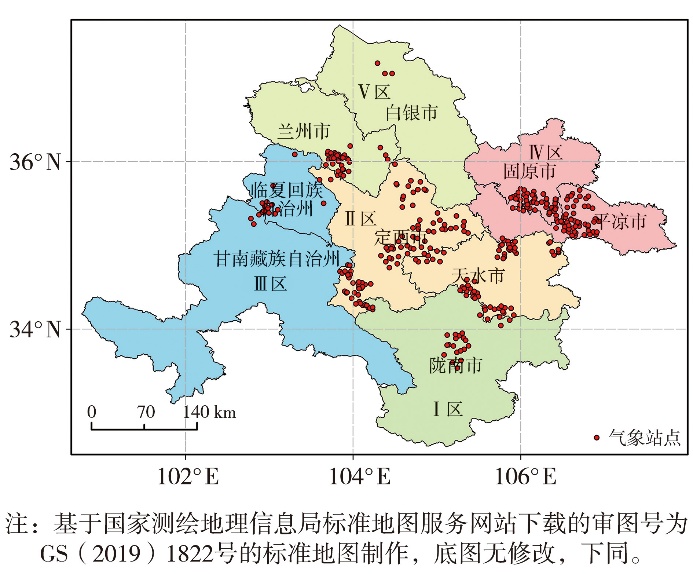
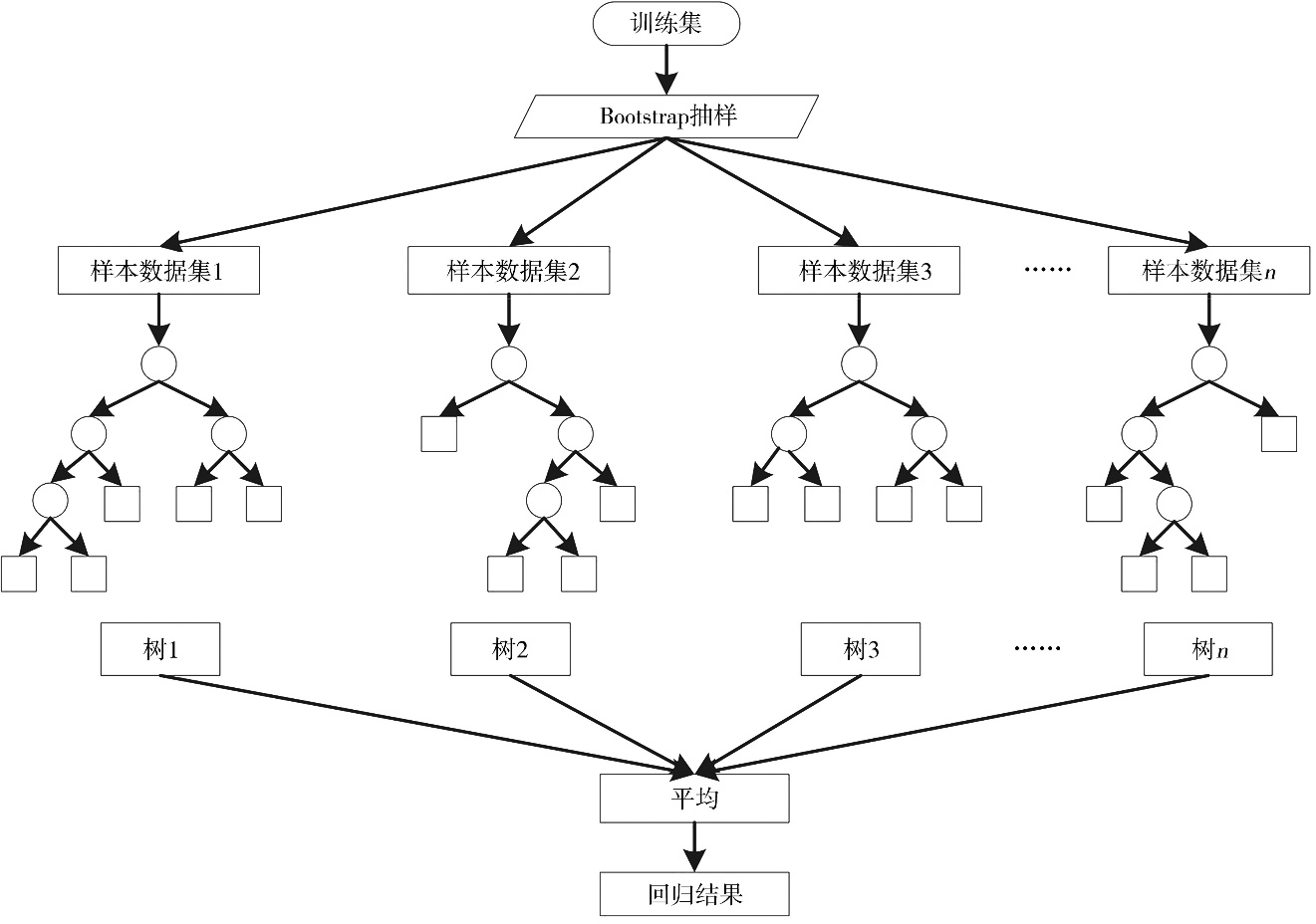
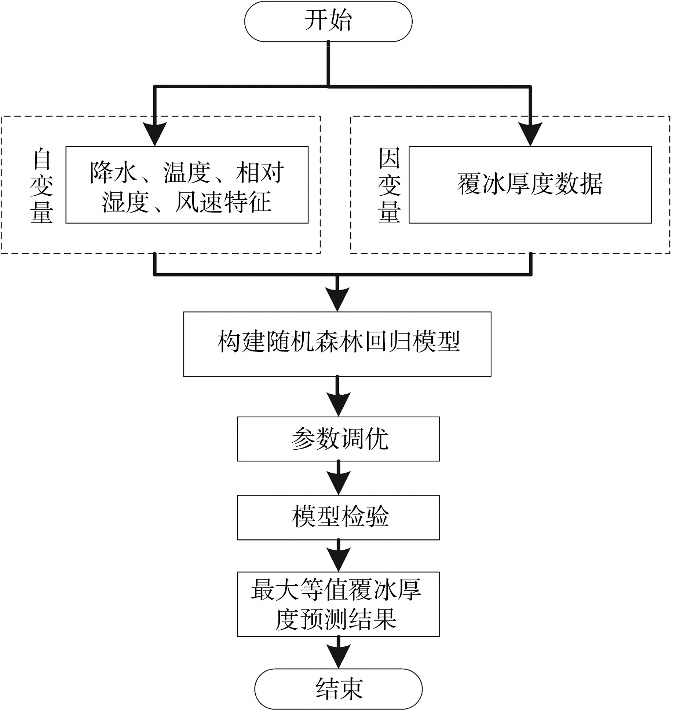
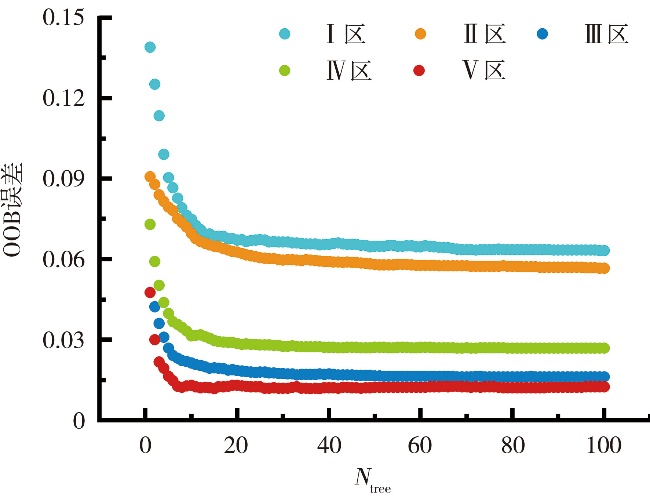
Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2025, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (3): 488-497.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-03-0488
• Technical Reports • Previous Articles Next Articles
Wire icing thickness prediction model of transmission line in the northeastern slope region of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau based on random forest algorithm
LYU Meixia( ), YAN Xinyang, HE Jinmei(
), YAN Xinyang, HE Jinmei( ), CHENG Peng, WANG Xiaoyong, LI Xiaoqin
), CHENG Peng, WANG Xiaoyong, LI Xiaoqin
- Meteorological Service Center of Gansu Province, Lanzhou 730020, China
-
Received:2024-05-14Revised:2025-04-01Online:2025-06-30Published:2025-07-12
基于随机森林算法的青藏高原东北边坡输电线路覆冰厚度预报模型
吕玫霞( ), 闫昕旸, 何金梅(
), 闫昕旸, 何金梅( ), 程鹏, 王小勇, 李晓琴
), 程鹏, 王小勇, 李晓琴
- 甘肃省气象服务中心,甘肃 兰州 730020
-
通讯作者:何金梅 -
作者简介:吕玫霞(1995—),女,甘肃武威人,硕士,主要从事专业气象预报服务工作。E-mail: 957985776@qq.com。 -
基金资助:甘肃省自然科学基金项目(23JRRA1574);甘肃省青年科技基金计划(24JRRA1186);及甘肃省气象局重点项目(Zd2022-04)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LYU Meixia, YAN Xinyang, HE Jinmei, CHENG Peng, WANG Xiaoyong, LI Xiaoqin. Wire icing thickness prediction model of transmission line in the northeastern slope region of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau based on random forest algorithm[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(3): 488-497.
