Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (1): 54-63.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2024)-01-0054
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Characteristics of 10-20 days low-frequency oscillation of autumn precipitation over the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in 2021
HAN Shiru1,2,3( ), CHE Shaojing1,2,3(
), CHE Shaojing1,2,3( ), YU Changwen3, MA Guidong3
), YU Changwen3, MA Guidong3
- 1. China Meteorological Administration Xiong’an Atmospheric Boundary Layer Key Laboratory,Baoding 071800,Hebei,China
2. Key Laboratory of Meteorology and Ecological Environment of Hebei Province,Shijiazhuang 050021,China
3. Hebei Climate Center,Shijiazhuang 050021,China
-
Received:2023-06-28Revised:2023-11-22Online:2024-02-29Published:2024-03-06
2021年京津冀秋季降水10~20 d低频振荡特征
韩世茹1,2,3( ), 车少静1,2,3(
), 车少静1,2,3( ), 于长文3, 马贵东3
), 于长文3, 马贵东3
- 1.中国气象局雄安大气边界层重点开放实验室,河北 保定 071800
2.河北省气象与生态环境重点实验室,河北 石家庄 050021
3.河北省气候中心,河北 石家庄 050021
-
通讯作者:车少静(1976—),女,硕士,正高级工程师,主要从事短期气候预、农业气象研究。E-mail: checlimate@sina.com。 -
作者简介:韩世茹(1990—),女,硕士,工程师,主要从事短期气候预测及相关工作。E-mail: hanshiru615@163.com。 -
基金资助:中国气象局复盘总结专项(FPZJ2023-015);河北省气象局科研开发项目(21ky02);河北省气象局创新团队-延伸期重要天气过程智能预测技术创新团队共同资助
