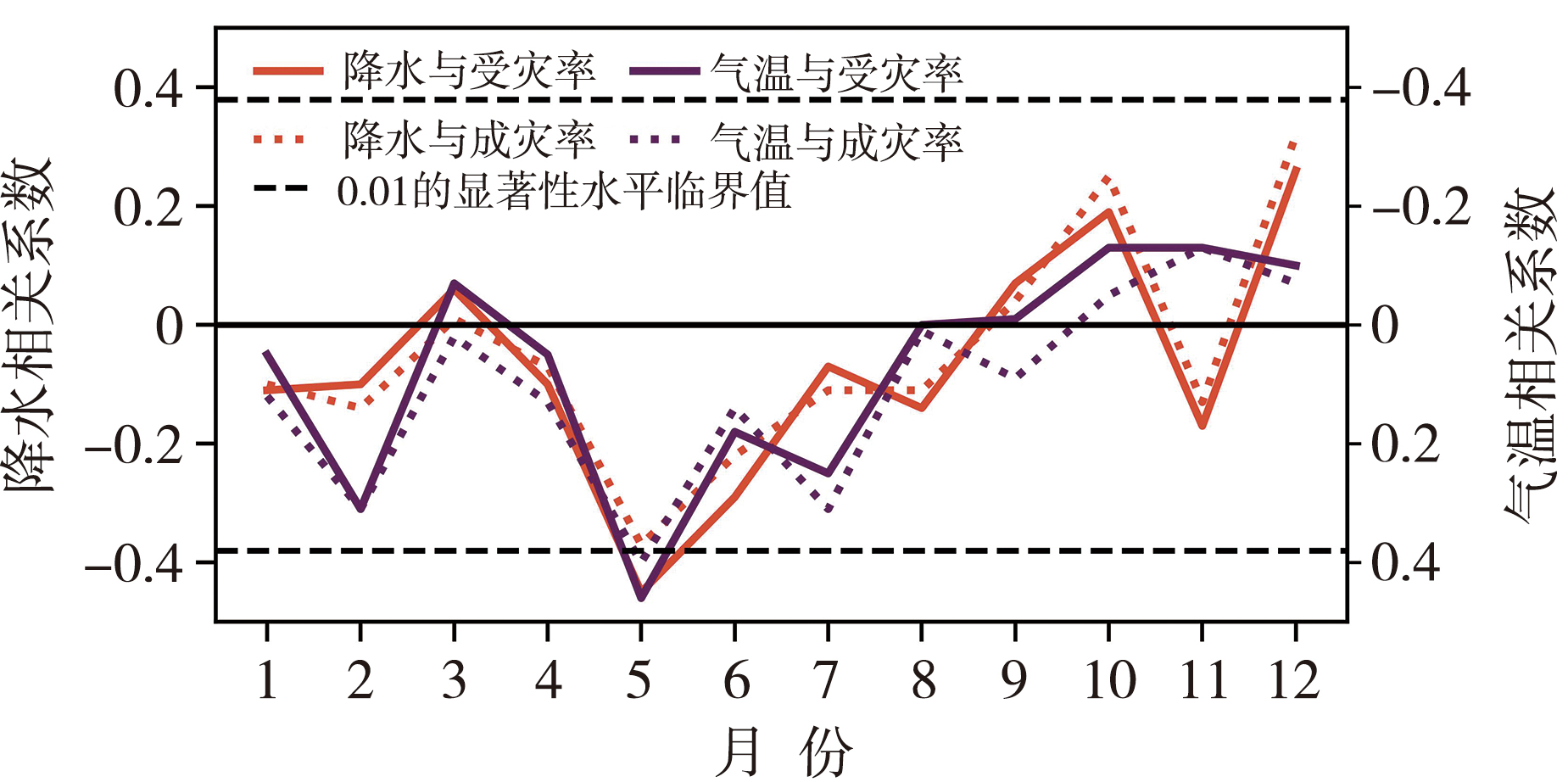
Fig.3 The monthly variation of correlation coefficients between disaster-affected rate and disaster-damaged rate of agricultural drought with precipitation and temperature in Yunnan from 1978 to 2022
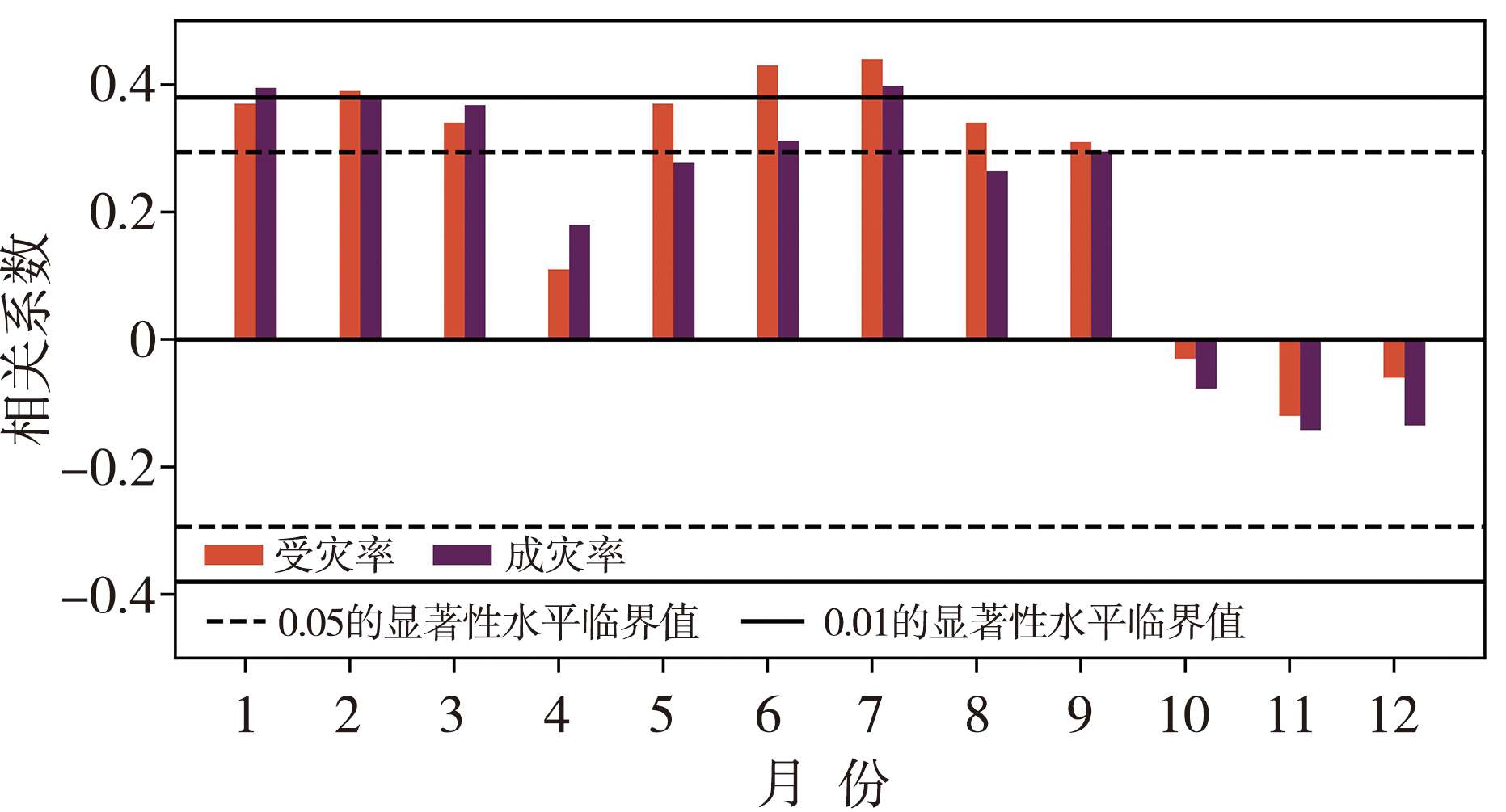
Fig.4 The monthly variation of correlation coefficients between disaster-affected rate and disaster-damaged rate of agricultural drought and the number of stations of moderate drought and above in Yunnan from 1978 to 2022

Fig.5 Standardized sequences of disaster-affected rate and disaster-damaged rate of agricultural drought,May precipitation,May average temperature,and the number of moderate drought and above stations from January to March and from May to September in Yunnan from 1978 to 2022
| 时段 | 受灾率与降水 | 成灾率与降水 | 受灾率与气温 | 成灾率与气温 | 受灾率与干旱站次数 | 成灾率与干旱站次数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1978—2022年 | -0.45** | -0.38** | 0.46** | 0.40** | 0.63** | 0.58** |
| 1978—2013年 | -0.57** | -0.48** | 0.67** | 0.59** | 0.71** | 0.65** |
