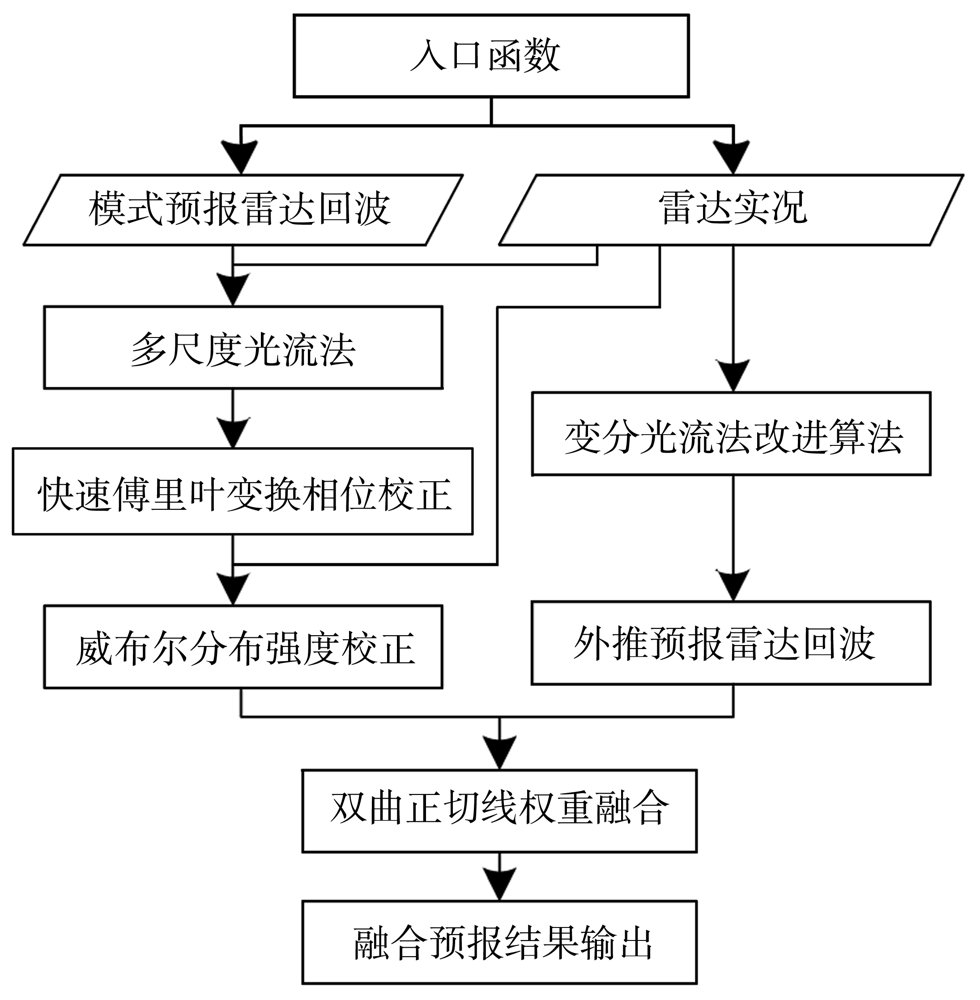
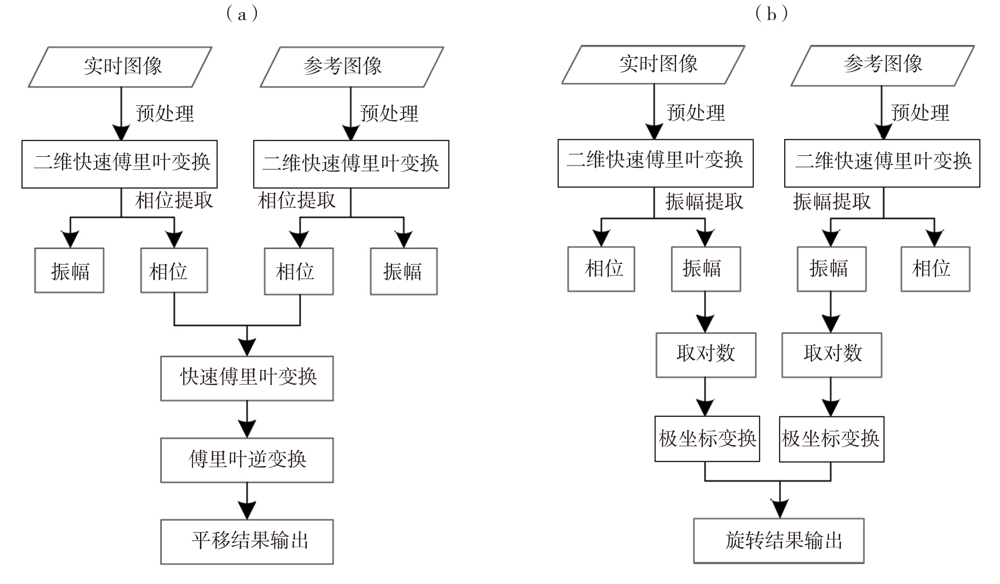
Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2022, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (3): 485-499.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-03-0485
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Experimental study on short-term and impending prediction of precipitation echo based on blending method of numerical prediction and radar extrapolation prediction
WANG Junchao1,2,3( ), WANG Zhibin1(
), WANG Zhibin1( ), LAI Anwei1,2, XIAO Yanjiao1, WANG Jue1
), LAI Anwei1,2, XIAO Yanjiao1, WANG Jue1
- 1. Hubei Key Laboratory for Heavy Rain Monitoring and Warning Research, Institute of Heavy Rain, China Meteorological Administration, Wuhan 430205, China
2. State Key Laboratory of Severe Weather, Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences, Beijing 100081, China
3. Three Gorges National Climatic Station, Yichang 443000, Hubei, China
-
