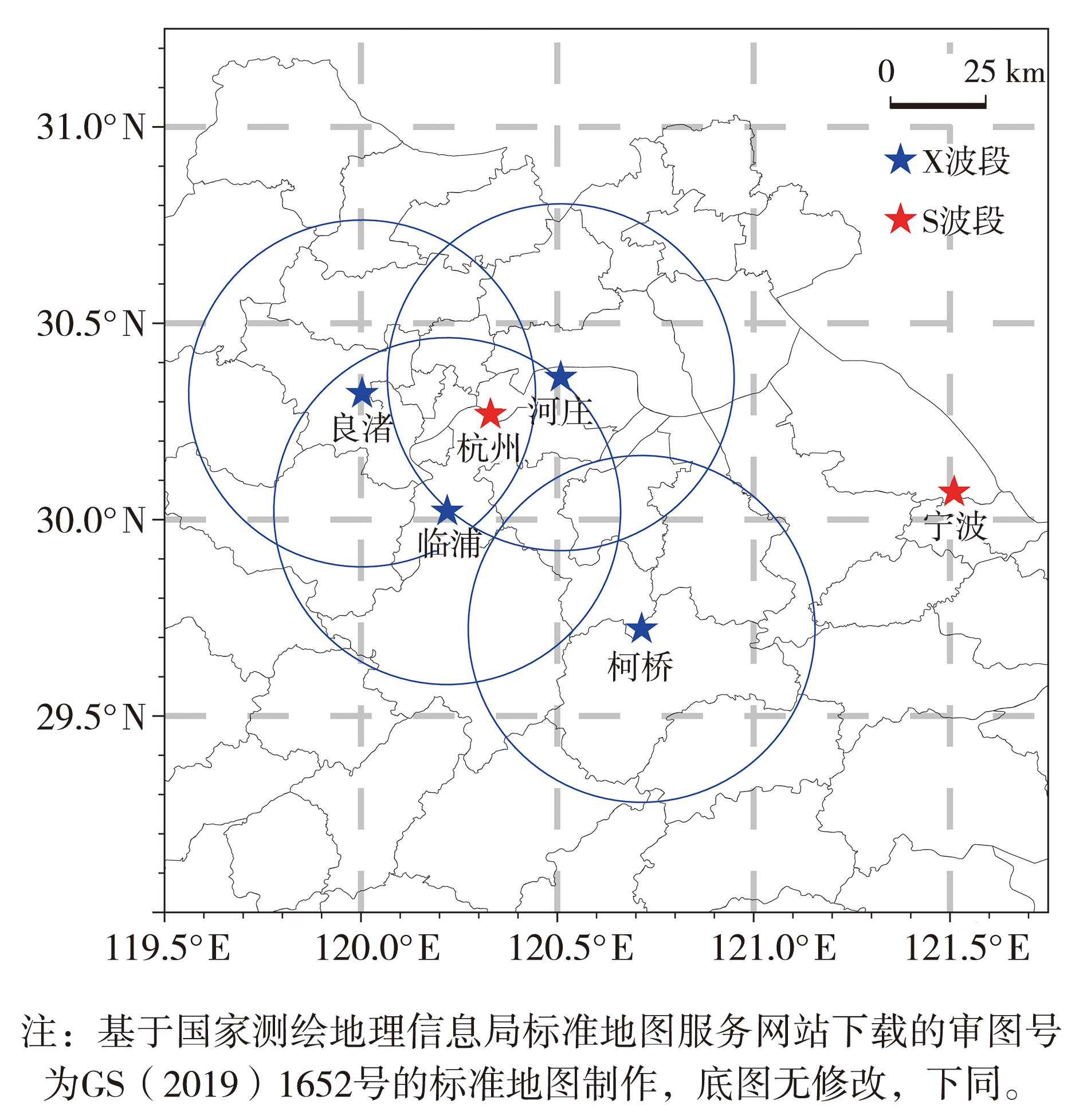
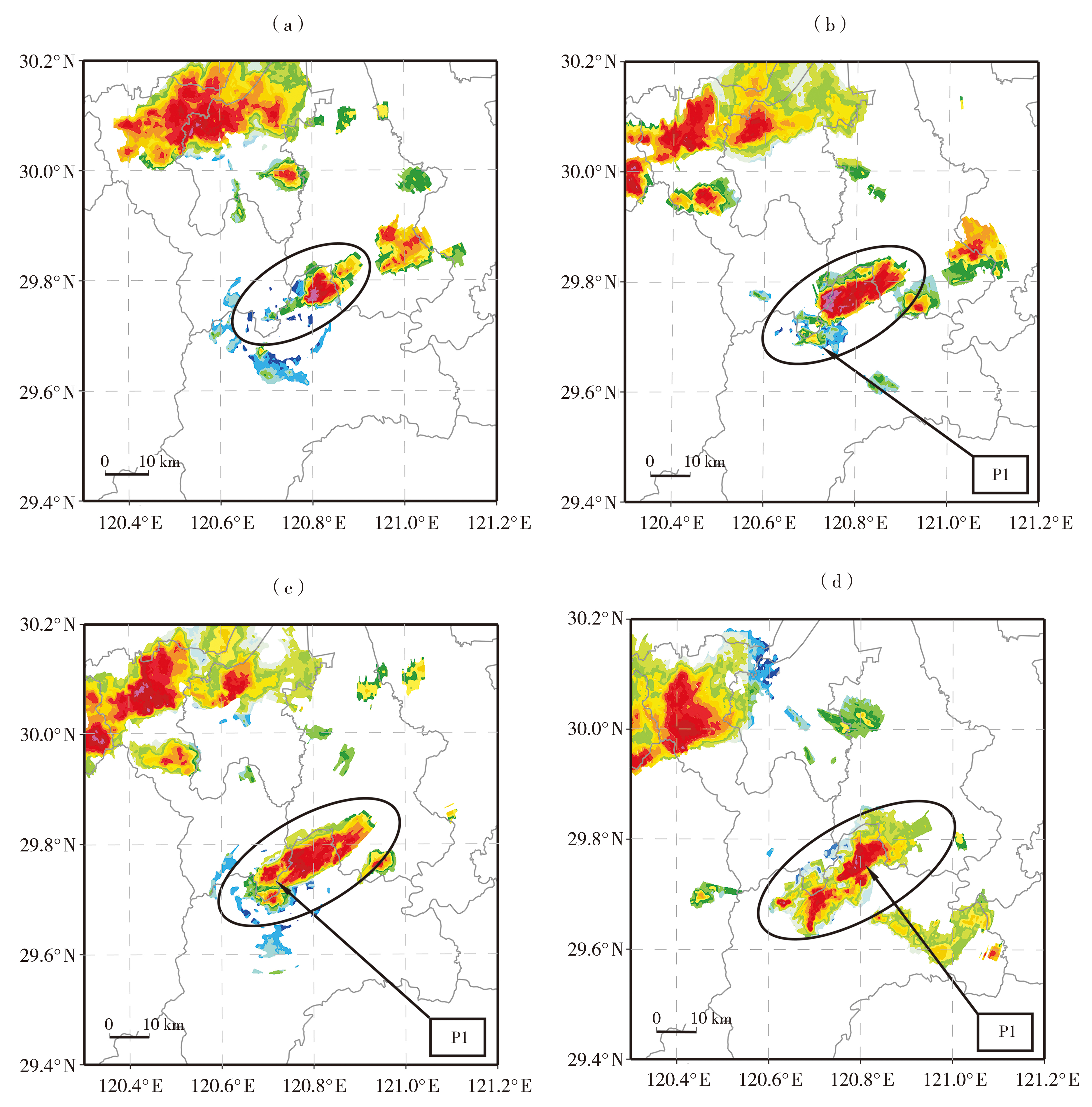
| [1] |
车军辉, 郭红艳, 史茜, 等, 2017. 地面辐合线演变与多尺度天气过程的相互作用分析[J]. 干旱气象, 35(1):91-99.
DOI
|
| [2] |
高丽, 潘佳文, 蒋璐璐, 等, 2021. 一次长生命史超级单体降雹演化机制及双偏振雷达回波分析[J]. 气象, 47(2):170-182.
|
| [3] |
高晓梅, 孙雪峰, 秦瑜蓬, 等, 2018. 山东一次强对流天气的环境条件和对流风暴特征[J]. 干旱气象, 36(3):447-455.
DOI
|
| [4] |
何娜, 丁青兰, 俞小鼎, 等, 2020. 北京及周边地区雷暴阵风锋特征统计分析[J]. 气象学报, 78(2):250-259.
|
| [5] |
胡文东, 杨侃, 黄小玉, 等, 2015. 一次阵风锋触发强对流过程雷达资料特征分析[J]. 高原气象, 34(5):1452-1 464.
|
| [6] |
李彩玲, 蔡康龙, 黄先香, 等, 2021. 桂林一次强下击暴流成因分析[J]. 气象, 47(2):242-252.
|
| [7] |