| 2014—2022年 | -0.63 | -0.70* | 0.68* | 0.77* | 0.57 | 0.54 |
Tab.4 Correlation coefficients between the disaster-affected rate and disaster-damaged rate of agricultural drought with May precipitation,May average temperature,and the number of meteorological drought stations from January to March and from May to September in Yunnan during different periods
| 时段 | 受灾率与降水 | 成灾率与降水 | 受灾率与气温 | 成灾率与气温 | 受灾率与干旱站次数 | 成灾率与干旱站次数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1978—2022年 | -0.45** | -0.38** | 0.46** | 0.40** | 0.63** | 0.58** |
| 1978—2013年 | -0.57** | -0.48** | 0.67** | 0.59** | 0.71** | 0.65** |
| 2014—2022年 | -0.63 | -0.70* | 0.68* | 0.77* | 0.57 | 0.54 |

Fig.6 The planting area and the proportion of effectively irrigated area of main crops from 1978 to 2022 (a), the number and capacity of reservoirs in Yunnan from 1987 to 2022 (b)
| 时段 | 气候因子 | 受灾率 | 成灾率 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 相关系数 | 标准误差/% | 平均绝对误差/% | 相关系数 | 标准误差/% | 平均绝对误差/% | ||
| 全年 | 气温 | 0.11 | 8.90 | 6.23 | 0.17 | 5.68 | 3.62 |
