Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (4): 598-610.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2024)-04-0598
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Research on a hailstorm process in Chongqing based on multi-source observation data
ZOU Qian1( ), ZUO Chunyan2(
), ZUO Chunyan2( ), WU Zhengqian1, ZHAI Danhua1, MU Rong1
), WU Zhengqian1, ZHAI Danhua1, MU Rong1
- 1. CMA Key Open Laboratory of Transforming Climate Resources to Economy, Chongqing Meteorological Observatory, Chongqing 401147, China
2. Chongqing Shapingba Meteorological Bureau, Chongqing 400030, China
-
Received:2023-11-02Revised:2024-04-01Online:2024-08-31Published:2024-09-13
基于多源观测资料研究重庆地区一次风雹过程
邹倩1( ), 左春艳2(
), 左春艳2( ), 吴政谦1, 翟丹华1, 牟容1
), 吴政谦1, 翟丹华1, 牟容1
- 1.中国气象局气候资源经济转化重点开放实验室,重庆市气象台,重庆 401147
2.重庆沙坪坝区气象局,重庆 400030
-
通讯作者:左春艳(1983—),女,广西贺州人,工程师,主要从事地面观测及预报服务。E-mail:215022594@qq.com 。 -
作者简介:邹倩(1982—),女,重庆忠县人,硕士,工程师,主要从事灾害性天气预报及研究。E-mail: zoultby@sohu.com。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金面上项目(42175040);中国气象局预报员专项(CMAYBY2020-107)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZOU Qian, ZUO Chunyan, WU Zhengqian, ZHAI Danhua, MU Rong. Research on a hailstorm process in Chongqing based on multi-source observation data[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(4): 598-610.
邹倩, 左春艳, 吴政谦, 翟丹华, 牟容. 基于多源观测资料研究重庆地区一次风雹过程[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(4): 598-610.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2024)-04-0598

