Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (1): 117-128.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2024)-01-0117
• Technical Reports • Previous Articles Next Articles
Research on multi-model integrated precipitation forecast based on feed forward neural network
ZHU Wengang1,2( ), SHENG Chunyan1,2(
), SHENG Chunyan1,2( ), FAN Sudan1,2, RONG Yanmin1,2, QU Meihui3
), FAN Sudan1,2, RONG Yanmin1,2, QU Meihui3
- 1. Key Laboratory for Meteorological Disaster Prevention and Mitigation of Shandong Province,Jinan 250031,China
2. Shandong Institute of Meteorological Sciences,Jinan 250031,China
3. Jilin Institute of Meteorological Sciences,Changchun 130062,China
-
Received:2022-11-28Revised:2023-09-08Online:2024-02-29Published:2024-03-06
基于前馈神经网络的多模式集成降水预报研究
朱文刚1,2( ), 盛春岩1,2(
), 盛春岩1,2( ), 范苏丹1,2, 荣艳敏1,2, 曲美慧3
), 范苏丹1,2, 荣艳敏1,2, 曲美慧3
- 1.山东省气象防灾减灾重点实验室,山东 济南 250031
2.山东省气象科学研究所,山东 济南 250031
3.吉林省气象科学研究所,吉林 长春 130062
-
通讯作者:盛春岩(1972—),女,山东栖霞人,博士,正高级工程师,主要从事数值预报和天气预报技术开发。E-mail: sdqxscy@126.com。 -
作者简介:朱文刚(1985—),男,山东郯城人,硕士,高级工程师,主要从事数值天气预报和人工智能技术应用研究。E-mail: zhu122812@163.com。 -
基金资助:山东省自然科学基金面上项目(ZR2020MD055);人工智能气象应用技术创新团队项目(SDCXTD2023-3);山东省重点研发计划项目(2016GSF120017);山东省气象局重点课题项目(2019sdqxz07);山东省气象局重点课题项目(2023sdqxz08);山东省气象科学研究所开放基金项目(SDQXKF2015Z01);山东省气象科学研究所开放基金项目(SDQXKF2015M03)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZHU Wengang, SHENG Chunyan, FAN Sudan, RONG Yanmin, QU Meihui. Research on multi-model integrated precipitation forecast based on feed forward neural network[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(1): 117-128.
朱文刚, 盛春岩, 范苏丹, 荣艳敏, 曲美慧. 基于前馈神经网络的多模式集成降水预报研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(1): 117-128.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2024)-01-0117

Fig.2 Threat score (a) and weight coefficients (b) of 24 h accumulated precipitation of different grades predicted by different models from April to September 2019
| 方案 | 模式 | 简称 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ECMWF、CMA-SH9 | ES |
| 2 | ECMWF、CMA-MESO | EM |
| 3 | CMA-SH9、CMA-MESO | SM |
| 4 | ECMWF、CMA-SH9、CMA-MESO | ESM |
| 5 | ECMWF、CMA-SH9、CMA-MESO | Mul-OTS |
Tab.1 Design scheme
| 方案 | 模式 | 简称 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ECMWF、CMA-SH9 | ES |
| 2 | ECMWF、CMA-MESO | EM |
| 3 | CMA-SH9、CMA-MESO | SM |
| 4 | ECMWF、CMA-SH9、CMA-MESO | ESM |
| 5 | ECMWF、CMA-SH9、CMA-MESO | Mul-OTS |
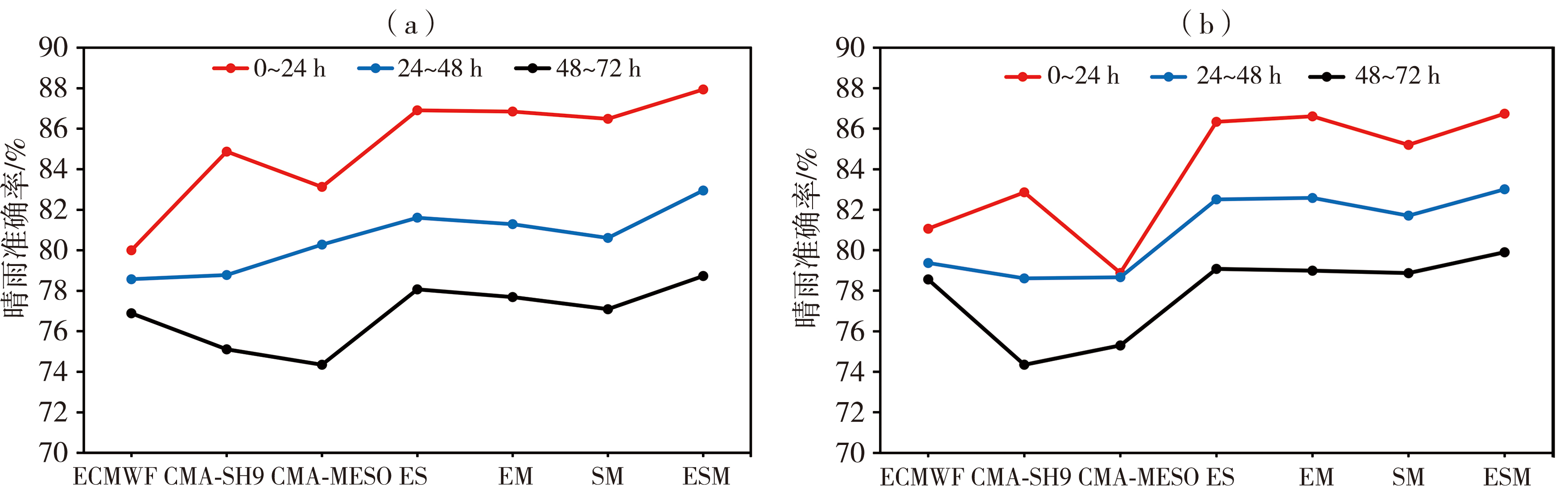