| 降水 | 0.35* | 8.40 | 5.60 | 0.27 | 5.56 | 3.44 | |
| 干旱站次数 | 0.48*** | 7.85 | 5.52 | 0.43** | 5.20 | 3.39 | |
| 综合因子 | 0.53*** | 7.61 | 5.57 | 0.48** | 5.06 | 3.38 | |
| 关键期 | 气温 | 0.46** | 7.97 | 5.57 | 0.40** | 5.28 | 3.46 |
| 降水 | 0.45** | 7.99 | 5.54 | 0.37* | 5.35 | 3.22 | |
| 干旱站次数 | 0.63*** | 6.93 | 4.90 | 0.57*** | 4.70 | 3.09 | |
| 综合因子 | 0.69*** | 6.51 | 4.69 | 0.61*** | 4.58 | 2.99 | |
Tab.5 Correlation parameters of the statistical values and estimated values of the disaster-affected rate and disaster-damaged rate of agricultural drought fitting models based on the temperature,precipitation,the number of meteorological drought stations and effective irrigation area in the whole year and the critical period
| 时段 | 气候因子 | 受灾率 | 成灾率 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 相关系数 | 标准误差/% | 平均绝对误差/% | 相关系数 | 标准误差/% | 平均绝对误差/% | ||
| 全年 | 气温 | 0.11 | 8.90 | 6.23 | 0.17 | 5.68 | 3.62 |
| 降水 | 0.35* | 8.40 | 5.60 | 0.27 | 5.56 | 3.44 | |
| 干旱站次数 | 0.48*** | 7.85 | 5.52 | 0.43** | 5.20 | 3.39 | |
