Journal of Arid Meteorology ›› 2022, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (1): 1-10.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-01-0001
• Articles • Next Articles
Estimation of climate change in the 21st century in North China by RegCM4
CHEN Ying1( ), ZHANG Dongfeng1(
), ZHANG Dongfeng1( ), WANG Lin2, LIU Yueli1, WANG Dayong1
), WANG Lin2, LIU Yueli1, WANG Dayong1
- 1. Shanxi Climate Center, Taiyuan 030006, China
2. Shanxi Meteorological Disaster Prevention Technology Center, Taiyuan 030032, China
-
Received:2021-04-26Revised:2021-09-28Online:2022-02-28Published:2022-02-28 -
Contact:ZHANG Dongfeng
RegCM4对华北区域21世纪气候变化预估研究
陈颖1( ), 张冬峰1(
), 张冬峰1( ), 王林2, 刘月丽1, 王大勇1
), 王林2, 刘月丽1, 王大勇1
- 1.山西省气候中心,山西 太原 030006
2.山西省气象灾害防御技术中心,山西 太原 030032
-
通讯作者:张冬峰 -
作者简介:陈颖(1990— ),女,工程师,硕士,从事气候预测与气候变化研究. E-mail: 375760961@qq.com。 -
基金资助:中国气象局预报员专项项目(CMAYBY2020-018);山西省气象局面上项目(SXKMSQH20205213);山西省气象局重点项目共同资助(SXKZDQH20185103)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
