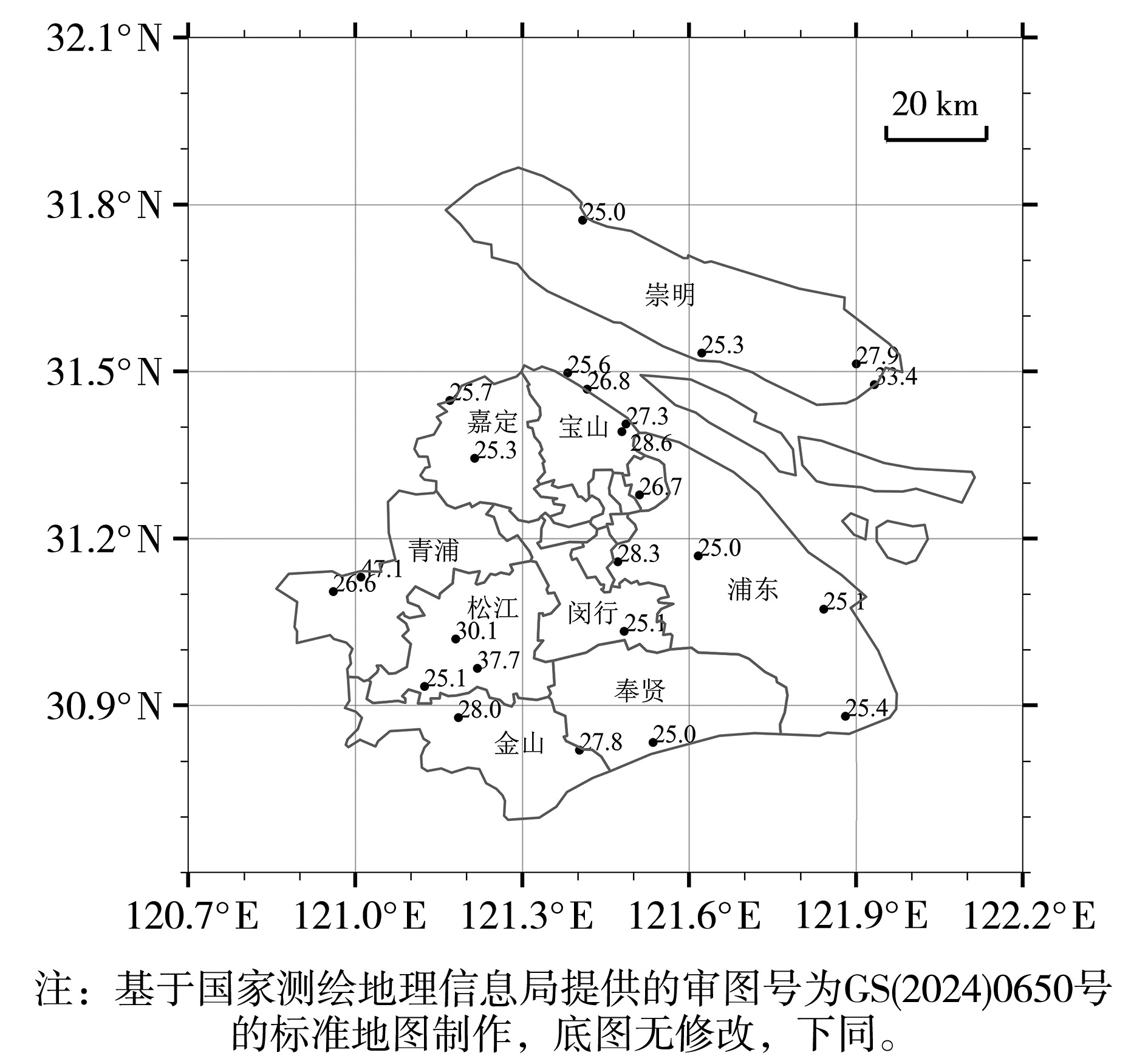
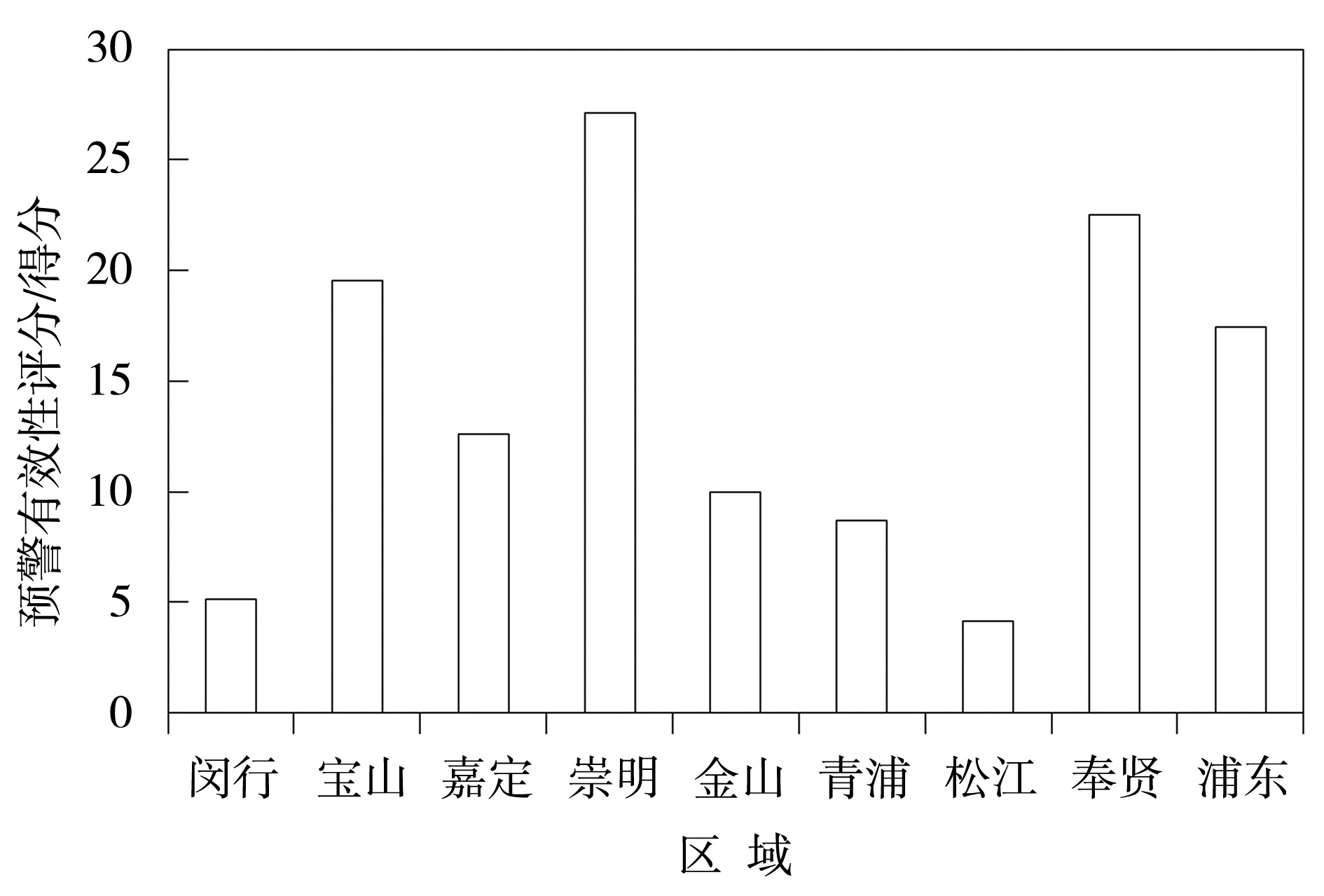
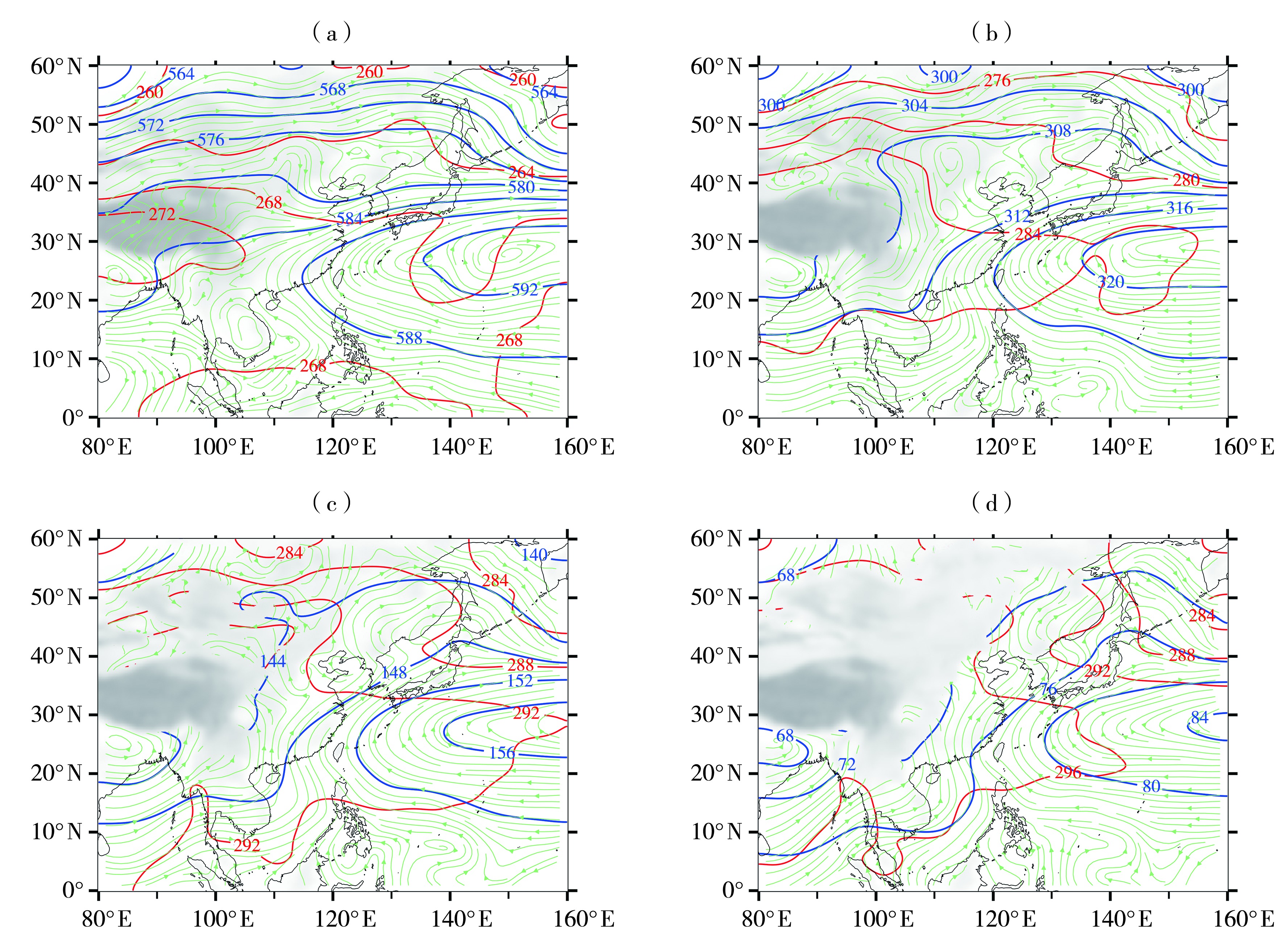
| [1] |
鲍丽丽, 王小勇, 段秀兰, 等, 2024. 2022年陇南“4·19”强对流天气成因及其对配电线路故障的影响分析[J]. 干旱气象, 42(3):437-446.
DOI
|
| [2] |
曹晓岗, 姚建群, 2017. 上海天气预报手册[M]. 北京: 气象出版社.
|
| [3] |
费海燕, 王秀明, 周小刚, 等, 2016. 中国强雷暴大风的气候特征和环境参数分析[J]. 气象, 42(12):1513-1 521.
|
| [4] |
符式红, 王秀明, 俞小鼎, 2018. 相似环流背景下海南两次不同类型强对流天气对比研究[J]. 气象学报, 76(5):742-754.
|
| [5] |
高帆, 俞小鼎, 王秀明, 2023. 山东较大范围致灾雷暴大风的多普勒天气雷达特征[J]. 气象, 49(7):790-804.
|
| [6] |
高建平, 马中元, 罗燕, 2019. 2017年江西上高雷暴大风雷达回波特征分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 13(2):55-62.
|
| [7] |
高晓梅, 俞小鼎, 王令军, 等, 2018. 鲁中地区分类强对流天气环境参量特征分析[J]. 气象学报, 76(2):196-212.
|
| [8] |
顾问, 张晶, 谈建国, 等, 2017. 上海夏季海风锋及其触发对流的时空分布和环流背景分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 33(5):644-653.
|
| [9] |
郭丽娜, 马艳, 于慧珍, 2022. 青岛沿海地区大风特征及其预警评估[J]. 海洋气象学报, 42(2):90-98.
|
| [10] |
井宇, 陈闯, 赵强, 等, 2024. 陕西雷暴大风时空分布和气象条件分析[J]. 干旱气象, 42(4):576-587.