Fig.1 The temperature profile (a) and water vapor density profile (b) from radiosonde and retrieved by microwave radiometer data and their average errors (c) at Shapingba Station from March to August 2014 (The error bars represent the standard deviation σ, and the line segment length is 2 σ. the same as below)

Fig.2 The evolution of reflectivity factors on the elevation of 0.5° (the left), 4.3° (the middle) and average radial velocity on the elevation of 0.5° (the right) of Yongchuan radar in Chongqing from 23:44 April 17 to 00:02 April 18, 2014 (The black circle is the position of Zengjia in Shapingba, the azimuth of Zengjia relative to Yongchuan radar is 52°, and the distance is 57 km)

Fig.3 The variation of different meteorological elements observed by microwave radiometer and the measured minute-by-minute precipitation at Shapingba Station in Chongqing from 18:00 on 17 to 02:00 on 18 April 2014
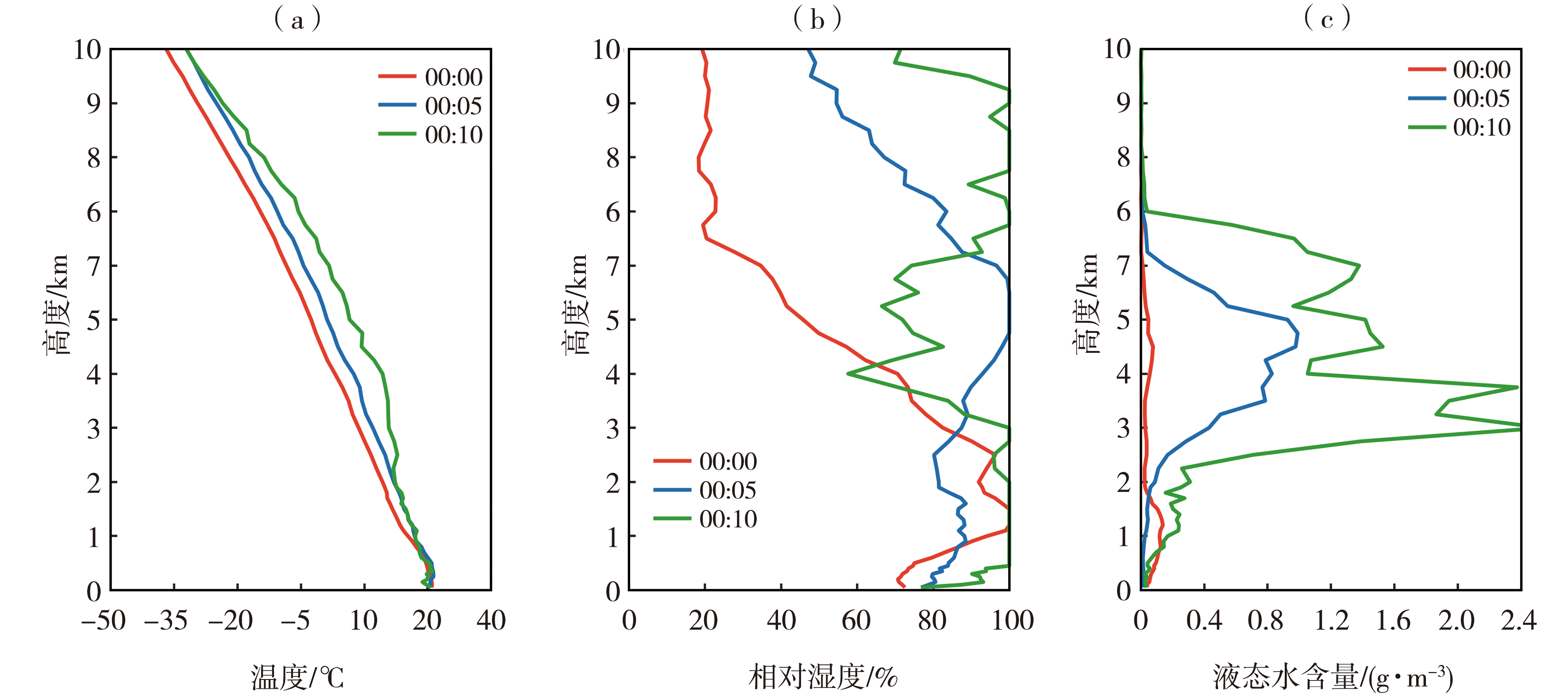
Fig.4 The vertical profiles of temperature (a), humidity (b) and liquid water content (c) observed by microwave radiometer at Shapingba Station in Chongqing at 00:00, 00:05 and 00:10 April 18, 2014
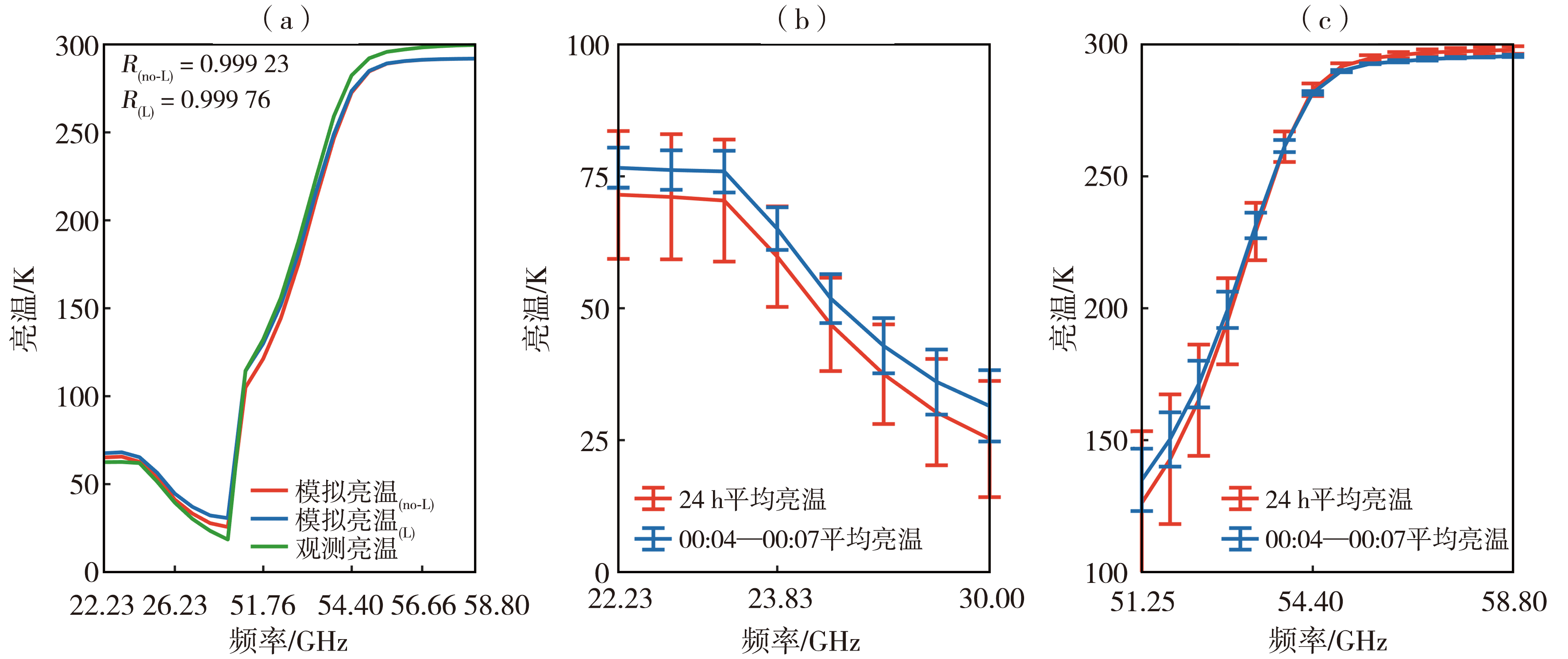