CHEN Ying, ZHANG Dongfeng, WANG Lin, LIU Yueli, WANG Dayong. Estimation of climate change in the 21st century in North China by RegCM4[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(1): 1-10.
陈颖, 张冬峰, 王林, 刘月丽, 王大勇. RegCM4对华北区域21世纪气候变化预估研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(1): 1-10.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ghqx.org.cn/EN/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-01-0001
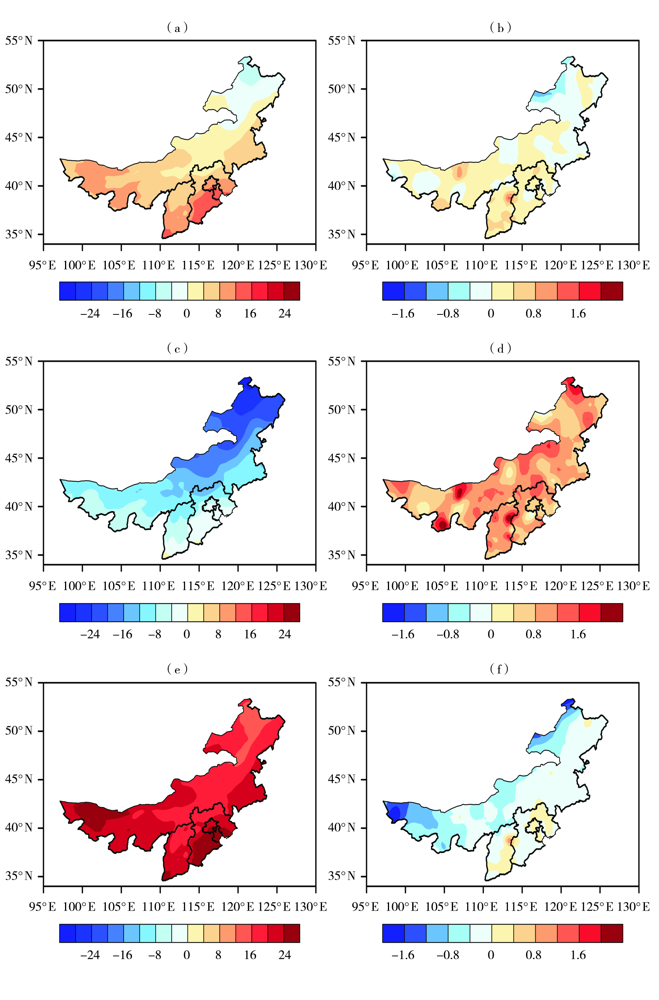
Fig.1 The observation (a, c, e) of mean temperature and the difference between simulation and observation (b, d, f) in the whole year (a, b), winter (c, d) and summer (e, f) in North China during the baseline period (Unit: ℃)
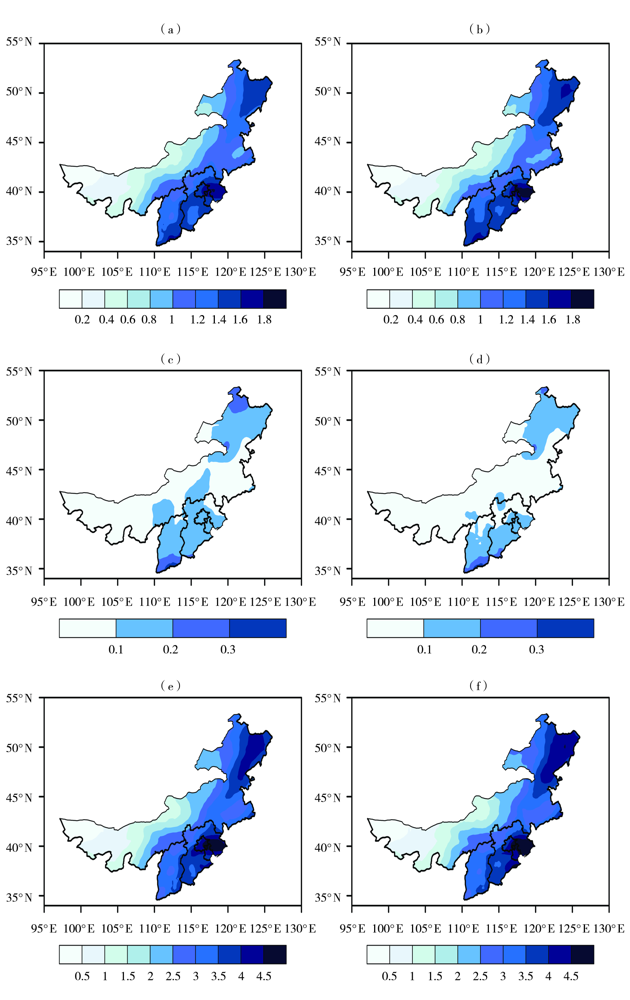
Fig.2 The observation (a, c, e) and simulation (b, d, f) of mean precipitation in the whole year (a, b), winter (c, d) and summer (e, f) in North China during the baseline period (Unit: mm·d-1)

Fig.3 The temperature anomaly (a, b) and precipitation anomaly percentage (c, d) simulated by RegCM4 under RCP4.5 (a, c) and RCP8.5 (b, d) scenarios in North China from 2021 to 2098
