干旱气象 ›› 2025, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 510-520.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2025-04-0510
山东省6月区域性持续高温过程的变化特征及成因分析
陈君芝1,2( ), 伯忠凯1,2(
), 伯忠凯1,2( ), 徐玮平1,2, 孟祥新1,2, 曹洁1,2
), 徐玮平1,2, 孟祥新1,2, 曹洁1,2
- 1.山东省气象防灾减灾重点实验室,山东 济南 250031
2.山东省气候中心,山东 济南 250031
-
收稿日期:2024-04-01修回日期:2025-03-12出版日期:2025-08-31发布日期:2025-09-08 -
通讯作者:伯忠凯(1987—),男,山东济南人,高级工程师,主要从事短期气候预测业务及研究工作。E-mail: bozhongkai@163.com。
-
作者简介:陈君芝(1998—),女,山东淄博人,助理工程师,主要从事短期气候预测研究。E-mail: 3462918502@qq.com。 -
基金资助:山东省气象局科研项目(SDTQ2023-02);山东省气象局科研项目(SDYBY2020-02);山东省气象局科研项目(2023sdqxz11);山东省自然科学基金项目(ZR202211080149)
Characteristics and mechanisms of regional persistent high-temperature processes in June in Shandong
CHEN Junzhi1,2( ), BO Zhongkai1,2(
), BO Zhongkai1,2( ), XU Weiping1,2, MENG Xiangxin1,2, CAO Jie1,2
), XU Weiping1,2, MENG Xiangxin1,2, CAO Jie1,2
- 1. Key Laboratory for Meteorological Disaster Prevention and Mitigation of Shandong, Jinan 250031, China