CLC Number:
Cite this article
HAN Shiru, CHE Shaojing, YU Changwen, MA Guidong. Characteristics of 10-20 days low-frequency oscillation of autumn precipitation over the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in 2021[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(1): 54-63.
韩世茹, 车少静, 于长文, 马贵东. 2021年京津冀秋季降水10~20 d低频振荡特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(1): 54-63.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2024)-01-0054
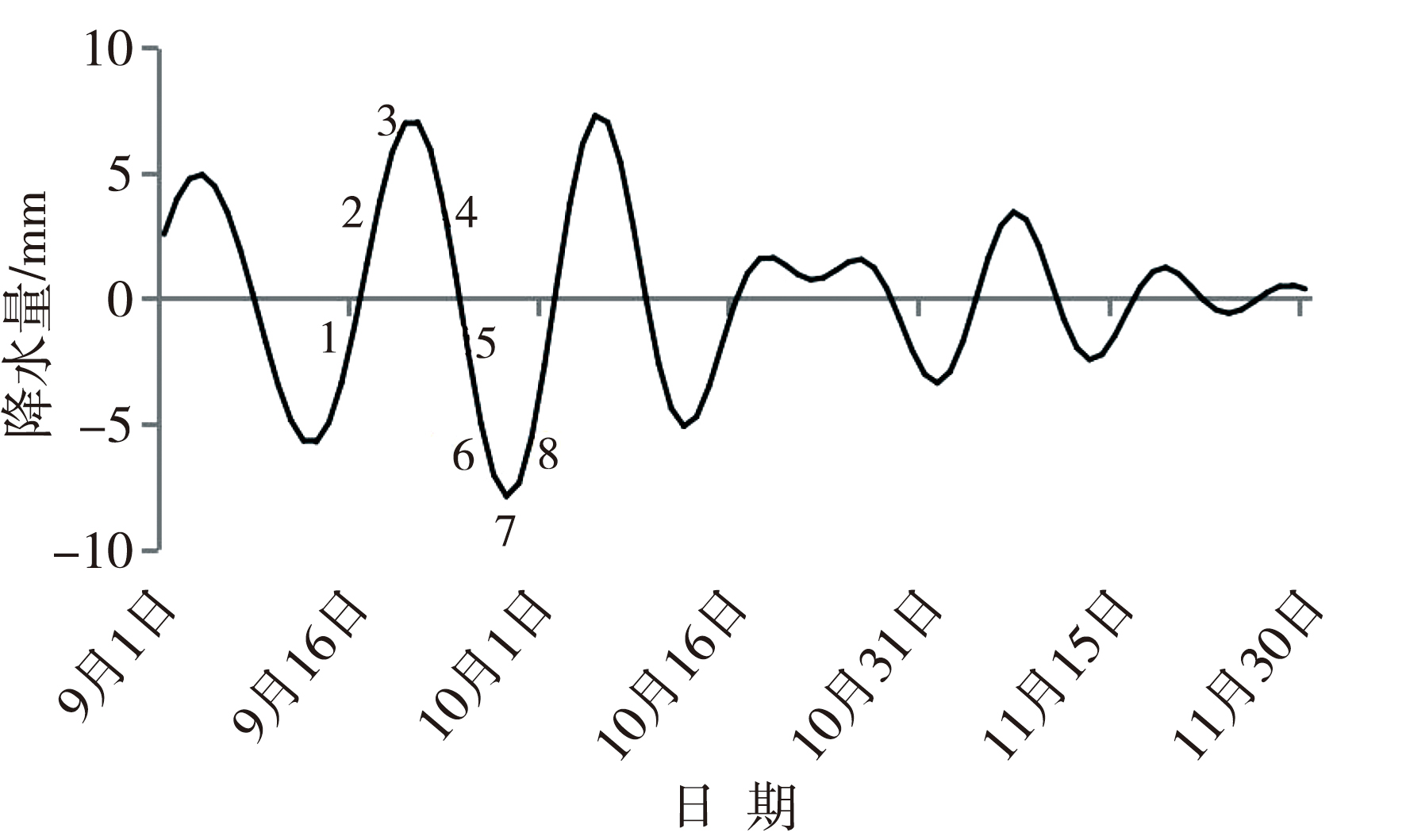
Fig.3 Morlet wavelet analysis of autumn precipitation in 2021 in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region (Shadows are regions that pass the 90% confidence level test)

Fig.5 The distribution of geopotential height field anomaly (contours, Unit: dagpm) and divergency anomaly (the shaded, Unit: 10-6s-1) at 500 hPa in different phases (The “H” is for high pressure, and the “L” is for low pressure, the box shows the location of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, the same as below)

Fig.6 The distribution of wind field anomaly (arrow vectors, Unit: m·s-1) at 850 hPa and vertical velocity anomaly (the shaded, Unit: Pa·s-1) at 700 hPa in different phases (The “A” and “C” are for abnormal anticyclone and abnormal cyclone, respectively)
