Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (5): 792-801.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-05-0792
• Technical Reports • Previous Articles Next Articles
The application of three interpolation methods to temperature in southwestern China
GAI Changsong1( ), CAO Lijuan2(
), CAO Lijuan2( ), YANG Yuanyan1,3
), YANG Yuanyan1,3
- 1. CMA Key Open Laboratory of Transforming Climate Resources to Economy, Chongqing Meteorological Information and Technology Support Centre, Chongqing 401147, China
2. National Meteorological Information Centre, Beijing 100081, China
3. Chongqing Institute of Meteorological Sciences, Chongqing 401147, China
-
Received:2022-10-25Revised:2023-05-25Online:2023-10-31Published:2023-11-03
三种气温插补方法在中国西南地区的应用分析
- 1.中国气象局气候资源经济转化重点开放实验室,重庆市气象信息与技术保障中心,重庆 401147
2.国家气象信息中心,北京 100081
3.重庆市气象科学研究所,重庆 401147
-
通讯作者:曹丽娟(1980—),女,正高级工程师,主要从事气候资料分析与气候变化研究。E-mail:caolj@cma.gov.cn 。 -
作者简介:盖长松(1977—),男,高级工程师,主要从事气象观测数据质量控制研究。E-mail: gai_cs@163.com。 -
基金资助:重庆市气象部门业务技术攻关项目“基于融合实况产品与机器学习的温/湿度要素质量控制与数据插补技术研究”(YWJSGG-202209);中国气象局创新发展专项“全球关键气候要素长序列数据产品研制”(CXFZ2023J049)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
GAI Changsong, CAO Lijuan, YANG Yuanyan. The application of three interpolation methods to temperature in southwestern China[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(5): 792-801.
盖长松, 曹丽娟, 阳园燕. 三种气温插补方法在中国西南地区的应用分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(5): 792-801.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2023)-05-0792
