Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2025, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (2): 195-206.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-02-0195
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Scaling laws in wind speed, particle number and kinetic energy in Gobi sand movement
WANG Zhenting1( ), MENG Xiaonan2,3, WANG Xuesong2, LI Qing4
), MENG Xiaonan2,3, WANG Xuesong2, LI Qing4
- 1. Key Laboratory of Ecological Safety and Sustainable Development in Arid Lands, Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Lanzhou 730000, China
2. State Key Laboratory of Earth Surface Processes and Resource Ecology/MOE Engineering Research Center of Desertification and Blown-Sand Control,Faculty of Geographical Science,Beijing Normal University, Beijing 100875, China
3. Beijing No. 80 Middle School Rui De Branch, Beijing 100176, China
4. Institute of Geographical Sciences/Hebei Engineering Research Center for Geographic Information Application, Hebei Academy Science, Shijiazhuang 050011, China
-
Received:2024-06-27Revised:2024-08-21Online:2025-04-30Published:2025-05-13
戈壁沙尘运动中风速与颗粒数及动能的标度律
- 1.干旱区生态安全与可持续发展重点实验室,中国科学院西北生态环境资源研究院,甘肃 兰州 730000
2.北京师范大学地理科学学部,地表过程与资源生态国家重点实验室/防沙治沙教育部工程研究中心,北京 100875
3.北京市第八十中学睿德分校,北京 100176
4.河北省科学院地理科学研究所/河北省地理信息开发应用工程技术研究中心,河北 石家庄 050011
-
作者简介:王振亭(1975—),男,研究员,主要从事风沙物理与风沙地貌研究。E-mail: ztwang@lzb.ac.cn。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(42371005);国家自然科学基金项目(U21A2001)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
