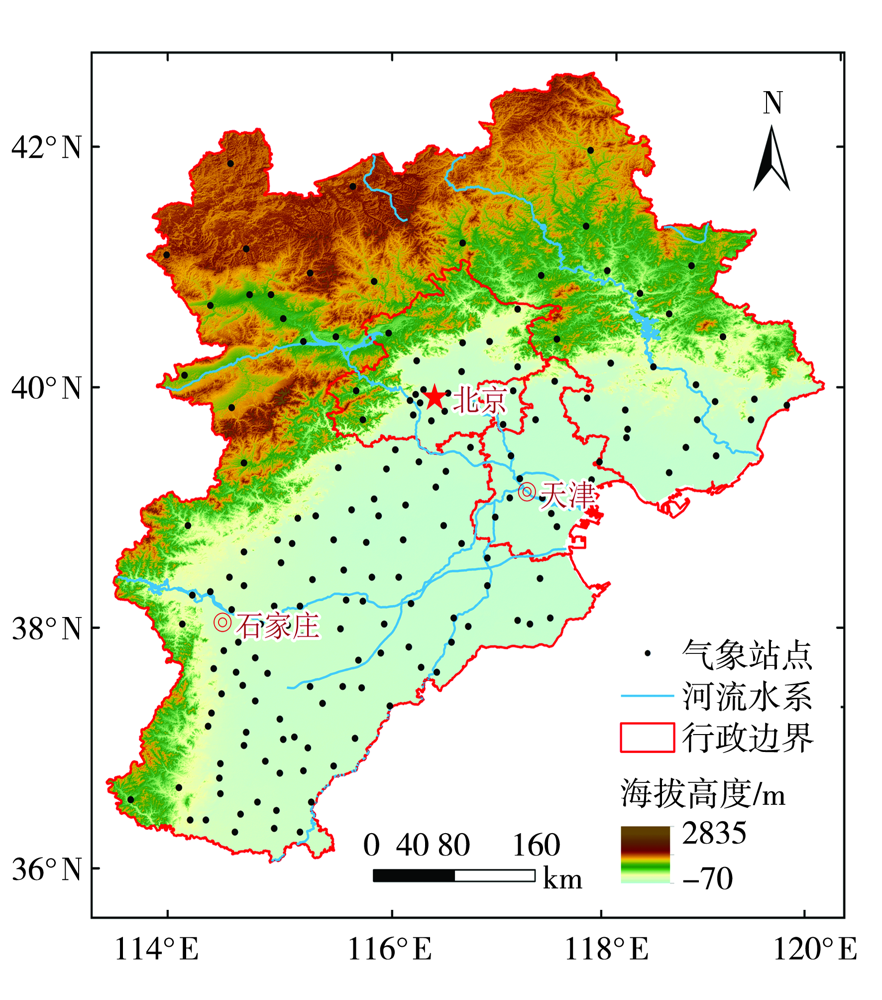
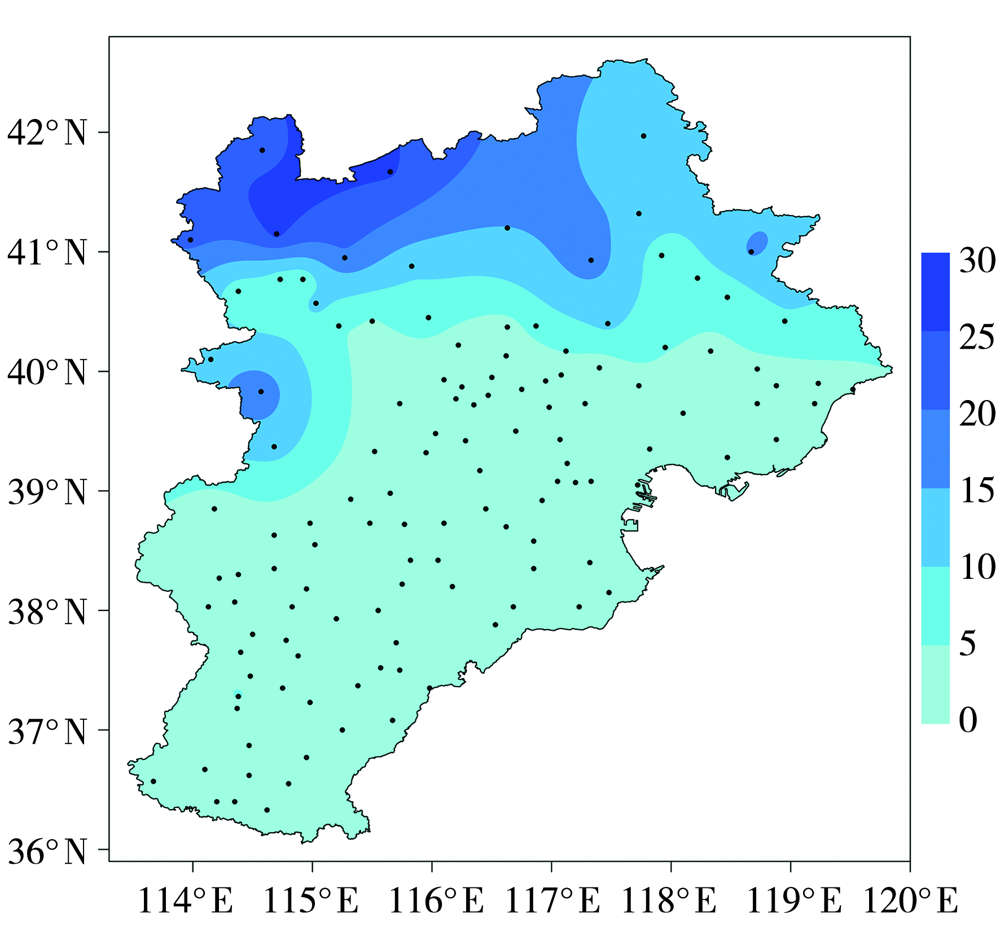
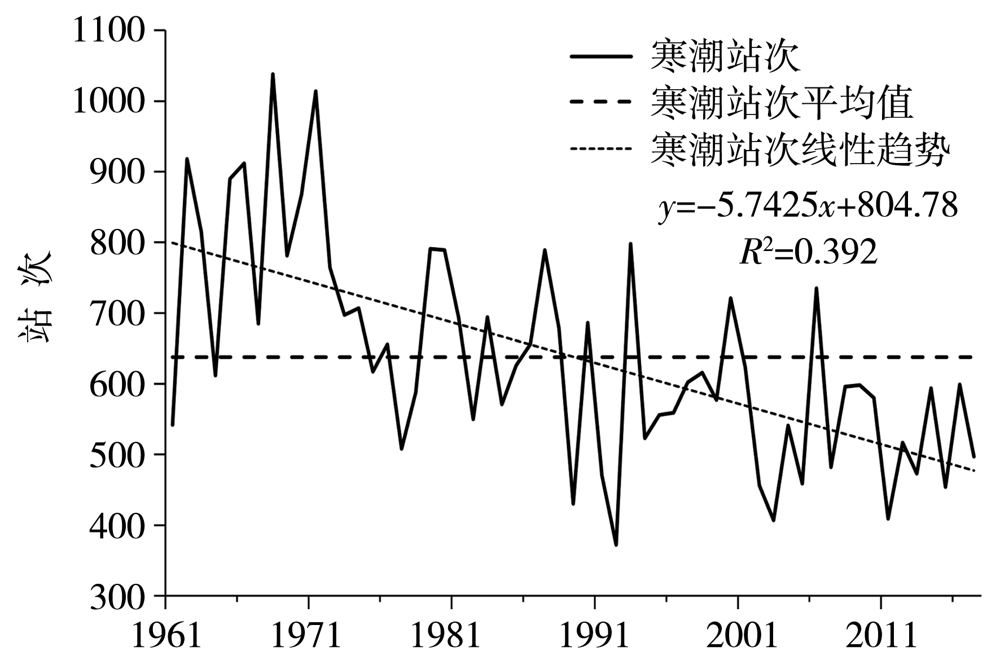
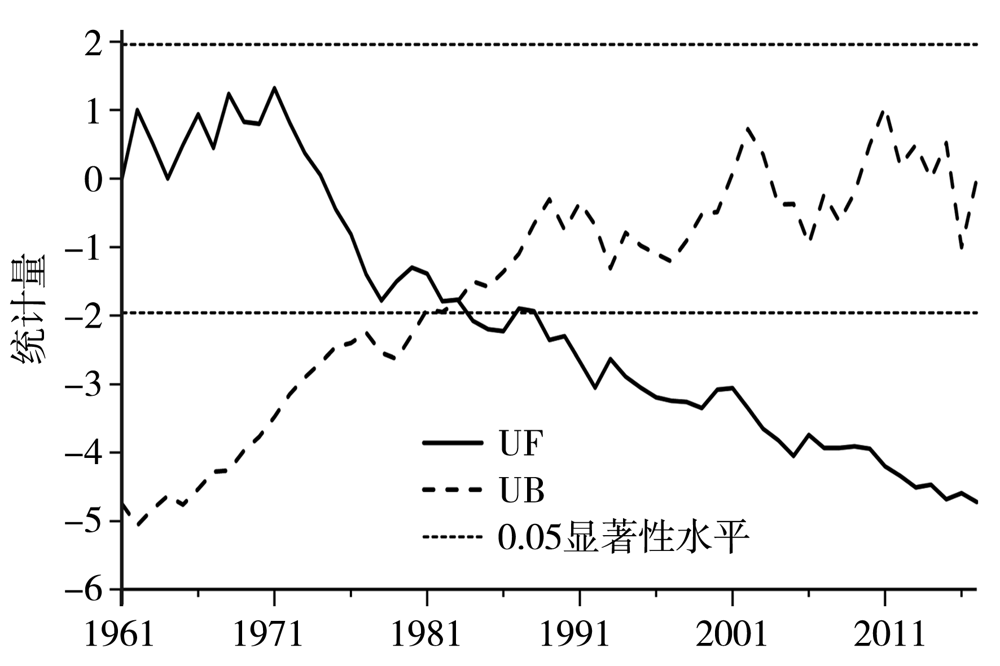
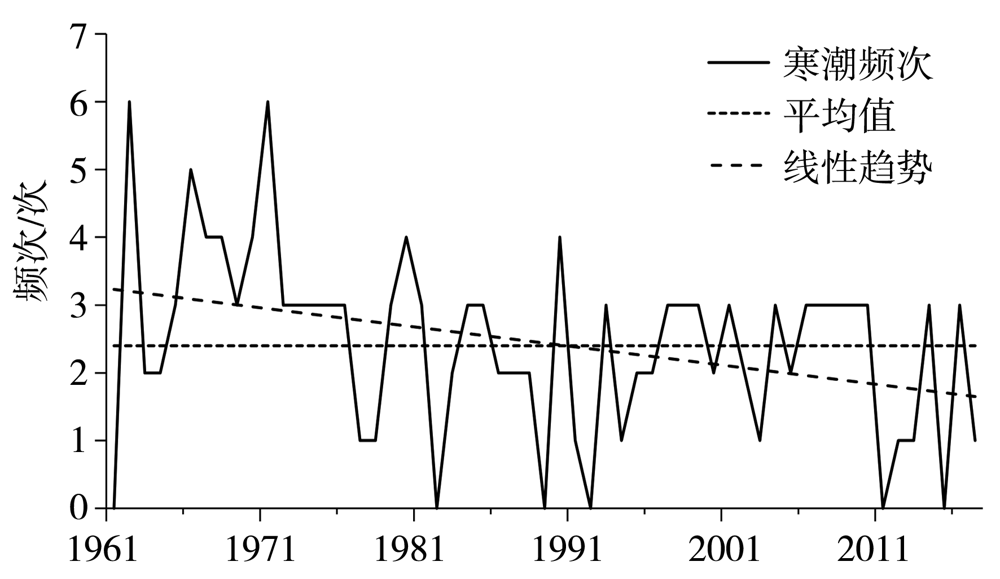
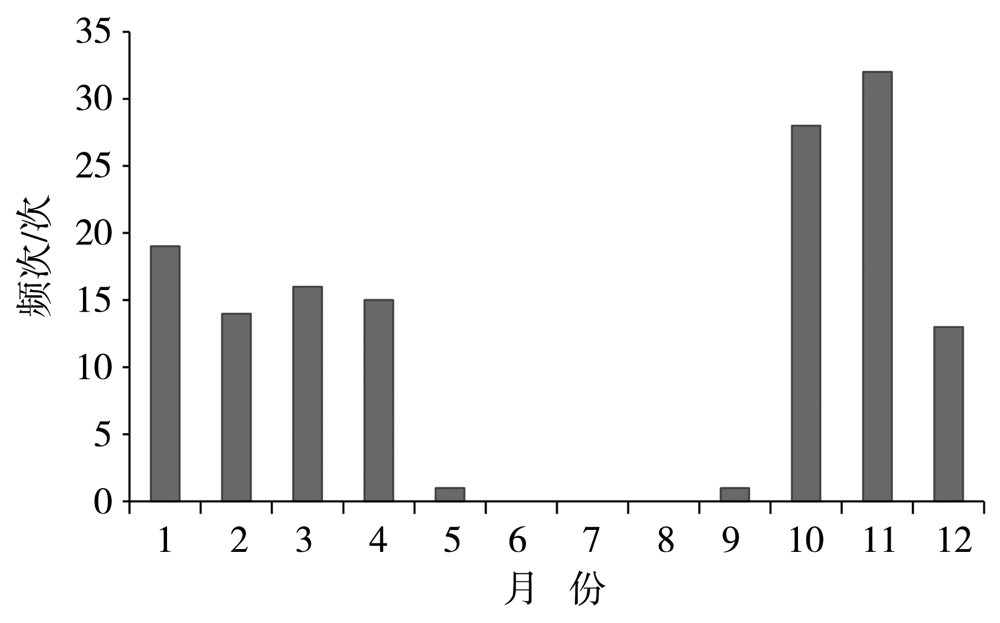
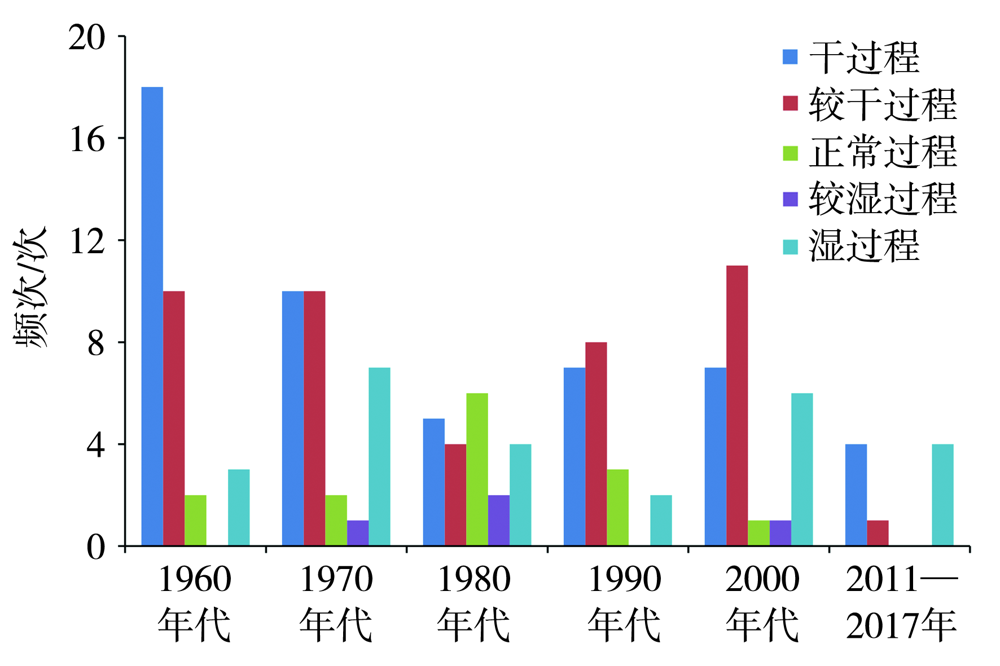
Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2022, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (1): 41-48.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-01-0041
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Characteristics of cold wave activities in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region from 1961 to 2017
LI Hongying1( ), LIN Shu2(
), LIN Shu2( ), WANG Yunpeng1, HUANG Pengcheng2, YU Yanan1
), WANG Yunpeng1, HUANG Pengcheng2, YU Yanan1
- 1. Jiuquan Meteorological Bureau of Gansu Province,Jiuquan 735000, Gansu, China
