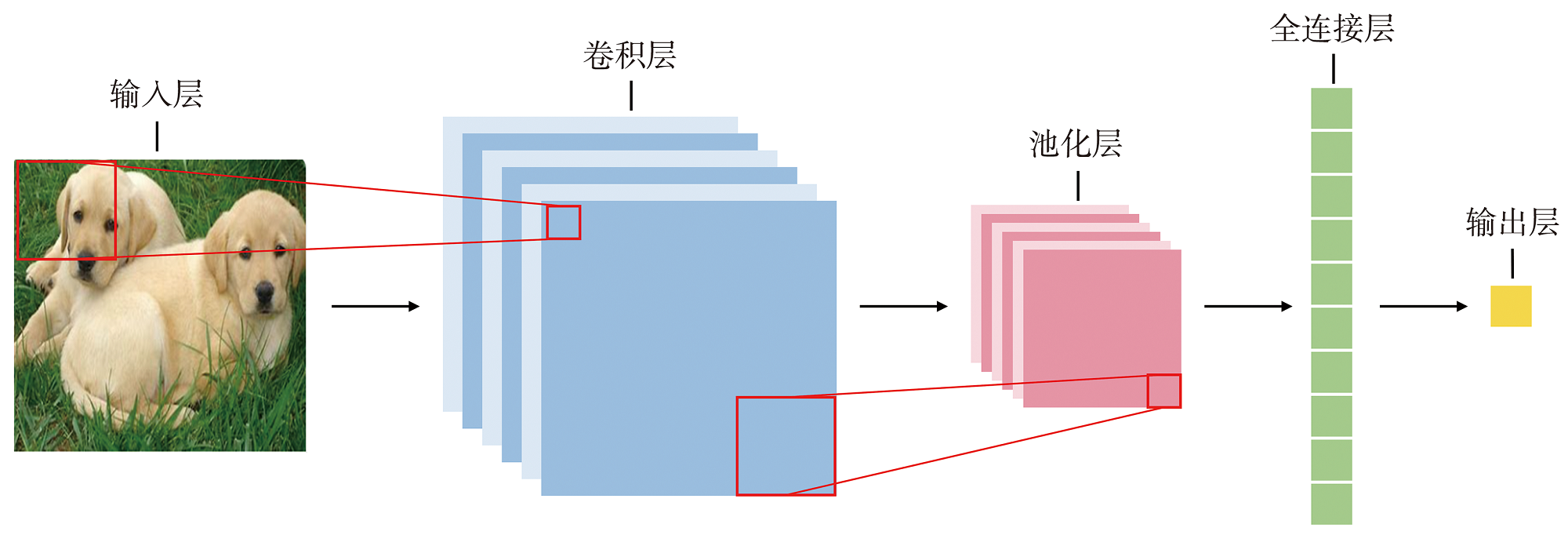
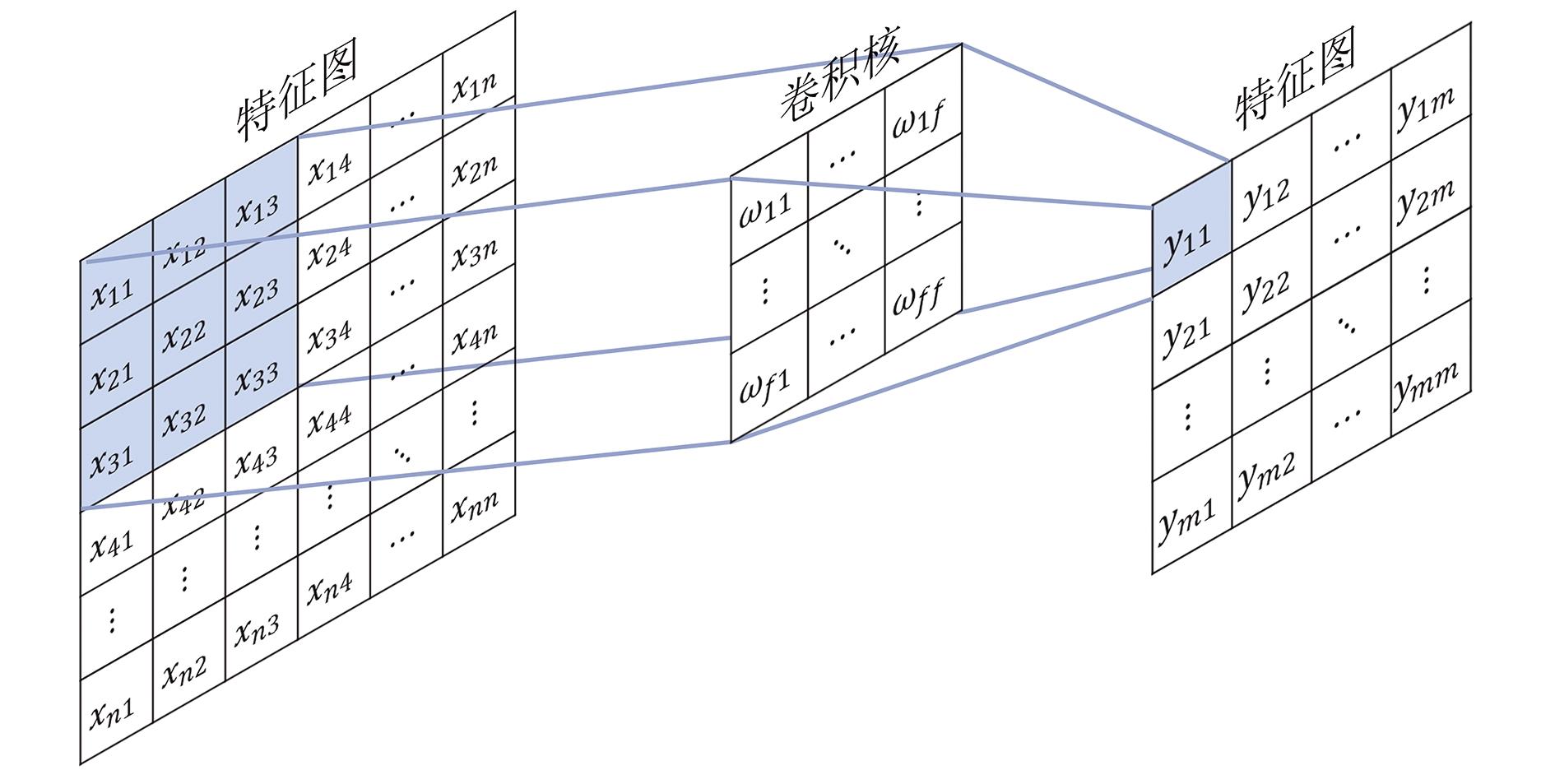
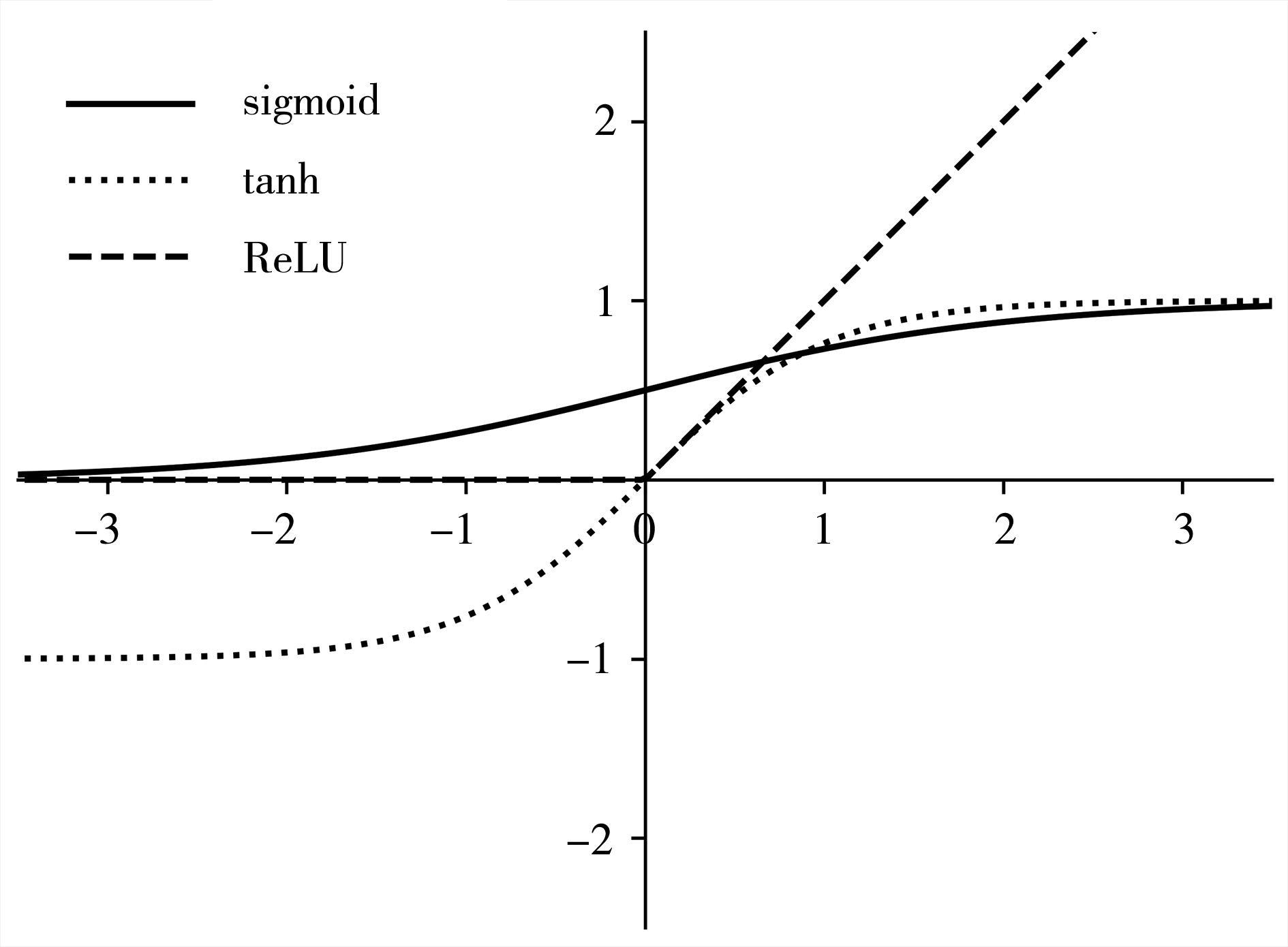
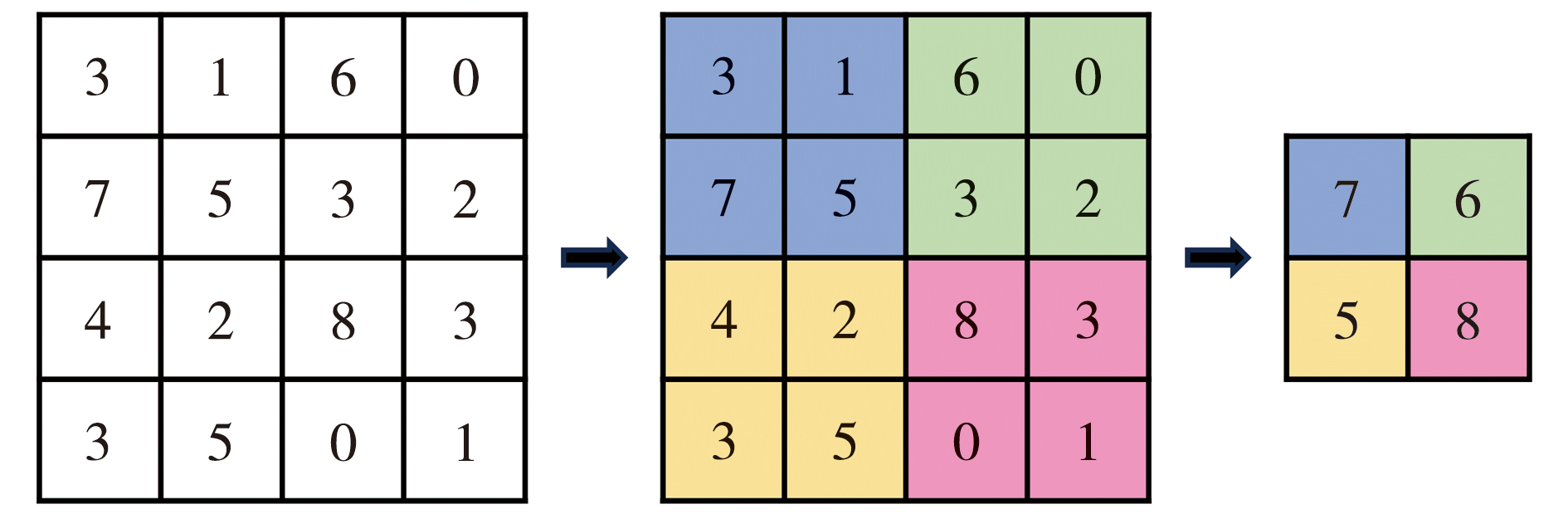
Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (5): 719-733.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2024-05-0719
• Special Column: Application of Artificial Intelligence in Drought Meteorology and Related Fields • Previous Articles Next Articles
Advances in convolutional neural networks and their applications in atmospheric science
MA Minjin( ), CHEN Ran, CAO Yidan, ZHANG Xingyu, LI Yuebin