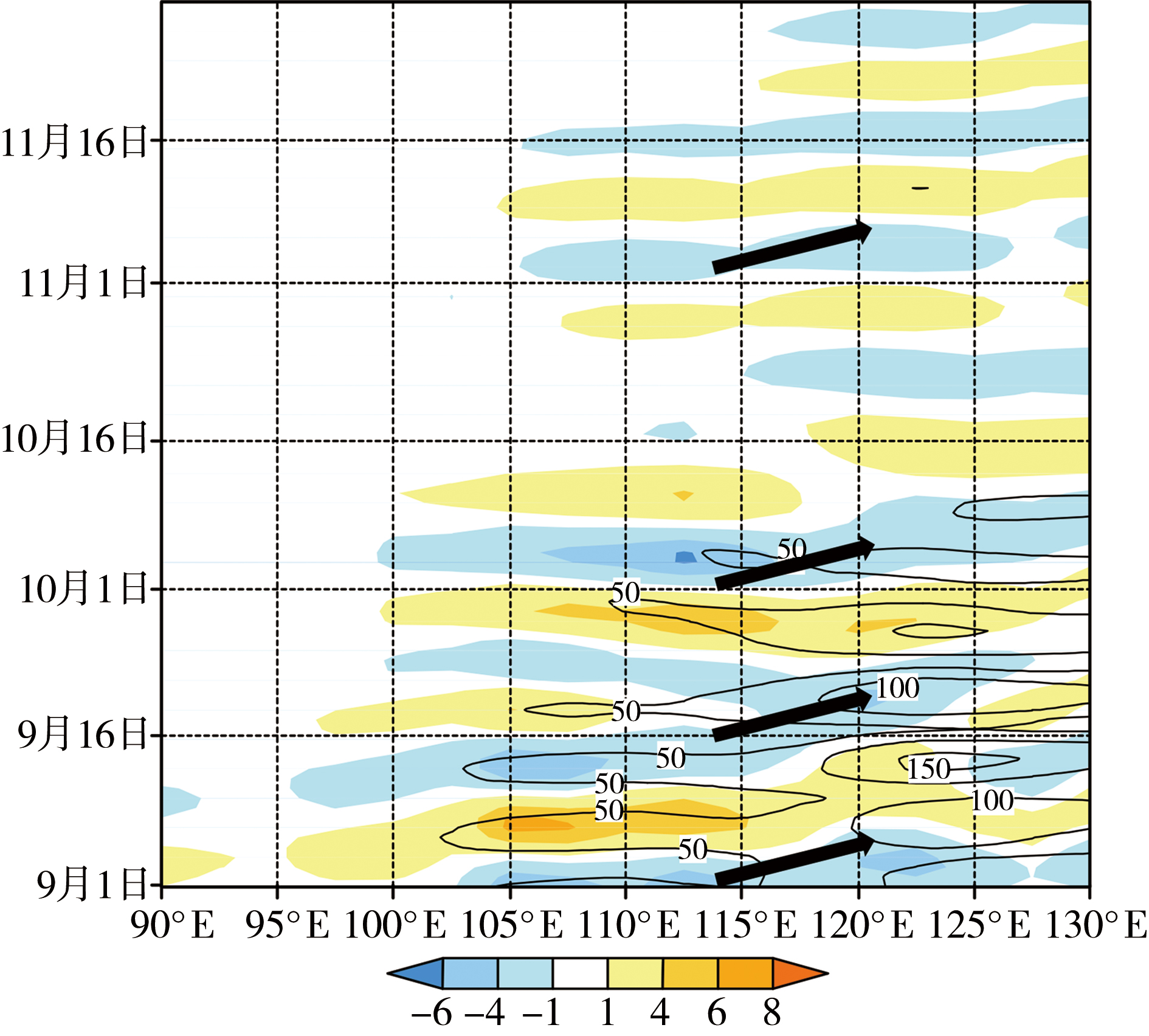
Fig.7 The time-longitude profile of averaged low-frequency water vapor flux anomaly(isolines,Unit: kg·m-1·s-1) and water vapor flux divergence anomaly(the shaded,Unit: 10-5 kg·m-2·s-1) integrated of the whole layer along 32.5°N-45.0°N (The arrows represent each precipitation process,the same as below)

Fig.8 The time-latitude profile of averaged low-frequency water vapor flux anomaly(isolines,Unit: kg·m-1·s-1) and water vapor flux divergence anomaly(the shaded,Unit: 10-5 kg·m-2·s-1) integrated of the whole layer along 110°E-120°E
| [1] | 车少静, 李想, 丁婷, 等, 2021. 秋行夏令: 2021年10月初北方致灾性持续暴雨及水汽极端性分析[J]. 大气科学学报, 44(6): 825-834. |
| [2] | 陈官军, 2014. 中国南方夏季区域持续性强降水与大气季节内振荡[D]. 北京: 中国气象科学研究院. |
| [3] | 丁一汇, 梁萍, 2011. 基于MJO的延伸预报[J]. 气象, 36(7): 111-122. |
| [4] |
郭飞燕, 刁秀广, 褚颖佳, 等, 2023. 两次极端强降水风暴双偏振参量特征对比分析[J]. 干旱气象, 41(1): 103-113.
DOI |
| [5] |
郭静妍, 肖栋, 2023. 孟加拉地区夏季水汽变化及其与太平洋年代际振荡的联系[J]. 干旱气象, 41(3): 380-389.
DOI |
| [6] | 郝立生, 马宁, 何丽烨, 等, 2021. 北半球夏季大气低频振荡演变特征及其与华北夏季降水的关系[J]. 大气科学, 45(6): 1 259-1 272. |
| [7] |
郝立生, 向亮, 周须文, 2015. 华北平原夏季降水准双周振荡与低频环流演变特征[J]. 高原气象, 34(2): 486-493.