WANG Zhenting, MENG Xiaonan, WANG Xuesong, LI Qing. Scaling laws in wind speed, particle number and kinetic energy in Gobi sand movement[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(2): 195-206.
王振亭, 孟小楠, 王雪松, 李庆. 戈壁沙尘运动中风速与颗粒数及动能的标度律[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(2): 195-206.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-02-0195
| 数据来源 | 高度/m | 物理量 | 传感器(厂家) | 采样频率/Hz | 采样精度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
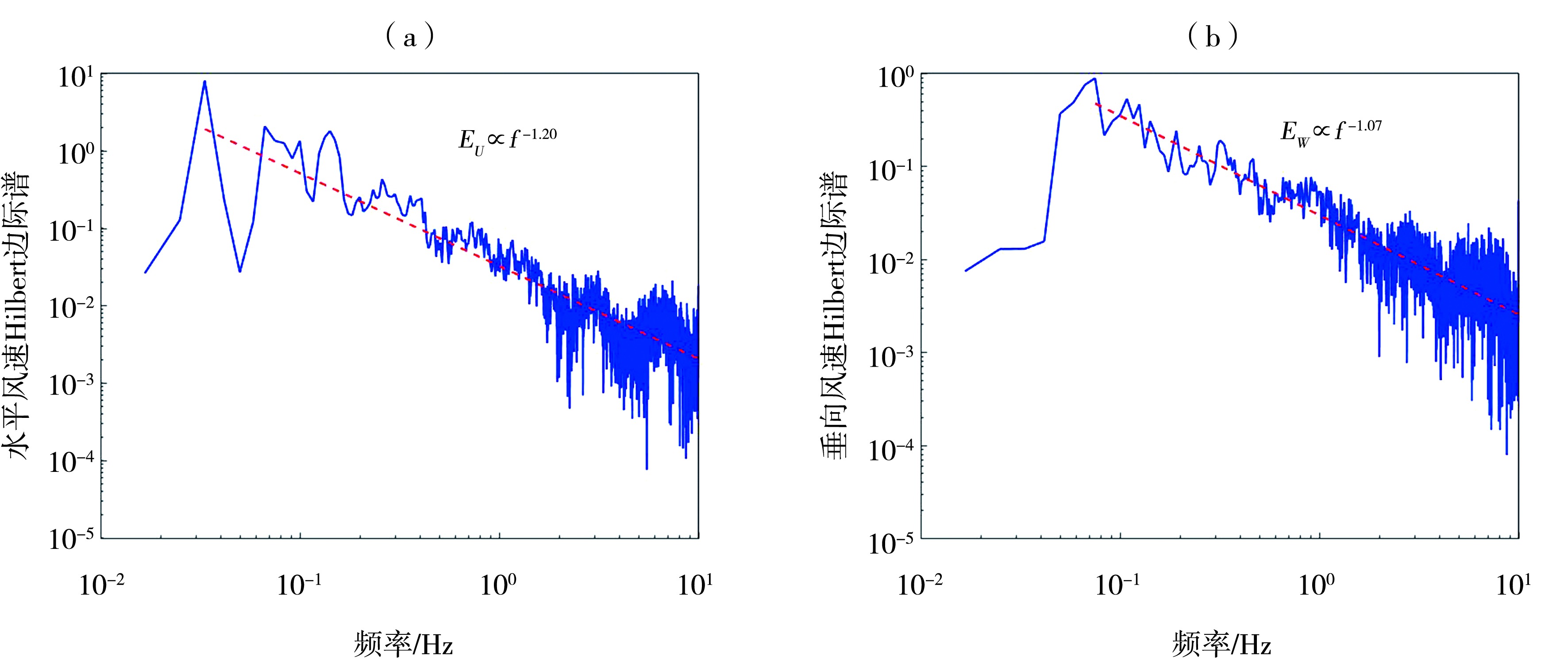
| Wang et al., | 0.30、0.83、3.00 | U、V、W | WindMaster Pro(Gill) | 20 | 0.001 m·s-1 |
| Tan et al., | 0.05、0.12、0.38、0.80、1.38 | KE、PC | H11-Lin(Sensit) | 1 | 1×10-7 J·s-1、s-1 |
| 0.70、2.00 | U、φ、θ | Young-81000(RM Young) | 20 | 0.01 m·s-1、0.1° | |
| Wang et al., | 0.05、0.12、0.38、0.80、1.41 | KE、PC | H11-Lin(Sensit) | 1 | 1×10-7 J·s-1、s-1 |
| 1.20、2.80 | U、V、W | WindMaster Pro(Gill) | 1 | 0.001 m·s-1 | |
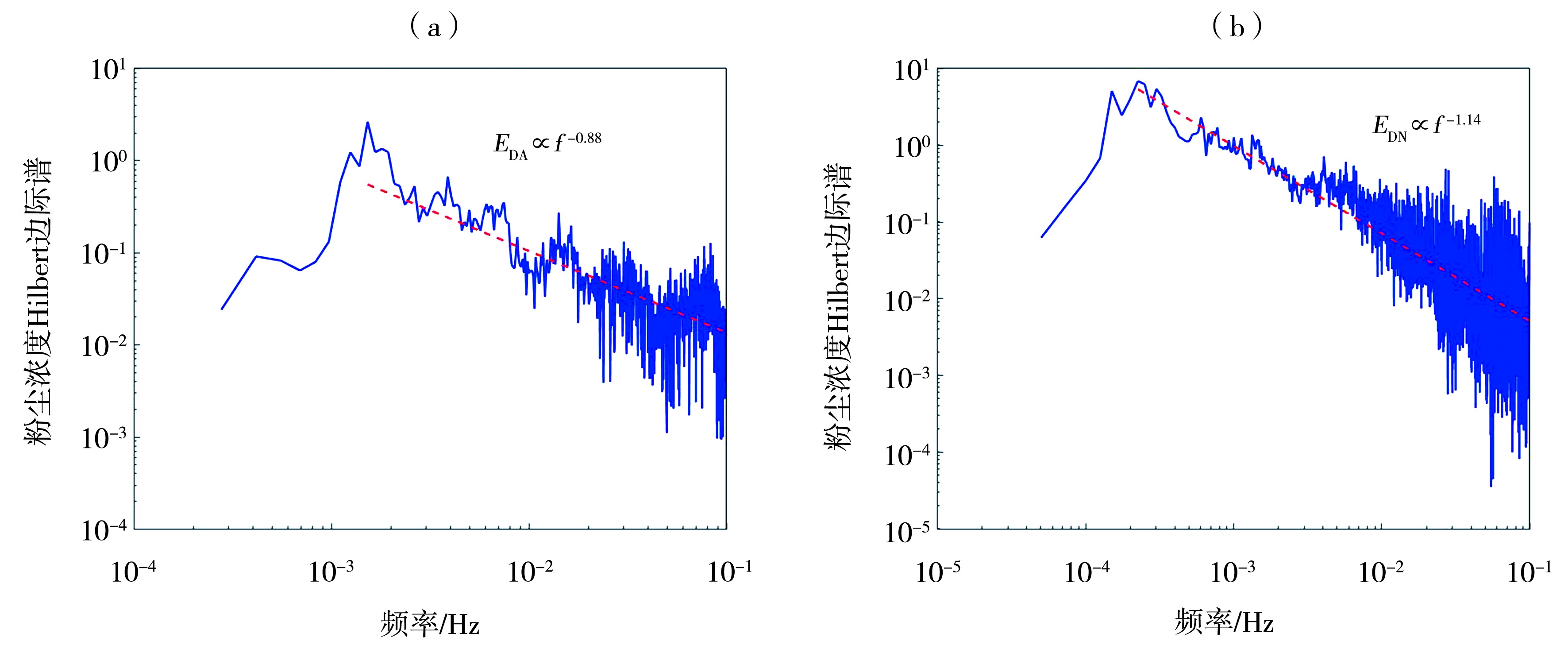
| 本研究团队 | 0.10、0.20、0.50、1.00、1.50、2.00 | DA、DN | DustTrak-II(TSI) | 0.2 | 0.001 mg·m-3 |
| 0.50、1.00 | U、V、W | Young-81000(RM Young) | 20 | 0.01 m·s-1 |
Tab.1 Datasets of aeolian sand and dust motions over Gobi and measurement conditions
| 数据来源 | 高度/m | 物理量 | 传感器(厂家) | 采样频率/Hz | 采样精度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wang et al., | 0.30、0.83、3.00 | U、V、W | WindMaster Pro(Gill) | 20 | 0.001 m·s-1 |
| Tan et al., | 0.05、0.12、0.38、0.80、1.38 | KE、PC | H11-Lin(Sensit) | 1 | 1×10-7 J·s-1、s-1 |
| 0.70、2.00 | U、φ、θ | Young-81000(RM Young) | 20 | 0.01 m·s-1、0.1° | |
| Wang et al., | 0.05、0.12、0.38、0.80、1.41 | KE、PC | H11-Lin(Sensit) | 1 | 1×10-7 J·s-1、s-1 |
