Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2025, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (1): 104-113.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-01-0104
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Diurnal variation characteristics of warm season precipitation in Xinjiang based on K-means clustering method
LI Anbei( ), ZHANG Meng, LI Ruqi(
), ZHANG Meng, LI Ruqi( ), MU Huan, WAN Yu
), MU Huan, WAN Yu
- Xinjiang Meteorological Observatory,Urumqi 830002,China
-
Received:2024-03-15Revised:2024-05-16Online:2025-02-28Published:2025-03-15
基于K-means聚类的新疆暖季降水日变化特征
- 新疆维吾尔自治区气象台,新疆 乌鲁木齐 830002
-
通讯作者:李如琦(1974—),男,四川成都人,正高级工程师,主要从事天气预报和灾害性天气机理研究。E-mail:liruqi@sohu.com。 -
作者简介:李桉孛(1992—),女,湖南邵东人,高级工程师,主要从事天气预报业务及雨雪研究。E-mail:634200781@qq.com。 -
基金资助:新疆维吾尔自治区自然基金项目(2022D01A292);新疆维吾尔自治区自然基金项目(2022D01D086);新疆维吾尔自治区重点研发计划项目(2023B03019-2)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LI Anbei, ZHANG Meng, LI Ruqi, MU Huan, WAN Yu. Diurnal variation characteristics of warm season precipitation in Xinjiang based on K-means clustering method[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(1): 104-113.