2. Shandong Climate Center, Jinan 250031, China
-
Received:2024-04-01Revised:2025-03-12Online:2025-08-31Published:2025-09-08
摘要:
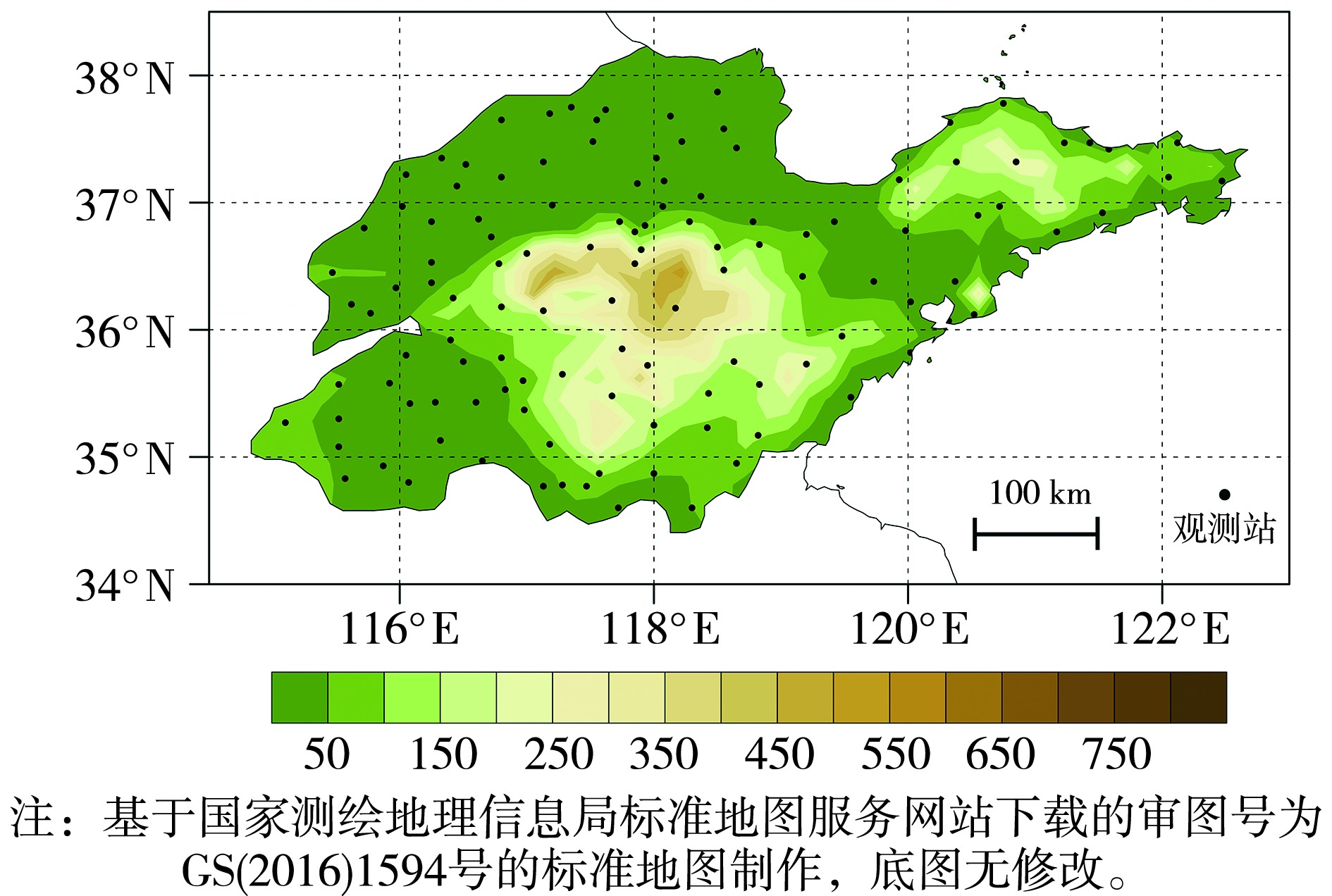
研究区域性持续高温过程的变化特征及其发生机理,有利于提取预测指标,为短期气候预测提供参考。本文基于1979—2023年山东省122个国家气象观测站的6月日最高气温资料,结合区域高温过程的变化特征,构建了山东省6月区域持续高温指数(Regional Persistent High-temperature events,RPH)。进一步利用ERA5逐年6月再分析资料,并以北大西洋海温异常为切入点,分析RPH与同期大气环流和海温等背景场之间的关系。 结果表明:山东省6月区域性高温过程具有明显的年际变化特征和线性上升趋势,2000年以后区域高温过程明显增多且强度增强;典型区域高温强年期间,500 hPa位势高度距平场在中高纬呈现“+-+-”型波列结构,850 hPa温度距平场呈现与之对应的“+-+-”冷暖中心分布;北大西洋“+-+”三极型海温异常(North Atlantic Tripole,NAT)与RPH显著正相关,NAT负位相所激发的欧亚遥相关波列与区域高温强年中高纬“+-+-”波列结构密切相关;NAT负位相可激发大气低层向高层的能量上输并向外辐散,其波作用通量沿偏北路径东传至山东上空,造成山东上空能量辐合,有利于正距平高度场维持,此背景下山东上空受下沉运动控制,促进区域高温过程发展。
中图分类号:
引用本文
陈君芝, 伯忠凯, 徐玮平, 孟祥新, 曹洁. 山东省6月区域性持续高温过程的变化特征及成因分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(4): 510-520.
CHEN Junzhi, BO Zhongkai, XU Weiping, MENG Xiangxin, CAO Jie. Characteristics and mechanisms of regional persistent high-temperature processes in June in Shandong[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2025, 43(4): 510-520.