| 时期 | 情景 | 气温距平/℃ | 降水距平百分率/% | CDD 距平/d | R95p距平 百分率/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年 | 冬季 | 夏季 | 年 | 冬季 | 夏季 | |||||
| 近期 | RCP4.5 | 1.23 | 0.82 | 1.56 | 5.1 | 5.8 | 3.8 | -1 | 19.2 | |
| RCP8.5 | 1.77 | 0.83 | 2.31 | 8.1 | 20.6 | 6.0 | -3 | 30.8 | ||
| 中期 | RCP4.5 | 2.58 | 2.50 | 2.80 | 8.9 | 22.1 | 7.7 | -3 | 28.3 | |
| RCP8.5 | 3.44 | 2.53 | 3.79 | 14.0 | 32.9 | 13.1 | -3 | 41.9 | ||
| 远期 | RCP4.5 | 3.49 | 3.50 | 3.69 | 9.2 | 37.7 | 6.8 | -7 | 27.2 | |
| RCP8.5 | 5.82 | 4.68 | 6.40 | 19.3 | 70.4 | 11.2 | -12 | 69.8 | ||
Tab.1 The change of temperature, precipitation and extreme precipitation indexes simulated by RegCM4 under different scenarios in North China in each period of the 21st century
| 时期 | 情景 | 气温距平/℃ | 降水距平百分率/% | CDD 距平/d | R95p距平 百分率/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年 | 冬季 | 夏季 | 年 | 冬季 | 夏季 | |||||
| 近期 | RCP4.5 | 1.23 | 0.82 | 1.56 | 5.1 | 5.8 | 3.8 | -1 | 19.2 | |
| RCP8.5 | 1.77 | 0.83 | 2.31 | 8.1 | 20.6 | 6.0 | -3 | 30.8 | ||
| 中期 | RCP4.5 | 2.58 | 2.50 | 2.80 | 8.9 | 22.1 | 7.7 | -3 | 28.3 | |
| RCP8.5 | 3.44 | 2.53 | 3.79 | 14.0 | 32.9 | 13.1 | -3 | 41.9 | ||