吕玫霞, 闫昕旸, 何金梅, 程鹏, 王小勇, 李晓琴. 基于随机森林算法的青藏高原东北边坡输电线路覆冰厚度预报模型[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(3): 488-497.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-03-0488
| 样本 | Ⅰ区 | Ⅱ区 | Ⅲ区 | Ⅳ区 | Ⅴ区 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 训练集 | 635 | 2 923 | 790 | 1 883 | 218 |
| 测试集 | 159 | 731 | 198 | 471 | 55 |
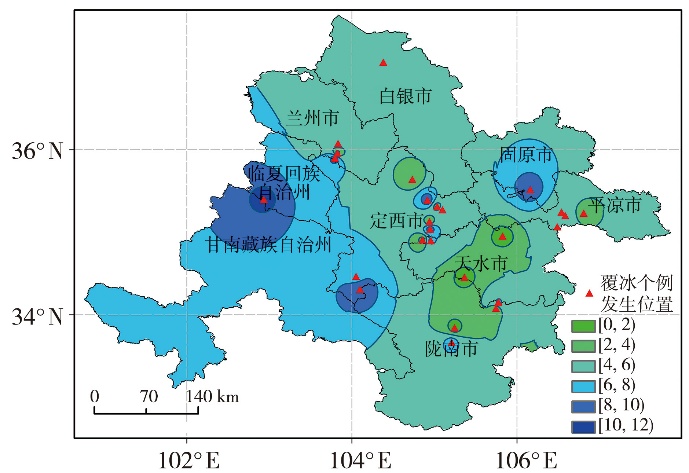
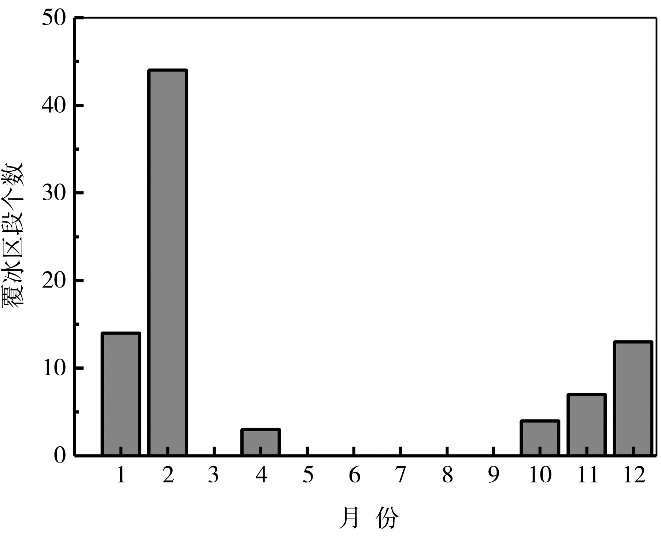
Tab.1 The number of training set and test set samples in the study area
| 样本 | Ⅰ区 | Ⅱ区 | Ⅲ区 | Ⅳ区 | Ⅴ区 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 训练集 | 635 | 2 923 | 790 | 1 883 | 218 |
| 测试集 | 159 | 731 | 198 | 471 | 55 |
| 区域 | Ntree | f | Lmin |
|---|---|---|---|
| I区 | 70 | 6 | 5 |
| II区 | 80 | 6 | 6 |
| III区 | 90 | 6 | 2 |
| IV区 | 50 | 6 | 1 |
| V区 | 50 | 6 | 5 |
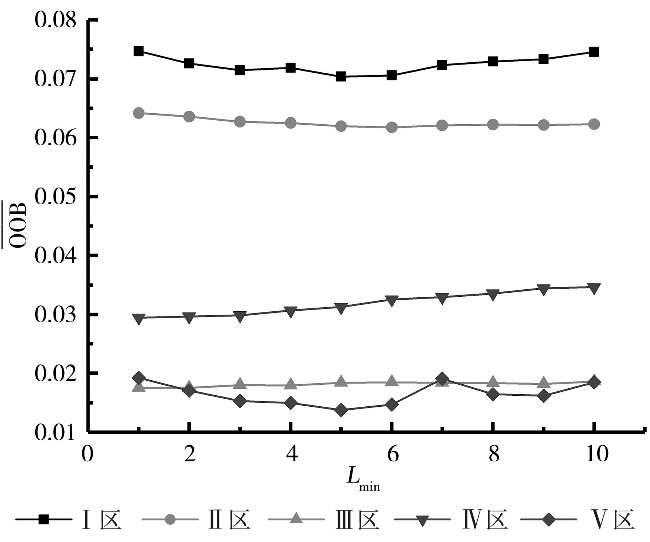
Tab.2 The results of model parameter tuning for each zone
| 区域 | Ntree | f | Lmin |
|---|---|---|---|
| I区 | 70 | 6 | 5 |
| II区 | 80 | 6 | 6 |
| III区 | 90 | 6 | 2 |
| IV区 | 50 | 6 | 1 |
| V区 | 50 | 6 | 5 |
| 区域 | MAE/mm | MBE/mm | R² | RMSE/mm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 训练集 | 测试集 | 训练集 | 测试集 | 训练集 | 测试集 | 训练集 | 测试集 | |