Received:2021-07-13Revised:2021-11-23Online:2022-06-30Published:2022-06-28 -
Contact:WANG Zhibin
基于数值预报与雷达外推预报融合方法的降水回波短临预报试验研究
王俊超1,2,3( ), 王志斌1(
), 王志斌1( ), 赖安伟1,2, 肖艳姣1, 王珏1
), 赖安伟1,2, 肖艳姣1, 王珏1
- 1.中国气象局武汉暴雨研究所,暴雨监测预警湖北省重点实验室,湖北 武汉 430205
2.中国气象科学研究院灾害天气国家重点实验室,北京 100081
3.三峡国家气候观象台,湖北 宜昌 443000
-
通讯作者:王志斌 -
作者简介:王俊超(1982—),男,硕士,高级工程师,主要从事数据融合和系统分析集成研究. E-mail: nanxingong@163.com。 -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划项目(2018YFC1507200);灾害天气国家重点实验室开放课题(2021LASW-A03);湖北省气象局科技课题(2019YJ01)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
WANG Junchao, WANG Zhibin, LAI Anwei, XIAO Yanjiao, WANG Jue. Experimental study on short-term and impending prediction of precipitation echo based on blending method of numerical prediction and radar extrapolation prediction[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(3): 485-499.
王俊超, 王志斌, 赖安伟, 肖艳姣, 王珏. 基于数值预报与雷达外推预报融合方法的降水回波短临预报试验研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(3): 485-499.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-03-0485