| 远期 | RCP4.5 | 3.49 | 3.50 | 3.69 | 9.2 | 37.7 | 6.8 | -7 | 27.2 | |
| RCP8.5 | 5.82 | 4.68 | 6.40 | 19.3 | 70.4 | 11.2 | -12 | 69.8 | ||
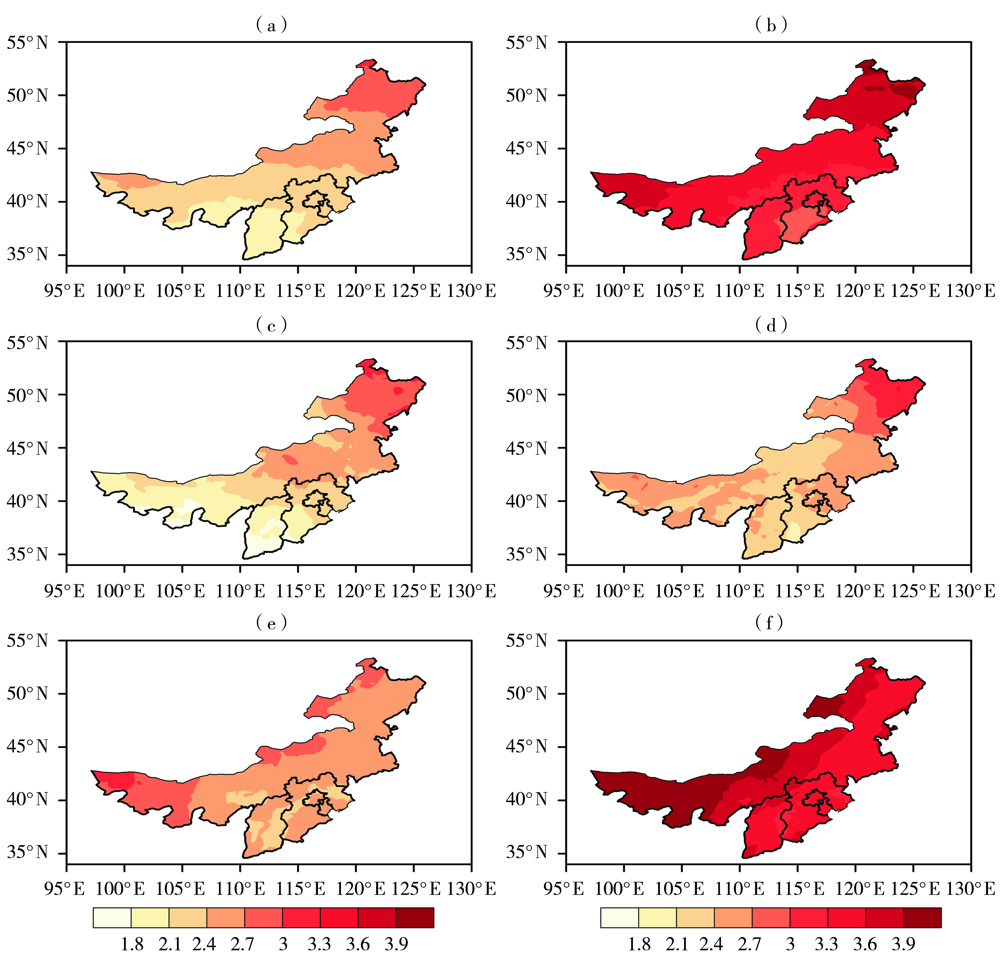
Fig.4 The anomaly of mean temperature in the whole year (a, b), winter (c, d) and summer (e, f ) simulated by RegCM4 under RCP4.5 (a, c, e) and RCP8.5 (b, d, f) scenarios in North China in the mid-21st century (Unit: ℃)
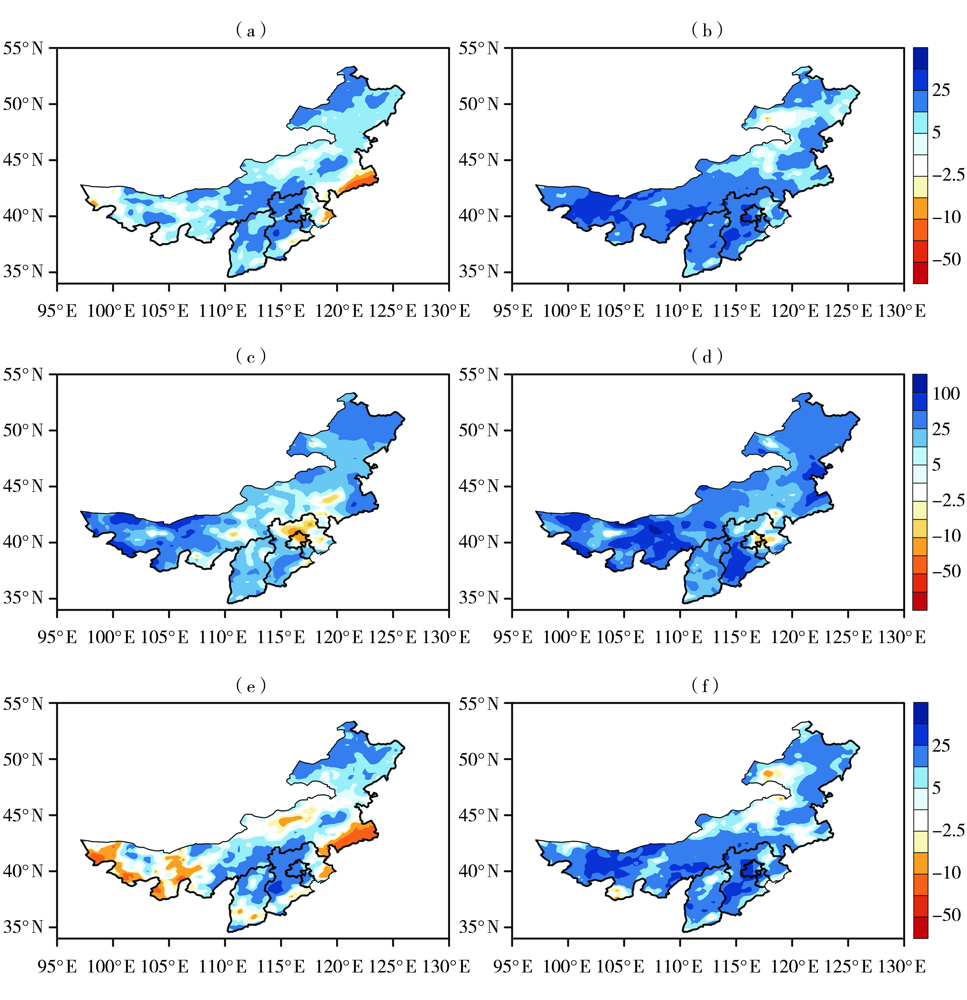
Fig.5 The anomaly percentage of mean precipitation in the whole year (a, b), winter (c, d) and summer (e, f) simulated by RegCM4 under RCP4.5 (a, c, e) and RCP8.5 (b, d, f) scenarios in North China in the mid-21st century (Unit: %)
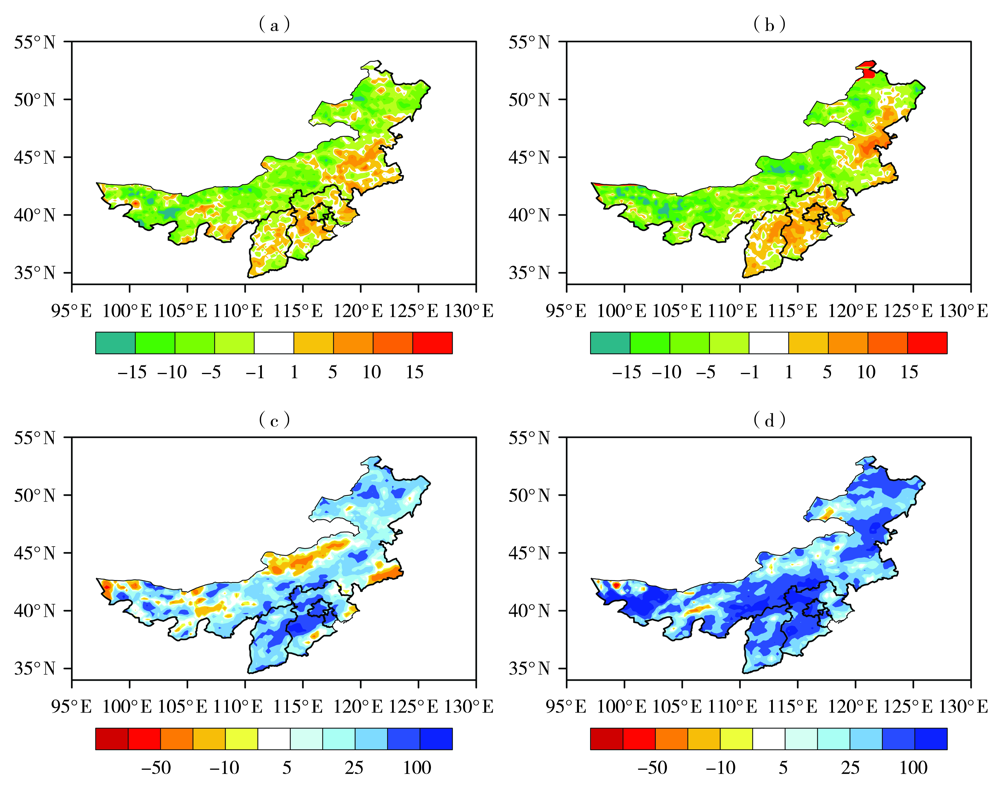
Fig.6 The anomaly of CCD (a, b, Unit: d) and anomaly percentage of R95p (c, d, Unit: %) simulated by RegCM4 under RCP4.5 (a, c) and RCP8.5 (b, d) scenarios in North China in the mid-21st century
| [1] |
MEINSHAUSEN M, SMITH S J, CALVIN K, et al. The RCP greenhouse gas concentrations and their extensions from 1765 to 2300[J]. Climatic Change, 2011, 109(1):213-241.
DOI URL |
| [2] | IPCC. Climate change 2013: The physical science basis[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2013:743-866. |
| [3] | IPCC. Climate change 2021: The physical science basis[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2021. |
| [4] | 王素仙, 张永领, 郭灵辉, 等. 1981—2010年内蒙古气温变化特征及未来趋势预估[J]. 气象与环境科学, 2017, 40(4):114-120. |
| [5] |
GAO X J, SHI Y, ZHANG D F, et al. Climate change in China in the 21st century as simulated by a high resolution regional climate model[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 57(10):1188-1195.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
GAO X J, WANG M L, GIORGI F. Climate change over China in the 21st century as simulated by BCC_CSM1.1-RegCM4.0[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 2013, 6(5):381-386.
DOI URL |
| [7] | 张冬峰, 高学杰, 罗勇, 等. RegCM4.0对一个全球模式20世纪气候变化试验的中国区域降尺度:温室气体和自然变率的贡献[J]. 科学通报, 2015, 60(17):1631-1642. |
| [8] |
GIORGI F, BATES G T. The climatological skill of a regional model over complex terrain[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 1989, 117(11):2325-2347.