2. Lanzhou Regional Climate Center, Lanzhou 730020, China
-
Received:2021-09-21Revised:2021-11-11Online:2022-02-28Published:2022-02-28 -
Contact:LIN Shu
1961—2017年京津冀地区寒潮活动特征
李红英1( ), 林纾2(
), 林纾2( ), 王云鹏1, 黄鹏程2, 于亚楠1
), 王云鹏1, 黄鹏程2, 于亚楠1
- 1.甘肃省酒泉市气象局,甘肃 酒泉 735000
2.兰州区域气候中心,甘肃 兰州 730020
-
通讯作者:林纾 -
作者简介:李红英(1979— ),女,高级工程师,主要从事决策气象服务与气候变化研究. E-mail: 16439597@qq.com。 -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划项目资助(2018YFC1505601)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LI Hongying, LIN Shu, WANG Yunpeng, HUANG Pengcheng, YU Yanan. Characteristics of cold wave activities in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region from 1961 to 2017[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(1): 41-48.
李红英, 林纾, 王云鹏, 黄鹏程, 于亚楠. 1961—2017年京津冀地区寒潮活动特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(1): 41-48.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-01-0041
| 年代 | 全年 | 春季 | 秋季 | 冬季 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1960年代 | 33 | 6 | 12 | 15 |
| 1970年代 | 30 | 10 | 15 | 5 |
| 1980年代 | 21 | 4 | 11 | 6 |
| 1990年代 | 20 | 3 | 10 | 7 |
| 2000年代 | 26 | 9 | 8 | 9 |
| 2011—2017年 | 9 | 0 | 5 | 4 |
| 合计 | 139 | 32 | 61 | 46 |
Tab.1 Occurrence frequency of regional cold wave in BTH region from 1961 to 2017 in different decadal periods
| 年代 | 全年 | 春季 | 秋季 | 冬季 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1960年代 | 33 | 6 | 12 | 15 |
| 1970年代 | 30 | 10 | 15 | 5 |
| 1980年代 | 21 | 4 | 11 | 6 |
| 1990年代 | 20 | 3 | 10 | 7 |
| 2000年代 | 26 | 9 | 8 | 9 |
| 2011—2017年 | 9 | 0 | 5 | 4 |
| 合计 | 139 | 32 | 61 | 46 |
| 干湿过程 | DW |