| 降水过程 | 强降水时段(北京时) |
|---|---|
| “6·12” | 6月12日02:00—06:00和18:00—23:00 |
| “6·27” | 6月27日20:00至28日08:00 |
| “7·02” | 7月2日08:00—18:00 |
| “7·05” | 7月5日04:00—12:00和5日23:00至6日06:00 |
Tab.1 The occurrence period of heavy precipitation during four precipitation processes from June to July 2020 in Hubei Province
| 降水过程 | 强降水时段(北京时) |
|---|---|
| “6·12” | 6月12日02:00—06:00和18:00—23:00 |
| “6·27” | 6月27日20:00至28日08:00 |
| “7·02” | 7月2日08:00—18:00 |
| “7·05” | 7月5日04:00—12:00和5日23:00至6日06:00 |

Fig.3 Comparison of 1-hour precipitation echo forecast with different scales from radar extrapolation (a, e),RUC-Wuhan model (b, f) and blending technology (e, g) initiated from 12:00 UTC 12 June 2020 with the observation of radar (d, h) (Unit: dBZ) (The red box represents the intensive region of heavy precipitation. the same as below) (a, b, c, d) 0.01°× 0.01°, (e, f, g, h) 0.02°× 0.02°
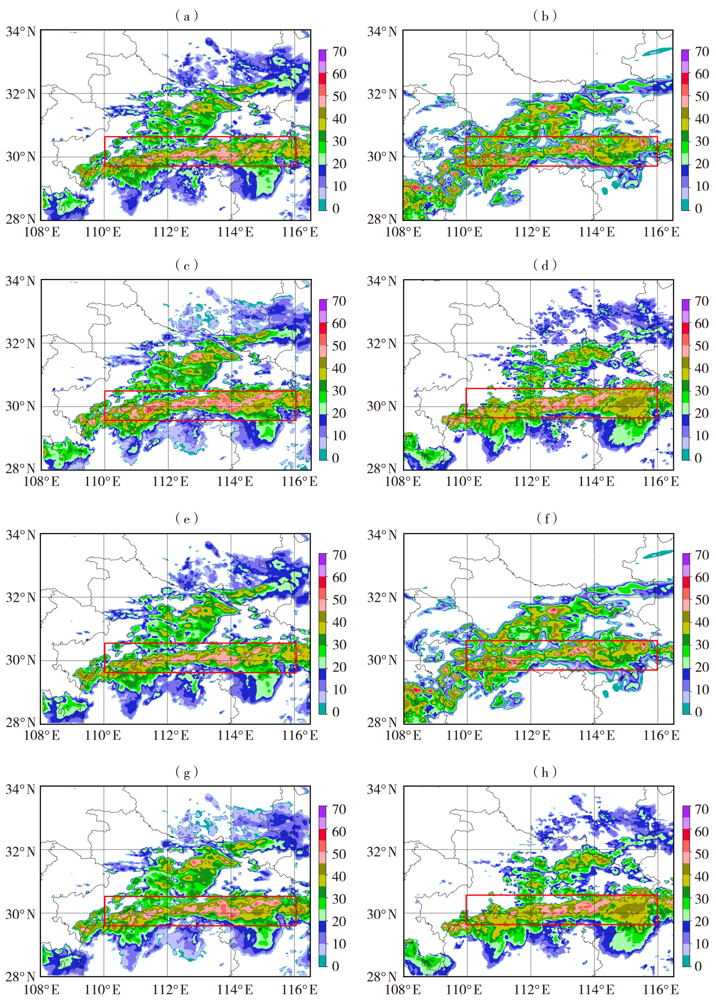