DOI URL |
| [9] | 石英. RegCM3对21世纪中国区域气候变化的高分辨率数值模拟[D]. 北京:中国科学院大气物理研究所, 2010. |
| [10] | 吉振明. 新排放情景下中国气候变化的高分辨率数值模拟研究[D]. 北京:中国科学院研究生院, 2012. |
| [11] |
ZHANG D F, HAN Z Y, SHI Y. Comparison of climate projections between driving CSIRO-Mk3.6.0 and downscaling simulation of RegCM4.4 over China[J]. Advances in Climate Change Research, 2017, 8(4):245-255.
DOI URL |
| [12] | 张冬峰, 高学杰. 中国21世纪气候变化的RegCM4多模拟集合预估[J]. 科学通报, 2020, 65(23):2516-2526. |
| [13] |
GAO X J, SHI Y, ZHANG D F, et al. Uncertainties in monsoon precipitation projections over China: Results from two high-resolution RCM simulations[J]. Climate Research, 2012, 52:213-226.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
SHI Y, GAO X J, WU J, et al. Changes in snow cover over China in the 21st century as simulated by a high resolution regional climate model[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2011, 6(4):045401.
DOI URL |
| [15] | 张冬峰, 石英. 区域气候模式RegCM3对华北地区未来气候变化的数值模拟[J]. 地球物理学报, 2012, 55(9):2854-2866. |
| [16] |
WU J, GAO X J. Present day bias and future change signal of temperature over China in a series of multi-GCM driven RCM simulations[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2020, 54:1113-1130.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
ZHOU B T, WU J, XU Y, et al. Projected changes in autumn rainfall over West China: Results from an ensemble of dynamical downscaling simulations[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2019, 39:4869-4882.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
GIORGI F, COPPOLA E, SOLMON F, et al. RegCM4: Model description and preliminary tests over multiple CORDEX domains[J]. Climate Research, 2012, 52:7-29.
DOI URL |
| [19] | COLLINS W J, BELLOUIN N, DOUTRIAUX-BOUCHER M, et al. Development and evaluation of an Earth-system model-HadGEM2[J]. Geoscientific Model Development Discussions, 2011, 4:997-1062. |
| [20] |
MARTIN G M, BELLOUIN N, COLLINS W J, et al. The HadGEM2 family of Met Office Unified Model climate configurations[J]. Geoscientific Model Development, 2011, 4(3):723-757.
DOI URL |
| [21] | GIORGI F, JONES C, ASRAR G R, et al. Addressing climate information needs at the regional level: The CORDEX framework[J]. WMO Bulletin, 2009, 58(3):175-183. |
| [22] | GAO X J, SHI Y, GIORGI F. Comparison of convective parameterizations in RegCM4 experiments over China with CLM as the land surface model[J]. Atmospheric Ocean Science Letters, 2016, 9(4):246-254. |
| [23] |
GAO X J, SHI Y, HAN Z Y, et al. Performance of RegCM4 over major river basins in China[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2017, 34(4):441-455.
DOI URL |
| [24] | KIEHL J T, HACK J J, BONAN G B, et al. Description of the NCAR community climate model (CCM3)[J]. NCAR Technical Note, 1996, 108(2):55-60. |
| [25] |
HOLTSLAG A A M, DE BRUIJN E I F, PAN H L. A high resolution air mass transformation model for short-range weather forecasting[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 1990, 118:1561-1575.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
PAL J S, SMALL E E, ELTAHIR E A B. Simulation of regional-scale water and energy budgets: Representation of subgrid cloud and precipitation processes within RegCM[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2000, 105(D24):29579-29594.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
EMANUEL K A. A scheme for representing cumulus convection in large-scale models[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 1991, 48(21):2313-2329.
DOI URL |
| [28] | OLESON K W, NIU G Y, YANG Z L, et al. Improvements to the community land model and their impact on the hydrological cycle[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 2008, 113:G01021. |
| [29] | 韩振宇, 高学杰, 石英, 等. 中国高精度土地覆盖数据在RegCM4/CLM模式中的引入及其对区域气候模拟影响的分析[J]. 冰川冻土, 2015, 37(4):857-866. |
| [30] | 吴佳, 高学杰. 一套格点化的中国区域逐日观测资料及与其它资料的对比[J]. 地球物理学报, 2013, 56(4):1102-1111. |
| [31] |
ZHANG X B, ALEXANDER L, HEGERL G C, et al. Indices for monitoring changes in extremes based on daily temperature and precipitation data[J]. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Climate Change, 2011, 2(6):851-870.