| 1.20、2.80 | U、V、W | WindMaster Pro(Gill) | 1 | 0.001 m·s-1 | |
| 本研究团队 | 0.10、0.20、0.50、1.00、1.50、2.00 | DA、DN | DustTrak-II(TSI) | 0.2 | 0.001 mg·m-3 |
| 0.50、1.00 | U、V、W | Young-81000(RM Young) | 20 | 0.01 m·s-1 |

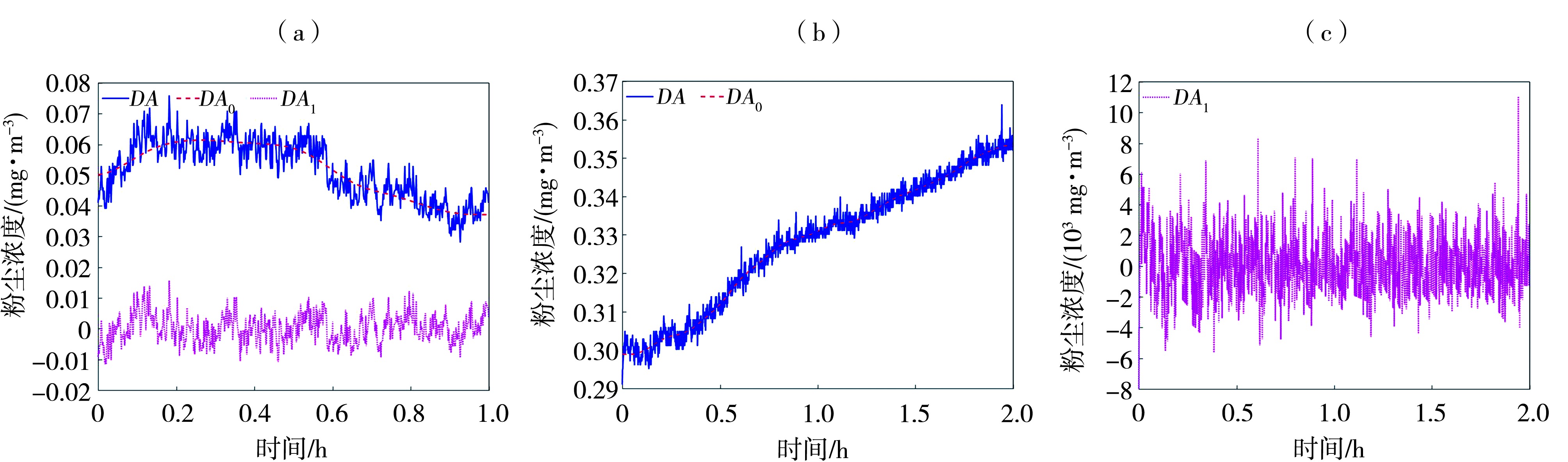
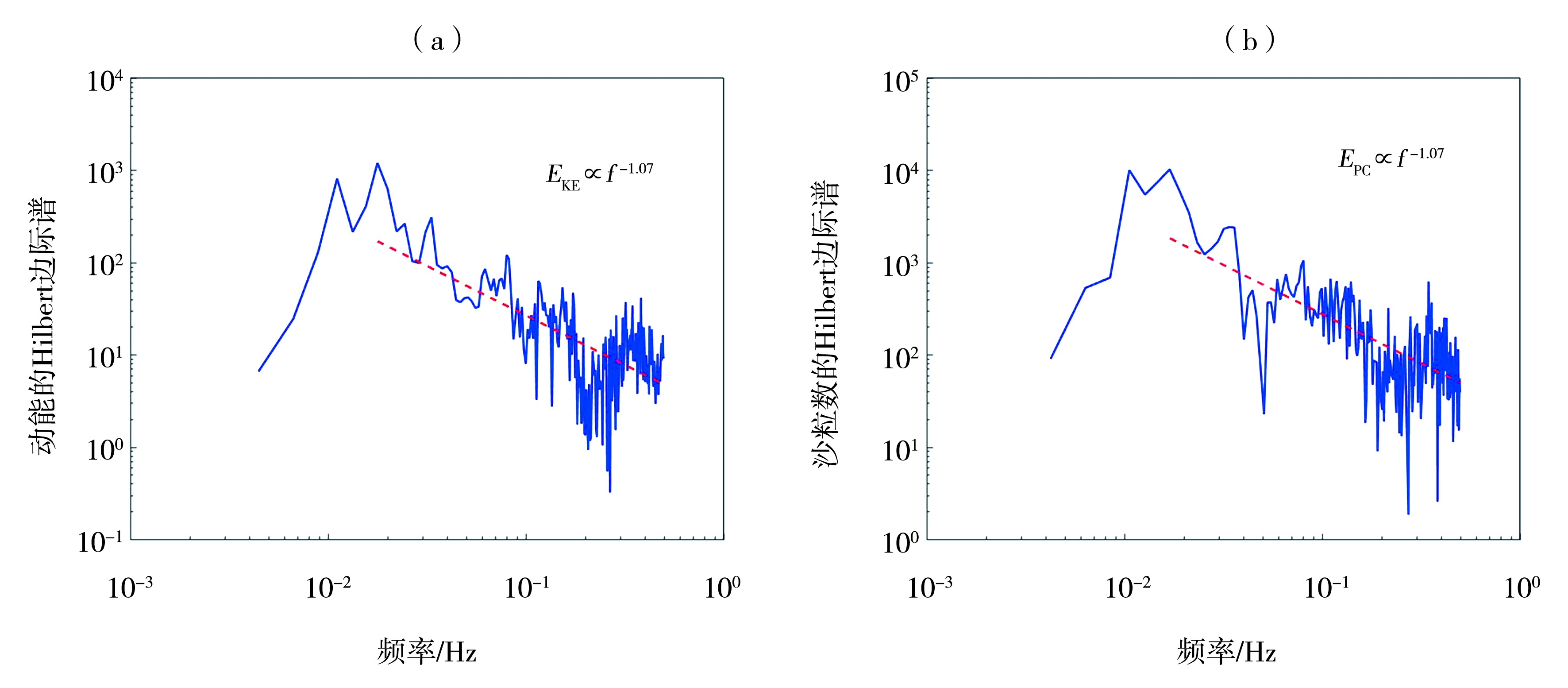
Fig.2 Decomposition of time series of kinetic energy (a) and count (b) of saltating sand grains (Data are sourced from the ref. (Tan et al., 2020), measured at 0.05 m height. Subscripts of variables 0 is for trend, 1 is for fluctuation, the same as follows)
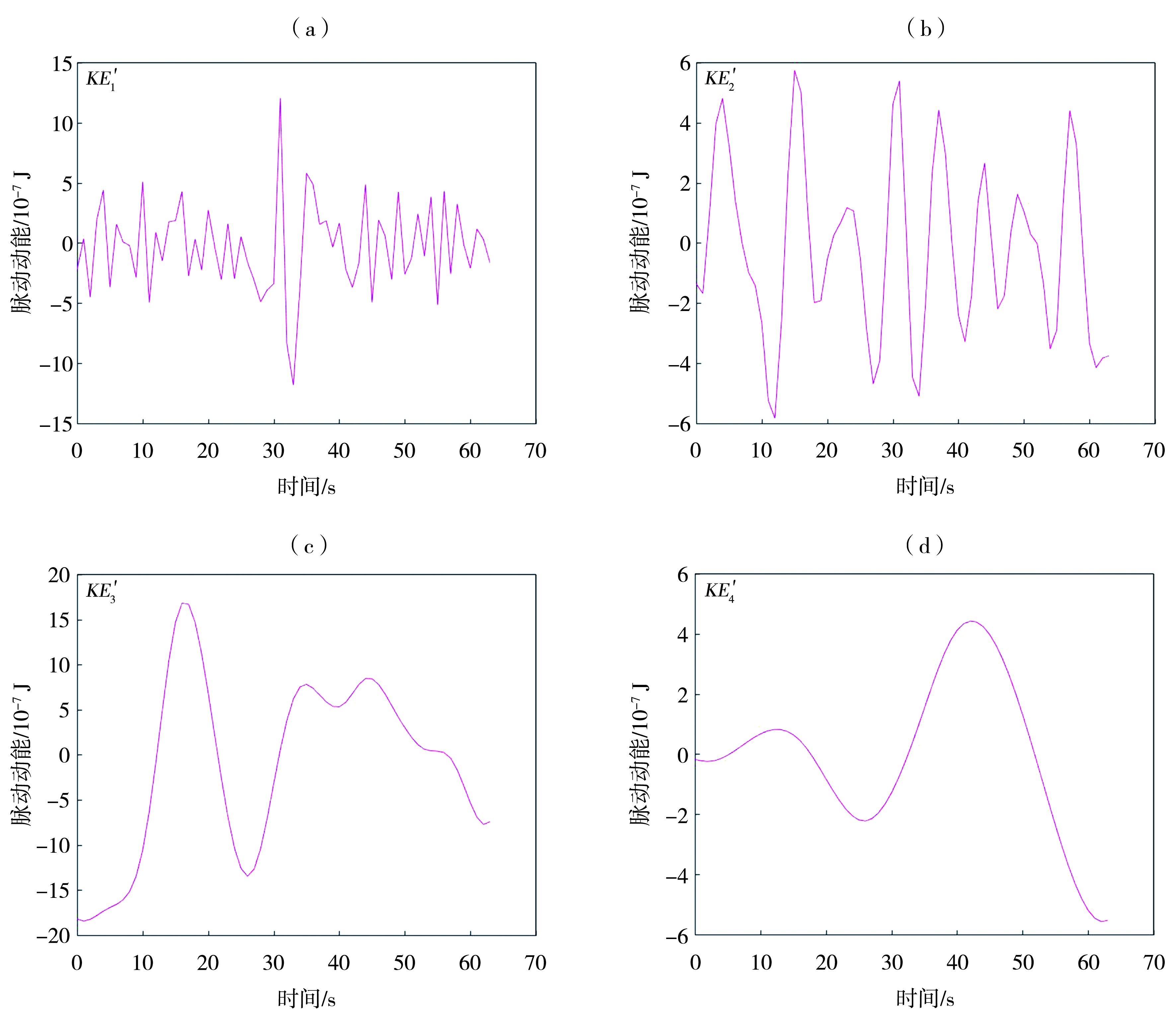
Fig.3 Fluctuation modes of kinetic energy of saltating sand grains after decomposition (a) the first mode, (b) the second mode, (c) the third mode, (d) the fourth mode (Data are sourced from the ref. (Tan et al., 2020), measured at 0.05 m height)
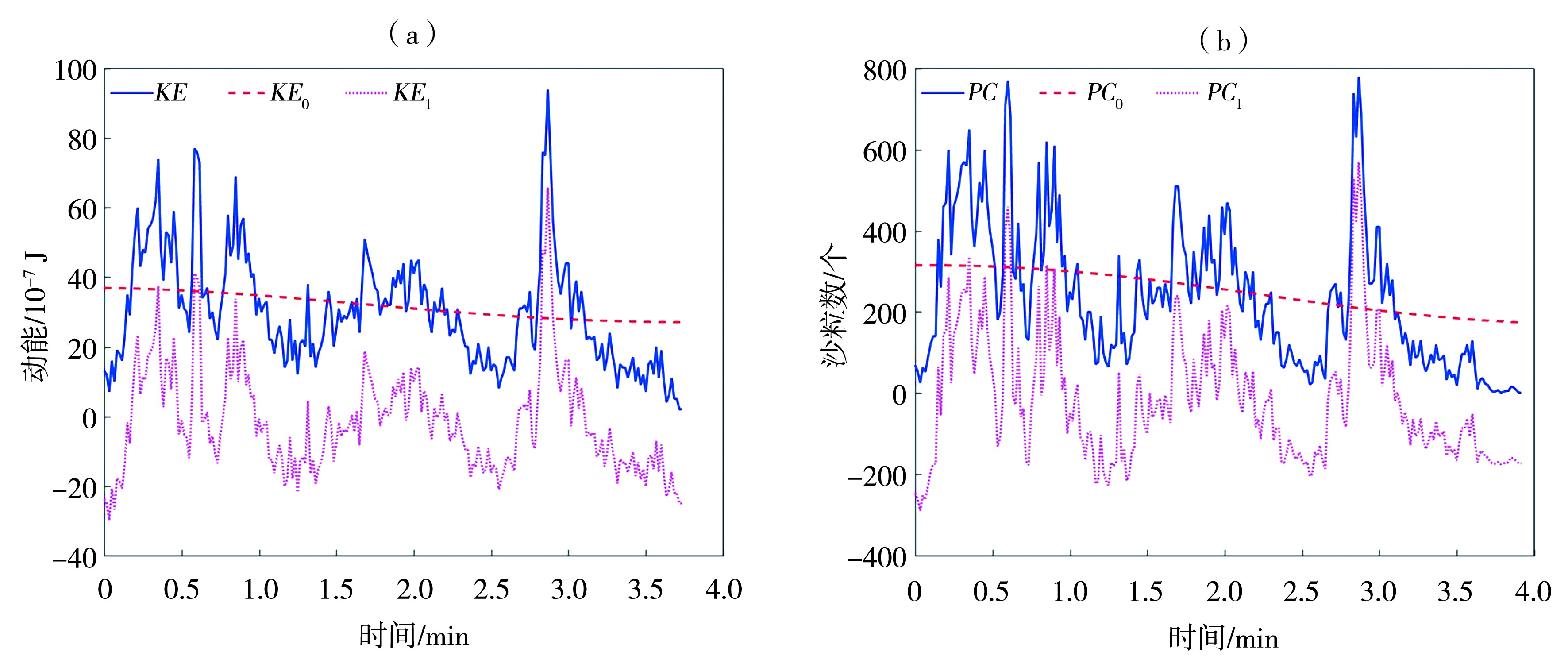
Fig.4 Decomposition of time series of kinetic energy (a) and count (b) of saltating sand grains (Data are sourced from the ref. (Wang et al., 2023), measured at 0.05 m height)
| 数据来源 | 高度/m | 物理量 | 序列数 | 均值 | 标准差 | 95%置信区间 | 物理量 | 序列数 | 均值 | 标准差 | 95%置信区间 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wang et al., | 0.30 | U | 1 724 | 1.438 | 0.418 | [1.418, 1.457] | W | 1 724 | 1.336 | 0.491 | [1.313, 1.360 ] |
| 0.83 | 1.445 | 0.345 | [1.429, 1.461] | 1.360 | 0.456 | [1.339, 1.382 ] | |||||
| 3.00 | 1.468 | 0.360 | [1.451, 1.485] | 1.404 | 0.508 | [1.380, 1.428] | |||||
| Tan et al., | 0.05 | KE | 37 | 1.141 | 0.175 | [1.083, 1.200] | PC | 34 | 1.393 | 0.295 | [1.290, 1.496] |