Fig.4 Comparison of 1-hour precipitation echo forecast with different scales from radar extrapolation (a, e), RUC-Wuhan model (b, f) and blending technology (e, g) initiated from 16:00 UTC 5 July 2020 with the observation of radar (d, h) (Unit: dBZ) (a、b、c、d)0.01°× 0.01°,(e、f、g、h)0.04°× 0.04°
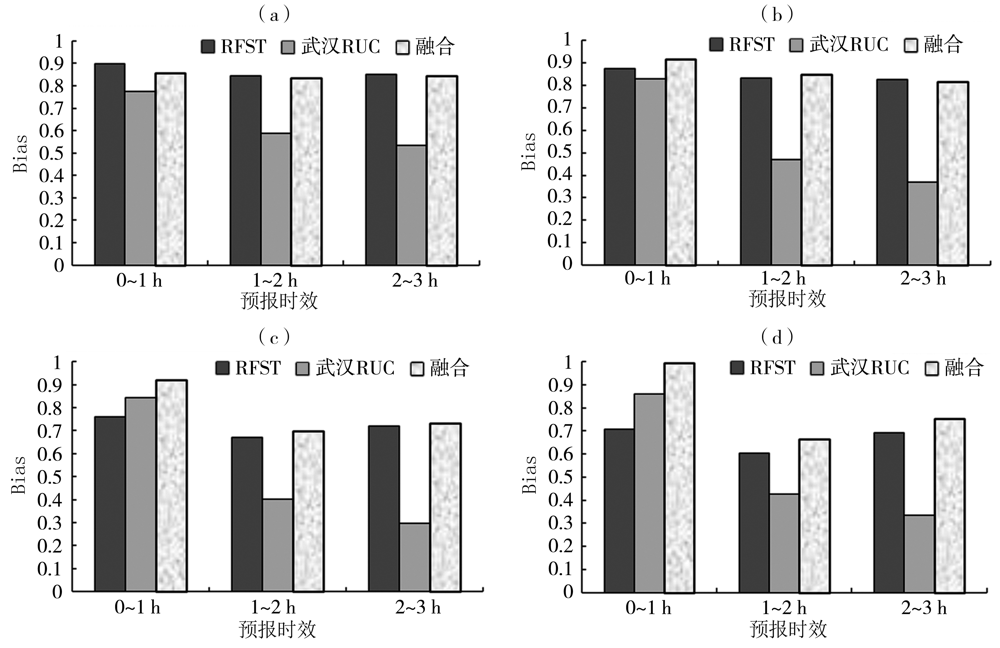
Fig.5 The change of average Bias of precipitation echo prediction by three methods for different thresholds with prediction time for four precipitation processes (a)10 dBZ,(b) 20 dBZ,(c) 30 dBZ,(d) 40 dBZ
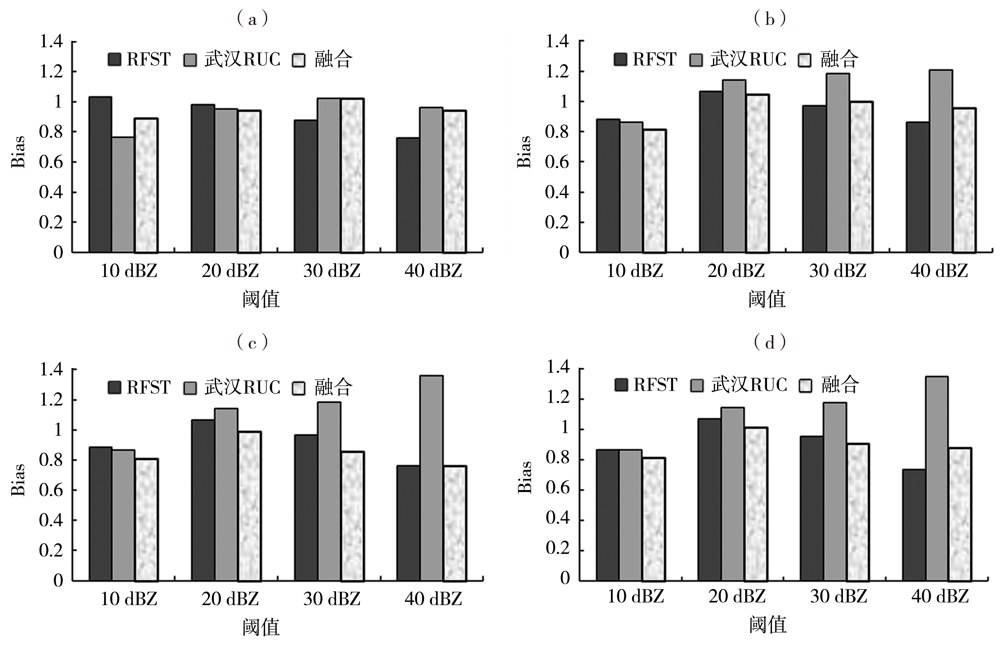
Fig.6 The change of average Bias of 0-1 h precipitation echo prediction by three methods for different scales with thresholds for four precipitation processes (a)0.01°× 0.01°,(b)0.02°× 0.02°,(c)0.04°× 0.04°,(d)0.08°× 0.08°
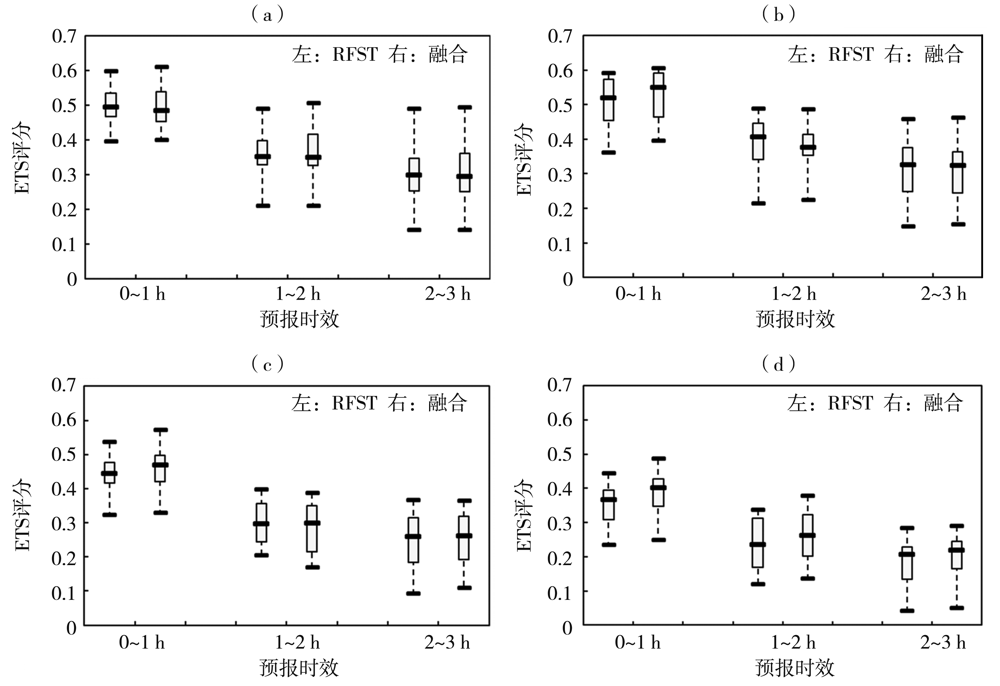
Fig.7 The change of average ETS scores of precipitation echo prediction by two methods for different thresholds with prediction time for four precipitation processes (a)10 dBZ,(b)20 dBZ,(c)30 dBZ,(d)40 dBZ