Fig.5 The brightness temperature observed by microwave radiometer and simulated brightness temperature at 20:00 on 17 April 2014 (a), the average brightness temperature from 00:04 to 00:07 on 18 April 2014 and the 24 h average brightness temperature of K-band water vapor channel (b), and V-band oxygen channel (c) at Shapingba Station in Chongqing

Fig.6 The variation of horizontal wind field of windprofile radar with time at Shapingba Station in Chongqing from 18:00 on 17 to 02:00 on 18 April 2014 (a) and from 23:00 on 17 to 01:00 on 18 April 2014 (b) (Unit: m·s-1) (The color shaded indicates vertical wind field)

Fig.7 Vertical profile of vertical velocity and atmospheric refractive index structure constant (Cn2) of wind profile radar before and after hail at Shapingba Station on April 18, 2014 (a) hail time (00:05 on 18), (b) before the hail (23:55 on 17), (c) before the hail (00:00 on 18), (d) after the hail (00:10 on 18)
| 项目 | K指数/℃ | TT/℃ | SI/℃ | θse850-500/℃ | CAPE/(J·kg-1) | SHR0-6/(m·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 探空观测 | 40.00 | 48.80 | -3.20 | 25.20 | 2 042.00 | 21.30 |
| 探空时间内微波辐射计和风廓线雷达计算的平均值 | 42.70 | 51.80 | -3.70 | 19.50 | 1 860.00 | 27.50 |
| 探空时间内微波辐射计和风廓线雷达计算的均方根误差 | 0.90 | 0.98 | 0.52 | 1.13 | 167.28 | 2.33 |
| 春季重庆地区风雹阈值 | 34.00 | 50.00 | -1.90 | 16.00 | 872.00 | 14.00 |
Tab.1 Comparison of some environment parameters calculated by microwave radiometer and wind profile radar data with radiosonde observations at 20:00 on April 17,2014