李桉孛, 张萌, 李如琦, 牟欢, 万瑜. 基于K-means聚类的新疆暖季降水日变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(1): 104-113.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-01-0104
| 聚类评价指标 | 样本初始类数k | 指标说明 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k=3 | k=4 | k=5 | k=6 | ||
| 轮廓系数 | 0.403 | 0.371 | 0.325 | 0.314 | 接近1的值表示分离良好的簇 |
| 方差比准则 | 160.191 | 171.244 | 160.884 | 140.499 | 数值越大表示簇之间内聚性越高 |
| Davies-Bouldin指数 | 0.818 | 0.815 | 0.929 | 1.068 | 数值越低表示簇越紧凑且分离良好 |
Tab.1 Test and evaluation of clustering results of different initial protocols
| 聚类评价指标 | 样本初始类数k | 指标说明 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k=3 | k=4 | k=5 | k=6 | ||
| 轮廓系数 | 0.403 | 0.371 | 0.325 | 0.314 | 接近1的值表示分离良好的簇 |
| 方差比准则 | 160.191 | 171.244 | 160.884 | 140.499 | 数值越大表示簇之间内聚性越高 |
| Davies-Bouldin指数 | 0.818 | 0.815 | 0.929 | 1.068 | 数值越低表示簇越紧凑且分离良好 |
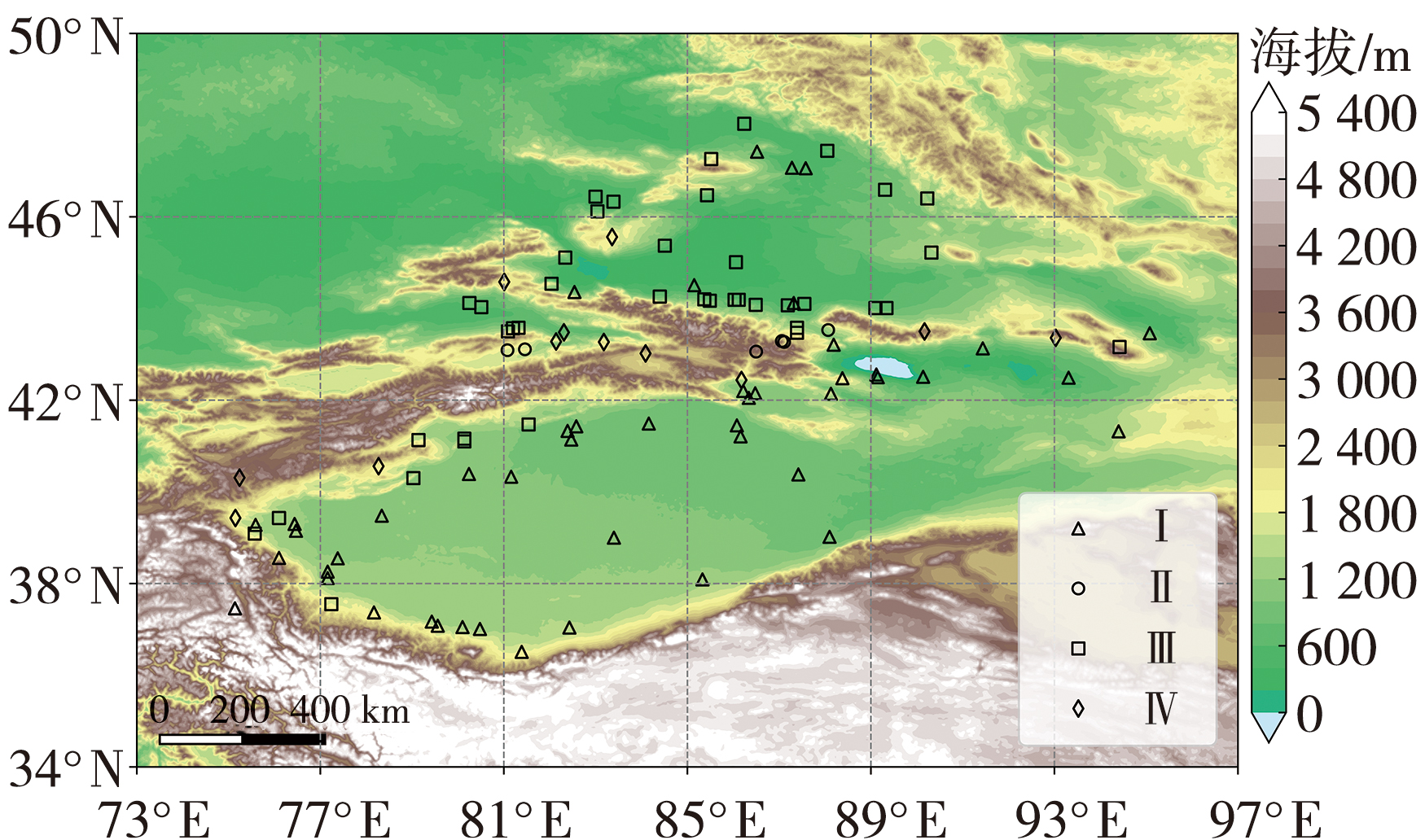