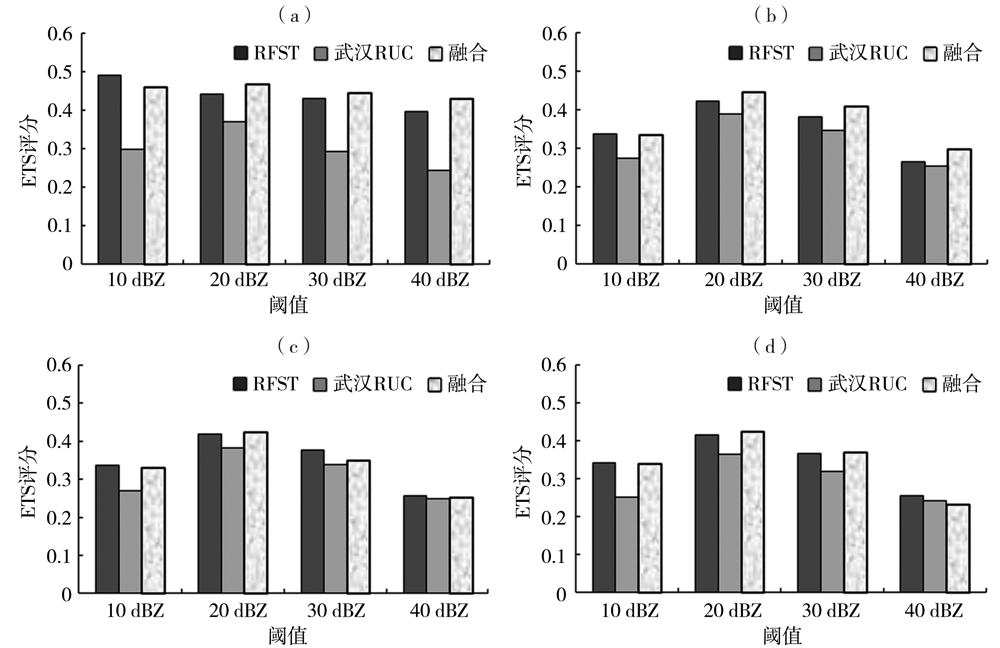
Fig.8 The change of average ETS scores of 0-1 h precipitation echo forecast by three methods for different scales with thresholds for four precipitation processes (a)0.01°× 0.01°,(b)0.02°× 0.02°,(c)0.04°× 0.04°,(d)0.08°× 0.08°
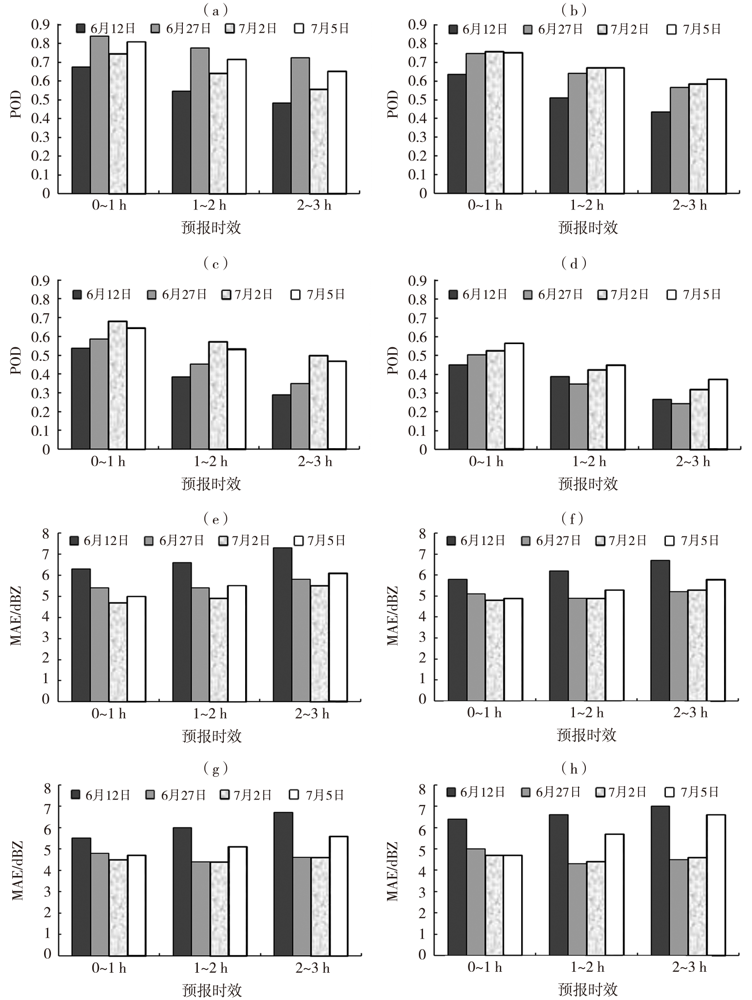
Fig.9 The change of average POD (a, b, c, d) and MAE (e, f, g, h) of blending forecast for different thresholds with forecast time for four precipitation processes (a、e)10 dBZ,(b、f)20 dBZ,(c、g)30 dBZ,(d、h)40 dBZ
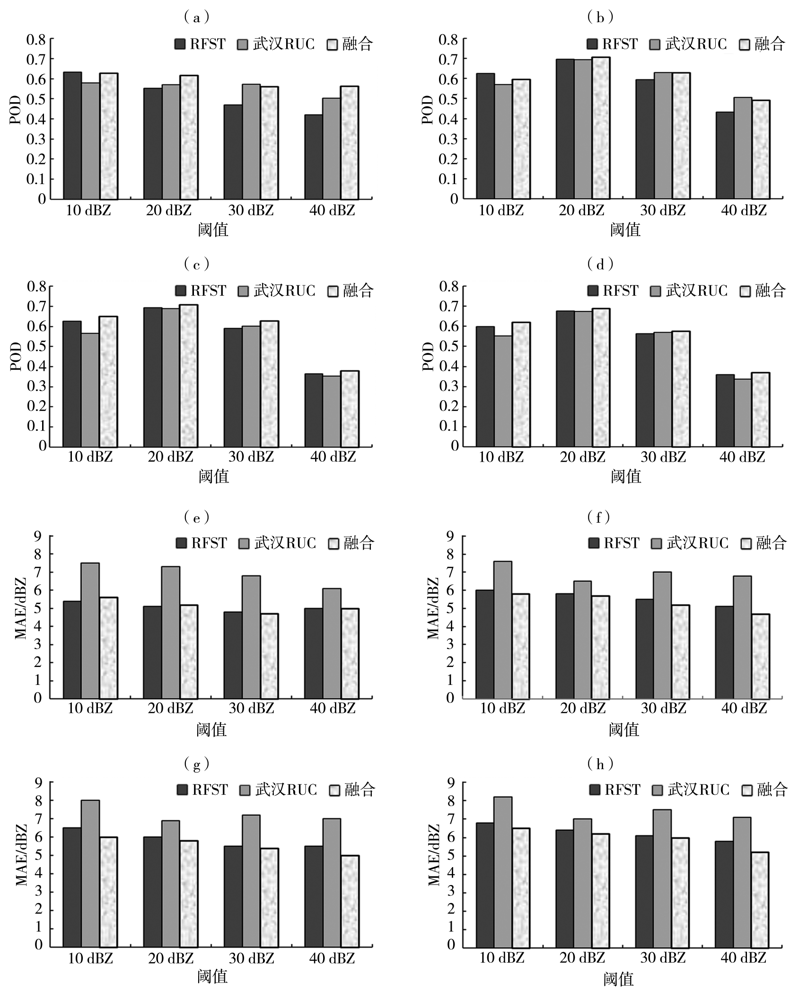
Fig.10 The change of average POD (a, b, c, d) and MAE (e, f, g, f) by three forecasts for different scales with thresholds for four precipitation processes (a、e)0.01°× 0.01°,(b、f)0.02°× 0.02°,(c、g)0.04°× 0.04°,(d、h)0.08°× 0.08°
| [1] |
RINEHART R E, GARVEY E T. Three-dimensional storm motion detection by conventional weather radar[J]. Nature, 1978, 273: 287-289.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
LI L, SCHMID W, JOSS J. Nowcasting of motion and growth of precipitation with radar over a complex orography[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 1995, 34(6): 1286-1300.
DOI URL |
| [3] | 王珏, 张家国, 万玉发. 多尺度合成的降水临近预报技术[J]. 气象科技, 2008, 36(5): 524-528. |
| [4] | 孔荣, 王建捷, 梁丰, 等. 尺度分解技术在定量降水临近预报检验中的应用[J]. 应用气象学报, 2010, 21(5): 535-544. |
| [5] | 罗义, 梁旭东, 王刚, 等. 雷达反演的多尺度风场在临近预报中的应用研究[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2021, 40(4): 401-409. |
| [6] | 韩雷, 王洪庆, 林隐静. 光流法在强对流天气临近预报中的应用[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 44(5): 751-755. |
| [7] | LUCAS B D, KANADE T. An iterative image registration technique with an application to stereo vision[C]// Proceedings of Seventh International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, 1981: 121-130. |
| [8] |
HORN B K P, SCHUNCK B G. Determing optical flow[J]. Artificial Intelligence, 1981, 17(1/2/3): 185-204.