| 综合因子 | 0.53*** | 7.61 | 5.57 | 0.48** | 5.06 | 3.38 | |
| 关键期 | 气温 | 0.46** | 7.97 | 5.57 | 0.40** | 5.28 | 3.46 |
| 降水 | 0.45** | 7.99 | 5.54 | 0.37* | 5.35 | 3.22 | |
| 干旱站次数 | 0.63*** | 6.93 | 4.90 | 0.57*** | 4.70 | 3.09 | |
| 综合因子 | 0.69*** | 6.51 | 4.69 | 0.61*** | 4.58 | 2.99 | |
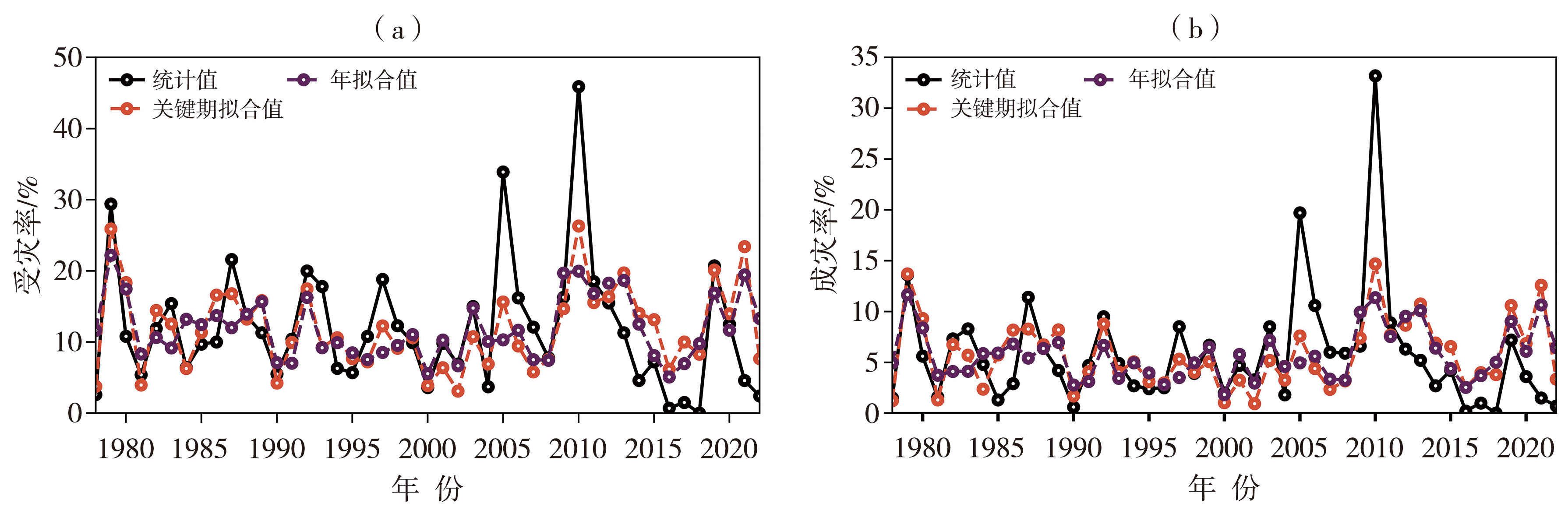
Fig.7 The inter-annual variation of the statistical values and estimated values of disaster-affected rate (a) and disaster-damaged rate (b) of agricultural drought by fitting models based on the multi-factors in the whole year and the critical period
| [1] | 白树明, 黄中艳, 2003. 云南旱灾特点和未来10年干旱趋势预测[J]. 人民珠江, 24(6): 4-6. |
| [2] | 段旭, 尤卫红, 郑建萌, 2000. 云南旱涝特征[J]. 高原气象, 19(1):84-90. |
| [3] | 范晓红, 沈才明, 任宾宾, 等, 2016. 近半个世纪云南持续数年干旱事件时空分布[J]. 云南师范大学学报:自然科学版, 36(1):71-78. |
| [4] | 国家统计局, 1979—2023. 中国统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社. |
| [5] | 韩兰英, 2016. 气候变暖背景下中国农业干旱灾害致灾因子、风险性特征及其影响机制研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学:1-134. |
| [6] |
韩兰英, 张强, 姚玉璧, 等, 2014. 近60年中国西南地区干旱灾害规律与成因[J]. 地理学报, 69(5):632-639.