| 类别 | 基本信息 | 5—9月 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 站点数/个 | 平均海拔高度/m | 降水量/mm | 降水量平均/mm | 降水时数/h | 降水时数平均/h | |
| Ⅰ类(南疆及荒漠区) | 47 | 987 | 6~82 | 54 | 16~116 | 67 |
| Ⅱ类(天山山区) | 6 | 2 057 | 298~400 | 354 | 274~357 | 311 |
| Ⅲ类(北疆及西天山南坡区) | 40 | 824 | 84~141 | 110 | 85~148 | 118 |
| Ⅳ类(山谷区) | 12 | 1 672 | 165~278 | 217 | 164~322 | 216 |
Tab.2 Statistical results of different station classifications in Xinjiang from 2010 to 2019
| 类别 | 基本信息 | 5—9月 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 站点数/个 | 平均海拔高度/m | 降水量/mm | 降水量平均/mm | 降水时数/h | 降水时数平均/h | |
| Ⅰ类(南疆及荒漠区) | 47 | 987 | 6~82 | 54 | 16~116 | 67 |
| Ⅱ类(天山山区) | 6 | 2 057 | 298~400 | 354 | 274~357 | 311 |
| Ⅲ类(北疆及西天山南坡区) | 40 | 824 | 84~141 | 110 | 85~148 | 118 |
| Ⅳ类(山谷区) | 12 | 1 672 | 165~278 | 217 | 164~322 | 216 |
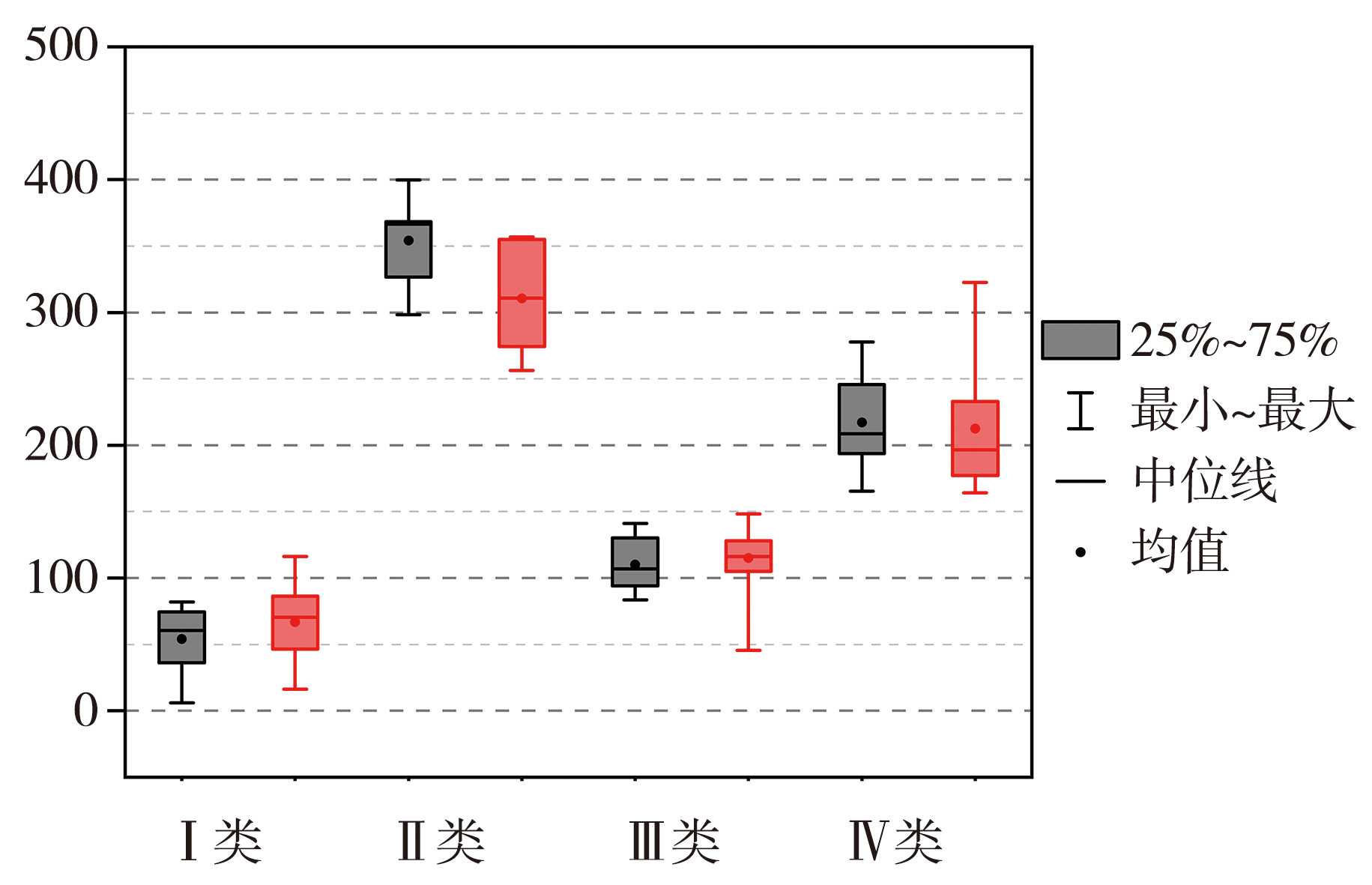
Fig.2 Box plots of the average precipitation (black box,Unit: mm) and precipitation hours (red box,Unit: h) in the warm season for four classifications of stations in Xinjiang from 2010 to 2019
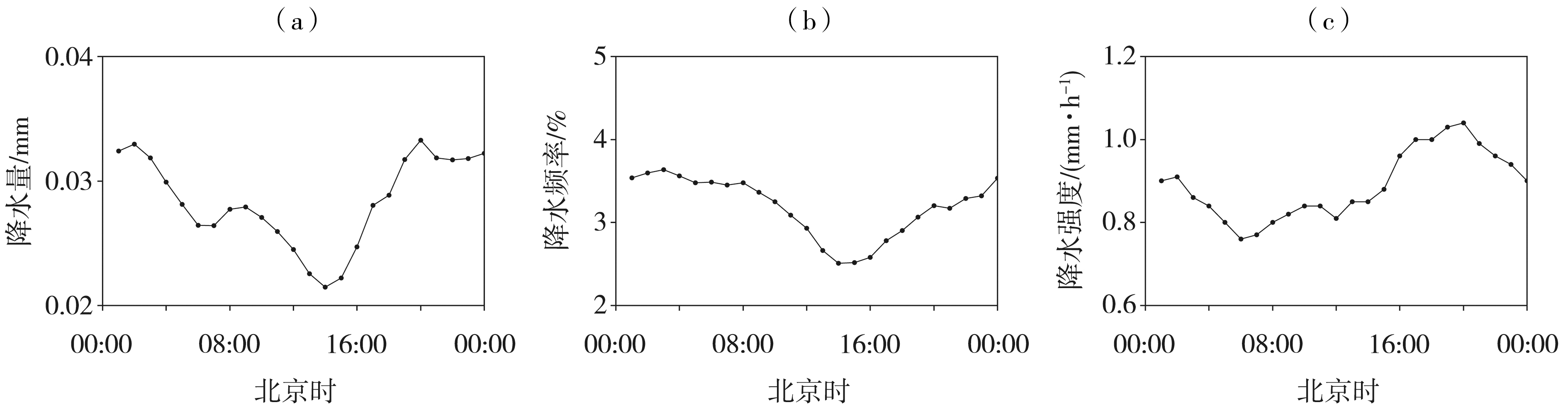