| 项目 | K指数/℃ | TT/℃ | SI/℃ | θse850-500/℃ | CAPE/(J·kg-1) | SHR0-6/(m·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 探空观测 | 40.00 | 48.80 | -3.20 | 25.20 | 2 042.00 | 21.30 |
| 探空时间内微波辐射计和风廓线雷达计算的平均值 | 42.70 | 51.80 | -3.70 | 19.50 | 1 860.00 | 27.50 |
| 探空时间内微波辐射计和风廓线雷达计算的均方根误差 | 0.90 | 0.98 | 0.52 | 1.13 | 167.28 | 2.33 |
| 春季重庆地区风雹阈值 | 34.00 | 50.00 | -1.90 | 16.00 | 872.00 | 14.00 |
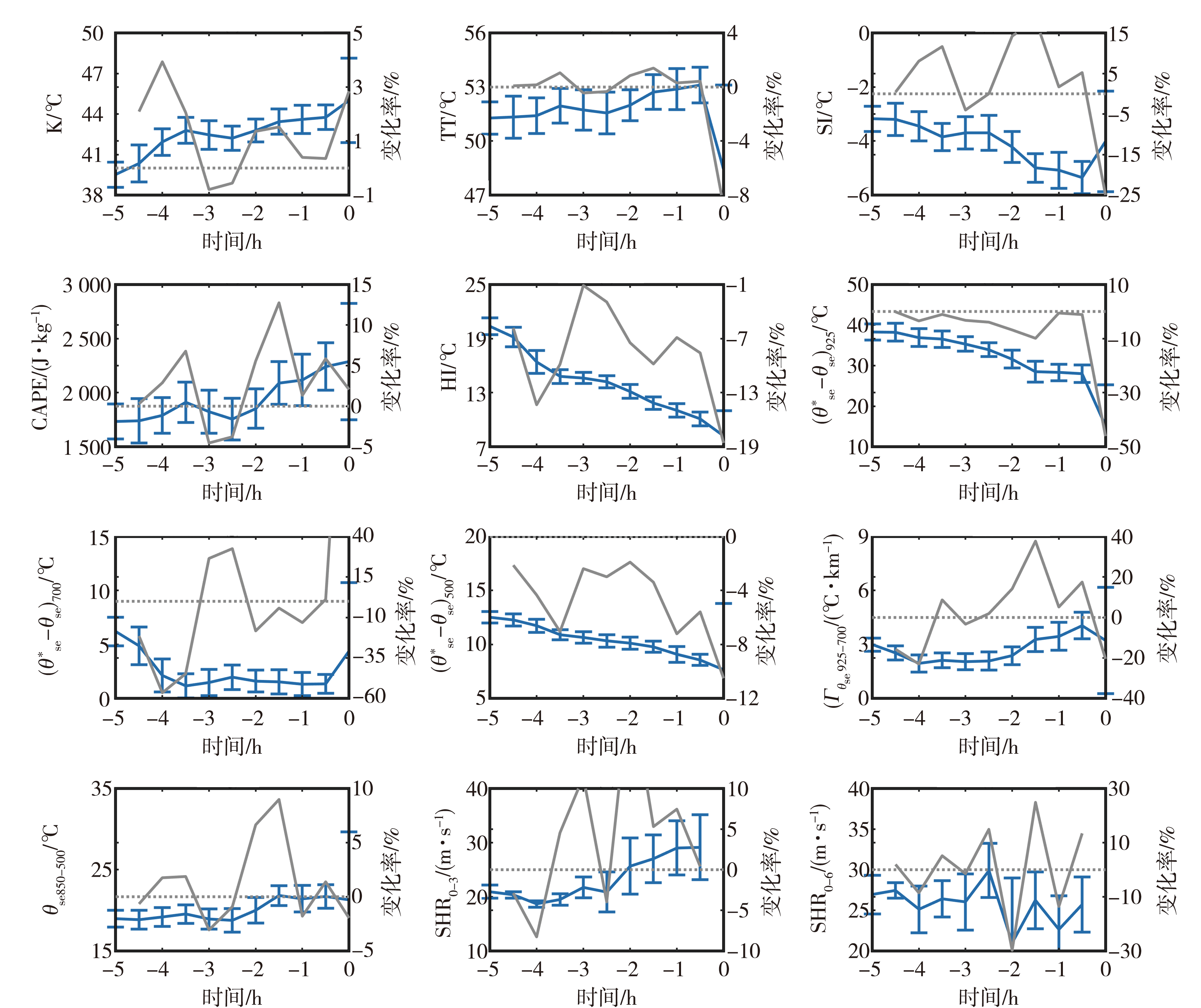
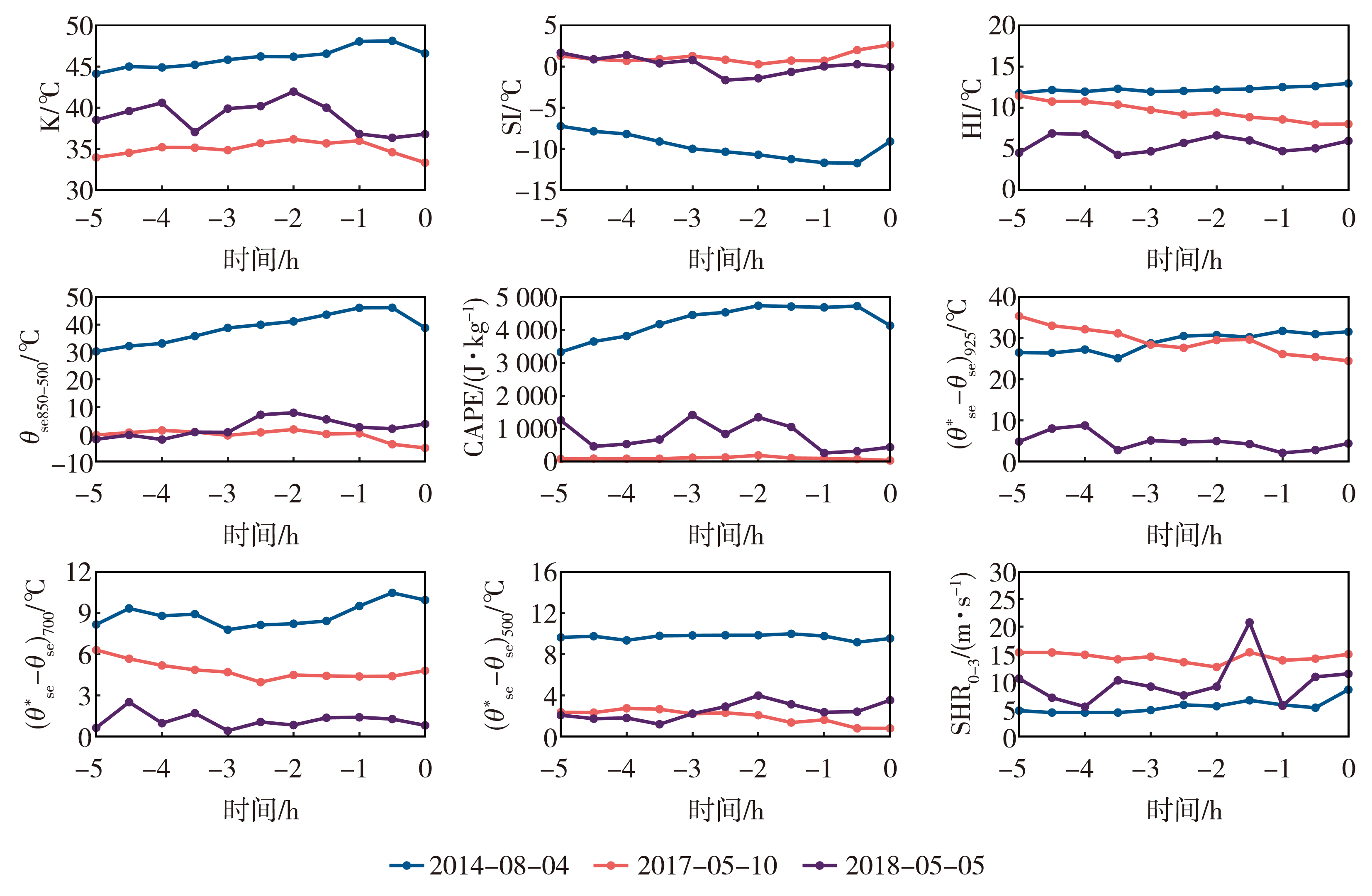
Fig.8 The 30 min average value and variation ratio of 12 thermal and dynamic instability parameters calculated by microwave radiometer and wind profile radar data in 5 hours before the occurrence of hailstorm

Fig.9 The variation of the 5 min average value of brightness temperature (a), atmospheric refractive index structure constant (b) and the area of atmospheric refractive index structure constant (c) in 2 hours before the occurrence of hailstorm
| 日期 | 主要时段 | 风雹中心区天气现象 | 冰雹最大直径/mm | 风雹发生前5 h 观测站降雨情况 | 风雹中心离观测站距离/km |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014-08-04 | 16:30—17:00 | 风雹、小雨 | 20 | 无降雨 | 8.8 |
| 2017-05-10 | 23:30—次日00:30 | 雷暴、风雹、短时强降雨 | <10(随降随化) | 无降雨 | 19.9 |
| 2018-05-05 | 19:30—20:30 | 风雹、小到中雨 | <10 | 弱降雨 | 29.4 |
Tab.2 The weather phenomena during main periods of the three hailstorm processes in Chongqing
| 日期 | 主要时段 | 风雹中心区天气现象 | 冰雹最大直径/mm | 风雹发生前5 h 观测站降雨情况 | 风雹中心离观测站距离/km |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014-08-04 | 16:30—17:00 | 风雹、小雨 | 20 | 无降雨 | 8.8 |