| 区域性高温事件强度等级划分 | 指标 |
|---|---|
| 特强 | 1≤RI<2 |
| 强 | 2≤RI<3 |
| 中等 | 3≤RI<4 |
| 弱 | RI≥4 |
表1 区域性持续高温过程强度等级划分
Tab.1 Classification of intensity levels for regional persistent high temperature processes
| 区域性高温事件强度等级划分 | 指标 |
|---|---|
| 特强 | 1≤RI<2 |
| 强 | 2≤RI<3 |
| 中等 | 3≤RI<4 |
| 弱 | RI≥4 |
| Gk | SI百分位取值区间 |
|---|---|
| 1 | ≥95% |
| 2 | [85%,95%) |
| 3 | [60%,85%) |
| 4 | <60% |
| 5 | 无高温 |
表2 单站高温综合强度等级划分
Tab.2 Classification of intensity levels for single station high temperature
| Gk | SI百分位取值区间 |
|---|---|
| 1 | ≥95% |
| 2 | [85%,95%) |
| 3 | [60%,85%) |
| 4 | <60% |
| 5 | 无高温 |
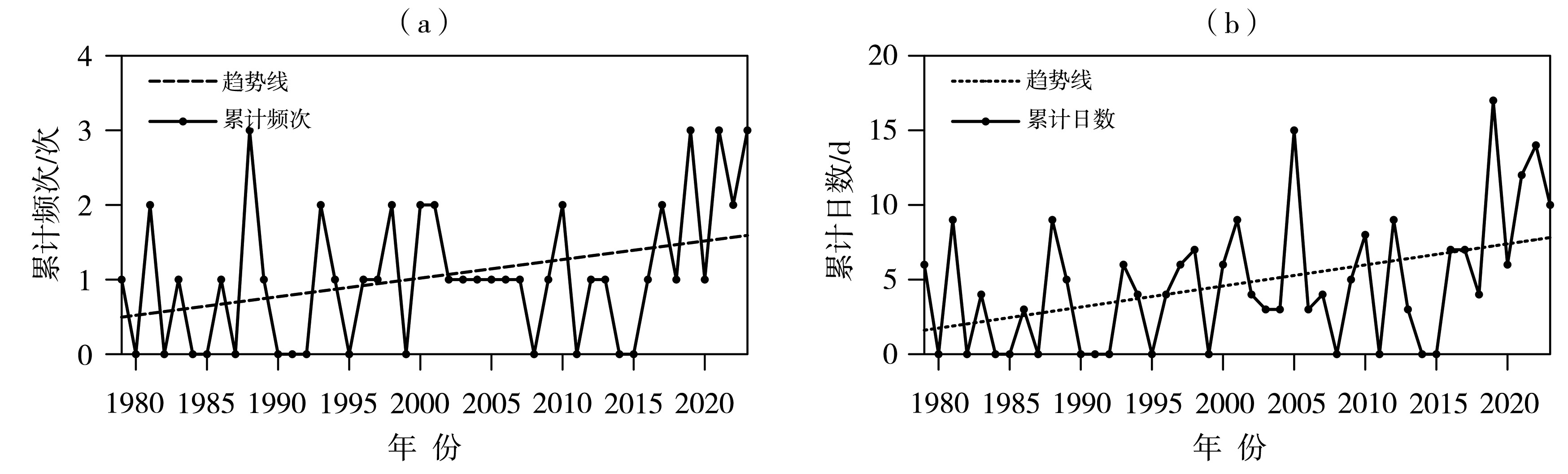
图2 1979—2023年山东省6月区域高温过程年累计频次(a)及累计日数(b)变化
Fig.2 Interannual changes in the cumulative frequency (a) and cumulative days (b) of regional high-temperature processes in June in Shandong Province from 1979 to 2023
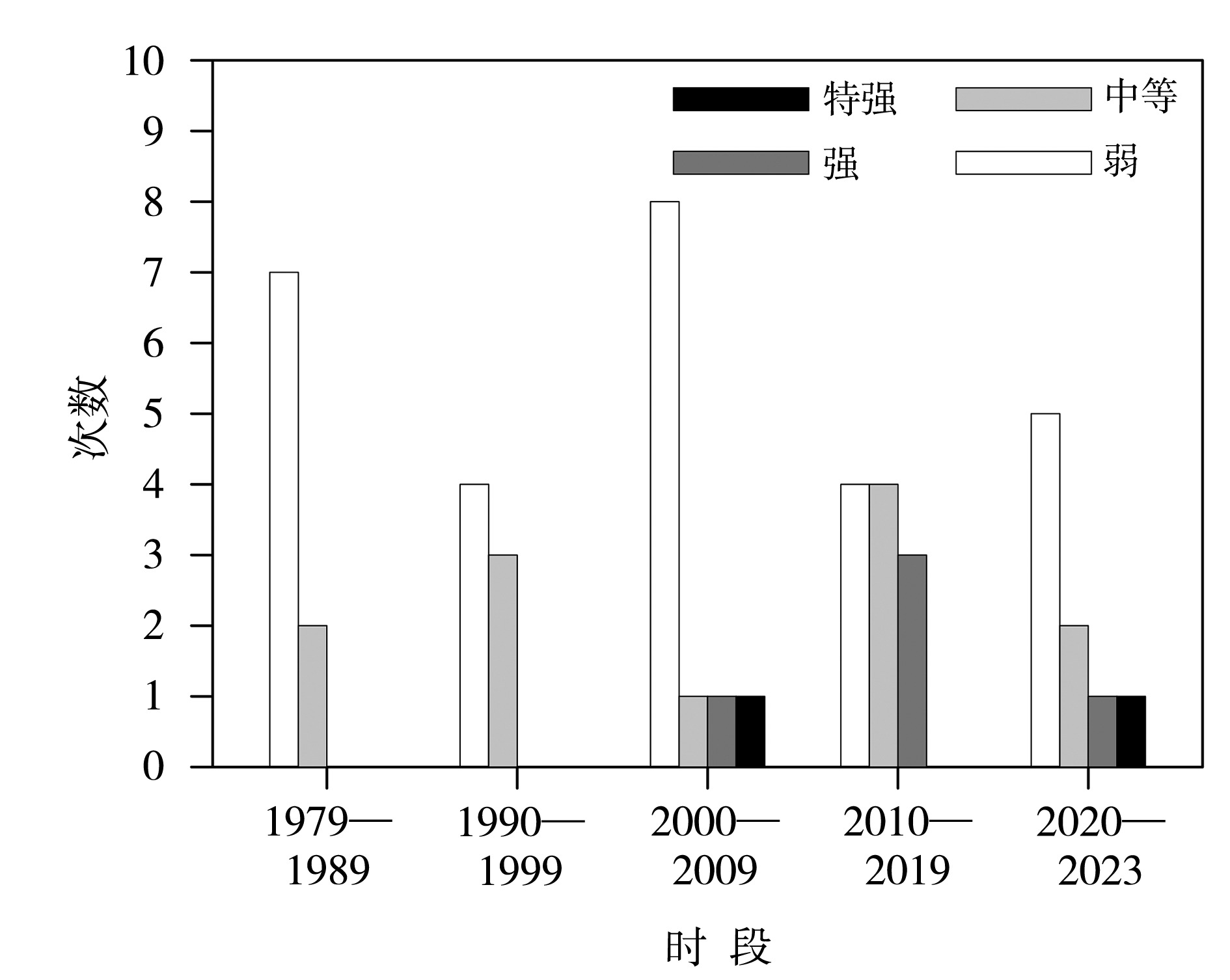
图3 山东省1979—2023年不同时段不同等级区域高温过程发生次数变化
