| [1] |
白爱娟, 刘晓东, 2010. 华东地区近50年降水量的变化特征及其与旱涝灾害的关系分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 26(2): 194-200.
|
| [2] |
别强, 何磊, 赵传燕, 2012. 基于分形方法的石羊河流域气候变化研究[J]. 干旱气象, 30(1): 21-26+38.
|
| [3] |
常远勇, 侯西勇, 毋亭, 等, 2012. 1998-2010年全球中低纬度降水时空特征分析[J]. 水科学进展, 23(4): 475-484.
|
| [4] |
陈宏, 尉英华, 王颖, 等, 2017. 基于VIC水文模型的滦河流域径流变化特征及其影响因素[J]. 干旱气象, 35(5): 776-783.
DOI
|
| [5] |
代晓颖, 许有鹏, 林芷欣, 等, 2019. 长江下游秦淮河流域径流变化及影响因素分析[J]. 水土保持研究, 26(4): 68-73.
|
| [6] |
宫爱玺, 张冬冬, 冯平, 2012. 大清河流域年径流系数变化趋势及影响因素分析[J]. 水利水电技术, 43(6): 1-4.
|
| [7] |
郭广芬, 周月华, 高正旭, 等, 2013. 2011年冬季长江流域气温持续偏低的可能成因探析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 32(2): 176-181.
