Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (6): 976-986.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2024-06-0976
• Technical Reports • Previous Articles Next Articles
Deviation characteristics in intelligent grid forecast of flood season precipitation in Hedong area of Gansu based on CRA spatial forecast verification
HAN Jing1( ), JIAO Meiling1, CAO Yanchao1(
), JIAO Meiling1, CAO Yanchao1( ), WANG Juan1, HE Tao1, XU Geng1, ZHOU Zhongwen1, JIN Manhui2
), WANG Juan1, HE Tao1, XU Geng1, ZHOU Zhongwen1, JIN Manhui2
- 1. Qingyang Meteorological Bureau of Gansu Province, Qingyang 745000, Gansu, China
2. Gannan Meteorological Bureau of Gansu Province, Gannan 747000, Gansu, China
-
Received:2024-03-18Revised:2024-07-22Online:2024-12-31Published:2025-01-15
基于CRA空间检验技术的甘肃河东汛期降水智能网格预报偏差特征分析
韩晶1( ), 焦美玲1, 曹彦超1(
), 焦美玲1, 曹彦超1( ), 王娟1, 贺涛1, 徐耕1, 周忠文1, 金满慧2
), 王娟1, 贺涛1, 徐耕1, 周忠文1, 金满慧2
- 1.甘肃省庆阳市气象局,甘肃 庆阳 745000
2.甘南藏族自治州气象局,甘肃 甘南 747000
-
通讯作者:曹彦超(1985—),男,甘肃庆阳人,高级工程师,主要从事气候变化及灾害性天气研究。E-mail:646891024@qq.com。 -
作者简介:韩晶(1988—),女,甘肃庆阳人,工程师,主要从事气候变化及灾害性天气研究。E-mail:446843809@qq.com。 -