), CHEN Ran, CAO Yidan, ZHANG Xingyu, LI Yuebin
- College of Atmospheric Sciences, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, China
-
Received:2024-04-17Revised:2024-07-09Online:2024-10-31Published:2024-11-17
卷积神经网络研究进展及其在大气科学中的应用
- 兰州大学大气科学学院,甘肃 兰州 730000
-
作者简介:马敏劲(1983—),男,云南昭通人,副教授,主要从事大气边界层数值模拟、气象领域的机器学习及应用、创新方法研究。E-mail: minjinma@lzu.edu.cn。 -
基金资助:干旱气象科学基金面上项目(IAM202002)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
MA Minjin, CHEN Ran, CAO Yidan, ZHANG Xingyu, LI Yuebin. Advances in convolutional neural networks and their applications in atmospheric science[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(5): 719-733.
马敏劲, 陈然, 曹译丹, 张星宇, 李岳彬. 卷积神经网络研究进展及其在大气科学中的应用[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(5): 719-733.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2024-05-0719
| [1] | 曹春燕, 陈元昭, 刘东华, 等, 2015. 光流法及其在临近预报中的应用[J]. 气象学报, 73(3): 471-480. |
| [2] | 陈锦鹏, 冯业荣, 黄奕丹, 等, 2024. 利用机器学习模拟湿物理参数化方案[J]. 气象学报, 82(1): 113-126. |
| [3] | 陈锦鹏, 冯业荣, 蒙伟光, 等, 2021. 基于卷积神经网络的逐时降水预报订正方法研究[J]. 气象, 47(1): 60-70. |
| [4] |
邓建国, 张素兰, 张继福, 等, 2020. 监督学习中的损失函数及应用研究[J]. 大数据, 6(1): 60-80.
DOI |
| [5] | 樊许磊, 2022. 用于资料同化预处理的卷积神经网络亮温重映射技术[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学. |
| [6] | 洪思弟, 赖绍钧, 林志玮, 等, 2020. 结合深度卷积网络及光学图像的降雨强度识别[J]. 福建农林大学学报:自然科学版, 49(4): 567-576. |
| [7] | 刘雅忱, 2020. 人工智能下深度学习在气象预报中应用综述[J]. 计算机产品与流通(11),121. |
| [8] | 刘亚伟, 郭辰婧, 赵绘萍, 2021. 卷积神经网络的发展及其在肿瘤影像学中的应用[J]. 吉林医药学院学报, 42(4): 290-292. |
| [9] |
孙书魁, 范菁, 孙中强, 等, 2024. 基于深度学习的图像数据增强研究综述[J]. 计算机科学, 51(1): 150-167.
DOI |
| [10] |
魏森涛, 王澄海, 张飞民, 等, 2023. 基于土壤温、湿度记忆性的土壤湿度预测方法研究[J]. 干旱气象, 41(5): 783-791.