Fig.3 Hour-by-hour distribution of mean precipitation amount (a),precipitation frequency (b),and precipitation intensity (c) in Xinjiang in the warm season from 2010 to 2019
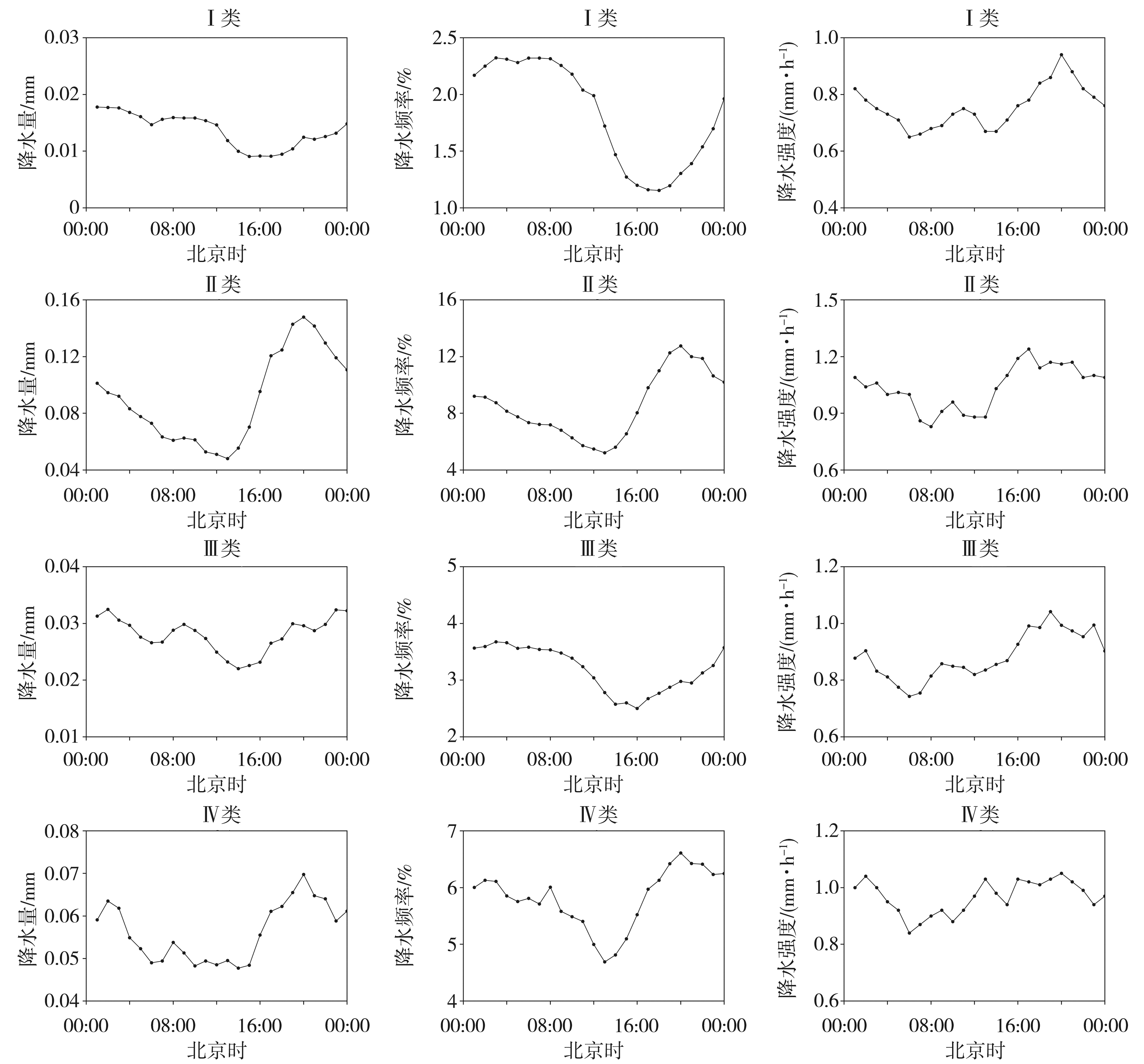
Fig.4 The hourly distributions of average precipitation amount (the left),precipitation frequency (the middle),and precipitation intensity (the right) for four types of stations in Xinjiang in warm season from 2010 to 2019

Fig.5 The hourly distributions of monthly average precipitation amount (the top,Unit: mm),precipitation frequency (the middle,Unit: %),and precipitation intensity (the bottom,Unit: mm·h-1) for average of the entire Xinjiang and four types of stations in worm season from 2010 to 2019 (The top line represents the monthly cumulative amount)

Fig.6 The hourly distribution of annual average precipitation amount (the top,Unit: mm),precipitation frequency (the middle,Unit: %),and precipitation intensity (the bottom,Unit: mm·h-1) for the regional average of the entire Xinjiang and four types of stations from 2010 to 2019 (The top line represents the year-by-year accumulation)