基金资助:甘肃省自然科学基金项目(22JRRM1045);甘肃省自然科学基金项目(24JRRM008);庆阳市科技计划项目(QY-STK-2022A-129);甘肃省气象局科研项目(ZcMs2022-33)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
HAN Jing, JIAO Meiling, CAO Yanchao, WANG Juan, HE Tao, XU Geng, ZHOU Zhongwen, JIN Manhui. Deviation characteristics in intelligent grid forecast of flood season precipitation in Hedong area of Gansu based on CRA spatial forecast verification[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(6): 976-986.
韩晶, 焦美玲, 曹彦超, 王娟, 贺涛, 徐耕, 周忠文, 金满慧. 基于CRA空间检验技术的甘肃河东汛期降水智能网格预报偏差特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(6): 976-986.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2024-06-0976
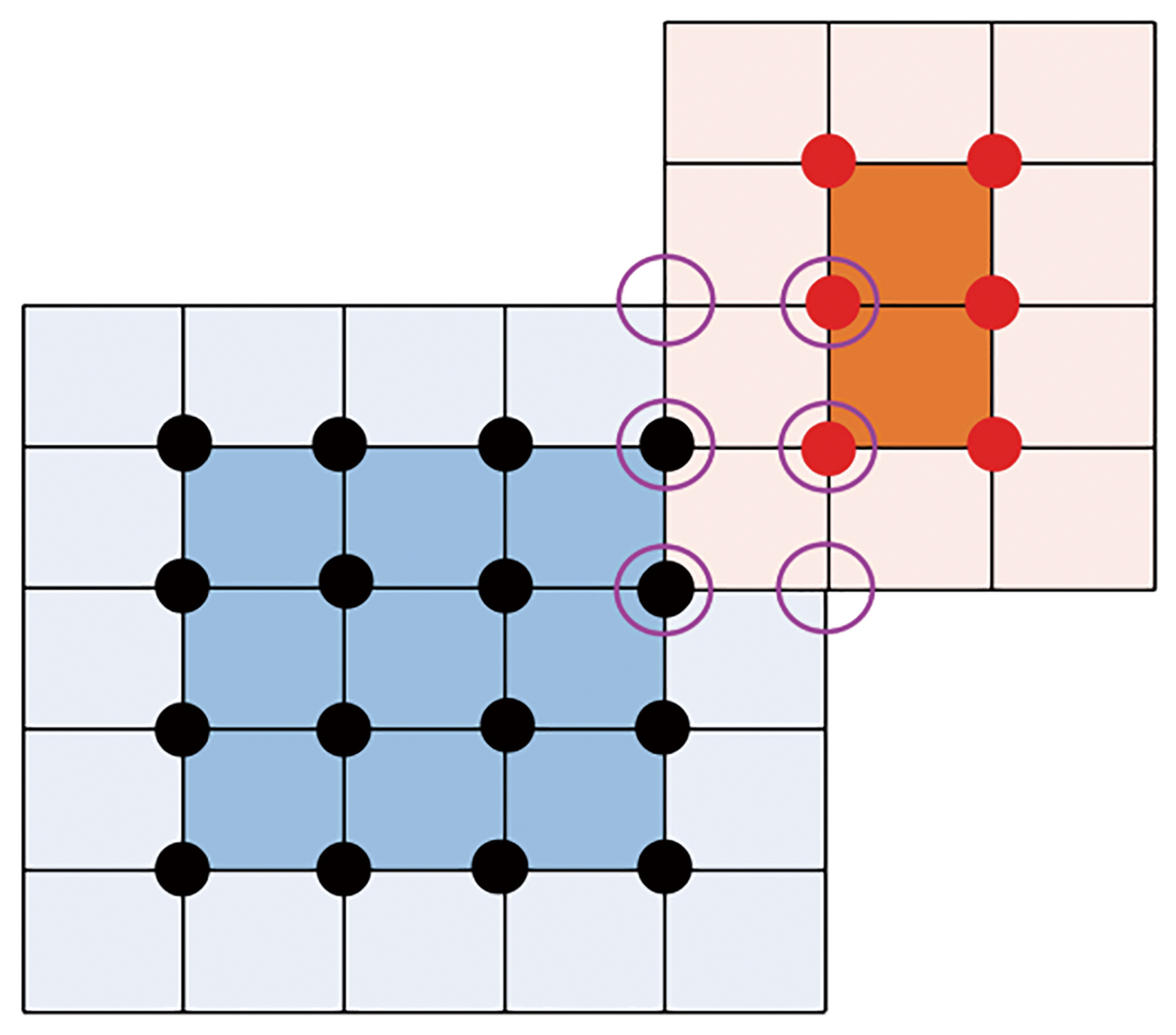
Fig.2 The CRA matching between forecast field and actual field (The blue area represents the forecast CRA, the surrounding light blue area represents the forecast extension area, the orange area represents the actual CRA, the surrounding light orange area represents the actual extension area, and the purple circle represents the intersection of the extension areas)
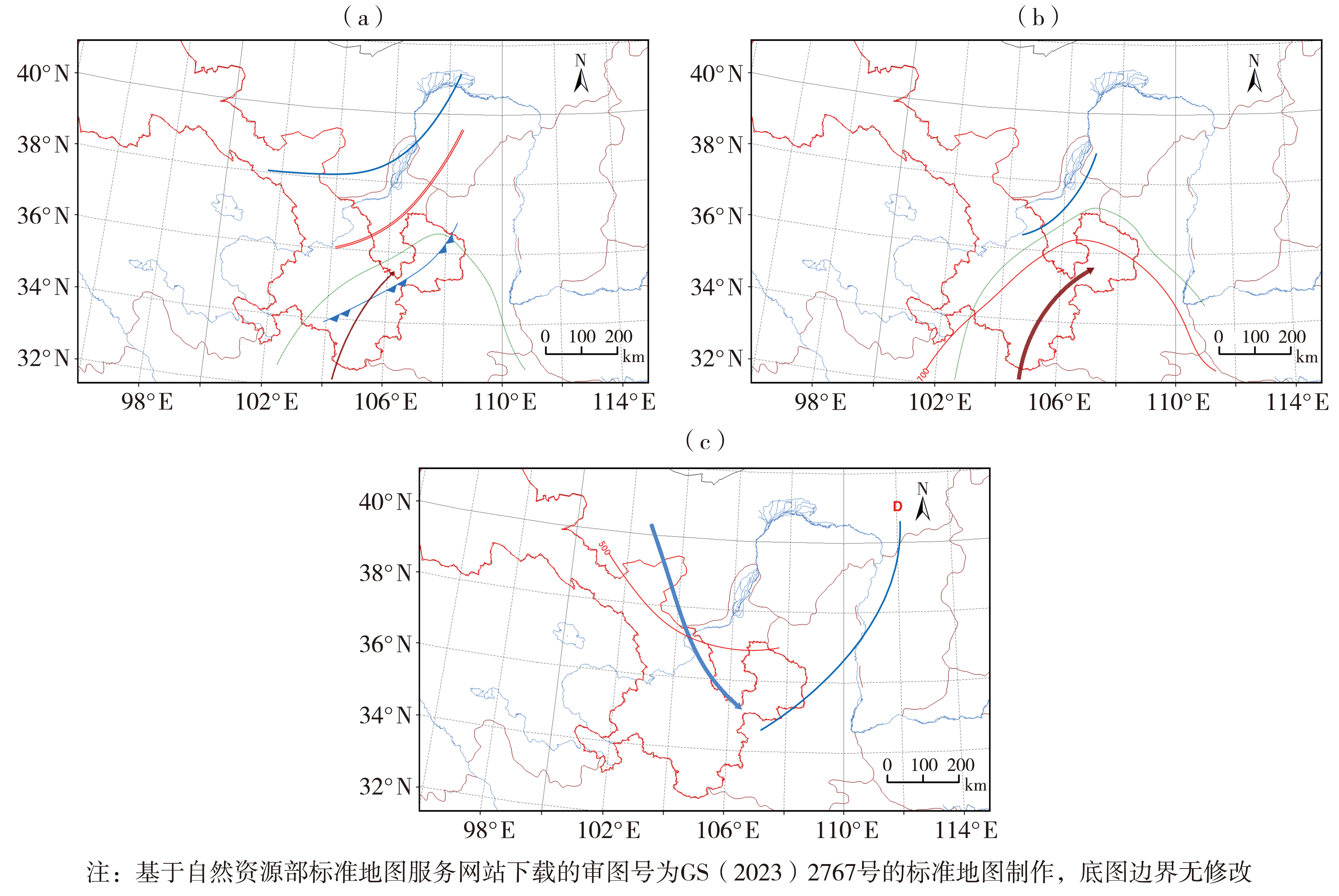