| 2017-05-10 | 23:30—次日00:30 | 雷暴、风雹、短时强降雨 | <10(随降随化) | 无降雨 | 19.9 |
| 2018-05-05 | 19:30—20:30 | 风雹、小到中雨 | <10 | 弱降雨 | 29.4 |

Fig.11 The variation of brightness temperature of 25.00 GHz (a) and 58.80 GHz (b), atmospheric refractive index structure constant (c) and the area of atmospheric refractive index structure constant (d) in 2 hours before the occurrence of the three hailstorm processes
| [1] |
把黎, 奚立宗, 蔡迪花, 等, 2023. 基于微波辐射计资料的祁连山东段大气水汽和液态水时空变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 41(1):64-72.
DOI |
| [2] | 鲍艳松, 钱程, 闵锦忠, 等, 2016. 利用地基微波辐射计资料反演0-10 km大气温湿廓线试验研究[J]. 热带气象学报, 32(2):163-171. |
| [3] |
曹艳察, 田付友, 郑永光, 等, 2018. 中国两级阶梯地势区域冰雹天气的环境物理量统计特征[J]. 高原气象, 37(1):185-196.
DOI |
| [4] | 方桃妮, 黄艳, 叶妍婷, 等, 2022. 边界层风廓线雷达资料在浙中强对流天气中的应用[J]. 气象科技, 50(3):369-379. |
| [5] |
苟阿宁, 吴翠红, 王玉娟, 等, 2022. 基于风廓线雷达的湖北梅雨期暴雨中小尺度特征[J]. 干旱气象, 40(1):84-94.
DOI |
| [6] | 黄兴友, 张曦, 冷亮, 等, 2013. 基于MonoRTM模型的微波辐射计反演方法研究[J]. 气象科学, 33(2):138-145. |
| [7] | 黄治勇, 徐桂荣, 王晓芳, 等, 2014. 基于地基微波辐射计资料对咸宁两次冰雹天气的观测分析[J].气象40(2):216-222. |
| [8] |
黄治勇, 周志敏, 徐桂荣, 等, 2015. 风廓线雷达和地基微波辐射计在冰雹天气监测中的应用[J]. 高原气象, 34(1):269-278.
DOI |
| [9] | 蓝渝, 郑永光, 毛冬艳, 等, 2014. 华北区域冰雹天气分型及云系特征[J]. 应用气象学报, 25(5):538-549. |
| [10] | 雷蕾, 孙继松, 魏东, 2011. 利用探空资料判别北京地区夏季强对流的天气类别[J]. 气象, 37(2):136-141. |
| [11] | 李聪, 姜有山, 姜迪, 等, 2017. 一次冰雹天气过程的多源资料观测分析[J]. 气象, 43(9):1084-1 094. |
| [12] | 刘春文, 郭学良, 段玮, 等, 2021. 云南一次典型降雹过程的冰雹微物理形成机理数值模拟研究[J]. 大气科学, 45(5):965-980. |