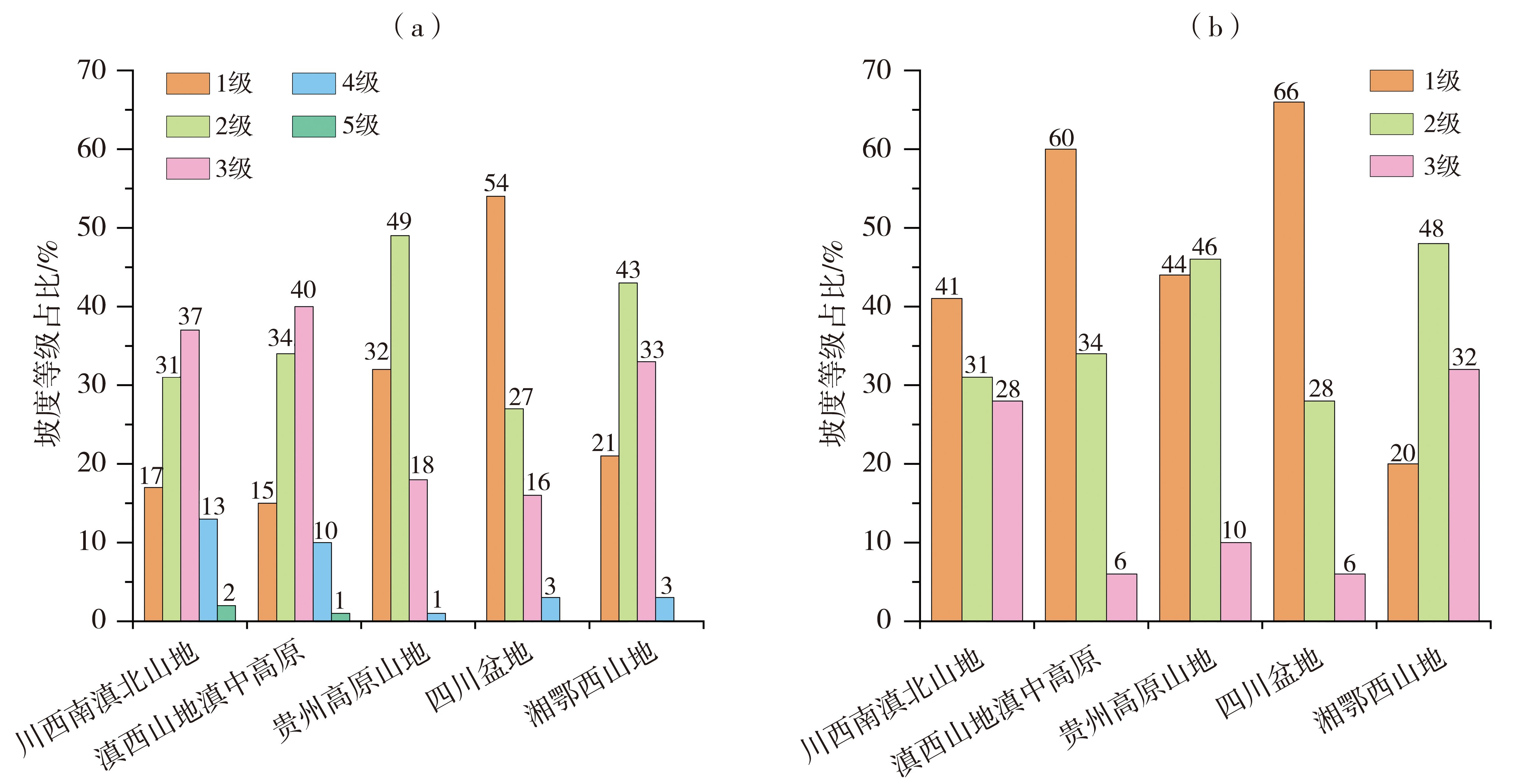
| 气候区 | 目标站 数量 | 参考站数量 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最大值 | 最小值 | 中位数 | ||
| 川西南滇北山地 | 21 | 9 | 2 | 4 |
| 滇西山地滇中高原 | 55 | 15 | 2 | 7 |
| 贵州高原山地 | 56 | 16 | 2 | 10 |
| 四川盆地 | 104 | 28 | 4 | 16 |
| 湘鄂西山地 | 27 | 16 | 3 | 7 |
Tab.1 The numbers of target and reference stations in five climatic divisions
| 气候区 | 目标站 数量 | 参考站数量 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最大值 | 最小值 | 中位数 | ||
| 川西南滇北山地 | 21 | 9 | 2 | 4 |
| 滇西山地滇中高原 | 55 | 15 | 2 | 7 |
| 贵州高原山地 | 56 | 16 | 2 | 10 |
| 四川盆地 | 104 | 28 | 4 | 16 |
| 湘鄂西山地 | 27 | 16 | 3 | 7 |

Fig.3 The relation between the accuracy of daily mean temperature interpolated by three methods and numbers of reference stations in five climatic divisions in southwestern China from 1970 to 2020 (a) western Yunnan mountains and central Yunnan plateau, (b) mountainous region of Guizhou plateau, (c) Sichuan Basin, (d) mountainous region of western Hunan and western Hubei, (e) mountainous region of southwestern Sichuan and northern Yunnan
| 气候区 | MAE | RMSE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 空间回归法 | 标准序列法 | 随机森林法 | 空间回归法 | 标准序列法 | 随机森林法 | |
| 川西南滇北山地 | 0.75 | 0.93 | 0.26 | 1.08 | 1.26 | 0.62 |
| 滇西山地滇中 高原 | 0.63 | 0.65 | 0.21 | 0.82 | 0.85 | 0.50 |
| 贵州高原山地 | 0.48 | 0.60 | 0.17 | 0.73 | 0.77 | 0.42 |
| 四川盆地 | 0.37 | 0.41 | 0.15 | 0.49 | 0.53 | 0.35 |
| 湘鄂西山地 | 0.52 | 0.60 | 0.18 | 0.69 | 0.77 | 0.43 |
Tab.2
| 气候区 | MAE | RMSE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 空间回归法 | 标准序列法 | 随机森林法 | 空间回归法 | 标准序列法 | 随机森林法 | |