Fig.3 Weather system configuration for oblique frontal (a), warm forcing (b) and cold forcing (c) precipitation in Hedong area of Gansu Province (The green dashed lines indicate the 700 hPa isobaric humidity line, Unit: g·kg-1; the brown thin arrow represents a significant streamline at 700 hPa; the brown thick arrow represents the 700 hPa low-level jet stream; the red double solid line represents the 700 hPa shear line; the red solid lines represent temperature lines at 500 and 700 hPa, Unit: ℃; the blue solid line represents the 500 hPa trough line; the blue thick arrow represents the 200 hPa high-altitude jet stream; the blue sawtooth line represents a cold front; D represents a low-pressure system)

Fig.4 Changes in the average hit rate, miss rate, and false alarm rate of CRA of intelligent grid precipitation forecasts in Hedong area of Gansu Province from May to September during 2018-2020

Fig.5 Changes of the hit rate and false alarm rate with the number of CRA grid points in the forecast field (a), and hit rate and miss rate with the number of CRA grid points in the actual field (b) of intelligent grid precipitation forecast in Hedong area of Gansu Province during 2018-2020
| 天气形势类型 | 西部平均格点数 | 东部平均格点数 |
|---|---|---|
| 暖强迫 | 766 | 1 143 |
| 冷强迫 | 136 | 898 |
| 斜压锋生 | 490 | 1 243 |
Tab.1 The CRA grid distribution characteristics of precipitation in eastern and western parts of Hedong area of Gansu Province under different weather patterns 单位:个
| 天气形势类型 | 西部平均格点数 | 东部平均格点数 |
|---|---|---|
| 暖强迫 | 766 | 1 143 |
| 冷强迫 | 136 | 898 |
| 斜压锋生 | 490 | 1 243 |
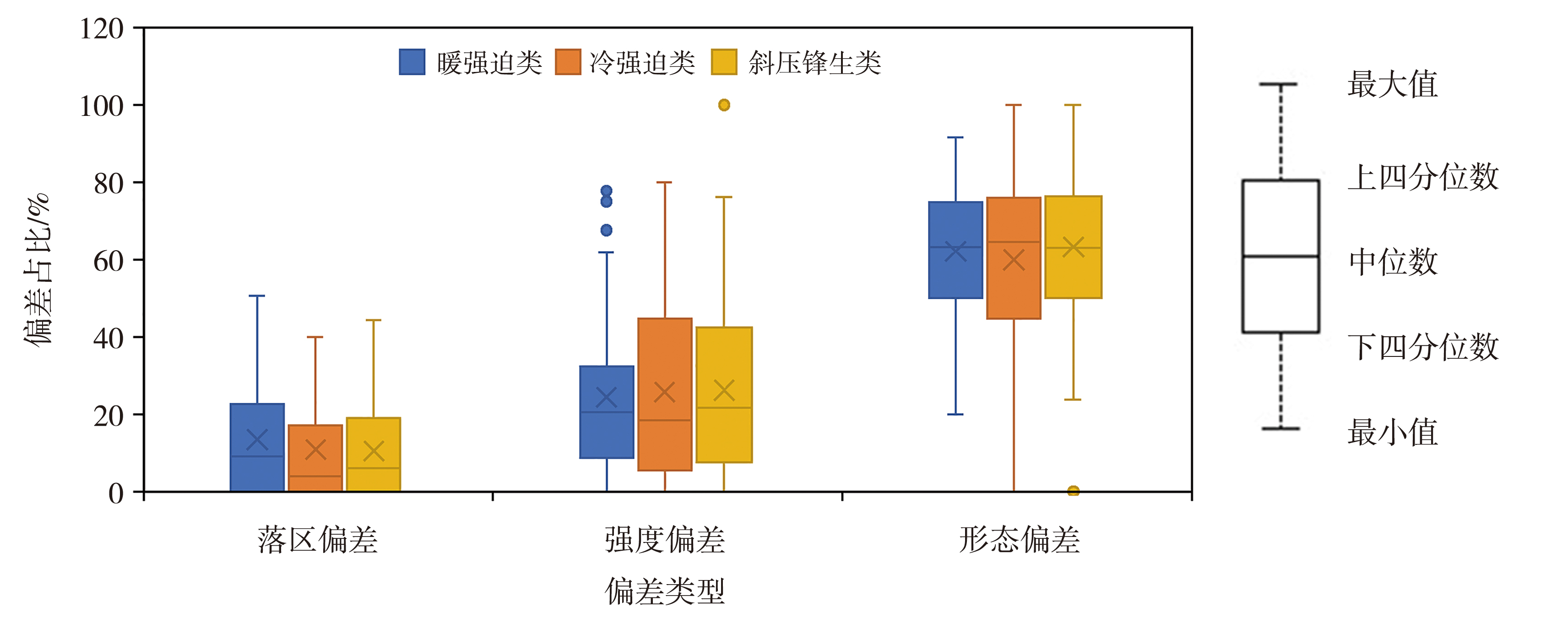
| 天气形势类型 | 平均值 | 中位数 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 落区偏差 占比/% | 强度偏差 占比/% | 形态偏差 占比/% | 平均纬向 偏差/(°) | 平均经向 偏差/(°) | 平均面积 偏差/% | 平均强度 偏差/% | 最大降水量 偏差/% | |
| 暖强迫 | 19.9 | 23.5 | 56.6 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 18.6 | 64.1 | -24.0 |
| 冷强迫 | 8.1 | 33.3 | 58.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 62.3 | 0.0 | -50.0 |
| 斜压锋生 | 15.7 | 21.2 | 63.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 12.8 | 63.9 | -29.9 |
Tab.2 Overall deviation of precipitation forecast
| 天气形势类型 | 平均值 | 中位数 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 落区偏差 占比/% | 强度偏差 占比/% | 形态偏差 占比/% | 平均纬向 偏差/(°) | 平均经向 偏差/(°) | 平均面积 偏差/% | 平均强度 偏差/% | 最大降水量 偏差/% | |