|---|---|
| 干过程 | ≤-50% |
| 较干过程 | (-50%,-20%] |
| 正常过程 | (-20%,20%) |
| 较湿过程 | [20%,50%) |
| 湿过程 | ≥50% |
Tab.2 Classification criteria of dry and wet of regional cold wave process
| 干湿过程 | DW |
|---|---|
| 干过程 | ≤-50% |
| 较干过程 | (-50%,-20%] |
| 正常过程 | (-20%,20%) |
| 较湿过程 | [20%,50%) |
| 湿过程 | ≥50% |
| 干湿过程 | 春季/次 | 秋季/次 | 冬季/次 | 年/次 | 占比/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干过程 | 10 | 19 | 22 | 51 | 36.7 |
| 较干过程 | 9 | 21 | 14 | 44 | 31.7 |
| 正常过程 | 3 | 6 | 5 | 14 | 10.1 |
| 较湿过程 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 2.9 |
| 湿过程 | 9 | 13 | 4 | 26 | 18.7 |
| 总频次 | 32 | 61 | 46 | 139 |
Tab.3 Distribution of frequency of dry and wet process of regional cold wave in BTH region
| 干湿过程 | 春季/次 | 秋季/次 | 冬季/次 | 年/次 | 占比/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干过程 | 10 | 19 | 22 | 51 | 36.7 |