DOI
|
| [11] |
李典南, 向淑君, 袁三明, 等, 2024. 贵州中北部一次冰雹和雷暴大风过程综合诊断[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 44(2):103-111.
|
| [12] |
李海俊, 单九生, 张帆, 2022. 新SWAN江西本地化平台产品应用和检验评估[J]. 气象与减灾研究, 45(2):151-160.
|
| [13] |
李强, 苗爱梅, 王洪霞, 等, 2023. 山西省雷暴大风的统计特征及概念模型[J]. 干旱气象, 41(3):423-433.
DOI
|
| [14] |
廖晓农, 于波, 卢丽华, 2009. 北京雷暴大风气候特征及短时临近预报方法[J]. 气象, 35(9):18-28.
|
| [15] |
马鸿青, 张江涛, 李彦, 等, 2019. 河北保定“7·9”致灾雷暴大风环境场与风暴特征[J]. 干旱气象, 37(4):613-621.
|
| [16] |
马志敏, 王将, 连钰, 等, 2023. 云南一次强对流暴雨天气学成因分析[J]. 干旱气象, 41(4):629-638.
DOI
|
| [17] |
毛卓成, 许建明, 瞿元昊, 等, 2023. 上海海陆风分类特征、环流背景及对O3的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 43(3):1002-1 013.
|
| [18] |
盛杰, 金荣花, 张小雯, 等, 2025. 临近气象预报大模型“风雷”V1版本检验及个例评估[J]. 气象, 51(4):389-399.
|
| [19] |
王福侠, 俞小鼎, 裴宇杰, 等, 2016. 河北省雷暴大风的雷达回波特征及预报关键点[J]. 应用气象学报, 27(3):342-351.
|
| [20] |
王秀明, 周小刚, 俞小鼎, 2013. 雷暴大风环境特征及其对风暴结构影响的对比研究[J]. 气象学报, 71(5):839-852.
|
| [21] |
徐晓芳, 邹玲, 2024. 阿坝州2023年一次弱降水雷暴大风天气过程分析[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 44(增刊1):65-70.
|
| [22] |
姚建群, 戴建华, 姚祖庆, 2005. 一次强飑线的成因及维持和加强机制分析[J]. 应用气象学报, 16(6):746-753.
|
| [23] |
俞小鼎, 郑永光, 2020. 中国当代强对流天气研究与业务进展[J]. 气象学报, 78(3):391-418.
|
| [24] |
周伟东, 韩宁, 戴建华, 等, 2022. 上海地区暴雨预警评估及不同天气型暴雨预警差异分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 41(4):405-412.
|
| [25] |
DOSWELL III C A, 1987. The distinction between large-scale and mesoscale contribution to severe convection: A case study example[J]. Weather and Forecasting, 2(1): 3-16.
|
| [26] |
FUJITA T T, WAKIMOTO R M, 1981. Five scales of airflow associated with a series of downbursts on 16 July 1980[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 109(7): 1 438-1 456.
|
| [27] |
JOHNS R H, DOSWELL III C A, 1992. Severe local storms forecasting[J]. Weather and Forecasting, 7(4): 588-612.
|
| [28] |
MARKOWSKI P, RICHARDSON Y, 2010. Mesoscale meteorology in midlatitutes[M]. Chichester, WestSussex, UK: Wiley Blackwell Publication: 27-31.
|
| [29] |
WAKIMOTO R M, 2001. Convectively driven high wind events[M]. Doswell III C A, Severe Convective Storms. Boston, MA: American Meteorological Society: 255-298.
|
 ), DAI Jianhua2, GUAN Li2, FU Jie1, CHEN Hao1, WANG Rui1, LYU Qing1
), DAI Jianhua2, GUAN Li2, FU Jie1, CHEN Hao1, WANG Rui1, LYU Qing1
 ), 戴建华2, 管理2, 傅洁1, 陈浩1, 王蕊1, 吕青1
), 戴建华2, 管理2, 傅洁1, 陈浩1, 王蕊1, 吕青1