| 暖强迫 | 19.9 | 23.5 | 56.6 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 18.6 | 64.1 | -24.0 |
| 冷强迫 | 8.1 | 33.3 | 58.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 62.3 | 0.0 | -50.0 |
| 斜压锋生 | 15.7 | 21.2 | 63.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 12.8 | 63.9 | -29.9 |

Fig.8 Scatter plot of precipitation forecast and actual precipitation grid points (a, c, e) and actual precipitotion grid distribution (b, d, f) of warm forcing type (a, b), cold forcing type (c, d) and oblique pressure frontogenesis type (e, f)
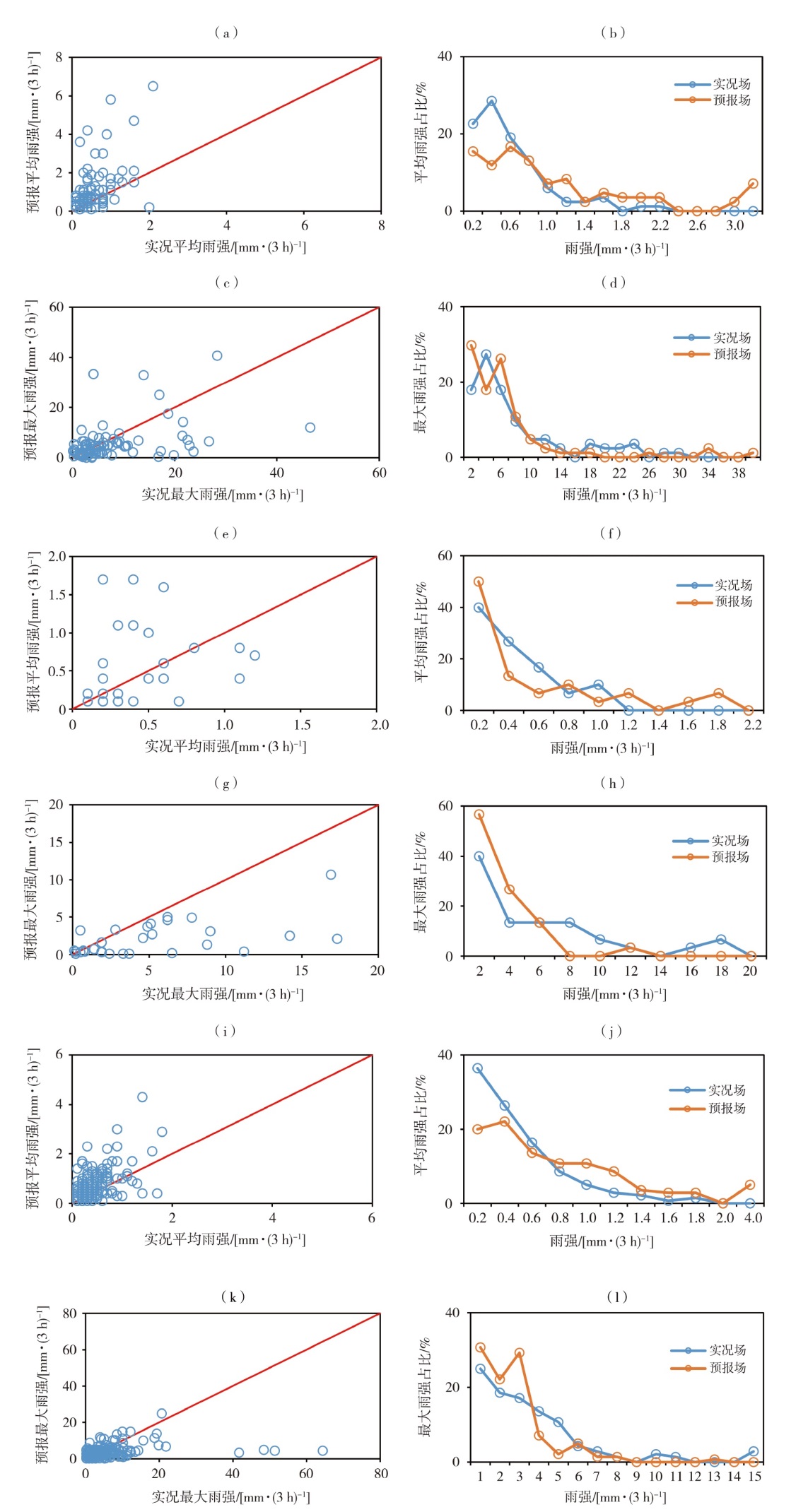
Fig.9 The scatter plots of average precipitation and forecasted rainfall intensity (a, e, i) and their proportions (b, f, j), and the scatter plots of maximum precipitation and forecasted rainfall intensity (c, g, k) and their proportions (d, h, l) of warm forcing type (a, b, c, d), cold forcing type (e, f, g, h), and oblique pressure frontogenesis type (i, j, k, l)
| [1] |
蔡怡, 徐枝芳, 龚玺, 等, 2023. 2021年夏季CMA-MESO模式降水预报评估[J]. 干旱气象, 41(3): 503-515.