DOI |
| [7] | 黄中艳, 朱勇, 2009. 1954—2007年云南农业气候变化研究[J]. 气象, 35(2):111-118. |
| [8] | 江铭诺, 向昆仑, 黄奕融, 等, 2023. 1978—2020年我国有效灌溉面积时空变化特征[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 28(7):164-174. |
| [9] | 金燕, 况雪源, 晏红明, 等, 2018. 近55年来云南区域性干旱事件的分布特征和变化趋势研究[J]. 气象, 44(9):1169-1 178. |
| [10] | 刘南江, 冯爱青, 张鹏, 等, 2023. 2023年西南地区冬春连旱时空特征及防范应对建议[J]. 中国防汛抗旱, 33(7):16-20. |
| [11] | 刘颖秋, 宋建军, 张庆杰, 2005. 干旱灾害对我国社会经济影响研究[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社. |
| [12] | 秦剑, 琚建华, 解明恩, 等, 1997. 低纬高原天气气候[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [13] | 全国气候与气候变化标准化技术委员会, 2017. 气象干旱等级:GB/T 20481—2017[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| [14] | 陶云, 张万诚, 段长春, 等, 2014. 云南2009—2012年4年连旱的气候成因研究[J]. 云南大学学报:自然科学版, 36(6): 866-874. |
| [15] | 王素萍, 王劲松, 张强, 等, 2015. 几种干旱指标对西南和华南区域月尺度干旱监测的适用性评价[J]. 高原气象, 34(6): 1 616-1 624. |
| [16] |
王莺, 张强, 王劲松, 等, 2022. 21世纪以来干旱研究的若干新进展与展望[J]. 干旱气象, 40(4):549-566.
DOI |
| [17] | 徐新创, 葛全胜, 郑景云, 等, 2011. 区域农业干旱风险评估研究:以中国西南地区为例[J]. 地理科学进展, 30(7):883-890. |
| [18] |
薛亮, 袁淑杰, 王劲松, 2023. 我国不同区域气象干旱成因研究进展与展望[J]. 干旱气象, 41(1):1-13.
DOI |
| [19] |
颜鹏程, 李忆平, 曾鼎文, 等, 2024. 2024年4—6月我国区域性高温干旱特征及其影响因子[J]. 干旱气象, 42(4): 507-518.
DOI |
| [20] | 杨辉, 宋洁, 晏红明, 等, 2012. 2009/2010年冬季云南严重干旱的原因分析[J]. 气候与环境研究, 17(3):315-326. |
| [21] | 杨育华, 杨洪福, 段燕楠, 等, 2019. 云南省水生态现状及其保护对策[J]. 环境科学导刊, 38(增刊1):22-26. |
| [22] | 云南省气象局, 2020. 云南省气候公报[EB/OL]. (2021-12-17) [2024-12-25]. http://yn.cma.gov.cn/zfxxgk/zwgk/qxbg/202112/t20211217_4313089.html. |
| [23] | 云南省统计局, 1997—2023. 云南统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社. |
| [24] | 《云南减灾年鉴》编委会, 1997—2023. 云南减灾年鉴[M]. 昆明: 云南科技出版社. |
| [25] | 张雷, 王杰, 黄英, 等, 2015. 1961—2010年云南省基于SPEI的干旱变化特征分析[J]. 气象与环境学报, 31(5): 141-146. |
| [26] | 张强, 韩兰英, 郝小翠, 等, 2015. 气候变化对中国农业旱灾损失率的影响及其南北区域差异性[J]. 气象学报, 73(6): 1 092-1 103. |
| [27] | 张强, 韩兰英, 王胜, 等, 2018. 影响南方农业干旱灾损率的气候要素关键期特征[J]. 科学通报, 63(23):2378-2 392. |
| [28] |
张强, 韩兰英, 张立阳, 等, 2014. 论气候变暖背景下干旱和干旱灾害风险特征与管理策略[J]. 地球科学进展, 29(1):80-91.