Fig.3 Changes in the number of regional high-temperature processes with different classes in Shandong Province in different periods from 1979 to 2023
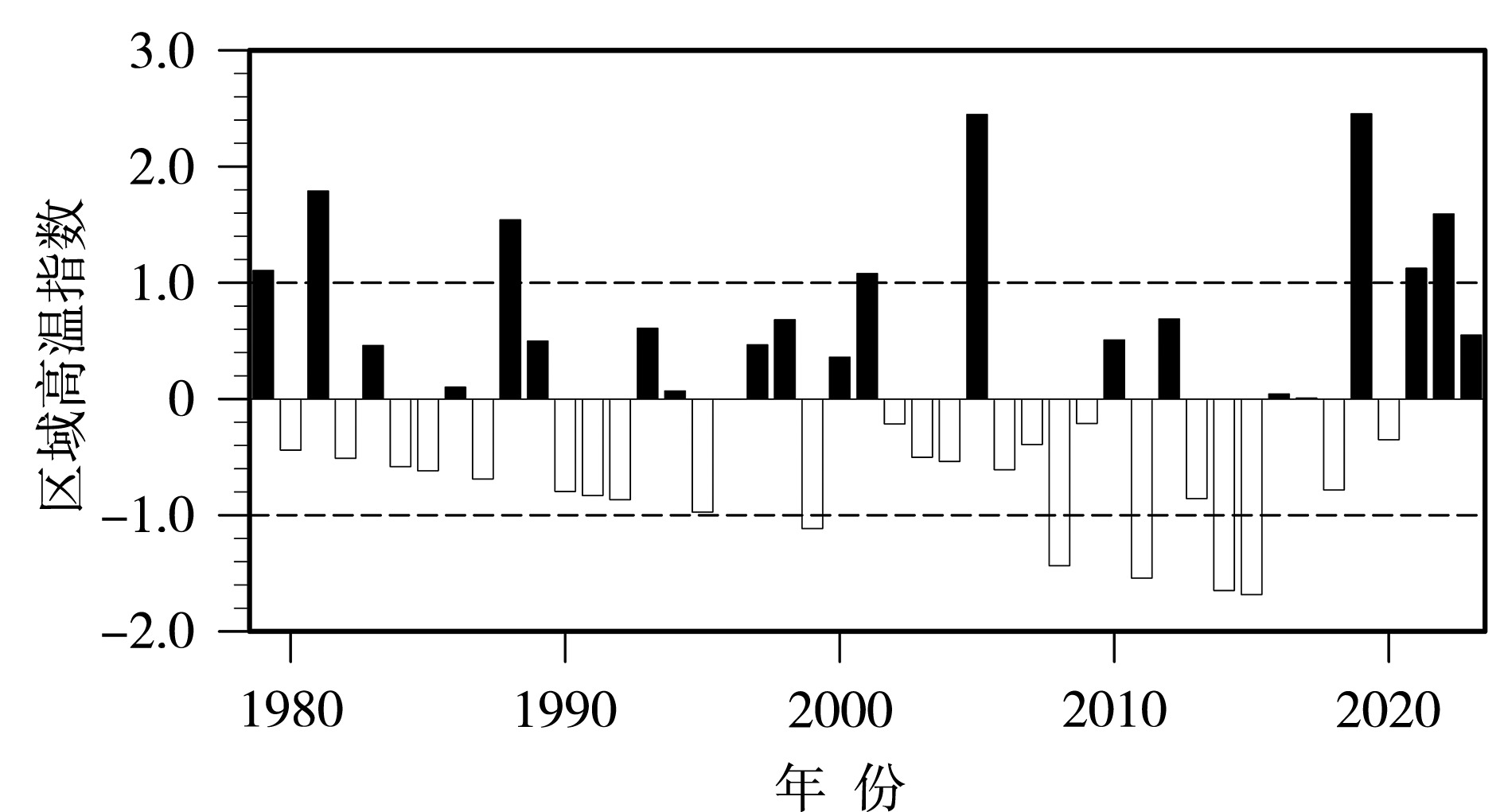
图4 山东省1979—2023年6月去趋势标准化区域高温指数逐年变化(黑色虚线代表±1个标准差)
Fig.4 The annual variation of the detrended standardized RPH in Shandong Province from 1979 to 2023(The black dashed lines represent ±1 standard deviation)

图5 山东区域高温强年500 hPa高度距平场(a)及850 hPa温度距平场(b)正距平频率(单位:%)(黑色框线内黑色线包围区域为山东省,下同)
Fig.5 The positive anomaly frequency of the 500 hPa height anomaly field (a) and 850 hPa temperature anomaly field (b) synthesized by the regional high temperature strong years in Shandong (Unit:%) (The enclosed by the black line within the black box indicates Shandong Province,the same as below)

图6 1979—2023年山东6月区域持续高温指数与海温距平场相关系数的空间分布(黑色圆点表示达到95%置信水平)
Fig.6 The spatial distribution of the correlation coefficients between sea surface temperature anomaly and RPH in Shandong during 1979-2023 (The black dots indicate reaching the 95% confidence level)