DOI |
| [11] | 夏旻, 申茂阳, 王舰锋, 等, 2018. 基于卷积神经网络的卫星云图云量计算[J]. 系统仿真学报, 30(5): 1 623-1 630. |
| [12] |
袁凯, 庞晶, 李武阶, 等, 2023. 深度学习模型在2021年汛期武汉市雷达回波临近预报中的应用评估[J]. 干旱气象, 41(1): 173-185.
DOI |
| [13] | 袁雅涵, 王烁, 王文青, 等, 2023. 基于深度学习的积层混合云对流泡降水粒子特征研究[J]. 干旱气象, 41(6): 933-943. |
| [14] | BADRINARAYANAN V, KENDALL A, CIPOLLA R, 2017. SegNet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 39(12): 2 481-2 495. |
| [15] | BAÑO-MEDINA J, MANZANAS R, GUTIÉRREZ J M, 2020. Configuration and intercomparison of deep learning neural models for statistical downscaling[J]. Geoscientific Model Development, 13(4): 2 109-2 124. |
| [16] | BARRON J T, 2017. Continuously differentiable exponential linear units[J/OL]. (2017-04-24)[2024-04-17]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.07483. |
| [17] | BOEING G, 2016. Visual analysis of nonlinear dynamical systems: Chaos, fractals, self-similarity and the limits of prediction[J]. Systems, 4(4): 37. DOI: 10.3390/systems4040037. |
| [18] | BRAJARD J, CARRASSI A, BOCQUET M, et al, 2020. Combining data assimilation and machine learning to emulate a dynamical model from sparse and noisy observations: A case study with the Lorenz 96 model[J]. Journal of Computational Science, 44: 101171. DOI: 10.1016/j.jocs.2020.101171. |
| [19] | BYUN J, JUN C, KIM J, et al, 2023. Deep learning-based rainfall prediction using cloud image analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 61: 1-11. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3263872. |
| [20] | CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, KOKKINOS I, et al, 2018. DeepLab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 40(4): 834-848. |
| [21] | CLEVERT D A, UNTERTHINER T, HOCHREITER S, 2015. Fast and accurate deep network learning by exponential linear units (ELUs)[C/OL]// International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). Caribe Hilton, San Juan, Puerto Rico. (2015-11-23)[2024-04-17]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.07289. |
| [22] | COHEN T S, GEIGER M, KOHLER J, et al, 2018. Spherical CNNs[J/OL]. (2018-01-30)[2024-04-17]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1801.10130. |
| [23] | DAWOOD M, ASIF A, MINHAS F U A A, 2020. Deep-PHURIE: Deep learning based hurricane intensity estimation from infrared satellite imagery[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 32(13): 9 009-9 017. |
| [24] | DOZAT T, 2016. Incorporating nesterov momentum into Adam[C]// Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). San Juan, Puerto Rico. |
| [25] | DUCHI J C, HAZAN E, SINGER Y, 2011. Adaptive subgradient methods for online learning and stochastic optimization[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 12: 2 121-2 159. |
| [26] | ELHOSEINY M, HUANG S, ELGAMMAL A, 2015. Weather classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]// IEEE. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). Quebec City, QC, Canada: IEEE: 3 349-3 353. |
| [27] | FENG C, WANG W D, TIAN Y, et al, 2017. Estimate air quality based on mobile crowd sensing and big data[C]// IEEE. 2017 IEEE 18th International Symposium on A World of Wireless, Mobile and Multimedia Networks (WoWMoM). Macau, China: IEEE: 1-9. |
| [28] |
FUKUSHIMA K, 1980. Neocognitron: A self organizing neural network model for a mechanism of pattern recognition unaffected by shift in position[J]. Biological Cybernetics, 36(4): 193-202.