李思腾, 仰美霖, 李林, 等, 2019. 基于标准差分析法的X波段双偏振天气雷达资料质量评估[J]. 干旱气象, 37(3):467-476.
|
| [8] |
李渝, 马舒庆, 杨玲, 等, 2020. 长沙机场阵列天气雷达风场验证[J]. 应用气象学报, 31(6):1-13.
|
| [9] |
林宗桂, 李耀先, 林开平, 等, 2009. 一个长生命期中尺度对流系统维持机制的研究[J]. 气象学报, 67(4):640-651.
|
| [10] |
刘黎平, 胡志群, 吴翀, 2016. 双线偏振雷达和相控阵天气雷达技术的发展和应用[J]. 气象科技进展, 6(3):28-33.
|
| [11] |
马淑萍, 王秀明, 俞小鼎, 2019. 极端雷暴大风的环境参量特征[J]. 应用气象学报, 30(3):292-301.
|
| [12] |
潘佳文, 彭婕, 魏鸣, 等, 2022. 副热带高压背景下极端短时强降水的双偏振相控阵雷达观测分析[J]. 气象学报, 80(5):748-764.
|
| [13] |
孙继松, 陶祖钰, 2012. 强对流天气分析与预报中的若干基本问题[J]. 气象, 38(2):164-173.
|
| [14] |
韦惠红, 吴翠红, 魏凡, 等, 2023. 湖北雷暴阵风锋特征及其对流触发作用分析[J]. 干旱气象, 41(1):73-81.