DOI |
| [2] |
陈晓燕, 孔祥伟, 彭筱, 等, 2022. 全球和区域数值模式在甘肃2020年汛期降水预报中的检验评估[J]. 干旱气象, 40(3): 524-535.
DOI |
| [3] | 符娇兰, 代刊, 2016. 基于CRA空间检验技术的西南地区东部强降水EC模式预报误差分析[J]. 气象, 42(12): 1 456-1 464 |
| [4] | 郭旭晖, 石文伯, 张曦丹, 2023. 河北省智能网格预报在张家口最高、最低气温中的检验[J]. 科技创新与应用, 13(35): 89-92. |
| [5] | 韩晶, 路亚奇, 曹彦超, 等, 2023. 基于空间检验技术的甘肃河东地区短时暴雨预报产品误差分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 17(1): 83-89. |
| [6] | 胡争光, 薛峰, 金荣花, 等, 2020. 智能网格预报应用分析平台设计与实现[J]. 气象, 46(10): 1 340-1 350 |
| [7] | 孔荣, 王建捷, 梁丰, 等, 2010. 尺度分解技术在定量降水临近预报检验中的应用[J]. 应用气象学报, 21(5): 535-544. |
| [8] | 孔祥伟, 2022. 甘肃河东短时强降水天气分类特征及模式预报评估研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学. |
| [9] | 孔祥伟, 张君霞, 杨晓军, 等, 2022. 西北地区东部强降水大尺度数值模式预报空间偏差分析[J]. 高原气象, 41(5): 1 109-1 123 |
| [10] | 李晓兰, 符娇兰, 2021. 基于CRA技术的华南前汛期强降水EC模式预报误差分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 37(2): 194-206. |
| [11] | 刘凑华, 牛若芸, 2013. 基于目标的降水检验方法及应用[J]. 气象, 39(6): 681-690. |
| [12] | 卢秀丽, 2008. 甘肃河东地区暴雨极值空间格局及地形影响分析[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学. |
| [13] | 潘留杰, 薛春芳, 梁绵, 等, 2022. 网格降水预报客观检验订正方法研究进展[J]. 气象科技进展, 12(3): 15-24. |