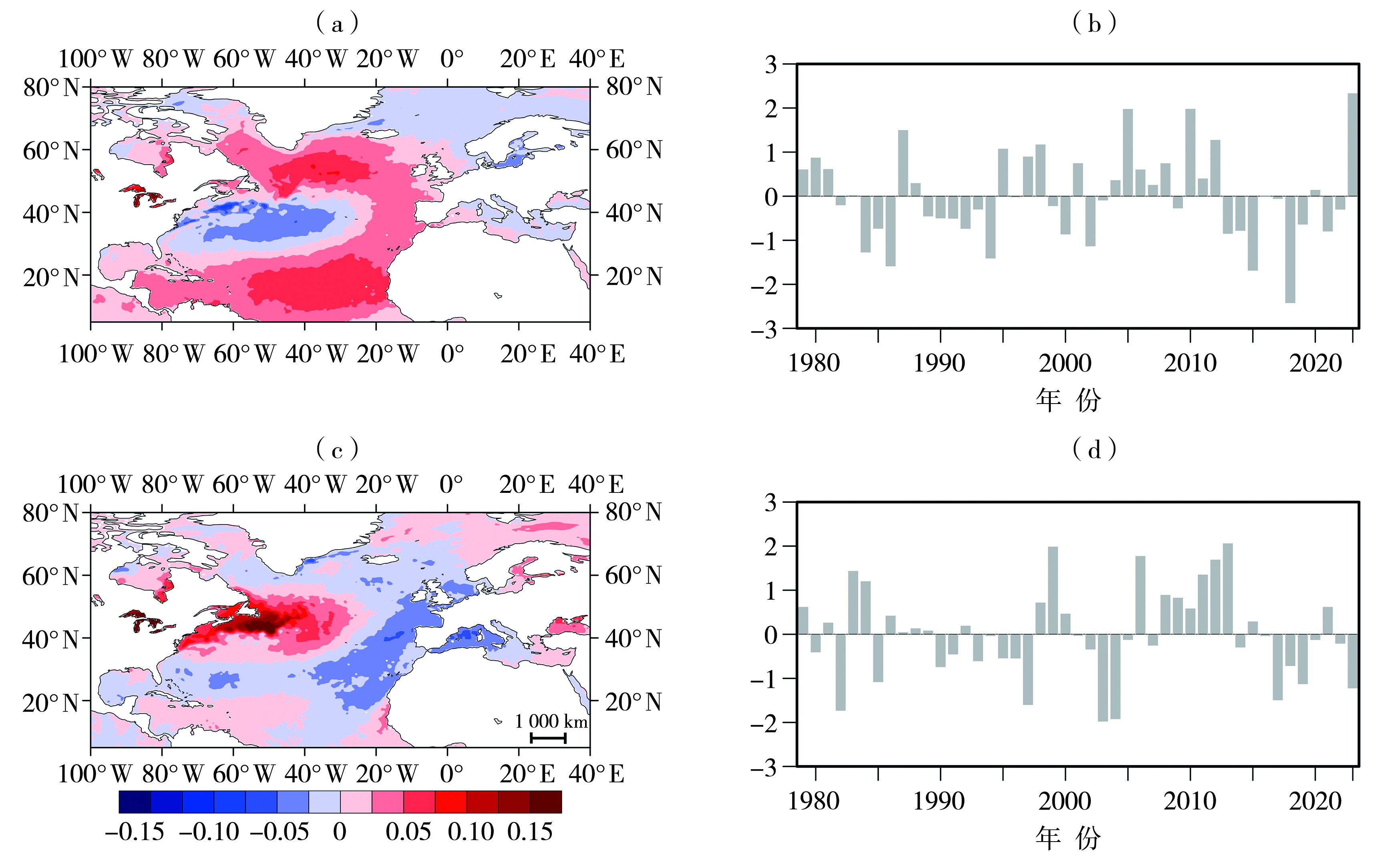
图7 1979—2023年6月海温EOF分解的第一(a、b)、第二(c、d)模态(a、c)及标准化时间系数(b、d)
Fig.7 The first (a, b) and second (c, d) EOF modes (a, c) of sea surface temperature in June with their standardized time coefficients (b, d) during 1979-2023

图8 1979—2023年6月海温EOF第一模态标准化时间系数及RPH随时间的变化
Fig.8 Time series of the standardized time coefficient of the first EOF mode of sea surface temperature in June and RPH from 1979 to 2023

图9 NAT负位相典型年200 hPa TN波作用通量的水平分量(箭矢,单位:m2·s-2)及其散度(填色,单位:m·s-2)(a)以及500 hPa TN波作用通量的垂直分量[b,单位:(hPa)2·s?1]的合成(黑色方框为关键区,红色箭头为TN波作用通量传播路径)
Fig.9 Composite of the TNX of the 200 hPa (arrow vectors, Unit: m2·s-2) and its divergence (the color shaded, Unit: m·s-2) (a) and the TNz of the 500 hPa (b, Unit: (hPa)2·s?1) during typical NAT negative-phase years (The black box is the critical zone, the red arrows indicate propagation pathways of TN wave activity flux)
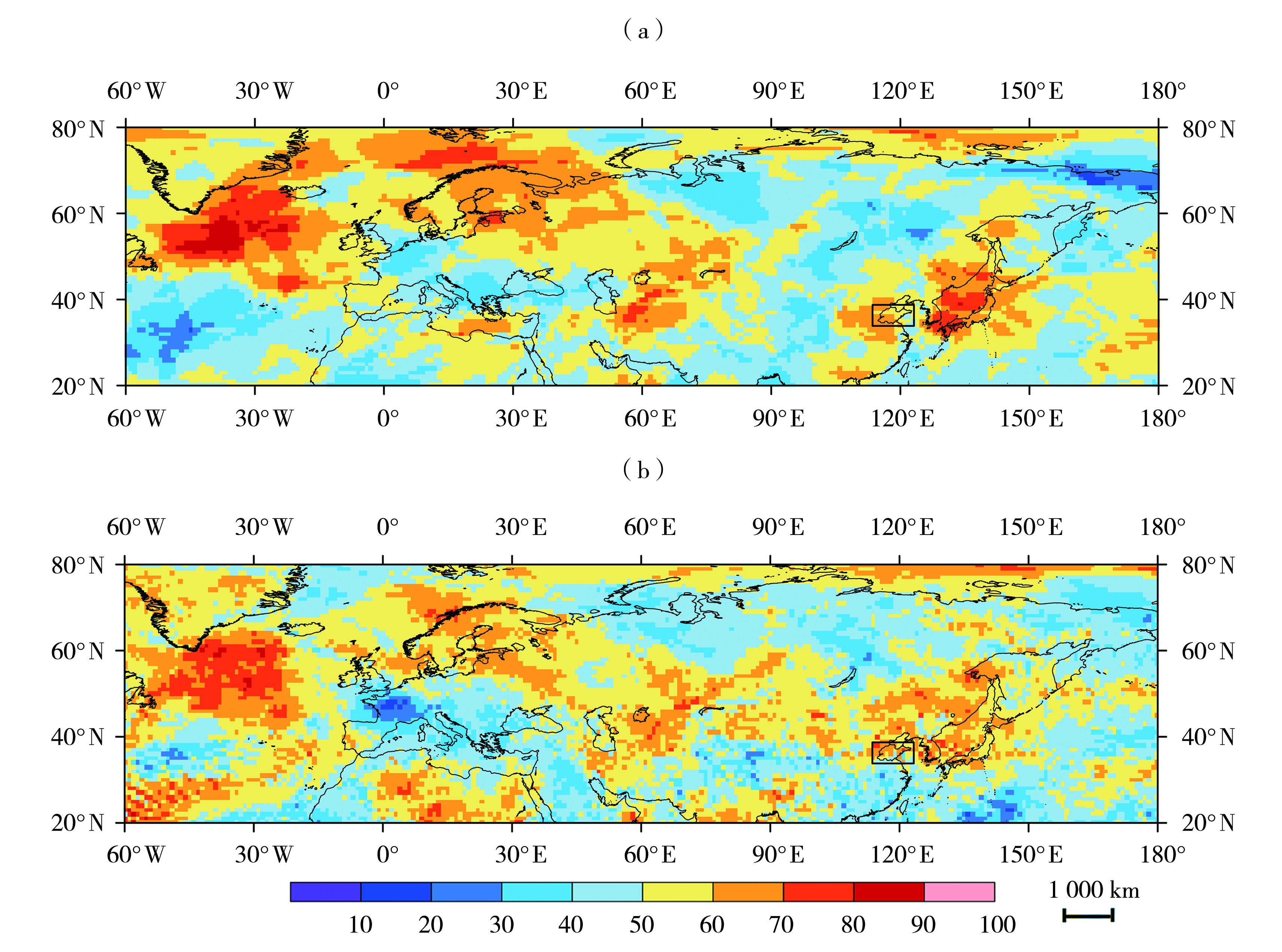