DOI URL |
| [1] | HU Zhenju, LI Lu, HUANG Xiaoyu, HE Binwen, YE Rixin. Analysis of mechanism of topographic influence and meso-scale convective characteristics of an extremely severe rainfall affected by typical easterly wave [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(1): 73-83. |
| [2] | LIU Na, HUANG Wubin, YANG Jiancai, WANG Jixin, WANG Yicheng, ZHANG Junxia. Objective forecast method of short-term quantitative precipitation in Gansu Province based on SCTP-RF algorithm [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(1): 146-155. |
| [3] | LI Rong, LIU Xinwei, WEI Dong, DUAN Haixia, DUAN Bolong, LI Jiarui, DI Xiaohong. Refined characteristics of precipitation in Lanzhou based on regional automatic weather stations data [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(1): 55-61. |
| [4] | JIANG Yuanhua, ZENG Xianghong, DUAN Lijie, TANG Yihao, WU Hao. Variation Characteristics of Precipitation Structure During Flood Season in Hunan Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(4): 554-562. |
| [5] | YANG Tao, YANG Lianmei, ZHANG Yunhui, ZHUANG Xiaocui, HUANG Yan. Circulation Configuration of Synoptic System and Radar Echo Characteristics of Shorttime Heavy Rainfall in Xinjiang [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(4): 631-640. |
| [6] | XIAO Wei, FU Zhao, XU Lili, LIU Weicheng, DI Xiaohong, ZHENG Xin, YANG Xiumei. Comparison of Dynamic Characteristics of Two Short-time Heavy Precipitation Processes of Baroclinic-Frontogenesis in the Early Flood Period of Southeast Gansu [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(4): 641-651. |
| [7] | CHEN Hong, YU Wentao, XU Wei, YANG Xiaojun, SUN Jianyuan, CHEN Kaihua. Study and Application of Discriminant Criterion of Winter Precipitation Phase in Tianjin [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(4): 670-677. |
| [8] | YANG Xia, ZHANG Junlan, HUA Ye, XU Tingting, ZHANG Linmei. Diurnal Variation Characteristics of Precipitation in Different Seasons in the Yili River Valley of Xinjiang [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(3): 394-405. |
| [9] | YI Nana, SU Lijuan, ZHENG Xucheng, ZHANG Min, GONG Hong, . Macro Characteristics of Precipitation Clouds in Western Inner Mongolia [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(3): 406-414. |
| [10] | ZHANG Wulong, KANG Lan, ZHOU Wei, YIN Hang, . Extreme Short-time Heavy Precipitation Forecast Based on GRAPES-MESO Model [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(3): 507-513. |
| [11] | ZHOU Yaman, SUN Di, ZHAO Yong, LI Anbei, GUO Yulin. Characteristics of Wide-range Extreme Precipitation in Summer and Its Circulation Anomalies in Northern Xinjiang#br# [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(2): 215-224. |
| [12] | GUO Guangfen, DU Liangmin, XIAO Ying, GAO Yaqi, WU Yao. Spatio-temporal Distribution Characteristics of Summer Extreme Precipitation in the Yangtze River Basin [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(2): 235-243. |
| [13] | YI Xue, YANG Sen, LIU Mingyan, LI Tao, HOU Yiling, CUI Yan. Spatio-temporal Variation Characteristics of Vegetation Coverage and Its Response to Climate Change in Liaoning Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(2): 252-261. |
| [14] | ZHENG Zheng, PAN Lingjie, QIAN Yanzhen, ZHAO Changyu, HUANG Xuanxuan, XIAO Wangxing. Evolution Characteristics of Extreme Heavy Precipitation in Coast of Zhejiang Province Caused by Typhoon Lekima [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(2): 269-278. |
| [15] | XIONG Xianping, ZHANG Wei, ZHU Rui, LI Erjie. Influence of Precipitation on Mass Concentration of Atmospheric Pollutants in Cangzhou of Hebei Province [J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2021, 39(2): 296-301. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||