DOI |
| [29] | 张强, 李栋梁, 姚玉璧, 等, 2024. 干旱形成机制与预测理论方法及其灾害风险特征研究进展与展望[J]. 气象学报, 82(1):1-21. |
| [30] | 张强, 姚玉璧, 李耀辉, 等, 2020. 中国干旱事件成因和变化规律的研究进展与展望[J]. 气象学报, 78(3): 500-521. |
| [31] | 周建琴, 黄玮, 李蒙, 等, 2022. 云南初夏干湿演变特征和基于CMIP6模式模拟的预估分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 18(4): 482-491. |
| [32] | 周建琴, 陶云, 符睿, 等, 2024. 云南2020年4—6月区域性气象干旱特征和成因分析[J]. 高原气象, 43(4): 1 052-1 063. |
| [33] | DOUVILLE H, RAGHAVAN K, RENWICK J, et al, 2021. Water cycle changes[M]∥IPCC. Climate Change 2021:The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working GroupⅠ to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. |
| [34] | WANG L, CHEN W, HUANG G, et al, 2024. Characteristics of super drought in Southwest China and the associated compounding effect of multiscalar anomalies[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 67(7): 2 084-2 102. |
| [35] |
YUAN X, WANG Y M, JI P, et al, 2023. A global transition to flash droughts under climate change[J]. Science, 380(6641):187-191.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | WANG Min, SUN Shujun, ZHANG Jian, LI Tianfang, CHEN Rui, YANG Xing, XIAO Yawen. Characteristics of vegetation cover change and its relationship with climate factors in Ganzi Prefecture [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(6): 944-952. |
| [2] | MA Siyuan, JIN Yan, ZHANG Si, WANG Chuqin, MA Zhimin. Different impacts of El Niño/Southern Oscillation events on autumn meteorological drought in Yunnan Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(6): 860-872. |
| [3] | ZENG Yingting, LI Cheng, LIN Yan, CHEN Li, LIN Binbin. Characteristics of LAI variation in East China and its relationship with climate factors from 1982 to 2016 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(5): 705-713. |
| [4] | LU Shan, GUO Yong, ZHENG Jiangping, WANG Shigong. Study on Climate Comfort Degree and Its Health Care Effect in Three Tourist Cities of Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(2): 317-325. |
| [5] | ZENG Yong, DING Min, LUO Xiong, ZOU Shuping, ZHOU Yunjun, LI Lili, HUANG Yu. Characteristics of Lightning Activity During a Large-scale Hail Weather Process in the Slope Transition Zone of Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(5): 771-781. |
| [6] | LIU Xuetao, XIE Yiran, XU Yingjie, SUN Jihua. Temporal and Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Lightning Activity over Yunnan Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(5): 729-735. |
| [7] | YANG Xueyan1, FU Shuai2, XU Shiqi1,3, CHEN Li’nan4. Analysis on Climate Condition and Comfortable Index in Jilin Province in Summer Tourism Period [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(3): 492-. |
| [8] | CHEN Yan, GUO Shichang, LIU Yu, JU Jianhua, REN Juzhang, ZHANG Huizhu. Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of the Onset Date of Rainy Season in Yunnan and Its Relationship with ENSO [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(4): 545-551. |
| [9] | ZHAO Nianwu, GUO Lianyun,ZHAO Henghe. Variation Characteristics of Climate Factors During Potato Growth Period and Their Effect on Yield in the Alpine Semiarid Zone [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(6): 1024-1030. |
| [10] | ZHOU Pengkang, QIN Jinmei, SUN Xiufen,LI linrun. Spatial-temporal Distribution of Continuous Rain from May to October in Recent 30 Years in Yunnan [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(5): 796-801. |
| [11] | . Climatic Characteristics of Extremely Heavy Precipitation Eventsin Flood Season in Yunnan Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2012, 30(1): 15-20. |
| [12] | CUI Ting, WU Guhui, ZHAO Yujin, YUAN Hongzhao, YANG Ling. Analysis on Structure and Formation Reason of Frontal Fogs Occurred in Yunnan and Guizhou [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2012, 30(1): 114-118. |
| [13] | . Influence of Atmospheric Circulation Anomalies in the Southern Hemisphere on May Precipitation in Yunnan [J]. J4, 2011, 29(4): 407-415. |
| [14] | LIU Yu, DIAO Er-Xu, BANG Gui-Fen, YANG Chu-Qun. Severe Drought in the Early Summer of 2005 in Yunnan and Middle—high Latitudes Circulation [J]. J4, 2008, 25(1): 32-37. |
| [15] | LIU Yu, DIAO Er-Xu, HUANG Wei, SHU Yong, DAO Yun. General Circulation Characteristic Before Beg inn ing of Yunnan Ra iny Season [J]. J4, 2007, 25(3): 17-22. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||