| [13] | 刘健文, 郭虎, 李耀东, 等, 2005. 天气分析预报物理量计算基础[M]. 北京: 气象出版社:1-10. |
| [14] | 孙继松, 戴建华, 何立富, 等, 2014. 强对流天气预报的基本原理与技术方法——中国强对流天气预报手册[M]. 北京: 气象出版社:50-63. |
| [15] | 孙炜文, 王璇, 肖潇, 2022. 江西一次冰雹过程的S波段双偏振雷达回波特征分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 41(6):621-630. |
| [16] | 唐仁茂, 李德俊, 向玉春, 等, 2012. 地基微波辐射计对咸宁一次冰雹天气过程的监测分析[J]. 气象学报, 70(4):806-813. |
| [17] | 田付有, 张小玲, 曹艳察, 等, 2022. 中国中低海拔地区三类强对流天气环境条件的基本气候特征[J]. 高原气象, 41(6):1446-1 459. |
| [18] | 王洪, 吴乃庚, 万齐林, 等, 2018. 一次华南超级单体风暴的S波段偏振雷达观测分析[J]. 气象学报, 76(1):92-103. |
| [19] | 王佳津, 张琪, 张涛, 等, 2021. 成都两次暴雨期间风廓线雷达观测的低空风场特征[J]. 干旱气象, 39(1):87-95. |
| [20] | 魏东, 孙继松, 雷蕾, 等, 2011. 三种探空资料在各类强对流天气中的应用对比分析[J]. 气象, 37(4):412-422. |
| [21] | 吴芳芳, 俞小鼎, 张志刚, 等, 2013. 苏北地区超级单体风暴环境条件与雷达回波特征[J]. 气象学报, 71(2):209-227. |
| [22] | 徐小红, 余兴, 刘贵华, 等, 2022. 冰雹云卫星早期识别与自动预警[J]. 大气科学, 46(1):98-110. |
| [23] | 杨引明, 陶祖钰, 2003. 上海LAP-3000边界层风廓线雷达在强对流天气预报中的应用初探[J]. 成都信息工程学院学报, 18(2):155-160. |
| [24] | 俞小鼎, 2014. 关于冰雹的融化层高度[J]. 气象, 40(6):649-654. |
| [25] | 俞小鼎, 周小刚, 王秀明, 2012. 雷暴与强对流临近天气预报技术进展[J]. 气象学报, 70(3):311-337. |
| [26] | 张秋晨, 王俊, 李雪, 2018. 地基微波辐射计资料在对流云降水前的变化特征初探[J]. 高原气象, 37(6):1578-1 589. |
| [27] | 张亚萍, 邓承之, 牟容, 等, 2015. 重庆市强对流天气分析图集[M]. 北京: 气象出版社:91-97. |
| [28] | 章国材, 2011. 强对流天气分析与预报[M]. 北京: 气象出版社:65-94. |
| [29] | 郑婧, 陈娟, 徐星生, 等, 2020. 一次低空急流加强下的暴雨过程成因分析[J]. 干旱气象, 38(3):411-422. |
| [30] | 周志敏, 万蓉, 崔春光, 等, 2010. 风廓线雷达资料在一次冰雹过程分析中的应用[J]. 暴雨灾害, 29(3):251-256. |