| Ⅰ区 | 1.048 | 1.387 | -0.001 | -0.064 | 0.842 | 0.695 | 1.558 | 2.117 |
| Ⅱ区 | 1.326 | 1.962 | -0.003 | -0.184 | 0.701 | 0.409 | 1.827 | 2.633 |
| Ⅲ区 | 1.438 | 2.765 | 0.023 | 0.660 | 0.945 | 0.857 | 2.883 | 4.833 |
| Ⅳ区 | 0.379 | 0.947 | 0.003 | 0.014 | 0.960 | 0.765 | 0.707 | 1.670 |
| Ⅴ区 | 0.259 | 0.420 | 0.009 | 0.038 | 0.913 | 0.841 | 0.995 | 1.266 |
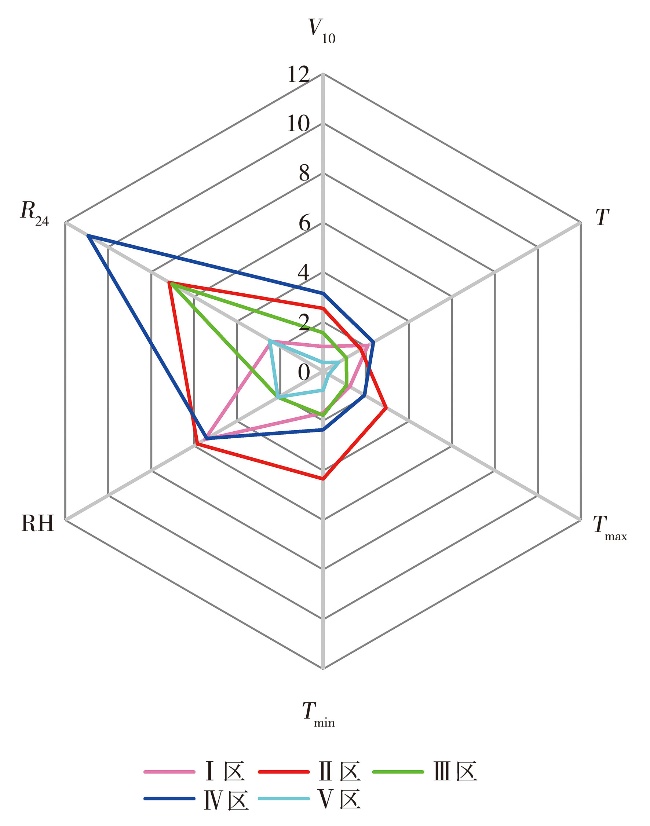
Tab.3 Evaluation results of maximum equivalent ice cover thickness prediction model for transmission lines
| 区域 | MAE/mm | MBE/mm | R² | RMSE/mm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 训练集 | 测试集 | 训练集 | 测试集 | 训练集 | 测试集 | 训练集 | 测试集 | |
| Ⅰ区 | 1.048 | 1.387 | -0.001 | -0.064 | 0.842 | 0.695 | 1.558 | 2.117 |
| Ⅱ区 | 1.326 | 1.962 | -0.003 | -0.184 | 0.701 | 0.409 | 1.827 | 2.633 |
| Ⅲ区 | 1.438 | 2.765 | 0.023 | 0.660 | 0.945 | 0.857 | 2.883 | 4.833 |
| Ⅳ区 | 0.379 | 0.947 | 0.003 | 0.014 | 0.960 | 0.765 | 0.707 | 1.670 |
| Ⅴ区 | 0.259 | 0.420 | 0.009 | 0.038 | 0.913 | 0.841 | 0.995 | 1.266 |
| 区域 | 样本集 | POD | FAR | MAR | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y≤10 mm | 10<Y<20 mm | Y≥20 mm | Y≤10 mm | 10<Y<20 mm | Y≥20 mm | Y≤10 mm | 10<Y<20 mm | Y≥20 mm | ||
| Ⅰ区 | 训练集 | 0.794 | 0.545 | / | 0.206 | 0 | / | 0 | 0.455 | / |