DOI PMID |
| [29] | GAGNE D J, HAUPT S E, NYCHKA D W, et al, 2019. Interpretable deep learning for spatial analysis of severe hailstorms[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 147(8): 2 827-2 845. |
| [30] | GIYENKO A, PALVANOV A, CHO Y, 2018. Application of convolutional neural networks for visibility estimation of CCTV images[C]// IEEE. 2018 International Conference on Information Networking (ICOIN). Chiang Mai, Thailand: IEEE: 875-879. |
| [31] | GLOROT X, BORDES A, BENGIO Y, 2011. Deep sparse rectifier neural networks[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 15: 315-323. |
| [32] | GRÖNQUIST P, YAO C Y, BEN-NUN T, et al, 2021. Deep learning for post-processing ensemble weather forecasts[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 379(2194): 20200092. DOI: 10.1098/rsta.2020.0092. |
| [33] | HAM Y G, KIM J H, LUO J J, 2019. Deep learning for multi-year ENSO forecasts[J]. Nature, 573(7775): 568-572. |
| [34] | HAN L, CHEN M X, CHEN K K, et al, 2021. A deep learning method for bias correction of ECMWF 24-240 h forecasts[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 38(9): 1 444-1 459. |
| [35] | HE K M, SUN J, TANG X O, 2011. Single image haze removal using dark channel prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 33(12): 2 341-2 353. |
| [36] | HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al, 2015. Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on ImageNet classification[C]// IEEE. Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). IEEE Computer Society: 1 026-1 034. |
| [37] | HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al, 2016. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]// IEEE. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR). Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE: 770-778. |
| [38] |
HINTON G E, SALAKHUTDINOV R R, 2006. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks[J]. Science, 313(5786): 504-507.
DOI PMID |
| [39] | HINTON G E, SRIVASTAVA N, KRIZHEVSKY A, et al, 2012. Improving neural networks by preventing co-adaptation of feature detectors[J/OL]. (2012-07-03)[2024-07-09]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1207.0580. |
| [40] | HOWARD A G, ZHU M, CHEN B, et al, 2017. MobileNets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications[J/OL]. (2017-04-17)[2024-04-17]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.04861. |
| [41] | HUANG G, LIU Z, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al, 2017. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]// IEEE. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, HI, USA: IEEE: 2 261-2 269. |
| [42] | HUBEL D H, WIESEL T N, 1962. Receptive fields, binocular interaction and functional architecture in the cat’s visual cortex[J]. Journal of Physiology, 160(1): 106-154. |
| [43] | JIANG Y H, CHENG W, GAO F, et al, 2022. A cloud classification method based on a convolutional neural network for FY-4A satellites[J]. Remote Sensing, 14(10): 2314. DOI: 10.3390/rs14102314. |
| [44] | KINGMA D P, BA J, 2014. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[C/OL]// International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). San Diego, CA, USA. (2014-12-22)[2024-04-17]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980. |
| [45] | KLAMBAUER G, UNTERTHINER T, MAYR A, et al, 2017. Self-Normalizing neural networks[C/OL]// Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS). Long Beach, CA, USA. (2017-09-07)[2024-04-17]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.02515. |
| [46] | KOPP M, TUO Y, DISSE M, 2019. Fully automated snow depth measurements from time-lapse images applying a convolutional neural network[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 697: 134213. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134213. |
| [47] | KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G E, 2017. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 60(6): 84-90. |
| [48] | KURTH T, TREICHLER S, ROMERO J, et al, 2018. Exascale deep learning for climate analytics[C]// IEEE. SC18:International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis. Dallas, TX, USA: IEEE: 649-660. |
| [49] | LAGERQUIST R, MCGOVERN A, GAGNE D J, 2019. Deep learning for spatially explicit prediction of synoptic-scale fronts[J]. Weather and Forecasting, 34(4): 1 137-1 160. |
| [50] | LECUN Y, BENGIO Y, HINTON G, 2015. Deep learning[J]. Nature, 521(7553): 436-444. |
| [51] | LECUN Y, BOTTOU L, BENGIO Y, et al, 1998. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 86(11): 2 278-2 324. |
| [52] | LI Y, MOMEN M, 2021. Detection of weather events in optical satellite data using deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 12(12): 1 227-1 237. |
| [53] | LIN M, CHEN Q, YAN S C, 2013. Network In Network[J/OL]. (2013-12-16)[2024-04-17]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1312.4400. |
| [54] | LIU Y J, RACAH E, PRABHAT, et al, 2016. Application of deep convolutional neural networks for detecting extreme weather in climate datasets[J/OL]. (2016-05-04)[2024-04-17]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1605.01156. |
| [55] | LIU Z M, WANG Y X, VAIDYA S, et al, 2024. KAN: Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks[J/OL]. (2024-06-16)[2024-04-17]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.19756. |
| [56] | LIU Z, LIN Y T, CAO Y, et al, 2021. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows[C]// IEEE. International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Montreal, QC, Canada: IEEE: 10 012-10 022. |
| [57] | LONG J, SHELHAMER E, DARRELL T, 2015. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[C]// IEEE. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Boston, MA, USA: IEEE: 3 431-3 440. |
| [58] | LU C W, LIN D, JIA J Y, et al, 2014. Two-class weather classification[C]// IEEE. 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Columbus, OH, USA: IEEE: 3 718-3 725. |
| [59] | MAAS A L, HANNUN A Y, NG A Y, 2013. Rectifier nonlinearities improve neural network acoustic models[C]// International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). Atlanta, USA. |
| [60] | NESTEROV Y, 1983. A method for solving the convex programming problem with convergence rate O(1/k^2)[J]. Proceedings of the USSR Academy of Sciences, 269: 543-547. |
| [61] |
PRADHAN R, AYGUN R S, MASKEY M, et al, 2018. Tropical cyclone intensity estimation using a deep convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 27(2): 692-702.