| [14] | 潘留杰, 张宏芳, 刘静, 等, 2023. 智能网格SCMOC及多模式降水预报对比[J]. 大气科学学报, 46(2): 217-229. |
| [15] | 钱磊, 邱学兴, 郑淋淋, 等, 2022. 基于降水空间分布相似的最优集成降水预报及其检验[J]. 暴雨灾害, 41(3): 324-335. |
| [16] | 邱雨楠, 2023. 基于深度学习的短临降水预报方法研究[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学. |
| [17] | 谌芸, 曹勇, 孙健, 等, 2021. 中央气象台精细化网格降水预报技术的发展和思考[J]. 气象, 47(6): 655-670. |
| [18] | 屠妮妮, 衡志炜, 何光碧, 等, 2022. 多数值模式对2021年7月两次大暴雨过程预报能力检验评估[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 42(2): 46-55. |
| [19] | 王新敏, 栗晗, 2020. 多数值模式对台风暴雨过程预报的空间检验评估[J]. 气象, 46(6): 753-764. |
| [20] |
王雅琦, 冯娟, 李建平, 等, 2020. 西北地区东部夏季降水年际变化特征及其与环流的关系[J]. 高原气象, 39(2): 290-300.
DOI |
| [21] |
王奕丹, 胡泽勇, 孙根厚, 等, 2019. 高原季风特征及其与东亚夏季风关系的研究[J]. 高原气象, 38(3): 518-527.
DOI |
| [22] | 韦惠红, 许冠宇, 刘希文, 等, 2022. 湖北省不同类型雷暴大风的时空分布及环境参数特征[J]. 暴雨灾害, 41(1): 66-75. |
| [23] | 韦青, 李伟, 彭颂, 等, 2019. 国家级天气预报检验分析系统建设与应用[J]. 应用气象学报, 30(2): 245-256. |
| [24] | 殷菲, 韩兰英, 王鑫, 等, 2022. 甘肃省2022年度十大天气气候事件[J]. 干旱气象, 40(6): 1 099. |
| [25] | 张博, 张芳华, 李晓兰, 等, 2024. “23·7”华北特大暴雨数值预报检验评估[J]. 应用气象学报, 35(1): 17-32. |
| [26] |
张君霞, 孔祥伟, 刘新伟, 等, 2022. 青藏高原东北侧暴雨数值模式预报空间误差特征[J]. 干旱区研究, 39(1): 64-74.