| 川西南滇北山地 | 0.75 | 0.93 | 0.26 | 1.08 | 1.26 | 0.62 |
| 滇西山地滇中 高原 | 0.63 | 0.65 | 0.21 | 0.82 | 0.85 | 0.50 |
| 贵州高原山地 | 0.48 | 0.60 | 0.17 | 0.73 | 0.77 | 0.42 |
| 四川盆地 | 0.37 | 0.41 | 0.15 | 0.49 | 0.53 | 0.35 |
| 湘鄂西山地 | 0.52 | 0.60 | 0.18 | 0.69 | 0.77 | 0.43 |
| 气候区 | 站点平均地形起伏度 | 区域平均地形起伏度 |
|---|---|---|
| 川西南滇北山地 | 2.20 | 3.13 |
| 滇西山地滇中高原 | 1.88 | 3.02 |
| 贵州高原山地 | 1.06 | 1.33 |
| 四川盆地 | 0.59 | 0.90 |
| 湘鄂西山地 | 0.70 | 1.43 |
Tab.3 The station and regional average relief in five climatic divisions in southwestern China
| 气候区 | 站点平均地形起伏度 | 区域平均地形起伏度 |
|---|---|---|
| 川西南滇北山地 | 2.20 | 3.13 |
| 滇西山地滇中高原 | 1.88 | 3.02 |
| 贵州高原山地 | 1.06 | 1.33 |
| 四川盆地 | 0.59 | 0.90 |
| 湘鄂西山地 | 0.70 | 1.43 |

Fig.6 The relation between P0.5, P0.8 test indexes of monthly mean temperature with two interpolation methods and numbers of reference station at Qianwei (a) and Beibei (b) stations
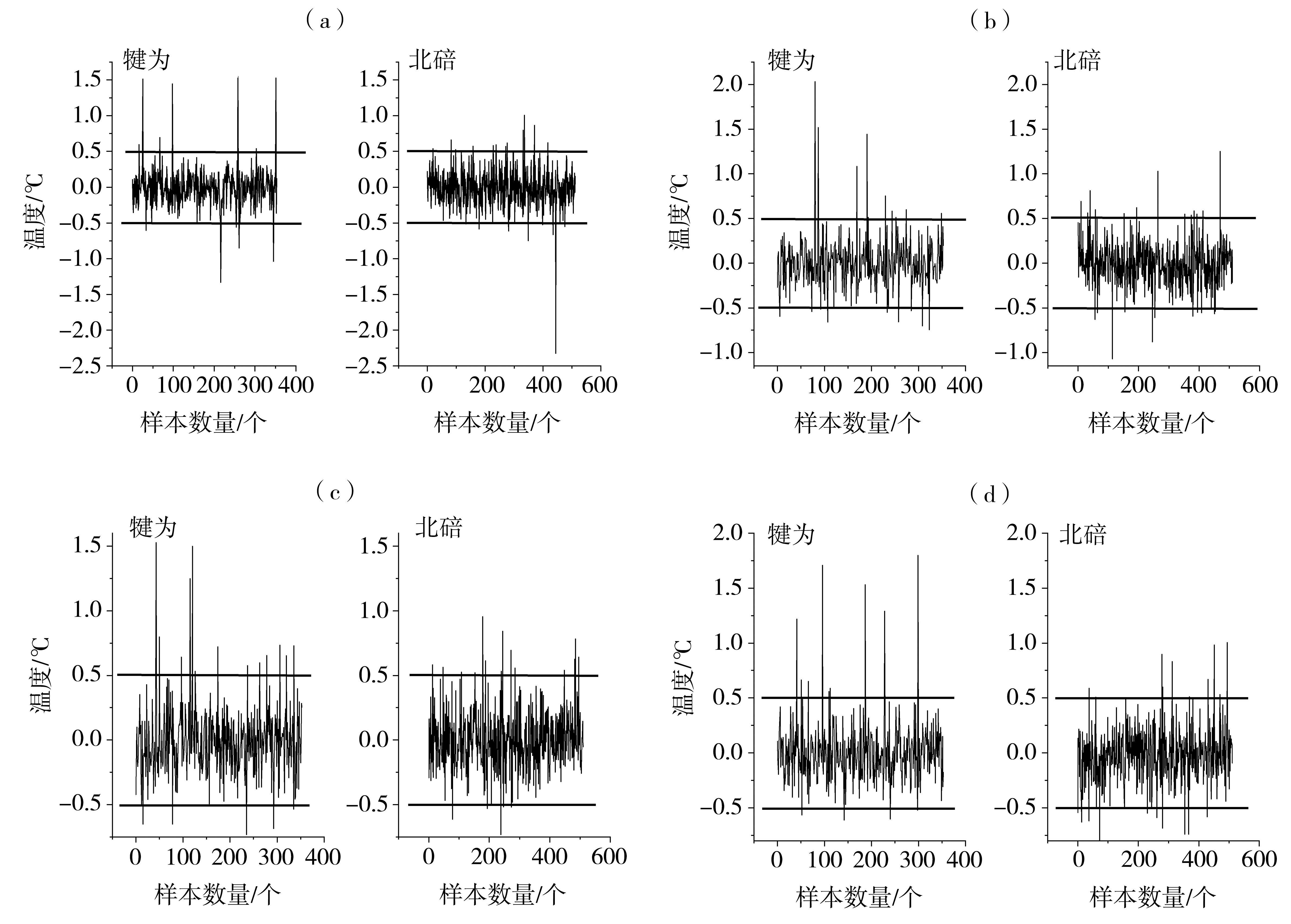
Fig.7 The variation of difference between monthly mean temperature interpolated by random forest method and observation with sample numbers at Qianwei and Beibei stations (a) the first test, (b) the second test, (c) the third test, (d) the forth test

Fig.8 The proportion of extreme temperature samples in extreme value months to all samples of extreme value in four interpolation tests with random forest method
| [1] | 陈鹏翔, 江远安, 刘精, 2014. 新疆区域逐月缺测气温序列的插补及重建[J]. 冰川冻土, 36(5): 1 237-1 244. |
| [2] |
邓国富, 李明启, 2021. 树轮密度对气候的响应及重建研究进展[J]. 地理科学进展, 40(2): 343-356.