DOI PMID |
| [62] | RACAH E, BECKHAM C, MAHARAJ T, et al, 2016. Semi-supervised detection of extreme weather events in large climate datasets[C/OL]// Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS). Long Beach, CA, USA. (2016-12-07)[2024-04-17]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1612.02095v1. |
| [63] | RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, BROX T, 2015. U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]// Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Munich, Germany: Springer International Publishing: 234-241. |
| [64] | RUDER S, 2016. An overview of gradient descent optimization algorithms[J/OL]. (2016-09-15)[2024-04-17]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1609.04747. |
| [65] | RUMELHART D E, HINTON G E, WILLIAMS R J, 1986. Learning representations by back-propagating errors[J]. Nature, 323: 533-536. |
| [66] | SABOUR S, FROSST N, HINTON G E, 2017. Dynamic Routing Between Capsules[C/OL]// Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS). Long Beach, CA, USA. (2017-11-07)[2024-04-17]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1710.09829. |
| [67] | SCHER S, 2018. Toward data-driven weather and climate forecasting: Approximating a simple general circulation model with deep learning[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 45(22): 12 616-12 622. |
| [68] | SCHER S, MESSORI G, 2018. Predicting weather forecast uncertainty with machine learning[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 144(717): 2 830-2 841. |
| [69] | SCHER S, MESSORI G, 2019. Weather and climate forecasting with neural networks: using general circulation models (GCMs) with different complexity as a study ground[J]. Geoscientific Model Development, 12(7): 2 797-2 809. |
| [70] | SCHULTZ M G, BETANCOURT C, GONG B, et al, 2021. Can deep learning beat numerical weather prediction?[J] Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 379(2194): 20200097. DOI: 10.1098/rsta.2020.0097. |
| [71] | SELVARAJU R R, COGSWELL M, DAS A, et al, 2020. Grad-CAM: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 128(2): 336-359. |
| [72] | SHI C Z, WANG C H, WANG Y, et al, 2017a. Deep convolutional activations-based features for ground-based cloud classification[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 14(6): 816-820. |
| [73] | SHI X J, CHEN Z R, WANG H, et al, 2015. Convolutional LSTM network: A machine learning approach for precipitation nowcasting[C]// Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montreal, Canada: MIT Press: 802-810. |
| [74] | SHI X J, GAO Z H, LAUSEN L, et al, 2017b. Deep learning for precipitation nowcasting: A benchmark and a new model[C]// Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Curran Associates Inc., Long Beach, California, USA: 5 622-5 632. |
| [75] | SINHA N K, GRISCIK M P, 1971. A stochastic approximation method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, SMC-1(4): 338-344. |
| [76] | SPRINGENBERG J T, DOSOVITSKIY A, BROX T, et al, 2014. Striving for simplicity: The all convolutional net[C/OL]// International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). San Diego, CA, USA. (2014-12-21)[2024-04-17]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6806. |
| [77] | SZEGEDY C, LIU W, JIA Y Q, et al, 2015. Going deeper with convolutions[C]// IEEE. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Boston, MA, USA: IEEE: 1-9. |
| [78] | TIELEMAN T, HINTON G, 2012. Lecture 6.5-rmsprop: divide the gradient by a running average of its recent magnitude. COURSERA: Neural networks for machine learning, 4(2): 26-31. |
| [79] | VANDAL T, KODRA E, GANGULY S, et al, 2017. DeepSD: Generating high resolution climate change projections through single image super-resolution[C]// 27th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI). Halifax, NS, Canada, 1703.03126. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.1703.03126. |