| 较干过程 | 9 | 21 | 14 | 44 | 31.7 |
| 正常过程 | 3 | 6 | 5 | 14 | 10.1 |
| 较湿过程 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 2.9 |
| 湿过程 | 9 | 13 | 4 | 26 | 18.7 |
| 总频次 | 32 | 61 | 46 | 139 |
| [1] | 钱维宏, 张玮玮. 我国近46年来的寒潮时空变化与冬季增暖[J]. 大气科学, 2007, 31(6):1266-1278. |
| [2] | 魏凤英. 气候变暖背景下我国寒潮灾害的变化特征[J]. 自然科学进展, 2008, 18(3):289-295. |
| [3] | 王遵娅, 丁一汇. 近53年中国寒潮的变化特征及其可能原因[J]. 大气科学, 2006, 30(6):1068-1076. |
| [4] | 康志明, 金荣花, 鲍媛媛. 1951—2006 年期间我国寒潮活动特征分析[J]. 高原气象, 2010, 29(2):420-428. |
| [5] | 乔雪梅, 刘普幸. 中国北方地区寒潮时空特征及其成因分析[J]. 冰川冻土, 2020, 42(2):357-367. |
| [6] | 姚永明, 姚雷, 邓伟涛. 长江中下游地区类寒潮发生频次的变化特征分析[J]. 气象, 2011, 37(3):339-344. |
| [7] | 刘晓冉, 胡祖恒, 李永华, 等. 重庆地区冬季冷暖变化及其异常成因分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(3):404-410. |
| [8] | 海云莎, 田永丽, 陈新梅. 云南寒潮时空特征及变化分析[J]. 云南大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 33(增刊1):147-152. |