DOI
|
| [15] |
吴举秀, 周青, 杨传凤, 等, 2017. 2015年7月14日阵风锋及锋后大风多普勒天气雷达产品特征分析[J]. 高原气象, 36(4):1082-1 090.
|
| [16] |
席宝珠, 俞小鼎, 孙力, 等, 2015. 我国阵风锋类型与产生机制分析及其主观识别方法[J]. 气象, 41(2):133-142.
|
| [17] |
许长义, 卜清军, 黄安宁, 2022. 环渤海湾连续两条阵风锋的关联与成因分析[J]. 气象, 48(6):729-745.
|
| [18] |
俞小鼎, 周小刚, 王秀明, 2012. 雷暴与强对流临近天气预报技术进展[J]. 气象学报, 70(3):311-337.
|
| [19] |
禹梁玉, 王啸华, 顾荣直, 等, 2021. 江苏一次下击暴流过程致灾大风成因分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 37(5):801-811.
|
| [20] |
袁琳, 孙棋, 阿不都外力·阿不力克木, 等, 2024. 塔里木盆地东北缘一次强对流天气过程中的阵风锋特征[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象,2024, 18(3):47-55.
|
| [21] |
张涛, 李柏, 杨洪平, 等, 2013. 三次雷暴导致的阵风锋过程分析[J]. 气象, 39(10): 1 275-1 283.
|
| [22] |
张蔚然, 刘黎平, 吴翀, 2023. X波段相控阵偏振雷达观测墨脱地区云降水宏观特征的统计研究[J]. 大气科学, 47(1):70-85.
|
| [23] |
张羽, 陈炳洪, 曾琳, 等, 2023. 基于X波段双偏振相控阵雷达的超级单体风暴观测分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 39(2):218-229.
|
| [24] |
CHOWDHURI S, TODEKAR K, PRABHA T V, 2021a. The characterization of turbulent heat and moisture transport during a gust-front event over the Indian peninsula[J]. Environmental Fluid Mechanics, 21(4): 907-924.
|
| [25] |
CHOWDHURI S, TODEKAR K, MURUGAVEL P, et al, 2021b. Unravelling the turbulent structures of temperature variations during a gust front event:A case study[J]. Environmental Fluid Mechanics, 21(1):263-281.
|
| [26] |
CORFIDI S F, 2003. Cold pools and MCS propagation:Forecasting the motion of downwind-developing MCSs[J]. Weather and Forecasting, 18(6): 997-1 017.
|
| [27] |
HENNEBERG O, MEYER B, HAERTER J O, 2020. Particle-based tracking of cold pool gust fronts[J]. Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, 12(5):e2019MS001910. DOI:10.1029/2019MS001910.
|
| [28] |
NORTH K W, OUE M, KOLLIAS P, et al, 2017. Vertical air motion retrievals in deep convective clouds using the ARM scanning radar network in Oklahoma during MC3E[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 10(8):2785-2 806.
|
| [29] |
POTVIN C K, SHAPIRO A, XUE M, 2012. Impact of a vertical vorticity constraint in variational dual-Doppler wind analysis: Tests with real and simulated supercell data[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 29(1): 32-49.
|
| [30] |
QUAN W Q, XU X, WANG Y, 2014. Observation of a straight-line wind case caused by a gust front and its associated fine-scale structures[J]. Journal of Meteorological Research, 28(6):1137-1 154.
|
| [31] |
RICHARDSON Y P, 1999. The influence of horizontal variations in vertical shear and low-level moisture on numerically simulated convective storms[D]. Norman: School of Meteorology,University of Oklahoma:209-210.
|
| [32] |
ROBERTS R D, WILSON J W, 1989. A proposed microburst nowcasting procedure using single-Doppler radar[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 28(4): 285-303.
|
| [33] |
WEISMAN M L, KLEMP J B, ROTUNNO R, 1988. Structure and evolution of numerically simulated squall lines[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 45(14):1990-2 013.
|
| [34] |
WILSON J W, ROBERTS R D, 2006. Summary of convective storm initiation and evolution during IHOP:Observational and modeling perspective[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 134(1): 23-47.
|
| [35] |
ZHANG Y, BAI L Q, MENG Z Y, et al, 2020. Rapid-scan and polarimetric phased-array radar observations of a tornado in the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Journal of Tropical Meteorology, 26(3): 81-86.
|
| [36] |
ZHANG Y, LIU X T, CHEN B H, et al, 2023. Application of X-band polarimetric phased-array radars in quantitative precipitation estimation[J]. Journal of Tropical Meteorology, 29(1): 142-152.
|
 ), CEN Lulin3, ZHANG Chaoqin1, ZHANG Weiwei4
), CEN Lulin3, ZHANG Chaoqin1, ZHANG Weiwei4