DOI |
| [3] | 丁玲玲, 葛全胜, 郑景云, 等, 2013. 1736-2009年华南地区冬季年平均气温序列重建[J]. 第四纪研究, 33(6): 1 191-1 198. |
| [4] | 杜泽玉, 曹富强, 杨荣, 2021. 基于CRU资料的山西百年气温时空演变特征[J]. 高原气象, 40(1): 123-132. |
| [5] | 冯蜀青, 王海娥, 柳艳香, 等, 2019. 西北地区未来10 a气候变化趋势模拟预测研究[J]. 干旱气象, 37(4): 557-564. |
| [6] | 黄嘉佑, 2004. 气象统计分析与预报方法[M]. 3版. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [7] |
黄蓉, 胡泽勇, 关婷, 等, 2014. 藏北高原气温资料插补及其变化的初步分析[J]. 高原气象, 33(3): 637-646.
DOI |
| [8] | 金红梅, 颜鹏程, 柏庆顺, 等, 2019. 近70 a来中亚极端高温事件时空分布[J]. 干旱气象, 37(4): 550-556. |
| [9] | 李庆祥, 黄嘉佑, 鞠晓慧, 2008. 上海地区最高气温资料的恢复试验[J]. 热带气象学报, 24(4): 349-353. |
| [10] | 廖捷, 周自江, 2018. 全球常规气象观测资料质量控制研究进展与展望[J]. 气象科技进展, 8(1): 56-63. |
| [11] | 刘炳涛, 张健, 满志敏, 2018. 1724—2016年上海地区冬季平均气温重建与特征分析[J]. 中国历史地理论丛, 33(4): 70-77. |
| [12] |
刘蕾, 李鸾, 张丽, 等, 2022. 1880—2020年安徽芜湖气温长序列构建及年代际特征[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5): 831-839.
DOI |
| [13] |
马士彬, 安裕伦, 2012. 基于ASTER GDEM数据喀斯特区域地貌类型划分与分析[J]. 地理科学, 32(3): 368-373.
DOI |
| [14] | 孟欣宁, 焦瑞莉, 刘念, 等, 2020. 基于随机森林插值的中亚夏季极端高温变化特征[J]. 干旱区研究, 37(4): 966-973. |
| [15] | 彭嘉栋, 廖玉芳, 刘珺婷, 等, 2014. 洞庭湖区近百年气温序列构建及其变化特征[J]. 气象与环境学报, 30(5): 62-68. |
| [16] | 司鹏, 郭军, 赵煜飞, 等, 2022. 北京1841年以来均一化最高和最低气温日值序列的构建[J]. 气象学报, 80(1): 136-152. |
| [17] | 司鹏, 郝立生, 罗传军, 等, 2017. 河北保定气象站长序列气温资料缺测记录插补和非均一性订正[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 13(1): 41-51. |
| [18] |
唐懿, 蔡雯悦, 翟建青, 等, 2022. 2021年夏季中国气候异常特征及主要气象灾害[J]. 干旱气象, 40(2): 179-186.