| 测试集 | 0.783 | 0.600 | / | 0.217 | 0 | / | 0 | 0.400 | / | |
| Ⅱ区 | 训练集 | 0.858 | 0.136 | / | 0.133 | 0.319 | / | 0.012 | 0.854 | / |
| 测试集 | 0.834 | 0.098 | / | 0.158 | 0.350 | / | 0.012 | 0.896 | / | |
| Ⅲ区 | 训练集 | 0.859 | 0.913 | 0.883 | 0.141 | 0 | 0.117 | 0 | 0.087 | 0 |
| 测试集 | 0.775 | 0.810 | 0.797 | 0.184 | 0.021 | 0.203 | 0.061 | 0.175 | 0 | |
| Ⅳ区 | 训练集 | 0.946 | 0.791 | / | 0.001 | 0.207 | / | 0.054 | 0.003 | / |
| 测试集 | 0.896 | 0.611 | / | 0.019 | 0.347 | / | 0.088 | 0.096 | / | |
| Ⅴ区 | 训练集 | 0.980 | 0.818 | / | 0.015 | 0.053 | / | 0.005 | 0.143 | / |
| 测试集 | 0.981 | 0.667 | / | 0.019 | 0 | / | 0 | 0.333 | / | |
Tab.4 Evaluation of model fitting effect of maximum equivalent ice thickness (Y) for transmission lines
| 区域 | 样本集 | POD | FAR | MAR | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y≤10 mm | 10<Y<20 mm | Y≥20 mm | Y≤10 mm | 10<Y<20 mm | Y≥20 mm | Y≤10 mm | 10<Y<20 mm | Y≥20 mm | ||
| Ⅰ区 | 训练集 | 0.794 | 0.545 | / | 0.206 | 0 | / | 0 | 0.455 | / |
| 测试集 | 0.783 | 0.600 | / | 0.217 | 0 | / | 0 | 0.400 | / | |
| Ⅱ区 | 训练集 | 0.858 | 0.136 | / | 0.133 | 0.319 | / | 0.012 | 0.854 | / |
| 测试集 | 0.834 | 0.098 | / | 0.158 | 0.350 | / | 0.012 | 0.896 | / | |
| Ⅲ区 | 训练集 | 0.859 | 0.913 | 0.883 | 0.141 | 0 | 0.117 | 0 | 0.087 | 0 |