| [31] |
邹倩, 陈小敏, 邓承之, 等, 2022. 重庆不同天气条件下地基微波辐射计探测特征[J]. 干旱气象, 40(1):114-124.
DOI |
| [32] | 曾智琳, 谌芸, 朱克云, 等, 2019. 广东省大冰雹事件的层结特征与融化效应[J]. 大气科学, 43(3):598-617. |
| [33] | CHAKRABORTY R, DAS S, JANA S, et al, 2014. Nowcasting of rain events using multi-frequency radiometric observations[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 513(5): 467-474. |
| [34] | CHAN P W, HON K K, 2011. Application of ground-based, multi-channel microwave radiometer in the nowcasting of intense convective weather through instability indices of the atmosphere[J]. Meteorologische Zeitschrift, 20(4): 431-440. |
| [35] | MADHULATHA A, RAJEEVAN M, VENKAT RATNAM M, et al, 2013. Nowcasting severe convective activity over southeast India using ground-based microwave radiometer observations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 118(1):1-13. |
| [36] | WON H Y, KIM Y H, LEE H S, 2009. An application of brightness temperature received from a ground-based microwave radiometer to estimation of precipitation occurrences and rainfall intensity[J]. Asia-Pacific Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 45(1): 55-69. |
| [37] | ZHENG L N, ZHANG Z H, JIA X Q, 2017. Analysis of two hailstorm processes accompanied with weak precipitation in the north of Shandong[J]. Meteorological and Environmental Research, 8(6): 6-14. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||