| 0.12 | 37 | 1.110 | 0.193 | [1.046, 1.174] | 34 | 1.380 | 0.198 | [1.311, 1.449] | |||
| 0.38 | 18 | 1.038 | 0.165 | [0.956, 1.120] | 24 | 1.224 | 0.212 | [1.135, 1.314] | |||
| 0.80 | PC | 1 | 1.451 | ||||||||
| 0.70 | U | 1 006 | 1.192 | 0.055 | [1.188, 1.195] | W | 1 006 | 1.313 | 0.143 | [1.305, 1.322] | |
| 2.00 | 1.313 | 0.143 | [1.305, 1.322] | 1.134 | 0.184 | [1.123, 1.146] | |||||
| Wang et al., | 0.05 | KE | 30 | 1.021 | 0.208 | [0.943, 1.098] | PC | 23 | 1.234 | 0.145 | [1.172, 1.297] |
| 0.12 | 24 | 0.929 | 0.215 | [0.839, 1.020] | 28 | 1.176 | 0.186 | [1.104,1.248] | |||
| 0.38 | 15 | 0.992 | 0.138 | [0.916, 1.068] | 14 | 1.055 | 0.185 | [0.948,1.161] | |||
| 0.80 | 21 | 0.907 | 0.131 | [0.847, 0.966] | 15 | 1.121 | 0.137 | [1.045,1.197] | |||
| 1.41 | 19 | 0.781 | 0.183 | [0.692, 0.869] | 21 | 1.204 | 0.216 | [1.106,1.302] | |||
| 1.20 | U | 98 | 0.835 | 0.106 | [0.813, 0.856] | W | 98 | 0.590 | 0.089 | [0.572,0.608] | |
| 2.80 | 0.891 | 0.100 | [0.871, 0.911] | 0.629 | 0.104 | [0.608,0.650] | |||||
| 本研究 | 0.10 | DA | 11 | 1.513 | 0.228 | [1.360, 1.665] | DN | 12 | 1.015 | 0.210 | [0.882,1.149] |
| 0.20 | 7 | 1.400 | 0.192 | [1.224, 1.577] | 11 | 1.276 | 0.185 | [1.152,1.401] | |||
| 0.50 | 11 | 1.276 | 0.185 | [1.152, 1.401] | 18 | 0.965 | 0.164 | [0.883,1.046] | |||
| 1.00 | 23 | 0.922 | 0.199 | [0.837, 1.008] | 12 | 0.756 | 0.077 | [0.708,0.805] | |||
| 1.50 | 10 | 1.022 | 0.216 | [0.868, 1.176] | |||||||
| 2.00 | 15 | 0.901 | 0.108 | [0.842, 0.961] | 11 | 0.932 | 0.117 | [0.854, 1.010] | |||