| 测试集 | 0.775 | 0.810 | 0.797 | 0.184 | 0.021 | 0.203 | 0.061 | 0.175 | 0 | |
| Ⅳ区 | 训练集 | 0.946 | 0.791 | / | 0.001 | 0.207 | / | 0.054 | 0.003 | / |
| 测试集 | 0.896 | 0.611 | / | 0.019 | 0.347 | / | 0.088 | 0.096 | / | |
| Ⅴ区 | 训练集 | 0.980 | 0.818 | / | 0.015 | 0.053 | / | 0.005 | 0.143 | / |
| 测试集 | 0.981 | 0.667 | / | 0.019 | 0 | / | 0 | 0.333 | / | |
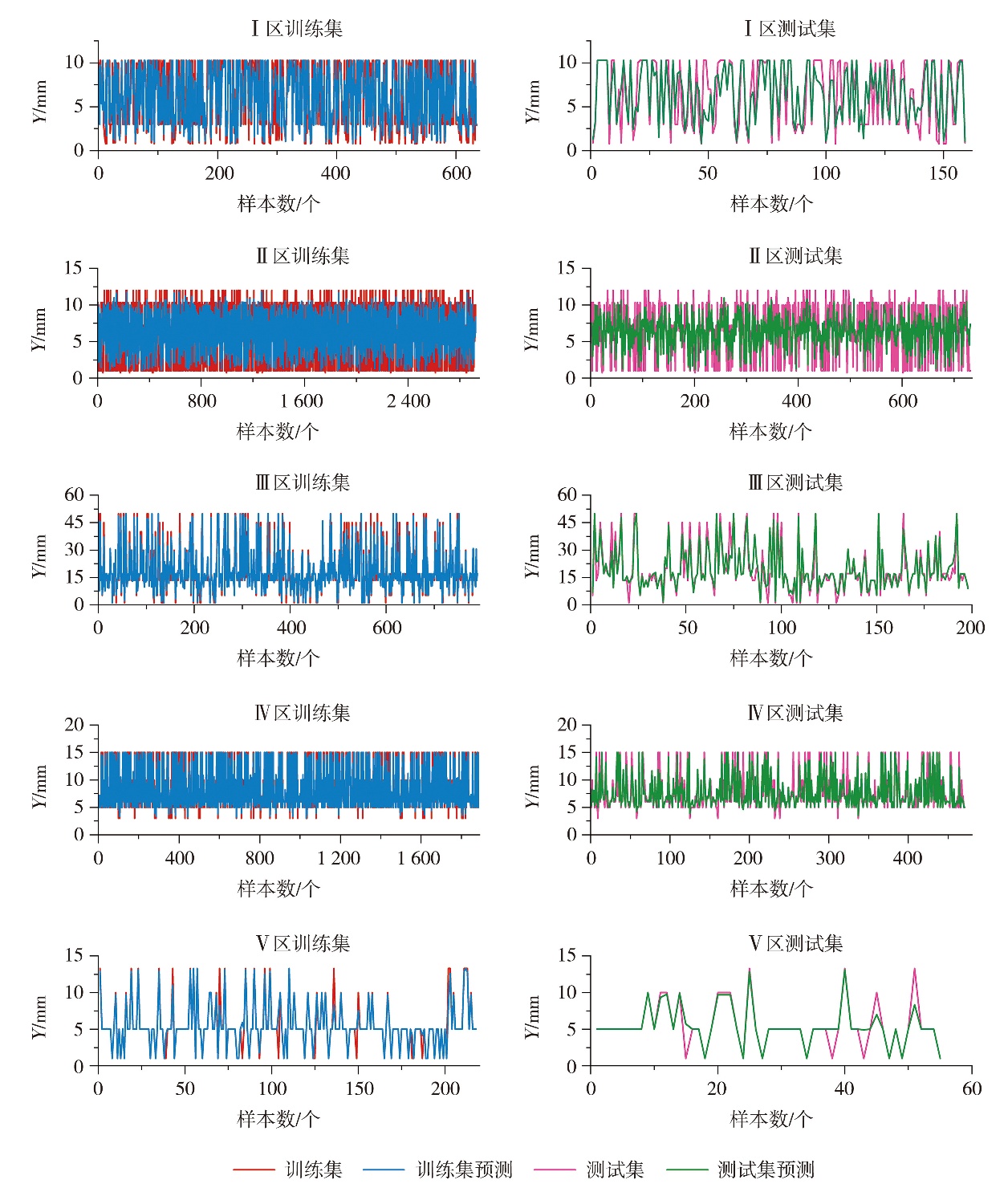
Fig.8 Comparison between the model prediction results of the maximum equivalent ice cover thickness (Y) and the real value of transmission lines in 5 zones
| [1] | 邓芳萍, 康丽莉, 姜瑜君, 等, 2017. 基于常规气象资料的小时标准冰厚模型及验证[J]. 应用气象学报, 28(2): 142-156. |
| [2] | 国家电网有限公司, 2024. 中重冰区架空输电线路设计技术规定:Q/GDW 10182—2024[S]. 北京: 国家电网有限公司. |
| [3] | 胡艳楠, 牛生杰, 吕晶晶, 等, 2017. 湖北电线积冰统计分析及积冰逆温层结研究[J]. 气候与环境研究, 22(1): 35-44. |
| [4] | 黄筱婷, 戴栋, 李昊, 等, 2013. 基于在线监测数据的输电线路覆冰形态研究[J]. 南方电网技术, 7(1): 76-79. |
| [5] | 黄新波, 刘家兵, 蔡伟, 等, 2008. 电力架空线路覆冰雪的国内外研究现状[J]. 电网技术, 32(4):23-28. |
| [6] | 黄新波, 欧阳丽莎, 王娅娜, 等, 2011. 输电线路覆冰关键影响因素分析[J]. 高电压技术, 37(7): 1 677-1 682. |
| [7] | 李晨曦, 2023. 基于WRF和机器学习混合模型的输电线覆冰厚度预测研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学. |
| [8] |
李清华, 孟洁, 李劲松, 等, 2022. 山西省不同重现期下电线覆冰厚度空间分布及区划[J]. 干旱气象, 40(1): 156-165.