DOI |
| [8] | 韩世茹, 王黎娟, 于波, 2015. 淮河流域夏季持续性降水与15-30天低频振荡的联系及前期信号[J]. 气象与环境科学, 38(4): 22-32. |
| [9] | 韩世茹, 周须文, 车少静, 等, 2021. 江淮流域夏季低频降水的前期预报信号[J]. 大气科学学报, 44(2): 199-208. |
| [10] | 蒋子瑶, 徐海明, 马静, 2021. 2016 年秋季中国南方降水异常的环流特征及海温影响[J]. 大气科学, 45(5): 1 023-1 038. |
| [11] |
金荣花, 马杰, 任宏昌, 等, 2019. 我国10-30天延伸期预报技术进展与发展对策[J]. 地球科学进展, 34(8): 814-825.
DOI |
| [12] | 李春晖, 潘蔚娟, 王婷, 2018. 广东省降水的多尺度时空投影预测方法[J]. 应用气象学报, 29(2): 217-231. |
| [13] | 梁苏洁, 丁一汇, 段丽瑶, 等, 2019. 近46年京津冀地区“夏雨秋下”现象及成因初探[J]. 大气科学, 43(3): 655-675. |
| [14] | 梁萍, 丁一汇, 2013. 强降水过程气候态季节内振荡及其在延伸期预报中的应用[J]. 高原气象, 32(5): 1 329-1 338. |
| [15] | 梁萍, 丁一汇, 2012. 基于季节内振荡的延伸预报试验[J]. 大气科学, 36(1): 102-116. |
| [16] | 苗青, 白自斌, 王洪霞, 等, 2021. 山西秋季一次极端暴雨过程的异常特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 39(6): 984-994. |
| [17] | 孙国武, 冯建英, 陈伯民, 等, 2012. 大气低频振荡在延伸期预报中的应用进展[J]. 气象科技进展, 2(1): 12-18. |
| [18] | 史学丽, 丁一汇, 2000. 1994年中国华南大范围暴雨过程的形成与夏季风活动的研究[J]. 气象学报, 58(6): 666-678. |
| [19] |
唐懿, 蔡雯悦, 翟建青, 等, 2022. 2021年夏季中国气候异常特征及主要气象灾害[J]. 干旱气象, 40(2): 179-186.
DOI |
| [20] | 王霄, 孔海江, 2014. 2011年秋季河南持续降水的低频环流特征[J]. 气象与环境科学, 37(1): 62-68. |
| [21] | 温克刚, 臧建升, 2008. 中国气象灾害大典(河北卷)[M]. 北京: 气象出版社:76-197. |
| [22] | 信飞, 孙国武, 陈伯民, 2008. 自回归统计模型在延伸期预报中的应用[J]. 高原气象, 27(增刊1): 69-75. |
| [23] | 徐曼琳, 周波涛, 程志刚, 2020. 2010年以来华西秋季降水量年代际增多原因初探[J]. 大气科学学报, 43(3): 568-576. |
| [24] |
许敏, 沈芳, 刘璇, 等, 2022. 京津冀“7·5”强对流天气形成的环境条件及中尺度特征[J]. 干旱气象, 40(6): 993-1 002.
DOI |
| [25] | 杨秋明, 2021. 冬季长江下游地区气温低频振荡和低温天气的延伸期预报研究[J]. 大气科学, 45(1): 21-36. |
| [26] | 杨玮, 何金海, 孙国武, 等, 2011. 低频环流系统的一种统计预报方法[J]. 气象与环境学报, 27(3): 1-5. |
| [27] | 余汶樯, 高庆九, 2020. 1996年冬季一次南方低温事件的低频特征分析及诊断[J]. 大气科学, 44(2): 257-268. |
| [28] | 尹志聪, 王亚非, 2011. 江淮夏季降水季节内振荡和海气背景场的关系[J]. 大气科学, 35(3): 495-505. |
| [29] | 郑国光, 矫梅燕, 丁一汇, 等, 2019. 中国气候[M]. 北京: 气象出版社: 319-326. |
| [30] | CHEN W, WANG L, XUE Y K, et al, 2009. Variabilities of the spring river runoff system in East China and their relations to precipitation and sea surface temperature[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 29: 1 381-1 394. |
| [31] | CHU J E, WANG B, LEE J Y, et al, 2017. Boreal summer intraseasonal phases identified by nonlinear multivariate empirical orthogonal function-based self-organizing map (ESOM) analysis[J]. Journal of Climate, 30(10): 3 513-3 528. |
| [32] | DONALD A, MEINKE H, POWER B, et al, 2006. Near-global impact of the Madden-Julian oscillation on rainfall[J]. Geophysical Researcg Letters, 33(9), L09704. DOI: 10.1029/2005GL025155. |
| [33] | DUCHON C E, 1979. Lanczos filtering in one and two dimensions[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 18(8): 1 016-1 022. |
| [34] | GALIN M B, 2007. Study of the low-frequency variability of the atmospheric general circulation with the use of time dependent empirical orthogonal functions[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Physics, 43(1): 15-23. |
| [35] | HAO L S, HE L Y, MA N, et al, 2020. Relationship between summer precipitation in North China and Madden-Julian oscillation during the boreal summer of 2018[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 8: 269-283. |
| [36] | HU F, LI T, GAO J Y, et al, 2020. Reexamining the moisture mode theories of the Madden-Julian oscillation based on observational analyses[J]. Journal of Climate, 34(2): 839-853. |