DOI URL |
| [9] | 曹春燕, 陈元昭, 刘东华, 等. 光流法及其在临近预报中的应用[J]. 气象学报, 2015, 73(3): 471-480. |
| [10] | 田刚, 陈良华, 魏凡, 等. 基于光流法雷达外推的2020年长江致洪降水临近预报检验评估[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2021, 40(3): 316-325. |
| [11] | 尹麒名, 甘建红, 漆慧, 等. 一种改进的循环神经网络雷达图像外推算法[J]. 气象科技, 2021, 49(1): 18-24. |
| [12] | 韩丰, 龙明盛, 李月安, 等. 循环神经网络在雷达临近预报中的应用[J]. 应用气象学报, 2019, 30(1): 61-69. |
| [13] | 陈元昭, 林良勋, 王蕊, 等. 基于生成对抗网络GAN的人工智能临近预报方法研究[J]. 大气科学学报, 2019, 42(2): 311-320. |
| [14] | 郭瀚阳, 陈明轩, 韩雷, 等. 基于深度学习的强对流高分辨率临近预报试验[J]. 气象学报, 2019, 77(4): 715-727. |
| [15] | 胡胜, 罗兵, 黄晓梅, 等. 临近预报系统(SWIFT)中风暴产品的设计及应用[J]. 气象, 2010, 36(1): 54-58. |
| [16] | 万玉发, 王志斌, 张家国, 等. 长江中游临近预报业务系统(MYNOS)及其应用[J]. 应用气象学报, 2013, 24(4): 504-512. |
| [17] | 陈明轩, 高峰, 孔荣, 等. 自动临近预报系统及其在北京奥运期间的应用[J]. 应用气象学报, 2010, 21(4): 395-404. |
| [18] | 韩丰, 沃伟峰. SWAN2.0系统的设计与实现[J]. 应用气象学报, 2018, 29(1): 25-34. |
| [19] | 郑永光, 张小玲, 周庆亮, 等. 强对流天气短时临近预报业务技术进展与挑战[J]. 气象, 2010, 36(7): 33-42. |
| [20] |
WARNER T T, BRANDS E A, SUN J Z, et al. Prediction of a flash flood in complex terrain. Part I: a comparison of rainfall estimates from radar, and very short range rainfall simulations from a dynamic model and an automated algorithmic system[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 2000, 39: 797-814.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
HU M, XUE M, BREWSTER K A. 3DVAR and cloud analysis with WSR-88D level-II data for the prediction of the Fort Worth, Texas, tornadic thunderstorm. Part I: cloud analysis and its impact[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 2006, 134(2): 675-698.
DOI URL |
| [22] | 刘黎平. 用双多普勒雷达反演降水系统三维风场试验研究[J]. 应用气象学报, 2003, 14(4): 502-504. |
| [23] | 王瑾, 刘黎平. CINRAD/CD雷达反射率因子同化对中尺度数值模式云微物理量场调整的分析[J]. 高原气象, 2009, 28(1): 173-185. |
| [24] | 马清云, 李泽椿, 陶士伟. 单部多普勒天气雷达风场反演及其在数值预报中的应用试验[J]. 应用气象学报, 2001, 12(4): 488-494. |
| [25] | 李永平, 袁招洪, 王晓峰. 用多普勒雷达反射率调整模式大气的云微物理变量[J]. 应用气象学报, 2004, 15(6): 658-663. |
| [26] |
GOLDING B W. Nimrod: a system for generating automated very short range forecasts[J]. Meteorological Applications, 1998, 5(1): 1-16.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
PIERCE C E, HARDAKER P J, COLLIER C G, et al. GANDOLF: a system for generating automated nowcasts of convective precipitation[J]. Meteorological Applications, 2000, 7(4): 341-360.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
BOWLER N E, PIERCE C E, SEED A W. STEPS: a probabilistic precipitation forecasting scheme which merges an extrapolation nowcast with downscaled NWP[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 2006, 132(620): 2127-2155.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
LIN C, VASIĆ S, ZAWADZKI I, et al. Precipitation forecast based on numerical weather prediction models and radar nowcasts[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2004, 32(14): L14801. DOI: 10.1029/2005GL023451.
DOI |
| [30] |
HAIDEN T, KANN A, PISTOTNIK G, et al. Integrated nowcasting through comprehensive analysis (INCA) system description[J]. Weather and Forecasting, 2010, 26:166-182.
DOI URL |
| [31] | 黄伟健, 黎守德. “急流”(RAPIDS) 暴雨预报系统-“小涡旋”与数值天气预报模式的融合[C]// 第20届粤港澳气象科技研讨会.澳门, 2006. |
| [32] |
LIANG Q, FENG Y, DENG W, et al. A composite approach of radar echo extrapolation based on TREC vectors in combination with model-predicted winds[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2010, 27(5): 1119-1130.
DOI URL |
| [33] | 王志斌, 肖艳姣, 吴涛. 基于改进光流法的雷达图像运动估计[J]. 计算机技术与发展, 2017, 27(12): 170-175. |
| [34] | 王志斌, 肖艳姣, 吴涛, 等. 改进变分光流法并行算法实现[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2019, 36(1): 105-110. |
| [35] |
AUBERT G, DERICHE R, KORNPROBST P. Computing optical flow via variational techniques[J]. SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, 1999, 60(1): 156-182.