图10 NAT负位相典型年500 hPa高度距平场(a)及850 hPa温度距平场(b)正距平频率(单位:%)
Fig.10 The positive anomaly frequency of the 500 hPa height anomaly field (a) and the 850 hPa temperature anomaly field (b) synthesized by the typical years of NAT-negative phase (Unit: %)
| [1] | 柏庆顺, 颜鹏程, 蔡迪花, 等, 2019. 近56 a中国西北地区不同强度干旱的年代际变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 37(5): 722-728. |
| [2] | 陈磊, 王式功, 尚可政, 等, 2011. 中国西北地区大范围极端高温事件的大气环流异常特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 31(4):1052-1 058. |
| [3] |
陈笑笑, 黄治勇, 秦鹏程, 等, 2024. 长江中游夏季高温异常的大气环流和海温特征[J]. 干旱气象, 42(4): 553-562.
DOI |
| [4] | 董少柔, 林爱兰, 董彦彤, 2023. 1961—2017年华南区域性持续高温过程年际变化成因分析[J]. 大气科学, 47(5):1325-1 340. |
| [5] | 范潇丹, 2020. 热带太平洋与热带大西洋的海温梯度统计关系研究[J]. 气候变化研究快报(6):700-710. |
| [6] | 冯蜀青, 王海娥, 柳艳香, 等, 2019. 西北地区未来10 a气候变化趋势模拟预测研究[J]. 干旱气象, 37(4): 557-564. |
| [7] | 葛家荣, 任雪娟, 2019. 南亚高压次季节尺度东西振荡对我国长江流域降水及水汽输送的影响[J]. 气象科学, 39(6):711-720. |
| [8] |
郝立生, 马宁, 何丽烨, 2022. 2022年长江中下游夏季异常干旱高温事件之环流异常特征[J]. 干旱气象, 40(5):721-732.