| [37] | HSU P C, LEE J Y, HA K J, 2016. Influence of boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation on rainfall extremes in southern China[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 36(3): 1 403-1 412. |
| [38] | HSU P C, LEE J Y, HA K J, et al, 2017. Influences of boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation on heat waves in monsoon Asia[J]. Journal of Climate, 30(18): 7 191-7 211. |
| [39] | JONES C, CARVALHO L M V, GOTTSCHALCK J, et al, 2011. The Madden-Julian oscillation and the relative value of deterministic forecasts of extreme precipitation in the contiguous United States[J]. Journal of Climate, 24(10): 2 421-2 428. |
| [40] | KOKUCHI K, WANG B, KAJIKAWA Y, 2012. Bimodal representation of the tropical intraseasonal oscillation[J]. Climate Dynamics., 38(9/10): 1 989-2 000. |
| [41] | LAU K M, CHAN P H, 1986. Aspects of the 40-50 day oscillation during the northern summer as inferred from outgoing longwave radiation[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 114(7): 1 354-1 367. |
| [42] | LEE J Y, WANG B, Wheeler M C, et al, 2013. Real-time multivariate indices for the boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation over the Asian summer monsoon region[J]. Climate Dynamics, 40(1/2): 493-509. |
| [43] | LI T M, WANG B, 1994. The influence of sea surface temperature on the tropical intraseasonal oscillation: A numerical study[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 122(10): 2 349-2 362. |
| [44] | LIN H, BRUNET G, 2009. The influence of the Madden-Julian oscillation on Canadian wintertime surface air temperature[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 137(7): 2 250-2 262. |
| [45] | MADDEN R A, JULINAN P R, 1970. Detection of a 40-50 day oscillation in the zonal wind in the tropical Pacific[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 28(5): 702-708. |
| [46] | MADDEN R A, JULIAN P R, 1972. Description of global-scale circulation cells in the tropics with a 40-50 day period[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 29(6): 1 109-1 123. |
| [47] | MATSUEDA S, TAKAYAY, 2015. The global influence of the Madden-Julian oscillation on extreme temperature events[J]. Journal of Climate, 28(10): 4 141-4 151. |
| [48] | NIU N, LI J P, 2008. Interannual variability of autumn precipitation over South China and its relation to atmospheric circulation and SST anomalies[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 25 (1): 117-125. |
| [49] | REN P F, REN H L, FU J X, et al, 2018. Impact of boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation on rainfall extremes in southeastern China and its predictability in CFSv2[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 123(9): 4 423-4 442. |
| [50] | WANG B, RUI H, 1990. Synoptic climatology of transient tropical intraseasonal convection anomalies: 1975-1985[J]. Meteorology Atmospheric Physics, 44(1/2/3/4): 43-61. |
| [51] | WHEELER M C, HENDON H H, 2004. An all-season real-time multivariate MJO index: Development of an index for monitoring and prediction[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 132(8): 1 917-1 932. |
| [52] | ZHANG C D, DONG M, 2004. Seasonality in the Madden-Julian oscillation[J]. Journal of Climate, 17(16): 3 169-3 180. |
| [53] | ZHANG L N, WANG B Z, ZENG Q C, 2009. Impact of the Madden-Julian oscillation on summer rainfall in Southeast China[J]. Journal of Climate, 22(2): 201-216. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||