| [9] | 孟鑫, 张瑜, 李慧琳, 等. 东北冬季气温变化异常特征及其与AO的联系[J]. 干旱气象, 2017, 35(3):383-390. |
| [10] | 唐孟琪, 曾刚. 近30多年中国东北地区春季寒潮的年代际变化及其可能原因[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2017, 22(4):473-486. |
| [11] | 阎琦, 田莉, 李爽, 等. 辽宁区域性冷空气多时间尺度变化特征及影响因子[J]. 冰川冻土, 2016, 38(2):379-387. |
| [12] |
贾宏元, 程彦杰, 周翠芳. 近52年宁夏冬季极端寒冷事件的演变特征[J]. 高原气象, 2015, 34(2):455-462.
DOI |
| [13] | 毛炜峄, 陈颖. 1951—2015 年乌鲁木齐市寒潮过程频数及强度气候特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2016, 34(3):403-411. |
| [14] | 林纾, 李丹华, 卢国阳, 等. 甘肃省春季强冷空气时空分布特征及其延伸期预报探索[J]. 干旱气象, 2017, 35(6):934-939. |
| [15] | 李万荣, 张弢. 1960—2017 年河西走廊东部寒潮时空变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2019, 37(5):747-753. |
| [16] |
刘宪锋, 朱秀芳, 潘耀忠, 等. 近53年内蒙古寒潮时空变化特征及其影响因素[J]. 地理学报, 2014, 69(7):1013-1024.