Fig.4 The accuracy of sunny and rainy of 10 times cross validation using DFNN method and the model prediction with different lead times in Shandong Province from April to September 2019 (a) starting at 08:00, (b) starting at 20:00
| 预报时效 | ECMWF | CMA-SH9 | CMA-MESO | ES | EM | SM | ESM | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 08:00 起报 | 20:00起报 | 08:00起报 | 20:00起报 | 08:00起报 | 20:00起报 | 08:00起报 | 20:00起报 | 08:00起报 | 20:00起报 | 08:00起报 | 20:00起报 | 08:00起报 | 20:00起报 | |
| 0~24 h | 0.51 | 0.52 | 0.59 | 0.59 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 0.46 | 0.48 | 0.49 | 0.46 | 0.45 |
| 24~48 h | 0.58 | 0.57 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.65 | 0.66 | 0.49 | 0.48 | 0.50 | 0.52 | 0.52 | 0.51 | 0.49 | 0.48 |
| 48~72 h | 0.63 | 0.62 | 0.65 | 0.65 | 0.69 | 0.70 | 0.52 | 0.52 | 0.53 | 0.54 | 0.55 | 0.54 | 0.51 | 0.52 |
Tab.2 The mean relative error of 10 times cross validation using DFNN method and model prediction with different start times and different lead times in Shandong Province from April to September 2019
| 预报时效 | ECMWF | CMA-SH9 | CMA-MESO | ES | EM | SM | ESM | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 08:00 起报 | 20:00起报 | 08:00起报 | 20:00起报 | 08:00起报 | 20:00起报 | 08:00起报 | 20:00起报 | 08:00起报 | 20:00起报 | 08:00起报 | 20:00起报 | 08:00起报 | 20:00起报 | |
| 0~24 h | 0.51 | 0.52 | 0.59 | 0.59 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 0.46 | 0.48 | 0.49 | 0.46 | 0.45 |
| 24~48 h | 0.58 | 0.57 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.65 | 0.66 | 0.49 | 0.48 | 0.50 | 0.52 | 0.52 | 0.51 | 0.49 | 0.48 |
| 48~72 h | 0.63 | 0.62 | 0.65 | 0.65 | 0.69 | 0.70 | 0.52 | 0.52 | 0.53 | 0.54 | 0.55 | 0.54 | 0.51 | 0.52 |
| 预报时效 | ECMWF | CMA-SH9 | CMA-MESO | ES | EM | SM | ESM | Mul-OTS | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 08:00 起报 | 20:00 起报 | 08:00起报 | 20:00起报 | 08:00起报 | 20:00起报 | 08:00起报 | 20:00起报 | 08:00起报 | 20:00起报 | 08:00起报 | 20:00起报 | 08:00起报 | 20:00起报 | 08:00起报 | 20:00起报 | |
| 0~24 h | 0.46 | 0.43 | 0.36 | 0.43 | 0.34 | 0.37 | 0.27 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.25 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.25 | 0.24 | 0.32 | 0.34 |
| 24~48 h | 0.48 | 0.45 | 0.46 | 0.45 | 0.41 | 0.40 | 0.32 | 0.30 | 0.31 | 0.28 | 0.34 | 0.30 | 0.29 | 0.30 | 0.40 | 0.37 |
| 48~72 h | 0.50 | 0.48 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.44 | 0.42 | 0.36 | 0.34 | 0.33 | 0.32 | 0.38 | 0.34 | 0.35 | 0.32 | 0.42 | 0.40 |