Fig.7 The average 500 hPa wind field (contours) and its anomaly (the color shaded) at 11:00 from May to September during 2010—2019, and average 500 hPa wind speed (wind vectors) in 2016 (a), and 850 hPa average wind speed anomaly (contours) at 11:00 from May to September during 2010—2019, and average wind speed (arrow vectors) in 2016 (b) (Unit: m·s-1)
| [1] | 陈春艳, 王建捷, 唐冶, 等, 2017. 新疆夏季降水日变化特征[J]. 应用气象学报, 28(1): 72-85. |
| [2] | 陈春艳, 赵克明, 阿不力米提江·阿布力克木, 等, 2015. 暖湿背景下新疆逐时降水变化特征研究[J]. 干旱区地理, 38(4): 692-702. |
| [3] | 戴泽军, 宇如聪, 陈昊明, 2009. 湖南夏季降水日变化特征[J]. 高原气象, 28(6): 1 463-1 470. |
| [4] | 段赛男, 焦瑞莉, 吴成来, 2024. 一种基于K-means聚类算法的沙尘天气客观识别方法[J]. 气候与环境研究, 29(2): 178-192. |
| [5] | 高旭旭, 于长文, 朱卫浩, 2018. 河北省不同区域降水日变化特征差异[J]. 河北农业科学, 22(4): 63-67. |
| [6] | 苟浩锋, 王遂缠, 杨银, 等, 2020. 基于聚类分析的兰州地区自动站降水特征分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 14(1): 108-114. |
| [7] |
郭玉琳, 赵勇, 周雅蔓, 等, 2022. 新疆天山山区夏季降水日变化特征及其与海拔高度关系[J]. 干旱区地理, 45(1): 57-65.