| 0.50 | U | 486 | 1.187 | 0.043 | [1.183, 1.190] | W | 486 | 0.899 | 0.067 | [0.893, 0.905] | |
| 1.00 | 1.214 | 0.042 | [1.211, 1.218] | 1.214 | 0.041 | [1.210, 1.218] |
Tab.2 The fitting results of scaling exponents of energy spectrum of physical variables describing aeolian sand and dust motions under different measurement conditions
| 数据来源 | 高度/m | 物理量 | 序列数 | 均值 | 标准差 | 95%置信区间 | 物理量 | 序列数 | 均值 | 标准差 | 95%置信区间 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wang et al., | 0.30 | U | 1 724 | 1.438 | 0.418 | [1.418, 1.457] | W | 1 724 | 1.336 | 0.491 | [1.313, 1.360 ] |
| 0.83 | 1.445 | 0.345 | [1.429, 1.461] | 1.360 | 0.456 | [1.339, 1.382 ] | |||||
| 3.00 | 1.468 | 0.360 | [1.451, 1.485] | 1.404 | 0.508 | [1.380, 1.428] | |||||
| Tan et al., | 0.05 | KE | 37 | 1.141 | 0.175 | [1.083, 1.200] | PC | 34 | 1.393 | 0.295 | [1.290, 1.496] |
| 0.12 | 37 | 1.110 | 0.193 | [1.046, 1.174] | 34 | 1.380 | 0.198 | [1.311, 1.449] | |||
| 0.38 | 18 | 1.038 | 0.165 | [0.956, 1.120] | 24 | 1.224 | 0.212 | [1.135, 1.314] | |||
| 0.80 | PC | 1 | 1.451 | ||||||||
| 0.70 | U | 1 006 | 1.192 | 0.055 | [1.188, 1.195] | W | 1 006 | 1.313 | 0.143 | [1.305, 1.322] | |
| 2.00 | 1.313 | 0.143 | [1.305, 1.322] | 1.134 | 0.184 | [1.123, 1.146] | |||||
| Wang et al., | 0.05 | KE | 30 | 1.021 | 0.208 | [0.943, 1.098] | PC | 23 | 1.234 | 0.145 | [1.172, 1.297] |
| 0.12 | 24 | 0.929 | 0.215 | [0.839, 1.020] | 28 | 1.176 | 0.186 | [1.104,1.248] | |||
| 0.38 | 15 | 0.992 | 0.138 | [0.916, 1.068] | 14 | 1.055 | 0.185 | [0.948,1.161] | |||
| 0.80 | 21 | 0.907 | 0.131 | [0.847, 0.966] | 15 | 1.121 | 0.137 | [1.045,1.197] | |||