Tab.3 The mean relative error of 24-hour cumulative precipitation predicted with different starting time and different lead times by different models and different schemes in Shandong Province from April to September 2020
| 预报时效 | ECMWF | CMA-SH9 | CMA-MESO | ES | EM | SM | ESM | Mul-OTS | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 08:00 起报 | 20:00 起报 | 08:00起报 | 20:00起报 | 08:00起报 | 20:00起报 | 08:00起报 | 20:00起报 | 08:00起报 | 20:00起报 | 08:00起报 | 20:00起报 | 08:00起报 | 20:00起报 | 08:00起报 | 20:00起报 | |
| 0~24 h | 0.46 | 0.43 | 0.36 | 0.43 | 0.34 | 0.37 | 0.27 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.25 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.25 | 0.24 | 0.32 | 0.34 |
| 24~48 h | 0.48 | 0.45 | 0.46 | 0.45 | 0.41 | 0.40 | 0.32 | 0.30 | 0.31 | 0.28 | 0.34 | 0.30 | 0.29 | 0.30 | 0.40 | 0.37 |
| 48~72 h | 0.50 | 0.48 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.44 | 0.42 | 0.36 | 0.34 | 0.33 | 0.32 | 0.38 | 0.34 | 0.35 | 0.32 | 0.42 | 0.40 |

Fig.5 The accuracy of sunny and rainy of 24-hour cumulative precipitation predicted by different models and different schemes with different lead times in Shandong Province from April to September 2020 (a) starting at 08:00, (b) starting at 20:00

Fig.6 Threat score (a), miss rate (b), false alarm rate (c), bias score (d) and equitable threat score (e) of 0-24 h cumulative precipitation predicted by different models and different schemes in Shandong Province from April to September 2020

Fig.7 Threat score (a), miss rate (b), false alarm rate (c), bias score (d) and equitable threat score (e) of 24-48 h cumulative precipitation predicted by different models and different schemes in Shandong Province from April to September 2020

Fig.8 The observed values and the predicted values of different models and different schemes of 24 h cumulative precipitation from 08:00 on 23 to 08:00 on 24 August 2021 (a) observation, (b) ECMWF, (c) CMA-SH9, (d) CMA-MESO, (e) ES, (f) EM, (g) SM, (h) ESM, (i) Mul-OTS

Fig.9 The accuracy of sunny and rainy (a, b) and equitable threat score (c, d) of cumulative precipitation in 12~36 h (a, c) and 36~60 h (b, d) from April to September 2020 in Shandong Province were predicted by different models and different schemes
| [1] | 阿斯顿·张, 李沐, 扎卡里C.立顿, 等, 2019. 动手学深度学习[M]. 北京: 人民邮电出版社. |
| [2] | 毕宝贵, 代刊, 王毅, 等, 2016. 定量降水预报技术进展[J]. 应用气象学报, 27(5): 534-549. |
| [3] |
曹萍萍, 肖递祥, 龙柯吉, 等, 2023. 基于分位数映射法的四川省ECMWF模式降水预报误差订正分析[J]. 干旱气象, 41(4): 666-675.