DOI |
| [9] | 候启, 赵玉洁, 陈小苏, 2024. 近60年山东省5—8月高温热浪变化特征分析[J]. 陕西气象(2):30-37. |
| [10] | 李蕾, 吴琼, 邓超, 2024. 1961—2022年中国东部高温日数区域差异特征[J]. 气象与减灾研究, 47(2):104-112. |
| [11] | 李瑞英, 吕桂恒, 郝晓雷, 等, 2024. 鲁西南区域性高温干旱复合事件特征及危险性分析[J]. 中国农业气象, 45(6):657-668. |
| [12] | 李艳, 栗晗, 叶培龙, 等, 2014. 1980—2010年华北地区极端高温天气气候事件特征分析[J]. 兰州大学学报:自然科学版, 50(6):832-837. |
| [13] | 林爱兰, 谷德军, 彭冬冬, 等, 2021. 近60年我国东部区域性持续高温过程变化特征[J]. 应用气象学报, 32(3):302-314. |
| [14] | 彭京备, 刘舸, 孙淑清, 2016. 2013年我国南方持续性高温天气及副热带高压异常维持的成因分析[J]. 大气科学, 40(5):897-906. |
| [15] | 全国气象防灾减灾标准化技术委员会, 2014. 区域性高温天气过程等级划分:QX/T 228-2014[S]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [16] | 时晓曚, 孙即霖, 孙雅文, 等, 2015. 北大西洋秋季“三极子”海温结构对冬季大气环流场的影响[J]. 海洋学报, 37(7):33-40. |
| [17] | 史军, 丁一汇, 崔林丽, 2009. 华东极端高温气候特征及成因分析[J]. 大气科学, 33(2):347-358. |
| [18] | 孙建奇, 王会军, 袁薇, 2011. 我国极端高温事件的年代际变化及其与大气环流的联系[J]. 气候与环境研究, 16(2):199-208. |
| [19] | 孙亚卿, 李春, 石剑, 2022. 长江流域夏季极端高温的年代际变化特征及其与大西洋多年代际振荡的关系[J]. 中国海洋大学学报:自然科学版, 52(2):13-22. |
| [20] | 王国复, 叶殿秀, 张颖娴, 等, 2018. 2017年我国区域性高温过程特征及异常大气环流成因分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 14(4):341-349. |
| [21] | 王慧美, 刘舸, 彭京备, 等, 2021. 热带大西洋海温异常季节内演变对中国江南地区夏季持续性高温事件影响的初步研究[J]. 大气科学, 45(2):300-314. |
| [22] | 王劲松, 费晓玲, 魏锋, 2008. 中国西北近50 a来气温变化特征的进一步研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 28(4):724-732. |
| [23] | 王林, 徐霈强, 2024. 北半球夏季急流遥相关:进展与展望[J]. 大气科学, 48(1):287-304. |
| [24] | 王喜元, 闫业超, 岳书平, 等, 2016. 1961—2010年长江流域高温热浪时空变化特征[J]. 云南大学学报:自然科学版, 38(4):602-609. |
| [25] | 王亚伟, 翟盘茂, 田华, 2006. 近40年南方高温变化特征与2003年的高温事件[J]. 气象, 32(10):27-33. |
| [26] | 卫捷, 孙建华, 2007. 华北地区夏季高温闷热天气特征的分析[J]. 气候与环境研究, 12(3):453-463. |
| [27] | 肖贻青, 2017. 乌拉尔山阻塞与北大西洋涛动的关系及其对中国冬季天气的影响[J]. 高原气象, 36(6):1499-1 511. |
| [28] |
许婷婷, 杨霞, 周鸿奎, 2022. 1981—2019年新疆区域性高温天气过程时空特征及其环流分型[J]. 干旱气象, 40(2):212-221.
DOI |
| [29] |
颜鹏程, 李忆平, 曾鼎文, 等, 2024. 2024年4—6月我国区域性高温干旱特征及其影响因子[J]. 干旱气象, 42(4): 507-518.
DOI |
| [30] |
杨涵洧, 封国林, 2016. 2013年盛夏中国持续性高温事件诊断分析[J]. 高原气象, 35(2):484-494.
DOI |
| [31] | 尹泽疆, 魏维, 杨崧, 2023. 北大西洋涛动和英国-鄂霍次克海走廊型遥相关对2022年盛夏长江中下游极端高温的影响[J]. 大气科学学报, 46(3):345-353. |
| [32] | 翟盘茂, 潘晓华, 2003. 中国北方近50年温度和降水极端事件变化[J]. 地理学报, 58(增刊1):1-10. |
| [33] |
张强, 2022. 科学解读“2022年长江流域重大干旱”[J]. 干旱气象, 40(4):545-548.
DOI |
| [34] | 张迎新, 张守保, 2010. 2009年华北平原大范围持续性高温过程的成因分析[J]. 气象, 36(10):8-13. |
| [35] | 邹瑾, 李君, 高理, 等, 2022. 山东区域性高温的变化特征及其对增暖的响应[J]. 气象科技, 50(6):802-811. |
| [36] | DING T, QIAN W H, YAN Z W, 2010. Changes in hot days and heat waves in China during 1961-2007[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 30(10): 1 452-1 462. |
| [37] |
DING T, YUAN Y, ZHANG J M, et al, 2019. 2018: The hottest summer in China and possible causes[J]. Journal of Meteorological Research, 33(4): 577-592.
DOI |
| [38] | EASTERLING D R, EVANS J L, GROISMAN P Y, et al, 2000. Observed variability and trends in extreme climate events: A brief review[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 81(3): 417-426. |
| [39] | GONG D Y, PAN Y Z, WANG J A, 2004. Changes in extreme daily mean temperatures in summer in Eastern China during 1955-2000[J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 77(1): 25-37. |
| [40] | HERSBACH H, BELL B, BERRISFORD P, et al, 2020. The ERA5 global reanalysis[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 146(730): 1 999-2 049. |
| [41] | HSU P C, QIAN Y T, LIU Y, et al, 2020. Role of abnormally enhanced MJO over the Western Pacific in the formation and subseasonal predictability of the record-breaking Northeast Asian heatwave in the summer of 2018[J]. Journal of Climate, 33(8): 3 333-3 349. |
| [42] | IPCC, 2021. Climate Change 2021: The physical science basis[R]. Cambridge and New York: Cambridge University Press. |
| [43] | ITO H, JOHNSON N C, XIE S P, 2013. Subseasonal and interannual temperature variability in relation to extreme temperature occurrence over East Asia[J]. Journal of Climate, 26(22): 9 026-9 042. |
| [44] | KANAMITSU M, EBISUZAKI W, WOOLLEN J, et al, 2002. NCEP-DOE AMIP-II reanalysis (R-2)[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 83(11): 1 631-1 644. |
| [45] | LOU W P, YAO Y P, SUN K, et al, 2019. Variability of heat waves and recurrence probability of the severe 2003 and 2013 heat waves in Zhejiang Province, Southeast China[J]. Climate Research, 79 (1): 63-75. |
| [46] |
MEEHL G A, TEBALDI C, 2004. More intense, more frequent, and longer lasting heat waves in the 21st century[J]. Science, 305(5686): 994-997.