| 1.41 | 19 | 0.781 | 0.183 | [0.692, 0.869] | 21 | 1.204 | 0.216 | [1.106,1.302] | |||
| 1.20 | U | 98 | 0.835 | 0.106 | [0.813, 0.856] | W | 98 | 0.590 | 0.089 | [0.572,0.608] | |
| 2.80 | 0.891 | 0.100 | [0.871, 0.911] | 0.629 | 0.104 | [0.608,0.650] | |||||
| 本研究 | 0.10 | DA | 11 | 1.513 | 0.228 | [1.360, 1.665] | DN | 12 | 1.015 | 0.210 | [0.882,1.149] |
| 0.20 | 7 | 1.400 | 0.192 | [1.224, 1.577] | 11 | 1.276 | 0.185 | [1.152,1.401] | |||
| 0.50 | 11 | 1.276 | 0.185 | [1.152, 1.401] | 18 | 0.965 | 0.164 | [0.883,1.046] | |||
| 1.00 | 23 | 0.922 | 0.199 | [0.837, 1.008] | 12 | 0.756 | 0.077 | [0.708,0.805] | |||
| 1.50 | 10 | 1.022 | 0.216 | [0.868, 1.176] | |||||||
| 2.00 | 15 | 0.901 | 0.108 | [0.842, 0.961] | 11 | 0.932 | 0.117 | [0.854, 1.010] | |||
| 0.50 | U | 486 | 1.187 | 0.043 | [1.183, 1.190] | W | 486 | 0.899 | 0.067 | [0.893, 0.905] | |
| 1.00 | 1.214 | 0.042 | [1.211, 1.218] | 1.214 | 0.041 | [1.210, 1.218] |
| [1] | 黄雨晖, 韩小元, 赵健, 等, 2019. 新疆戈壁地区风沙流结构及其粒径特征研究[J]. 气象与减灾研究, 42(3):199-205. |
| [2] | 蒋富强, 李荧, 李凯崇, 等, 2010. 兰新铁路百里风区风沙流结构特性研究[J]. 铁道学报, 32(3):105-110. |
| [3] | 李凯崇, 蒋富强, 薛春晓, 等, 2010. 兰新铁路十三间房段的戈壁风沙流特征分析[J]. 铁道工程学报, 27(3):15-18. |
| [4] | 刘江, 王元, 2009. 利用静态小波变换的非定常阵风分析与模拟[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 43(7):74-78. |
| [5] | 刘旭阳, 宁文晓, 王振亭, 2020. 两种戈壁地表风沙流特征的野外观测[J]. 干旱区研究, 37(4):1087-1 094. |
| [6] | 柳本立, 张伟民, 刘小宁, 等, 2010. 莫高窟顶戈壁偏东风作用下输沙率变化的观测研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 30(3):516-521. |
| [7] |
屈建军, 黄宁, 拓万全, 等, 2005. 戈壁风沙流结构特性及其意义[J]. 地球科学进展, 20(1):19-23.