| [80] | WANG L Y, TAN Z M, 2023. Deep learning parameterization of the tropical cyclone boundary layer[J]. Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, 15(1): e2022MS003034. DOI: 10.1029/2022MS003034. |
| [81] | WANG X, HAN Y L, XUE W, et al, 2022. Stable climate simulations using a realistic general circulation model with neural network parameterizations for atmospheric moist physics and radiation processes[J]. Geoscientific Model Development, 15(9): 3 923-3 940. |
| [82] | WEYN J A, DURRAN D R, CARUANA R, 2019. Can machines learn to predict weather? Using deep learning to predict gridded 500-hPa geopotential height from historical weather data[J]. Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, 11(8): 2 680-2 693. |
| [83] | XIE S N, GIRSHICK R, DOLLAR P, et al, 2017. Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks[C]// IEEE. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, HI: IEEE: 5 987-5 995. |
| [84] | XU B, WANG N Y, CHEN T Q, et al, 2015. Empirical evaluation of rectified activations in convolutional network[C]// International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). Lille, France. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.1505.00853. |
| [85] | YAO M Y, TAO D, WANG J T, et al, 2022. MARVAir: Meteorology augmented residual-based visual approach for crowdsourcing air quality inference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 71: 1-10. |
| [86] | YU D J, WANG H L, CHEN P Q, et al, 2014. Mixed pooling for convolutional neural networks[C]// The 9th International Conference on Rough Sets and Knowledge Technology. Shanghai, China. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-11740-9_34. |
| [87] | ZEILER M D, FERGUS R, 2013. Stochastic pooling for regularization of deep convolutional neural networks[C]// 1st International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). Scottsdale, United States. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.1301.3557. |
| [88] | ZEILER M D, FERGUS R, 2014. Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks[C]// European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Cham: Springer International Publishing. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-10590-1_53. |
| [89] | ZHANG J L, LIU P, ZHANG F, et al, 2018. CloudNet: Ground-based cloud classification with deep convolutional neural network[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 45(16): 8 665-8 672. |
| [90] | ZHANG X Y, ZHOU X Y, LIN M X, et al, 2018. ShuffleNet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices[C]// IEEE. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, UT: IEEE: 6 848-6 856. |
| [91] | ZHAO B, LI X L, LU X Q, et al, 2018. A CNN-RNN architecture for multi-label weather recognition[J]. Neurocomputing, 322: 47-57. |
| [92] | ZHAO X, WEI H K, WANG H, et al, 2019. 3D-CNN-based feature extraction of ground-based cloud images for direct normal irradiance prediction[J]. Solar Energy, 181: 510-518. |
| [93] | ZHOU B L, KHOSLA A, LAPEDRIZA À, et al, 2016. Learning deep features for discriminative localization[C]// IEEE. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE: 2 921-2 929. |
| [94] | ZHOU K H, ZHENG Y G, LI B, et al, 2019. Forecasting different types of convective weather: A deep learning approach[J]. Journal of Meteorological Research, 33(5): 797-809. |
| [95] | ZOPH B, LE Q V, 2016. Neural architecture search with reinforcement learning[C/OL]// International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). Caribe Hilton, San Juan, Puerto Rico. (2016-11-05)[2024-04-17]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.01578. |
| [1] | WEI Sentao, WANG Chenghai, ZHANG Feimin, YANG Kai. Study of soil moisture prediction method based on soil temperature and moisture persistence [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(5): 783-791. |
| [2] | YUAN Kai, PANG Jing, LI Wujie, LI Ming. Application evaluation of deep learning models in radar echo nowcasting in Wuhan in flood season of 2021 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2023, 41(1): 173-185. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||