DOI |
| [4] | 陈锦鹏, 冯业荣, 蒙伟光, 等, 2021. 基于卷积神经网络的逐时降水预报订正方法研究[J]. 气象, 47(1): 60-70. |
| [5] | 杜钧, 康志明, 2014. 天气预报中不确定性问题的调查分析[J]. 气象科技进展, 4(1): 58-67. |
| [6] | 顾建峰, 周国兵, 刘伯骏, 等, 2020. 人工智能技术在重庆临近预报业务中的初步研究与应用[J]. 气象, 46(10): 1 286-1 296. |
| [7] | 李金洁, 王爱慧, 2019. 基于西南地区台站降雨资料空间插值方法的比较[J]. 气候与环境研究, 24(1): 50-60. |
| [8] | 李莉, 李应林, 田华, 等, 2011. T213全球集合预报系统性误差订正研究[J]. 气象, 37(1): 31-38. |
| [9] | 李俊, 杜钧, 陈超君, 2014. 降水偏差订正的频率(或面积)匹配方法介绍和分析[J]. 气象, 40(5): 580-588. |
| [10] | 李俊, 杜钧, 陈超君, 2015. “频率匹配法”在集合降水预报中的应用研究[J]. 气象, 41(6): 674-684. |
| [11] |
李涛, 陈杰, 汪方, 等, 2022. 一种基于神经网络的中国区域夏季降水预测订正算法[J]. 干旱气象, 40(2): 308-316.
DOI |
| [12] | 穆穆, 陈博宇, 周菲凡, 等, 2011. 气象预报的方法和不确定性[J]. 气象, 37(1): 1-13. |
| [13] |
任宏利, 丑纪范, 2007. 数值模式的预报策略和方法研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 22(4): 376-385.
DOI |
| [14] | 孙健, 曹卓, 李恒, 等, 2021. 人工智能技术在数值天气预报中的应用[J]. 应用气象学报, 32(1): 1-11. |
| [15] | 童尧, 高学杰, 韩振宇, 等, 2017. 基于RegCM4模式的中国区域日尺度降水模拟误差订正[J]. 大气科学, 41(6): 1 156-1 166. |
| [16] | 吴启树, 韩美, 刘铭, 等, 2017. 基于评分最优化的模式降水预报订正算法对比[J]. 应用气象学报, 28(3): 306-317. |
| [17] | 危国飞, 刘会军, 吴启树, 等, 2020. 多模式降水分级最优化权重集成预报技术[J]. 应用气象学报, 31(6): 668-680. |
| [18] | 王海霞, 智协飞, 2015. 基于TIGGE多模式降水量预报的统计降尺度研究[J]. 气象科学, 35(4): 430-437. |
| [19] | 王在文, 郑祚芳, 陈敏, 等, 2012. 支持向量机非线性回归方法的气象要素预报[J]. 应用气象学报, 23(5): 562-570. |
| [20] | 王雨, 闫之辉, 2007. 降水检验方案变化对降水检验评估效果的影响分析[J]. 气象, 33(12): 53-61. |
| [21] | 叶笃正, 严中伟, 戴新刚, 等, 2006. 未来的天气气候预测体系[J]. 气象, 32(4): 3-8. |
| [22] |
袁凯, 庞晶, 李武阶, 等, 2023. 深度学习模型在2021年汛期武汉市雷达回波临近预报中的应用评估[J]. 干旱气象, 41(1): 173-185.