DOI PMID |
| [47] | ROBINE J M, CHEUNG S L K, ROY S L, et al, 2008. Death toll exceeded 70 000 in Europe during the summer of 2003[J]. Comptes Rendus Biologies, 331(2): 171-178. |
| [48] | SAHA S, MOORTHI S, PAN H L, et al, 2010. The NCEP climate forecast system reanalysis[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 91(8): 1 015-1 058. |
| [49] | TAKAYA K, NAKAMURA H, 1997. A formulation of a wave-activity flux for stationary Rossby waves on zonally varying basic flow[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 24(23): 2 985-2 988. |
| [50] | TANG Q H, ZHANG X J, FRANCIS J A, 2014. Extreme summer weather in northern mid-latitudes linked to a vanishing cryosphere[J]. Nature Climate Change, 4(1): 45-50. |
| [51] | WANG H M, LIU G, CHEN J M, 2017. Contribution of the tropical western Atlantic thermal conditions during the preceding winter to summer temperature anomalies over the lower reaches of the Yangtze River basin-Jiangnan region[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 37(13): 4 361-4 642. |
| [52] | WU B Y, FRANCIS J A, 2019. Summer arctic cold anomaly dynamically linked to East Asian heat waves[J]. Journal of Climate, 32(4): 1 137-1 150. |
| [53] | WU R G, YANG S, LIU S, et al, 2011. Northeast China summer temperature and North Atlantic SST[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 116(D16): D16116. DOI: 10.1029/2011JD015779. |
| [54] | WU X H, XU Y M, CHEN H J, 2020. Study on the spatial pattern of an extreme heat event by remote sensing: A case study of the 2013 extreme heat event in the Yangtze River Delta, China[J]. Sustainability, 12(11): 4 415. DOI: 10.3390/su12114415. |
| [55] | XU P Q, WANG L, DONG Z Z, et al, 2022. The British-Okhotsk Corridor pattern and its linkage to the Silk Road pattern[J]. Journal of Climate, 35(17): 5 787-5 804. |
| [56] | XU Y, GAO X J, SHEN Y, et al, 2009. A daily temperature dataset over China and its application in validating a RCM simulation[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 26(4): 763-772. |
| [57] | YU T T, FENG J, CHEN W, et al, 2022. The interdecadal change of the relationship between North Indian Ocean SST and tropical North Atlantic SST[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 127(6): e2022JD037078. DOI: 10.1029/2022JD037078. |
| [58] | ZHANG G W, ZENG G, LI C, et al, 2020. Impact of PDO and AMO on interdecadal variability in extreme high temperatures in North China over the most recent 40-year period[J]. Climate Dynamcis, 54(6): 3 003-3 020. |
| [1] | 胡跃鹏, 赵军平, 刘汉华, 付远, 孙善磊, 宋子祎. 2024年7—9月浙江省极端高温成因分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(4): 499-509. |
| [2] | 张丽, 沈柏竹, 李天宇, 金赫, 王凌. 东北地区低温春涝事件形成机制及其影响[J]. 干旱气象, 2025, 43(4): 586-594. |
| [3] | 陈笑笑, 黄治勇, 秦鹏程, 夏智宏, 姚瑶, 汤兴芝, 汪应琼. 长江中游夏季高温异常的大气环流和海温特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(4): 553-562. |
| [4] | 刘炜, 赵艳丽, 高晶, 李林惠, 王慧敏. 2022年7月内蒙古干旱半干旱区涝—旱转折事件的成因分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(1): 11-18. |
| [5] | 娄德君, 李永生, 王永光, 陈晨, 张健. 2020年7月黑龙江极端少雨成因初探[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(3): 396-405. |
| [6] | 吕星玥, 荣艳淑, 石丹丹. 长江中下游地区2010/2011年秋冬春连旱成因再分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2019, 37(2): 198-208. |
| [7] | 郑广芬,王素艳,杨建玲,丁小谨,李欣. 基于前期海温异常的宁夏5~9月候降水量客观预测方法及检验评估[J]. 干旱气象, 2016, 34(1): 43-50. |
| [8] | 曾鼎文,李耀辉,张文波,苟 尚. CAM3.0模式中北大西洋风暴轴对;三核型;海温异常的响应[J]. 干旱气象, 2015, 33(1): 70-77. |
| [9] | 魏锋, 王劲松. 中国西北地区7~9月上旬降水与北太平洋海温异常的关系[J]. J4, 2010, 28(4): 396-400. |
| [10] | 郝立生, 陆维松. 热带海温异常影响华北夏季降水的机制研究[J]. J4, 2006, 24(2): 5-11. |
| [11] | 王谦谦, 陈绍东. 江南地区汛期降水与热带海温关系的SVD 分析[J]. J4, 2004, 22(3): 11-16. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||