DOI |
| [17] | 赵慧, 郭庆元, 马鹏程, 等. 陇东南地区近50 a 极端低温事件演变特征及环流背景[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(6):900-908. |
| [18] | 朱晨玉, 黄菲, 石运昊, 等. 中国近50年寒潮冷空气的时空特征及其与北极海冰的关系[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 44(12):12-20. |
| [19] | 汪子琪, 张文君, 耿新. 两类ENSO对中国北方冬季平均气温和极端低温的不同影响[J]. 气象学报, 2017, 75(4):564-580. |
| [20] | CHANG C P. East Asian monsoon[M]. Singapore: World Scientific Publishing Co Pte Ltd, 2004:54-106. |
| [21] |
WATANABE M. Asian jet waveguide and a downstream extension of the North Atlantic Oscillation[J]. Journal of Climate, 2004, 17(24):4674-4691.
DOI URL |
| [22] | 周星妍, 朱伟军, 顾聪. 冬季北大西洋风暴轴异常对我国寒潮活动的可能影响[J]. 大气科学, 2015, 39(5):978-990. |
| [23] | 李峰, 矫梅燕, 丁一汇, 等. 北极区近30年环流的变化及对中国强冷事件的影响[J]. 高原气象, 2006, 25(2):209-219. |
| [24] | JEONG J H, HO C H. Changes in occurrence of cold surges over east Asia in association with Arctic Oscillation[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2005, 32:L14704. |
| [25] |
TAKAYA K, NAKAMURA H. Geographical dependence of upper-level blocking formation associated with intraseasonal amplification of the Siberian high[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 2005, 62(12):4441-4449.
DOI URL |
| [26] | 于波, 李桑, 黄富祥, 等. 2016年1月京津冀地区连续性寒潮事件对比分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2019, 37(6):954-963. |
| [27] | 段丽瑶, 刘爱霞, 于莉莉. 1961—2010年环渤海地区寒潮时空分布及变化特征[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2013, 29(4),54-58. |
| [28] | 宋善允, 彭军, 连志鸾, 等. 河北省天气预报手册[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2017:135-160. |
| [29] | 赵玉广, 何丽华, 张南, 等. 河北省寒潮天气形势分析及预报[J]. 干旱气象, 2012, 30(1):94-99. |
| [30] | 赵玉广, 于长文, 何丽华, 等. 河北省寒潮的气候特征与冬季增暖[J]. 干旱气象, 2012, 30(5):244-248. |
| [31] | 李林, 乔媛, 孙雪琪, 等. 北京延庆冬季风寒温度分布特征及变化趋势[J]. 干旱气象, 2018, 36(6):936-943. |
| [32] | 宋晓辉, 杜亮亮, 田秀霞, 等. 1976—2016年河北邯郸寒潮活动特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2019, 37(5):754-761. |
| [33] | 周庆亮, 李延香, 林玉成, 等. 冷空气等级:GB/T 20484—2017[S]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2017:1-2. |
| [34] | 陈宏, 余文韬, 徐威, 等. 天津地区冬季降水相态识别判据研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(4):670-677. |
| [35] | 赵春雨, 严晓瑜, 李栋梁, 等. 1961—2007年辽宁省积雪变化特征及其与温度、降水的关系[J]. 冰川冻土, 2010, 32(3):462-468. |
| [36] | 魏荣庆, 宗志平, 唐冶. 寒潮等级: GB/T 21987—2017[S]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2017:1-2. |
| [37] | 王遵娅, 司东, 段丽瑶. 冷空气过程监测指标: QX/T 393—2017[S]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2017:1-3. |
| [38] | 胡钰玲, 赵中军, 康彩燕, 等. 中国南方2008年与2016年两次低温雨雪冰冻天气过程对比分析[J]. 冰川冻土, 2017, 39(6):1180-1191. |
| [1] | CHEN Ying, ZHANG Dongfeng, WANG Lin, LIU Yueli, WANG Dayong. Estimation of climate change in the 21st century in North China by RegCM4 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(1): 1-10. |
| [2] | WANG Min, YIN Yixing, CHEN Xiaoyang, GUO Yang, XU Mei, LUO Chuanjun. Changing characteristics of meteorological drought in Tianjin for almost one century based on standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(1): 11-21. |
| [3] | CHENG Jianbo, ZUO Dongdong, YAN Pengcheng. Influence of fake below-ground meridional wind on regional Hadley circulation in Africa [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(06): 900-910. |