DOI |
| [8] | 屈建军, 张克存, 张伟民, 等, 2012. 几种典型戈壁床面风沙流特性比较[J]. 中国沙漠, 32(2):285-290. |
| [9] | 王涛, 陈广庭, 2008. 中国的沙漠·戈壁[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术文献出版社:216-224. |
| [10] | 王旭, 2019. 金阿铁路戈壁风沙流输沙量研究[J]. 科技资讯,2019, 17(13):180-182. |
| [11] | 王志强, 黄晟敏, 于涛, 等, 2010. 戈壁地表风沙运动特征的野外观测研究[J]. 新疆环境保护, 32(3):10-13. |
| [12] | 尹永顺, 1990. 砾漠大风地区风沙流及铁路防沙技术研究[J]. 铁道建筑, 30(5):5-8. |
| [13] | 张克存, 屈建军, 俎瑞平, 等, 2005. 戈壁风沙流结构和风速廓线特征研究[J]. 水土保持研究, 12(1):54-55. |
| [14] | 张正偲, 董治宝, 赵爱国, 2011. 人工模拟戈壁风沙流与风程效应观测[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 41(10):1505-1 510. |
| [15] | 邹学勇, 董光荣, 王周龙, 1995. 戈壁风沙流若干特征研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 15(4):368-373. |
| [16] | BAAS A C W, 2006. Wavelet power spectra of aeolian sand transport by boundary layer turbulence[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 33(5):L05403. DOI: 10.1029/2005GL025547. |
| [17] | BAAS A C W, 2008. Challenges in aeolian geomorphology: Investigating aeolian streamers[J]. Geomorphology, 93(1/2):3-16. DOI: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2006.12.015. |
| [18] | BUTTERFIELD G R, 1998. Transitional behaviour of saltation: Wind tunnel observations of unsteady winds[J]. Journal of Arid Environments, 39(3):377-394. DOI: 10.1006/jare. 1997.0367. |
| [19] | CHAMECKI M, KOK J F, 2023. Fundamental causes of model inaccuracies in predicting wind-blown sand fluxes[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 50(11):e2023GL103490. DOI: 10.1029/2023GL103490. |
| [20] | CHENG J J, JIANG F Q, XUE C X, et al, 2015. Characteristics of the disastrous wind-sand environment along railways in the Gobi area of Xinjiang, China[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 102:344-354. DOI: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.12.018. |
| [21] | COLOMINAS M A, SCHLOTTHAUER G, TORRES M E, 2014. Improved complete ensemble EMD: A suitable tool for biomedical signal processing[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 14:19-29. DOI: 10.1016/j.bspc.2014. 06.009. |
| [22] | DAVIDSON-ARNOTT R G D, BAUER B O, WALKER I J, et al, 2012. High-frequency sediment transport responses on a vegetated foredune[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 37(11):1227-1 241. DOI: 10.1002/esp.3275. |
| [23] | DE SOUZA U B, ESCOLA J P L, DA CUNHA BRITO L, 2022. A survey on Hilbert-Huang transform: Evolution, challenges and solutions[J]. Digital Signal Processing,120:103292. DOI: 10.1016/j.dsp.2021.103292. |
| [24] | ELLIS J T, SHERMAN D J, 2023. Cross-wavelet analysis of coherent wind and saltation events[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 48(2):406-414. DOI: 10.1002/esp.5493. |
| [25] | HUANG N E, SHEN Z, LONG S R, et al, 1998. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 454(1971):903-995. DOI: 10.1098/rspa.1998.0193. |
| [26] | HUANG N E, WU Z H, 2008. A review on Hilbert-Huang transform: Method and its applications to geophysical studies[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 46(2):RG2006. DOI: 10.1029/2007RG000228. |
| [27] | LIU B L, WANG Z Y, NIU B C, et al, 2021. Large scale sand saltation over hard surface: A controlled experiment in still air[J]. Journal of Arid Land, 13(6):599-611. DOI: 10.1007/s40333-021-0104-3. |
| [28] | LIU J Q, KIMURA R, 2018. Wind speed characteristics and blown sand flux over a gravel surface in a compact wind tunnel[J]. Aeolian Research, 35:39-46. DOI: 10.1016/j.aeolia.2018.09.005. |
| [29] | MARUSIC I, MONTY J P, 2019. Attached eddy model of wall turbulence[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 51(1):49-74. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-fluid-010518-040427. |
| [30] | SHERMAN D J, LI B L, ELLIS J T, et al, 2018. Intermittent aeolian saltation: A protocol for quantification[J]. Geographical Review, 108(2):296-314. DOI: 10.1111/gere.12249. |
| [31] | SHU K, WANG W J, DING H H, et al, 2022. Influence of sand transport rate on rolling wear and damage behaviors of wheel/rail in Gobi and desert windblown sand environments[J]. Tribology International,172:107584. DOI: 10.1016/j.triboint.2022.107584. |
| [32] | SPIES P J, MCEWAN I K, BUTTERFIELD G R, 2000. One-dimensional transitional behaviour in saltation[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 25(5):505-518. |
| [33] | STOUT J E, ZOBECK T M, 1997. Intermittent saltation[J]. Sedimentology, 44(5):959-970. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-3091.1997.d01-55.x. |
| [34] | TAN L H, AN Z S, ZHANG K, et al, 2020. Intermittent aeolian saltation over a gobi surface: Threshold, saltation layer height, and high-frequency variability[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 125(1):e2019JF005329. DOI: 10.1029/2019JF005329. |
| [35] | TAN L H, QU J J, WANG T, et al, 2021. Field observation evidence for kink points in the vertical kinetic energy flux profiles of wind-blown sand over gobi and its significance[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 48(3):e2020GL091224. DOI: 10.1029/2020GL091224. |
| [36] | TAN L H, QU J J, WANG T, et al, 2022. Vertical flux density and frequency profiles of wind-blown sand as a function of the grain size over gobi and implications for aeolian transport processes[J]. Aeolian Research,55:100787. DOI: 10.1016/j.aeolia.2022.100787. |
| [37] | TAN L H, ZHANG W M, AN Z S, et al, 2019. The effect of roughness density of gobi beds on the entrainment of sediment by wind: A wind tunnel study[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 190:183-189. DOI: 10.1016/j.jweia.2019.05.002. |