DOI |
| [19] | 王海军, 涂诗玉, 陈正洪, 2008. 日气温数据缺测的插补方法试验与误差分析[J]. 气象, 34(7): 83-91. |
| [20] | 吴国雄, 林海, 邹晓蕾, 等, 2014. 全球气候变化研究与科学数据[J]. 地球科学进展, 29(1): 15-22. |
| [21] | 伍清, 蒋兴文, 谢洁, 2018. 基于CMIP5资料的西南地区2020—2050年气温多模式集合预估[J]. 干旱气象, 36(6): 971-978. |
| [22] | 肖晶晶, 马浩, 张育慧, 等, 2021. 1905—2018年浙江地温序列构建及其变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 39(3): 386-393. |
| [23] | 闫丽莉, 温少妍, 高文晶, 等, 2019. 整点气温缺测的插补方法研究及其初步应用[J]. 震灾防御技术, 14(2): 446-455. |
| [24] | 严中伟, 丁一汇, 翟盘茂, 等, 2020. 近百年中国气候变暖趋势之再评估[J]. 气象学报, 78(3): 370-378. |
| [25] | 杨青, 刘新春, 霍文, 等, 2009. 塔克拉玛干沙漠腹地1961—1998年逐月平均气温序列的重建[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 5(2): 85-89. |
| [26] | 余君, 李庆祥, 张同文, 等, 2018. 基于贝叶斯模型的器测、古气候重建与气候模拟数据的融合试验[J]. 气象学报, 76(2): 304-314. |
| [27] | 余予, 李俊, 任芝花, 等, 2012. 标准序列法在日平均气温缺测数据插补中的应用[J]. 气象, 38(9): 1 135-1 139. |
| [28] | 曾剑, 徐晴晗, 张宇, 等, 2022. 中国西南地区百年气温的时空演变特征[J]. 成都信息工程大学学报, 37(4): 412-421. |
| [29] | 张永领, 丁裕国, 高全洲, 等, 2006. 一种基于SVD的迭代方法及其用于气候资料场的插补试验[J]. 大气科学, 30(3): 526-532. |
| [30] | 郑景云, 葛全胜, 郝志新, 等, 2014. 历史文献中的气象记录与气候变化定量重建方法[J]. 第四纪研究, 34(6):1186-1 196. |
| [31] |
郑景云, 刘洋, 葛全胜, 等, 2015. 华中地区历史物候记录与1850-2008年的气温变化重建[J]. 地理学报, 70(5): 696-704.
DOI |
| [32] | 郑景云, 尹云鹤, 李炳元, 2010. 中国气候区划新方案[J]. 地理学报, 65(1): 3-12. |
| [33] | 郑欣彤, 边婷婷, 张德强, 等, 2022. 基于深度学习的温度观测数据长时间缺失值插补方法[J]. 计算机系统应用, 31(4): 221-228. |
| [34] | CAO L J, YAN Z W, ZHAO P, et al, 2017. Climatic warming in China during 1901-2015 based on an extended dataset of instrumental temperature records[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 12(6), 064005. DOI: 10.1088/1748-9326/aa68e8 |
| [35] | CAO L J, ZHU Y N, TANG G L, et al, 2016. Climatic warming in China according to a homogenized dataset from 2419 stations[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 36(13): 4 384-4 392. |
| [36] |
DEGAETANO A T, EGGLESTON K L, KNAPP W W, 1995. A method to estimate missing daily maximum and minimum temperature observations[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 34(2): 371-380.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
HUBBARD K G, GUTTMAN N B, YOU J S, 2007. An improved QC process for temperature in the daily cooperative weather observations[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 24(2): 206-213.
DOI URL |
| [1] | SUN Zhaoxuan, ZHANG Qiang, SUN Rui, DENG Biao. Characteristics of the extreme high temperature and drought and their main impacts in southwestern China of 2022 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(5): 764-770. |
| [2] | MA Mengmeng, ZUO Hongchao, LI Licheng, DUAN Jikai. Individual and joint influence of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau summer monsoon and boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation on drought and flood in rainy season of southwestern China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(4): 577-588. |
| [3] | LIU Na, HUANG Wubin, YANG Jiancai, WANG Jixin, WANG Yicheng, ZHANG Junxia. Objective forecast method of short-term quantitative precipitation in Gansu Province based on SCTP-RF algorithm [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(1): 146-155. |
| [4] | ZHOU Xiyin, LI Xiehui. Characteristics of Spatial Temporal Variation of Dryness and Wetness from 1978 to 2017 in Southwestern China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(3): 357-365. |
| [5] | WU Qing1, JIANG Xingwen1, XIE Jie2, ZHU Hua3. Multimodel Superensemble Prediction of Air Temperature in Southwestern China During 2020-2050 Based on CMIP5 Data [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(6): 971-. |
| [6] | WANG Yanfeng, ZHANG Jie, ZHANG Hongyi,XIE Wei, Aru Hasi, WU Niyan. [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(5): 820-827. |
| [7] | LI Yiping, WANG Jinsong, Li Yaohui. Characteristics of a Regional Meteorological Drought Event in Southwestern China During 2009-2010 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2015, 33(4): 537-545. |
| [8] | LI Huijing,LIU Jianxi,LIU Dongsheng,WANG Weijia,LIN Dan. Variation Characteristics of Cloud Cover over Southwestern China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2014, 32(2): 194-200. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||