| [4] | ZHOU Yaman, SUN Di, ZHAO Yong, LI Anbei, GUO Yulin. Characteristics of Wide-range Extreme Precipitation in Summer and Its Circulation Anomalies in Northern Xinjiang#br# [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(2): 215-224. |
| [5] | GUO Guangfen, DU Liangmin, XIAO Ying, GAO Yaqi, WU Yao. Spatio-temporal Distribution Characteristics of Summer Extreme Precipitation in the Yangtze River Basin [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(2): 235-243. |
| [6] | HUANG Helou, DING Yeyi, TU Xiaoping, ZHAO Changyu, YAO Risheng. Impact of Urbanization on Extreme Temperature and Human Comfort Degree in Ningbo City [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(03): 396-403. |
| [7] | ZHU Yongning, FENG Dongpu, LI Hongying, DUAN Xiaofeng, ZHENG Fang. Temporal and Spatial Change Characteristics of the Minimum Temperature and Frost Days During the Spring Frost Stage in Ningxia [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2020, 38(2): 256-262. |
| [8] | JIN Hongmei, QIAO Liang, YAN Pengcheng, ZHANG Wei, GAO Shiyu, ZHANG Jin. Nonlinear Characteristics of Drought in Northwest China Based on Approximate Entropy [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(5): 713-721. |
| [9] | BAI Qingshun, YAN Pengcheng, CAI Dihua, JIN Hongmei, FENG Guolin, ZHANG Tiejun. Inter-decadal Change Characteristics of Different Grades Drought in Northwest China in Recent 56 Years [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(5): 722-728. |
| [10] | LI Wanrong, ZHANG Tao. Temporal and Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Cold Waves in Eastern Hexi Corridor During 1960-2017 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(5): 747-753. |
| [11] | JIN Hongmei, YAN Pengcheng, BAI Qinshun, ZHOU Ganlin, DUAN Haixia. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Extreme High Temperature Events in Central Asia over the Last 70 Years [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(4): 550-556. |
| [12] | CHEN Yanli, MENG Liangli, HUANG Xiaohan, MO Jianfei, WANG Ying, MO Weihua. Temporal and Spatial Distributions of Drought in Guangxi Karst Area During 1971-2017 Based on Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(3): 353-. |
| [13] | CAI Xinling, LI Yu, LI Qian, HU Shulan. Climatic Characteristics of Autumn Rain in Shaanxi and Their Relationship with Atmospheric Circulation and SST During 1961-2016 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(2): 226-232. |
| [14] | MA Li, GUO Yuanyuan, WANG Xiaoli, QIU Guiqiang, QIAO Yu, WANG Chendi. Variation Tendency of Cyclonic Wind Shear in Low-level and Its Causes in North China During 1955-2014 [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(2): 243-251. |
| [15] | SUN Xia, FAN Guangzhou, ZHANG Yongli, LAI Xin. Temporal and Spatial Variation Characteristics of Soil Moisture at Different Layers of the Tibetan Plateau in Summer [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2019, 37(2): 252-261. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||