DOI |
| [8] | 韩函, 吴昊旻, 黄安宁, 2017. 华北地区夏季降水日变化的时空分布特征[J]. 大气科学, 41(2): 263-274. |
| [9] | 黄艳, 杨莲梅, 唐鹏, 等, 2024. 新疆伊犁河谷暖季短历时强降水变化特征[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 18(6): 32-37. |
| [10] | 李晓婷, 刘利民, 李雪洋, 等, 2021. 基于逐小时数据的辽宁省夏季降水日变化特征分析[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 52(2): 129-136. |
| [11] | 林春泽, 刘琳, 林文才, 等, 2016. 湖北省夏季降水日变化特征[J]. 大气科学学报, 39(4): 490-500. |
| [12] | 刘伟东, 尤焕苓, 任国玉, 等, 2014. 北京地区自动站降水特征的聚类分析[J]. 气象, 40(7): 844-851. |
| [13] | 秦贺, 陈春艳, 阿不力米提江·阿布力克木, 等, 2019. 新疆暖季短时强降水特征[J]. 干旱区研究, 36(6): 1 440-1 449. |
| [14] | 孙倩倩, 刘晶淼, 2014. 基于聚类分析的中国东北地区气温和降水时空变化特征[J]. 气象与环境学报, 30(3): 59-65. |
| [15] | 唐红玉, 顾建峰, 俞胜宾, 等, 2011. 西南地区降水日变化特征分析[J]. 高原气象, 30(2): 376-384. |
| [16] |
王丽伟, 黄晓龙, 冯晓莉, 等, 2019. 2006—2015年吉林省夏季降水日变化特征[J]. 中国农学通报, 35(3): 122-130.
DOI |
| [17] |
王颖, 刘丹妮, 张玮玮, 等, 2019. 2004—2016年浙江省夏季降水的日变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 37(1): 1-9.
DOI |
| [18] |
肖安, 尹小飞, 刘献耀, 2022. 江西省降水日变化时空分布特征[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5): 840-848.
DOI |
| [19] | 谢泽明, 周玉淑, 杨莲梅, 2018. 新疆降水研究进展综述[J]. 暴雨灾害, 37(3): 204-212. |
| [20] | 杨森, 周晓珊, 高杰, 2011. 辽宁省夏季降水的日变化特征[J]. 气象, 37(8): 943-949. |
| [21] | 杨涛, 杨莲梅, 2003. 新疆强对流暴雨的气候特征和概率分布模式研究[J]. 灾害学, 18(1): 49-54. |
| [22] | 杨涛, 杨莲梅, 张云惠, 等, 2021. 新疆短时强降水天气系统环流配置及雷达回波特征[J]. 干旱气象, 39(4): 631-640. |
| [23] | 宇如聪, 李建, 陈昊明, 等, 2014. 中国大陆降水日变化研究进展[J]. 气象学报, 72(5): 948-968. |
| [24] |
张宏芳, 潘留杰, 陈昊明, 等, 2020. 秦岭及周边地区暖季降水日变化及其成因分析[J]. 高原气象, 39(5): 935-946.
DOI |
| [25] | 张家宝, 邓子风, 1987. 新疆降水概论[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [26] | 张俊兰, 杨霞, 肖俊安, 等, 2023. 昆仑山北部夏季降水多尺度时空变化特征[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 43(3): 1-10. |
| [27] | 赵勇, 黄丹青, 古丽格娜, 等, 2010. 新疆北部夏季强降水分析[J]. 干旱区研究, 27(5): 773-779. |
| [28] | 赵玉春, 王叶红, 2020. 我国东南沿岸及复杂山地后汛期降水日变化的数值研究[J]. 大气科学, 44(2): 371-389. |
| [29] | 中国气象局, 国家气候委员会, 2017. 2016年中国气候公报[R]. 北京: 中国气象局. |
| [30] | 朱小凡, 张明军, 王圣杰, 等, 2016. 2008—2013年新疆夏季降水的日变化特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 35(2): 478-488. |
| [31] | ANDERSSON T, 1969. The diurnal variation of precipitation in Sweden[J]. Geografiska Annaler: Series A, Physical Geography, 51(3): 176-184. |
| [32] | BOWMAN K P, COLLIER J C, NORTH G R, et al, 2005. Diurnal cycle of tropical precipitation in Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite and ocean buoy rain gauge data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 110(D21): D21104. DOI:10.1029/2005JD005763. |
| [33] | YU R C, ZHOU T J, XIONG A Y, et al, 2007a. Diurnal variations of summer precipitation over contiguous China[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 34(1): L01704. DOI:10.1029/2006GL028129. |
| [34] | YU R C, XU Y P, ZHOU T J, et al, 2007b. Relation between rainfall duration and diurnal variation in the warm season precipitation over central Eastern China[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 34(13): L13703. DOI:10.1029/2007GL030315. |
| [35] | ZHOU T J, YU R C, CHEN H M, et al, 2008. Summer precipitation frequency, intensity, and diurnal cycle over China: A comparison of satellite data with rain gauge observations[J]. Journal of Climate, 21(16): 3 997-4 010. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||