| [38] | TAN L H, ZHANG W M, QU J J, et al, 2013. Aeolian sand transport over gobi with different gravel coverages under limited sand supply: A mobile wind tunnel investigation[J]. Aeolian Research, 11:67-74. DOI: 10.1016/j.aeolia.2013. 10.003. |
| [39] | TAN L H, ZHANG W M, QU J J, et al, 2016. Aeolian sediment transport over gobi: Field studies atop the Mogao Grottoes, China[J]. Aeolian Research, 21:53-60. DOI: 10.1016/j.aeolia.2016.03.002. |
| [40] | WANG P, ZHENG X J, 2015. Unsteady saltation on Mars[J]. Icarus, 260:161-166. DOI: 10.1016/j.icarus.2015.07.012. |
| [41] | WANG T, QU J J, TAN L H, 2023. Aeolian sediment transport over sandy gobi: Field studies in the Nanhu gobi along the Hami-Lop Nor Railway[J]. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 11(1):125-134. DOI: 10.1016/j.iswcr.2022.03.009. |
| [42] | WANG T, QU J J, TAN L H, et al, 2022. Aeolian sediment transport over the Gobi with high gravel coverage under extremely strong winds in the Hundred Miles windy area along the Lanzhou-Xinjiang High-Speed Railway[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,220:104857. DOI: 10.1016/j.jweia.2021.104857. |
| [43] | WANG Z T, ZHANG C L, CEN S B, 2018. Unsteady aeolian saltation[J]. The European Physical Journal E, 41(10):121. DOI: 10.1140/epje/i2018-11730-8. |
| [44] | WANG Z T, 2024. Some statistical properties of aeolian saltation[J]. AIP Advances, 14(2):025342. DOI: 10.1063/5.019 2219. |
| [45] | WANG Z T, ZHANG C L, WANG H T, 2014. Intermittency of aeolian saltation[J]. The European Physical Journal E, 37(12):126. DOI: 10.1140/epje/i2014-14126-x. |
| [46] | WEI W, ZHANG H S, SCHMITT F G, et al, 2017. Investigation of turbulence behaviour in the stable boundary layer using arbitrary-order Hilbert spectra[J]. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 163(2):311-326. DOI: 10.1007/s10546-016-0227-9. |
| [47] | ZHANG C L, WEI G R, ZOU X Y, et al, 2022. The varying fetch effect of aeolian sand transport above a gobi surface and its implication for gobi development process[J]. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 10(4):623-634. DOI: 10.1016/j.iswcr.2022.03.002. |
| [1] | DONG Yuanzhu, WANG Tianhe, TAN Ruiqi, WANG Sichen, JIAO Yingzi, TANG Jingyi. A comparative study of two extreme dust events in the deserts and gobi regions in the arid regions of northwest China [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(2): 197-208. |
| [2] | LIANG Guohao, MAO Rui, SHAO Yaping, LI Xiaolan, GONG Daoyi. Research progress of convective turbulent dust emission [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(4): 531-539. |
| [3] | TU Aiqin, WANG Zhenzhu, ZHU Genghua, WANG Zhifei, ZHANG Hai, ZHANG Shuai, LIU Dong, WENG Ningquan. Pollution characteristics of two strong dust processes in northern China in March 2021 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(4): 607-619. |
| [4] | XU Luyang, ZHAI liang, WANG Yuanyuan, LEI Lei, YU Bo, HAO Cui, QIN Qingchang. Application evaluation of multi-source remote sensing data in spring dust weather monitoring in Beijing [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(2): 318-327. |
| [5] | DUAN Bolong, LIU Xinwei, GUO Runxia, SONG Qiang, DI Xiaohong, DUAN Mingkeng. Cause Analysis on Severe Dust Storm in Northern China on 15 March 2021 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(4): 541-553. |
| [6] |
CAO Xiaoyun, XIAO Jianshe, QIAO Bin, CHEN Guoqian, QUAN Chen, ZHU Cunxiong, SHI Feifei, .
Temporal and Spatial Variation Characteristics of DustIntensity in Qaidam Basin from 1961 to 2019#br#
#br#
[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(1): 46-53.
|
| [7] | . Characteristics of Atmospheric-boundary-layer Height and Its Relationship with Sand-dust Weather in Jiuquan of Gansu Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(6): 979-986. |
| [8] | QI Donglin1,2, ZHAO Quanning1, ZHAO Huifang1, HAN Tingfang3, SU Wenjiang1. Temporal and Spatial Variation Characteristics and Regional Differences of Dust Fall in Qinghai from 2004 to 2017 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(6): 927-. |
| [9] | JIANG Xuegong, LI Xiazi, WANG Dejun. Characteristics of Tropopause Evolution and Dust Vertical Transportation During a Mongolia Cyclone Dust Storm Process [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(1): 1-10. |
| [10] | BAI Bing, ZHANG Qiang,CHEN Xuhui,HAN Haitao . Moving Paths and Spatial Characteristics of Three Typical Dust Processes in East Asia [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(1): 11-16. |
| [11] | ZHOU Chenglong, YANG Xinghua, YANG Fan, HUO Wen,ZHONG Xinjie, PAN Honglin, HE Qing. Analysis of Calculated Dust Emission Threshold Wind Speed Based on the Field Experiments [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(1): 90-96. |
| [12] | WU Huanbo, CHEN Qiang, GU Xinbo, FENG Zhen, WANG Xudong. Analysis of a Severe Dust Weather and its Effect on Temporaland Spatial Distribution of PM10 Concentration [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2018, 36(1): 117-123. |
| [13] | . Variation Characteristic of Main Meteorological Elements During Summer Sand-Dust Storm Processes in East of Hexi Corridor [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(3): 427-. |
| [14] | WANG Yanfeng1, HUANG Wubin2, HE Cuiying3, HUANG Shan1. Analysis of a Haze and Sand-dust Mixed Pollution Weather in Spring of Beijing [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(1): 100-107. |
| [15] | YUAN Tiangang, CHEN Siyu, KANG Litai, CHEN Ziqi, LUO Yuan, ZOU Qian. Temporal and Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Change Trends of Dust Intensity in Dust Source Regions of Northern China During 1961-2010 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2016, 34(6): 927-935. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||