DOI |
| [27] | 赵一飞, 2013. 近50年来甘肃河东地区农业气候资源变化及其对农牧业的影响[D]. 兰州: 西北师范大学. |
| [28] | 朱国光, 陈鹤, 2022. 酉水流域智能网格降水预报产品及检验[J]. 科技创新与应用, 12(3): 30-35. |
| [29] | EBERT E E, MCBRIDE J L, 2000. Verification of precipitation in weather systems: Determination of systematic errors[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 239(1/2/3/4): 179-202. |
| [30] | MASS C F., OVENS D, WESTRICK K, et al, 2002. Does increasing horizontal resolution produce more skillful forecasts?[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 83(3): 407-430. |
| [31] | SHARMA K, ASHRIT R, EBERT E, et al, 2018. Assessment of Met Office Unified Model (UM) quantitative precipitation forecasts during the Indian summer monsoon: Contiguous Rain Area (CRA) approach[J]. Journal of Earth System Science, 128(4). DOI: 10.1007/s12040-018-1023-3. |
| [32] | WERNLI H, HOFMANN C, ZIMMER M, 2009. Spatial forecast verification methods intercomparison project: Application of the SAL technique[J]. Weather and Forecasting, 24(6): 1 472-1 484 |
| [1] | JIAO Yang, ZHENG Lina, ZHANG Yongjing, SU Yi. Correction of ECMWF ensemble average precipitation forecast using two objective precipitation statistical methods [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(2): 293-304. |
| [2] | ZHU Wengang, SHENG Chunyan, FAN Sudan, RONG Yanmin, QU Meihui. Research on multi-model integrated precipitation forecast based on feed forward neural network [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(1): 117-128. |
| [3] | CAO Pingping, XIAO Dixiang, LONG Keji, WANG Jiajin, YANG Kangquan. Deviation correction of precipitation forecast by ECMWF model based on quantile mapping method in Sichuan Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(4): 666-675. |
| [4] | PEI Kunning, WANG Yan, YAN Shiming, JIANG Yunsheng, GUO Wei. Influence of topography and weather situation on air pollution in Linfen City [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(5): 879-887. |
| [5] | QIAO Jinrong, YUAN Xinpeng, LIANG Xudong, XIE Yanxin. Application of agglomerative hierarchical clustering method in precipitation forecast assessment [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(4): 690-699. |
| [6] | LI Tao, CHEN Jie, WANG Fang, HAN Rui. A correction algorithm of summer precipitation prediction based on neural network in China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(2): 308-316. |
| [7] | WU Dan,LI Meiqi,GUO Rui,JIA Xiaowei,LIU Hao,LIU Quan. Low-level Wind Shear and Its Weather Situation at Shijiazhuang Zhengding International Airport from 2014 to 2017 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(5): 775-784. |
| [8] | REN Xuwei, CHEN Xiaoyan, CAI Dihua, LI Lanqian, SHAO Aimei. Evaluation of Precipitation Forecast Based on GRAPES_Meso Model and Its Cloud Analysis System in Northwest China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(2): 333-344. |
| [9] | WANG Binyan, CHEN Chaoping, HUANG Chuhui, . Application of SAL Method to Verification of Precipitation Forecasts in Sichuan Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(03): 472-479. |
| [10] | WANG Haiyan1, TIAN Gang1, XU Weili2, JIN Qi3, CHEN Lianghua2, CHEN Xuan1. Evaluation and Inspection of ECMWF Model Forecast Product During Dispatch Key Periods in Upper Reaches of the Yangtze River Basin [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(1): 142-147. |
| [11] | BAI Hui1,2,WU Zhanping1,LI Zhongyan1,ZHOU Tao1. Application of DERF Products to Forecast Precipitation Based on PCA Regression Forecast Model in Guizhou [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(2): 344-348. |
| [12] | NI Jiangbo,LI Wencai,SHANG Kezheng,WANG Shigong, LI Deshuai. Automatic Identificationand Prediction of Low Visibility Weather in North China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(1): 174-179. |
| [13] | WU Zhehong,CHEN Zhenhong,BAI Hui. Comparative Analysis on the Frontal Zone Feature of Two Freezing Rain and Snow Weather Processes in 2008 and 2011 in Guizhou Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2013, 31(4): 763-770. |
| [14] | WEI Yong,PENG Jun,RESULI Abula,WANG Cunliang,CHEN Jianmin. Comprehensive Analysis of a Severe Hail in the Middle Section on Northern Slope of Tianshan Mountain in Xinjiang [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2013, 31(4): 771-777. |
| [15] | DUAN Yuhui,WANG Wen,TIAN Zhiguang,ZHANG Nan. Comparison of Two Rain to Heavy Snowstorm Weather Processes Under the Similar Weather Situation in Northern Part of North China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2013, 31(4): 784-789. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||