DOI |
| [9] | 林刚, 王波, 彭辉, 等, 2018. 基于强泛化卷积神经网络的输电线路图像覆冰厚度辨识[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 38(11): 3 393-3 401. |
| [10] | 刘春城, 刘佼, 2011. 输电线路导线覆冰机理及雨凇覆冰模型[J]. 高电压技术, 37(1): 241-248. |
| [11] |
刘新伟, 蒋盈沙, 黄武斌, 等, 2021. 基于雷达产品和随机森林算法的冰雹天气分类识别及预报[J]. 高原气象, 40(4): 898-908.
DOI |
| [12] | 彭曙蓉, 郝伟伟, 翟云峰, 等, 2016. 电力线路覆冰机理及融冰技术研究综述[J]. 陕西电力, 44(6): 52-58. |
| [13] | 覃武, 罗小莉, 钟利华, 等, 2019. 广西输电线路典型年份的环流特征分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 13(1):110-116. |
| [14] |
沈润平, 郭佳, 张婧娴, 等, 2017. 基于随机森林的遥感干旱监测模型的构建[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 19(1): 125-133.
DOI |
| [15] | 孙才新, 蒋兴良, 熊启新, 等, 2003. 导线覆冰及其干湿增长临界条件分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 23(3): 141-145. |
| [16] | 唐文苑, 周庆亮, 刘鑫华, 等, 2017. 国家级强对流天气分类预报检验分析[J]. 气象, 43(1): 67-76. |
| [17] | 王传辉, 姚叶青, 苗开超, 等, 2019. 安徽省电线覆冰厚度推算初探[J]. 干旱气象, 37(3): 500-507. |
| [18] | 王可心, 包云轩, 朱承瑛, 等, 2021. 随机森林回归法在冬季路面温度预报中的应用[J]. 气象, 47(1): 82-93. |
| [19] | 王奇, 张厚荣, 宗莲, 等, 2021. 2015年广西区北部超高压输电线路一次连续覆冰事件的天气学特征[J]. 热带气象学报, 37(4): 579-589. |
| [20] | 王帅, 李劲松, 原辉, 等, 2024. 基于CALMET-WRF耦合的复杂地形下导线覆冰的精细化数值模拟研究[J]. 大气科学学报, 47(3): 509-520. |
| [21] | 王馨, 卢毅, 张旭, 等, 2020. 冀北地区输电线路覆冰风险预报研究[J]. 干旱气象, 38(1): 164-168. |
| [22] | 王莺, 王劲松, 姚玉璧, 2014. 甘肃省河东地区气象干旱灾害风险评估与区划[J]. 中国沙漠, 34(4): 1 115-1 124. |
| [23] | 吴息, 孙朋杰, 熊海星, 等, 2012. 利用常规气象资料建立的导线覆冰模型[J]. 大气科学学报, 35(3): 335-341. |
| [24] | 温华洋, 田红, 唐为安, 等, 2011. 安徽省电线积冰标准冰厚的气象估算模型[J]. 应用气象学报, 22(6): 747-752. |
| [25] | 杨明悦, 毛献忠, 2022. 基于变量重要性评分—随机森林的溶解氧预测模型:以深圳湾为例[J]. 中国环境科学, 42(8):3876-3 881. |
| [26] | 苑吉河, 蒋兴良, 易辉, 等, 2004. 输电线路导线覆冰的国内外研究现状[J]. 高电压技术, 30(1): 6-9. |
| [27] | 赵多青, 曾杰, 许中平, 等, 2022. 接触网覆冰绝缘子的多物理场分析及伞裙结构优化[J]. 绝缘材料, 55(7): 78-86. |
| [28] | 赵晓萌, 李栋梁, 熊海星, 等, 2011. 西南地区覆冰气象要素的变化特征及综合评估[J]. 自然资源学报, 26(5): 802-813. |
| [29] | 赵一飞, 张勃, 张多勇, 等, 2013. 甘肃河东地区地表湿润特征及其气候影响因子[J]. 地理科学进展, 32(1): 95-104. |
| [30] | 朱永灿, 黄新波, 贾建援, 等, 2015. 输电导线覆冰生长及影响因素数值分析模型[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 49(7): 120-125. |
| [31] | 朱君, 向卫国, 赵夏菁, 2011. 贵州导线覆冰的致灾机理研究[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 31(4):42-50. |
| [32] | COHEN J, PFEIFFER K, FRANCIS J A, 2018. Warm Arctic episodes linked with increased frequency of extreme winter weather in the United States[J]. Nature Communications, 9(1): 869. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-02992-9. |
| [33] | GROEMPING, 2009. Variable importance assessment in regression: Linear regression versus random forest[J]. The American Statistician, 63(4): 308-319. |
| [34] | HAO Y P, YAO Z H, WANG J K, et al, 2019. A classification method for transmission line icing process curve based on hierarchical K-means clustering[J]. Energies, 12(24): 4786. DOI: 10.3390/en12244786. |