DOI URL |
| [36] | 杨汉贤, 黄伟健, 郑子路. “多尺度光流变分法”在临近降雨预报的应用和表现[C]// 第24届粤港澳气象科技研讨会. 深圳, 2010. |
| [37] | 程从兰, 陈明轩, 王建捷, 等. 基于雷达外推临近预报和中尺度数值预报融合技术的短时定量降水预报试验[J]. 气象学报, 2013, 71(3): 397-415. |
| [38] |
王丹, 王改利, 刘黎平, 等. 基于雷达回波外推和中尺度模式预报的短时降水对比分析[J]. 高原气象, 2014, 33(3): 811-822.
DOI |
| [39] |
王改利, 赵翠光, 刘黎平, 等. 雷达回波外推预报的误差分析[J]. 高原气象, 2013, 32(3): 874-883.
DOI |
| [1] | WANG Yehong, ZHAO Yuchun. Verification and assessment of persistent rainfall forecasts of GRAPES-REPS in pre-summer of 2017 in southern China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(2): 328-340. |
| [2] | JI Xueshuai, WANG Lijing, GUO Hong, KANG Bosi, HUANG Shanjiang, ZHANG Xidan, GUO Xuhui. Analysis of characteristics of precipitation phase during a rain-snow weather process in Zhangjiakou based on multi-source observation data [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(3): 507-515. |
| [3] | HUANG Chuhui, NIU Jinlong, LI Guoping, CHEN Chaoping, XIAO Dixiang, ZHANG Ping. Correction method of precipitation in steep terrain transition zone forecasted based on southwest center WRF ADAS real-time modeling system [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(2): 317-326. |
| [4] | CHENG Peng, LUO Han, CHEN Peixuan, CAO Yanchao, LI Baozi, CHEN Qi. Statistical Characteristics and Early Warning Indicators of Short-term Heavy Rainfall in the Loess Plateau of Qingyang [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(2): 319-328. |
| [5] | DONG Wei, YANG Guangwu, MA Liangchen, ZHU Dan. Discrimination of Winter Precipitation Types Based on Temperature in Changchun City [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(3): 363-. |
| [6] | WANG Chengfu1, XIE Rui2, JI Zhejun1, AO Zejian1,LUO Wangjun1, CHEN Yang1, WEI Juanjuan1, JIN Manhui1. The Circulation Classification and Characteristics of Heavy Rainfall in Gannan Plateau [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(1): 97-108. |
| [7] | ZHANG Pingping, ZHANG Ning, DONG Liangpeng, ZHANG Mengmeng. Research on Concept Model of Sudden Mesoscale Rainstorms with Three Types in Sanxia Valley [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(6): 1027-1035. |
| [8] | SHI Weiheng, WANG Lei, HAN Fei, YU Wenjie,KONG Fanlong, SONG Haiqing. Research on Winter Precipitation Type Forecast Model in Liaocheng of Shandong Province Based on Physical Parameters [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(5): 822-829. |
| [9] | FANG Zheqing1,2, HUANG Ningli2, WANG Linwei3, FU Ying3. Application of Sun-Photometer and Microwave Radiometer Data to Improve Forecast Ability About Afternoon Severe Convection in Summer [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(1): 157-163. |
| [10] | XU Min, ZHANG Yu, ZHANG Shaohui. Application of Wind Profiler Radar Data in a Heavy Precipitation Process in Central Hebei Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2016, 34(5): 898-905. |
| [11] | DUAN Yunxia, LI Deqin, LI Dawei, LIANG Hong, CHAI Xiaoling, ZHANG Shuai. Analysis on Precipitation Phase Characteristics and Its Forecast Methods of Shenyang [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2016, 34(1): 51-57. |
| [12] | HUAN Haijun,LIU Huanbin, LIU Yan, XIA Fuhua. Revising Method of Rainstorm Intensity Formula in Main Urban in Middle Area of Shandong Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2016, 34(1): 188-194. |
| [13] | LV Tingzhen, DENG Shaoge, HU Yijia, ZHANG Kai. Quantitative Prediction of Precipitation in the East of Northwest China During the Flood Period by Using the Year-to-year Increment Approach [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(3): 386-394. |
| [14] | DANG Zhangli, ZHANG Jingpeng, QU Zongxi, ZHAO Hui, ZHANG Beidou, ZHANG Wenyu. The Application of Microwave Radiometer Observation Data on Precipitation Forecast [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(2): 340-343. |
| [15] | LIU Weicheng,WANG Yong,ZHOU Xiaojun. Error Statistics and Correction Method of QPE Product in SWAN System [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2014, 32(6): 1025-1030. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||