|
| [8] |
郭巧玲, 杨云松, 畅祥生, 等, 2011. 1957—2008年黑河流域径流年内分配变化[J]. 地理科学进展, 30(5): 550-556.
|
| [9] |
刘波, 陈刘强, 周森, 等, 2018. 长江上游重庆段径流变化归因分析[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 27(6): 1 333-1 341.
|
| [10] |
刘子豪, 陆建忠, 陈晓玲, 等, 2019. 基于Budyko假设的鄱阳湖抚河流域径流变化归因分析[J]. 河南科学, 37(8): 1 303-1 310.
|
| [11] |
马柱国, 任小波, 2007. 1951—2005年中国区域气候变化与干旱化趋势[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 3(4): 195-201.
|
| [12] |
邱新法, 张喜亮, 曾燕, 等, 2008. 1961—2005年江苏省降水变化趋势[J]. 气象, 34(5): 82-88.
|
| [13] |
芮孝芳, 2004. 水文学原理[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社.
|
| [14] |
石培礼, 李文华, 2001. 森林植被变化对水文过程和径流的影响效应[J]. 自然资源学报, 16(5): 481-487.
|
| [15] |
孙丞虎, 任福民, 周兵, 等, 2012. 2011/2012年冬季我国异常低温特征及可能成因分析[J]. 气象, 38(7): 884-889.
|
| [16] |
王劲松, 郭江勇, 周跃武, 等, 2007. 干旱指标研究的进展与展望[J]. 干旱区地理, 30(1): 60-65.
|
| [17] |
王绍武, 罗勇, 赵宗慈, 等, 2013. IPCC第5次评估报告问世[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 9(6): 436-439.
|
| [18] |
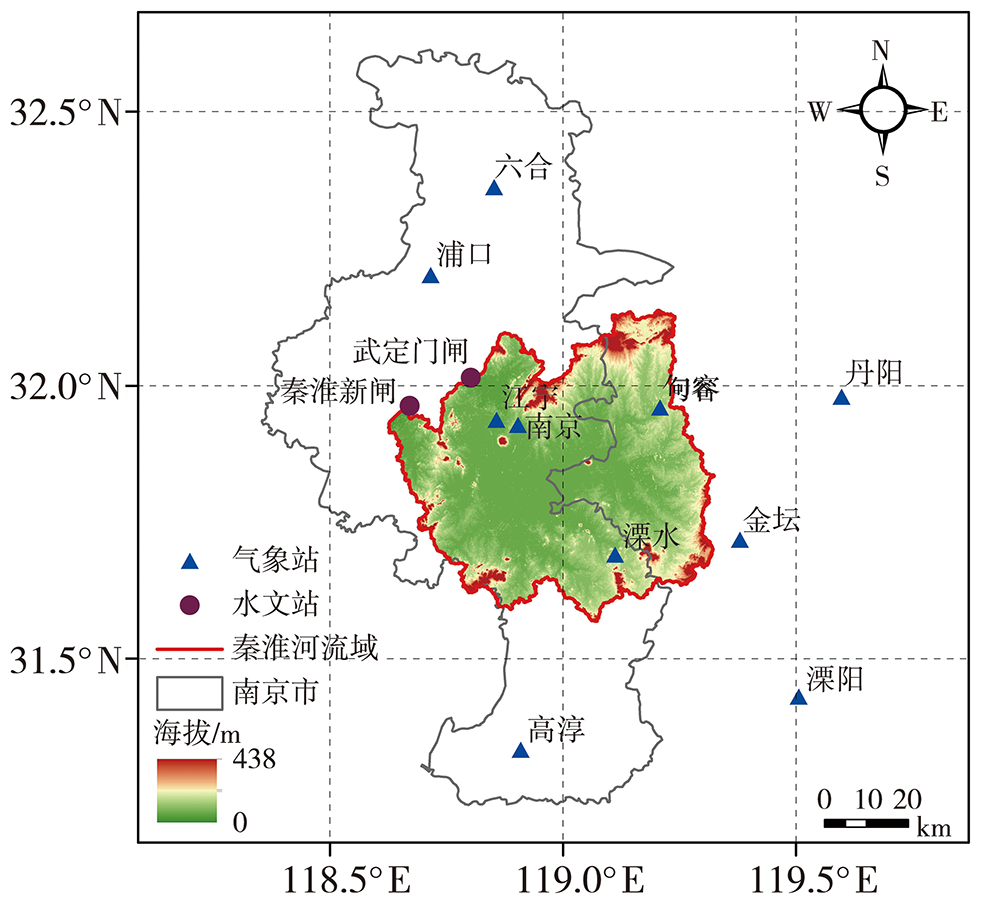
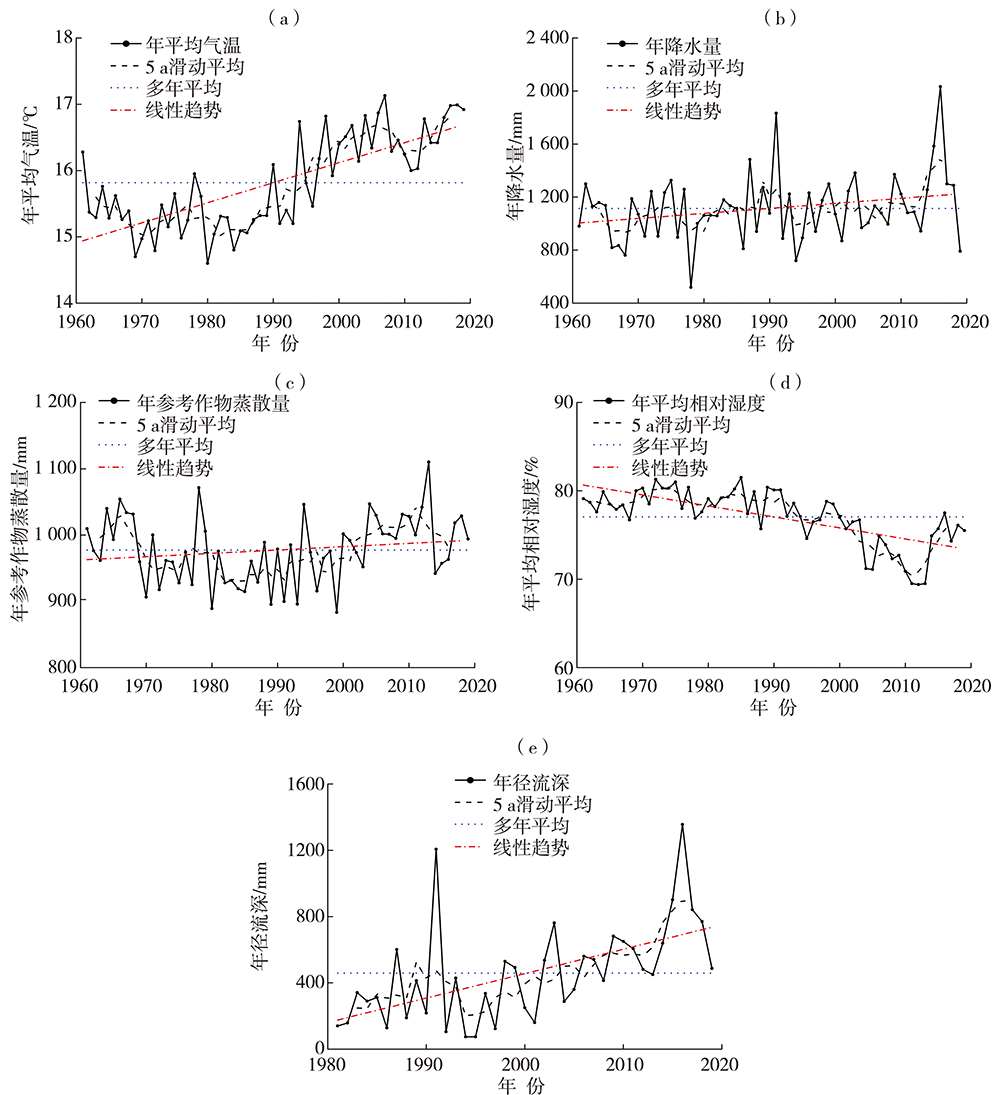
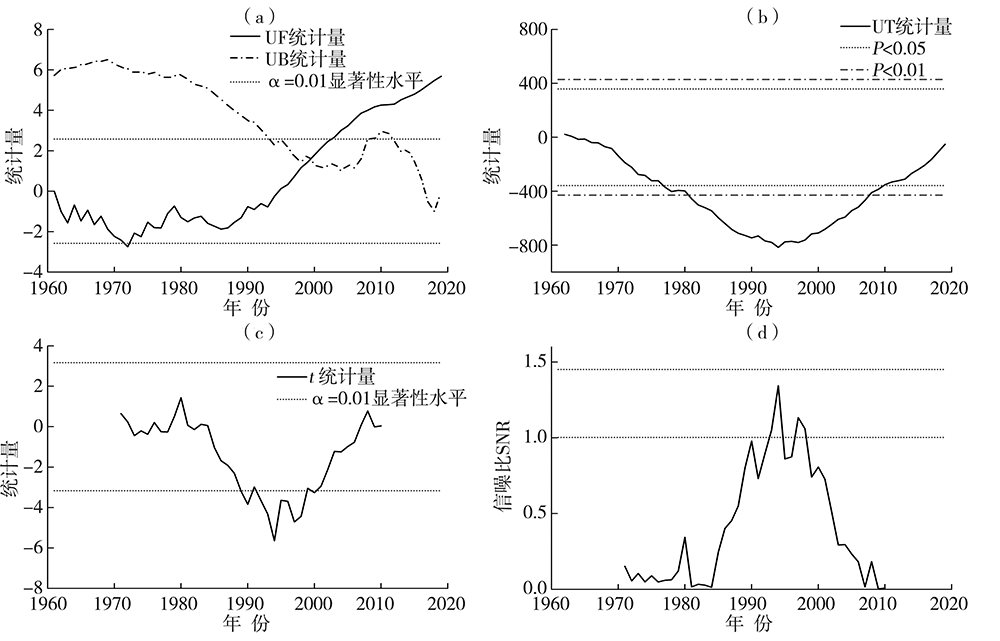
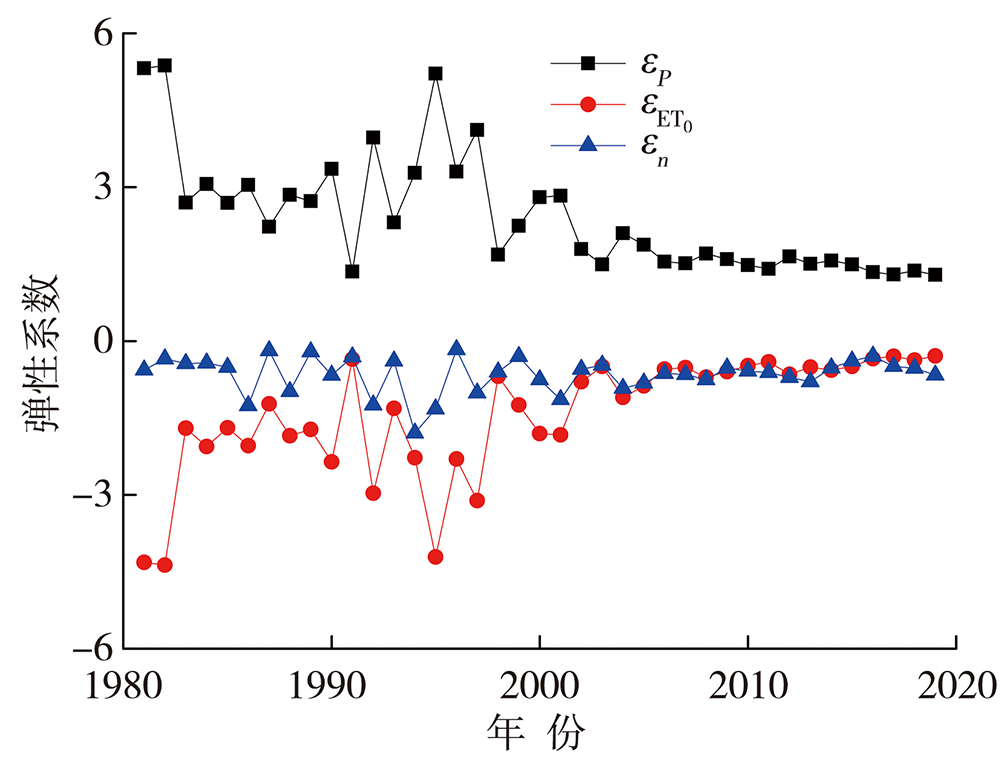
王艳君, 吕宏军, 施雅风, 等, 2009. 城市化流域的土地利用变化对水文过程的影响——以秦淮河流域为例[J]. 自然资源学报, 24(1): 30-36.