| [35] | KRINGLEBOTN NYGAARD B E, ÁGÚSTSSON H, SOMFALVI-TÓTH K, 2013. Modeling wet snow accretion on power lines: Improvements to previous methods using 50 years of observations[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 52(10): 2 189-2 203. DOI: 10.1175/JAMC-D-12-0332.1. |
| [36] | LI P, ZHAO N, ZHOU D H, et al, 2014. Multivariable time series prediction for the icing process on overhead power transmission line[J]. The Scientific World Journal, Article ID: 256815. DOI:10.1155/2014/256815. |
| [37] | NIU S J, ZHOU Y, JIA R, et al, 2012. The microphysics of ice accretion on wires: Observations and simulations[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 55(3): 428-437. DOI: 10.1007/s11430-011-4325-8. |
| [38] | NIU D X, WANG H C, CHEN H Y, et al, 2017. The general regression neural network based on the fruit fly optimization algorithm and the data inconsistency rate for transmission line icing prediction[J]. Energies, 10(12): 2 066. DOI: 10.3390/en10122066. |
| [39] | RAHMAN M, ZHU J P, CHENG Y T, 2006. Effect of bias and variance on estimation and classification error for prediction[J]. Journal of Data Analysis, 1(3): 113-135. |
| [40] | SUN W, WANG C F, 2019. Staged icing forecasting of power transmission lines based on icing cycle and improved extreme learning machine[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 208: 1 384-1 392. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.197. |
| [41] | ZHAO J, ZHANG H X, ZOU H L, et al, 2022. Probability prediction method of transmission line icing fault based on adaptive relevance vector machine[J]. Energy Reports, 8: 1 568-1 577. |
| [1] | GAI Changsong, CAO Lijuan, YANG Yuanyan. The application of three interpolation methods to temperature in southwestern China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(5): 792-801. |
| [2] | LIU Na, HUANG Wubin, YANG Jiancai, WANG Jixin, WANG Yicheng, ZHANG Junxia. Objective forecast method of short-term quantitative precipitation in Gansu Province based on SCTP-RF algorithm [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(1): 146-155. |
| [3] | ZHU Yongning, FENG Dongpu, LI Hongying, DUAN Xiaofeng, ZHENG Fang. Temporal and Spatial Change Characteristics of the Minimum Temperature and Frost Days During the Spring Frost Stage in Ningxia [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(2): 256-262. |
| [4] | WANG Xin, LU Yi, ZHANG Xu, YANG Linhan, WU Huiqin. Research on Risk Forecast of Transmission Lines Icing in Northern Hebei Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(1): 164-168. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||