DOI |
| [23] | 袁雅涵, 王烁, 王文青, 等, 2023. 基于深度学习的积层混合云对流泡降水粒子特征研究[J]. 干旱气象, 41(6): 933-943. |
| [24] | 周迪, 陈静, 陈朝平, 等, 2015. 暴雨集合预报-观测概率匹配订正法在四川盆地的应用研究[J]. 暴雨灾害, 34(2): 97-104. |
| [25] | 智协飞, 吕游, 2019. 基于频率匹配法的中国降水多模式预报订正研究[J]. 大气科学学报, 42(6): 814-823. |
| [26] | 智协飞, 赵忱, 2020. 基于集合成员订正的强降水多模式集成预报[J]. 应用气象学报, 31(3): 303-314. |
| [27] | 智协飞, 张珂珺, 田烨, 等, 2021. 基于神经网络和地理信息的华东及华南地区降水概率预报[J]. 大气科学学报, 44(3): 381-393. |
| [28] | EBERT E E, 2001. Ability of a poor man’s ensemble to predict the probability and distribution of precipitation[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 129(10): 2 461-2 480. |
| [29] | HINTON G E, OSINDERO S, TEH Y W, 2006. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets[J]. Neural Computation, 18(7): 1 527-1 554. |
| [30] | JOLLIFFE I T, STEPHENSON D B, 2003. Forecast verification: A practitioner's guide in atmospheric science[M]. Chichester: John Wiley&Sons. |
| [31] | PANOFSKY H A, BRIER G H, 1968. Some applications of statistics to meteorology[M]. Philadelphia: The Pennsylvania State University Press:224-225. |
| [1] | LU Ye, MENG Miaozhi, QIAO Danyang, REN Huan, HE Yao, HAN Jie. Fine objective forecast method of precipitation phases in the winter half-year in Baoji City [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(5): 820-827. |
| [2] | PAN Liujie, LIANG Mian, QI Chunjuan, LI Peirong, ZHU Qingliang. Characteristics of meteorological elements and objective forecast verification at the key venues of “the 14th National Games” [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(3): 491-502. |
| [3] | WANG Yehong, ZHAO Yuchun. Verification and assessment of persistent rainfall forecasts of GRAPES-REPS in pre-summer of 2017 in southern China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(2): 328-340. |
| [4] | WANG Junchao, WANG Zhibin, LAI Anwei, XIAO Yanjiao, WANG Jue. Experimental study on short-term and impending prediction of precipitation echo based on blending method of numerical prediction and radar extrapolation prediction [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(3): 485-499. |
| [5] | JI Xueshuai, WANG Lijing, GUO Hong, KANG Bosi, HUANG Shanjiang, ZHANG Xidan, GUO Xuhui. Analysis of characteristics of precipitation phase during a rain-snow weather process in Zhangjiakou based on multi-source observation data [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(3): 507-515. |
| [6] | HUANG Chuhui, NIU Jinlong, LI Guoping, CHEN Chaoping, XIAO Dixiang, ZHANG Ping. Correction method of precipitation in steep terrain transition zone forecasted based on southwest center WRF ADAS real-time modeling system [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(2): 317-326. |
| [7] | CHENG Peng, LUO Han, CHEN Peixuan, CAO Yanchao, LI Baozi, CHEN Qi. Statistical Characteristics and Early Warning Indicators of Short-term Heavy Rainfall in the Loess Plateau of Qingyang [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(2): 319-328. |
| [8] | DONG Wei, YANG Guangwu, MA Liangchen, ZHU Dan. Discrimination of Winter Precipitation Types Based on Temperature in Changchun City [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(3): 363-. |
| [9] | WANG Chengfu1, XIE Rui2, JI Zhejun1, AO Zejian1,LUO Wangjun1, CHEN Yang1, WEI Juanjuan1, JIN Manhui1. The Circulation Classification and Characteristics of Heavy Rainfall in Gannan Plateau [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(1): 97-108. |
| [10] | ZHANG Pingping, ZHANG Ning, DONG Liangpeng, ZHANG Mengmeng. Research on Concept Model of Sudden Mesoscale Rainstorms with Three Types in Sanxia Valley [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(6): 1027-1035. |
| [11] | SHI Weiheng, WANG Lei, HAN Fei, YU Wenjie,KONG Fanlong, SONG Haiqing. Research on Winter Precipitation Type Forecast Model in Liaocheng of Shandong Province Based on Physical Parameters [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(5): 822-829. |
| [12] | FANG Zheqing1,2, HUANG Ningli2, WANG Linwei3, FU Ying3. Application of Sun-Photometer and Microwave Radiometer Data to Improve Forecast Ability About Afternoon Severe Convection in Summer [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(1): 157-163. |
| [13] | XU Min, ZHANG Yu, ZHANG Shaohui. Application of Wind Profiler Radar Data in a Heavy Precipitation Process in Central Hebei Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2016, 34(5): 898-905. |
| [14] | DUAN Yunxia, LI Deqin, LI Dawei, LIANG Hong, CHAI Xiaoling, ZHANG Shuai. Analysis on Precipitation Phase Characteristics and Its Forecast Methods of Shenyang [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2016, 34(1): 51-57. |
| [15] | HUAN Haijun,LIU Huanbin, LIU Yan, XIA Fuhua. Revising Method of Rainstorm Intensity Formula in Main Urban in Middle Area of Shandong Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2016, 34(1): 188-194. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||