|
| [19] |
谢平, 雷红富, 陈广才, 等, 2008. 基于Hurst系数的流域降雨时空变异分析方法[J]. 水文, 28(5): 6-10.
|
| [20] |
徐东霞, 章光新, 尹雄锐, 2009. 近50年嫩江流域径流变化及影响因素分析[J]. 水科学进展, 20(3): 416-421.
|
| [21] |
杨大文, 张树磊, 徐翔宇, 2015. 基于水热耦合平衡方程的黄河流域径流变化归因分析[J]. 中国科学:技术科学, 45(10): 1 024-1 034.
|
| [22] |
张红华, 姚秀萍, 高媛, 等, 2018. 2016年江淮地区梅汛期首场持续性暴雨的持续原因初探[J]. 热带气象学报, 34(5): 674-684.
|
| [23] |
张丽梅, 赵广举, 穆兴民, 等, 2018. 基于Budyko假设的渭河径流变化归因识别[J]. 生态学报, 38(21): 7 607-7 617.
|
| [24] |
张利平, 陈小凤, 赵志鹏, 等, 2008. 气候变化对水文水资源影响的研究进展[J]. 地理科学进展, 27(3): 60-67.
DOI
|
| [25] |
周金玉, 张璇, 许杨, 等, 2020. 基于Budyko假设的滦河流域上游径流变化归因识别[J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 18(3): 15-30.
|
| [26] |
朱丽, 刘蓉, 文军, 等, 2018. 近50 a来洮河流域气候变化和干旱演变过程[J]. 干旱气象, 36(2): 234-242.
DOI
|
| [27] |
ALLEN R G, PEREIRA L S, RAES D, et al, 1998. Crop evapotranspiration: guidelines for computing crop water requirements-FAO irrigation and drainage paper 56[EB/OL]. [2021-01-08]. https://www.fao.org/3/X0490E/X0490E00.htm.
|
| [28] |
BUDYKO M I, 1974. Climate and life[M]. New York: Academic Press.
|
| [29] |
CHOUDHURY B J, 1999. Evaluation of an empirical equation for annual evaporation using field observations and results from a biophysical model[J]. Joumal of Hydrology, 216: 99-110.
|
| [30] |
DU Y, XIE Z Q, ZENG Y, et al, 2007. Impact of urban expansion on regional temperature change in the Yangtze River Delta[J]. Journal of Geography, 17(4): 387-398.
|
| [31] |
FARSI N, MAHJOURI N, 2019. Evaluating the contribution of the climate change and human activities to runoff change under uncertainty[J]. Journal of Hydrology,(574): 872-891.
|
| [32] |
HU S S, LIU C M, ZHENG H G, et al, 2012. Assessing the impacts of climate variability and human activities on streamflow in the water source area of Baiyangdian Lake[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 22(5): 895-905.
DOI
|
| [33] |
HURST H E, 1951. Long term storage capacity of reservoirs[J]. Transactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers,(116): 770-799.
|
| [34] |
MANN H B, 1945. Nonparametric tests against trend[J]. Econometrica, (13): 245-259.
|
| [35] |
MERRIAM C F, 1937. A comprehensive study of the rainfall on the Susquehanna Valley[J]. Transactions American Geophysical Union, 18(2): 471-476.
DOI
URL
|
| [36] |
PETTITT A N, 1979. A non-paramentic approach to the change problem[J]. Applied Staticstics, 28(2): 126-135.
|
| [37] |
YAMAMOTO R, IWASHIMA T, KAZADI S N, et al, 1985. Climatic jump: a hypothesis in climate diagnosis[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan, 63(6): 1 157-1 160.
|
| [38] |
YANG D, SUN F, LIU Z, et al, 2006. Interpreting the complementary relationship in non-humid environments based on the Budyko and Penman hypotheses[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 33(18): 122-140.
|
 ), HUANG Liang1,2, WANG Jiahu3, JIANG Zhihao4, LU Xiaoping5, LUO Xiaochun1(
), HUANG Liang1,2, WANG Jiahu3, JIANG Zhihao4, LU Xiaoping5, LUO Xiaochun1( )
)
 ), 黄亮1,2, 王加虎3, 蒋志昊4, 陆晓平5, 罗晓春1(
), 黄亮1,2, 王加虎3, 蒋志昊4, 陆晓平5, 罗晓春1( )
)