干旱气象 ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (6): 900-909.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639-2024-06-0900
山西省两次极端大暴雪过程对比分析
- 山西省气象台,山西 太原 030006
-
收稿日期:2024-02-23修回日期:2024-05-11出版日期:2024-12-31发布日期:2025-01-15 -
通讯作者:赵桂香(1965—),女,硕士,正高级工程师,从事中小尺度数值诊断和灾害性天气预报技术研究。E-mail:liyun0123@126.com。 -
作者简介:王思慜(1985—),女,硕士,高级工程师,从事灾害性天气预报技术研究。E-mail:280105280@qq.com。 -
基金资助:中国气象局创新发展专项(CXFZ2024J011)
Comparative analysis of two extreme snowstorms in Shanxi Province
WANG Simin( ), ZHAO Guixiang(
), ZHAO Guixiang( ), ZHAO Yu, ZHAO Jianfeng, SHEN Liwen
), ZHAO Yu, ZHAO Jianfeng, SHEN Liwen
- Shanxi Meteorological Observatory, Taiyuan 030006, China
-
Received:2024-02-23Revised:2024-05-11Online:2024-12-31Published:2025-01-15
摘要:
为加深对极端暴雪的认识,揭示异常影响因子导致极端暴雪的可能性,利用气象观测资料和再分析资料,对2021年2月24日和2月27日至3月1日(分别简称“过程Ⅰ”和“过程Ⅱ”)山西两次大暴雪天气过程的极端性进行对比分析。结果表明:过程Ⅰ是一次对流性暴雪过程,由高原槽、地面倒槽和回流的共同作用引起;强烈的西南暖湿急流在“冷垫”上迅速爬升和对称不稳定共同导致潜在不稳定能量快速释放,造成过程降水范围集中、降雪强度大、持续时间短;过程中,冷空气迅速侵入,降水相态由雨迅速转为雪。过程Ⅱ是以稳定性为主的降雪过程,受高空槽、地面气旋和倒槽共同影响;在系统性冷空气侵入过程中,形成降水范围大、持续时间长的极端暴雪过程;此次降雪过程降水相态变化复杂。两次过程在降水开始前,环流形势、水汽输送机制、不稳定机制和上升运动分布特征存在显著差异。过程期间,局地比湿、700 hPa能量和上升运动均较历史同期异常偏大,这是极端天气出现的重要原因之一。两次过程降水中心均位于降水前6~12 h异常物理量中心的下游,水汽输送和湿层增厚也对降水开始时间有一定指示意义。降水相态的转换与温度的垂直分布和锋面结构密切相关。
中图分类号:
引用本文
王思慜, 赵桂香, 赵瑜, 赵建峰, 申李文. 山西省两次极端大暴雪过程对比分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(6): 900-909.
WANG Simin, ZHAO Guixiang, ZHAO Yu, ZHAO Jianfeng, SHEN Liwen. Comparative analysis of two extreme snowstorms in Shanxi Province[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(6): 900-909.

图1 2021年2月24日08:00—25日08:00(a)、2月27日08:00—3月1日08:00(b)累计降水量空间分布(单位:mm)
Fig.1 The spatial distribution of accumulated precipitation from 08:00 on February 24 to 08:00 on February 25 (a) and from 08:00 on February 27 to 08:00 on March 1 (b), 2021 (Unit: mm)
| 降雪过程 | 出现时间 | 是否突破极值 | 降水范围 | 降水性质 | 持续时间 | 相态转换 | 雷电 | 伴随天气 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 过程Ⅰ | 2月下旬 | 是 | 山西南部 | 对流 | 8~15 h | 快 | 有 | 雾 |
| 过程Ⅱ | 2月下旬 | 是 | 山西全省 | 混合 | 27~32 h | 慢 | 有 | 雾 |
表1 两次降雪过程实况特征对比
Tab.1 Comparison of the characteristics of the two snowfall processes
| 降雪过程 | 出现时间 | 是否突破极值 | 降水范围 | 降水性质 | 持续时间 | 相态转换 | 雷电 | 伴随天气 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 过程Ⅰ | 2月下旬 | 是 | 山西南部 | 对流 | 8~15 h | 快 | 有 | 雾 |
| 过程Ⅱ | 2月下旬 | 是 | 山西全省 | 混合 | 27~32 h | 慢 | 有 | 雾 |

图2 2021年2月24日08:00 500 hPa高度场(黑色实线,单位:dagpm)及其标准化距平场(填色)(a),海平面气压场(黑色实线,单位:hPa)及其标准化距平场(填色)(b) (棕色实线表示槽线,字母“D”、“G”分别表示低压、高压中心位置,红色实线包围区域为山西省,下同)
Fig.2 The 500 hPa geopotential height field (black solid lines, Unit: dagpm) and its standardized anomaly field (the color shaded) (a), sea-level pressure field (black solid lines, Unit: hPa) and its standardized anomaly field (the color shaded) (b) at 08:00 on February 24, 2021 (Brown solid lines represent trough lines, the letters “D” and “G” denote the positions of low and high pressure centers respectively, and the area enclosed by the red solid line is Shanxi Province, the same as below)

图3 2021年2月27日14:00 500 hPa高度场(黑色实线,单位:dagpm)及其标准化距平场(填色)(a),海平面气压场(黑色实线,单位:hPa)及其标准化距平场(填色)(b)
Fig.3 The 500 hPa height field (black solid lines, Unit: dagpm) and its standardized anomaly field (the color shaded) (a), sea-level pressure field (black solid lines, Unit: hPa) and its standardized anomaly field (the color shaded) (b) at 14:00 on February 27, 2021
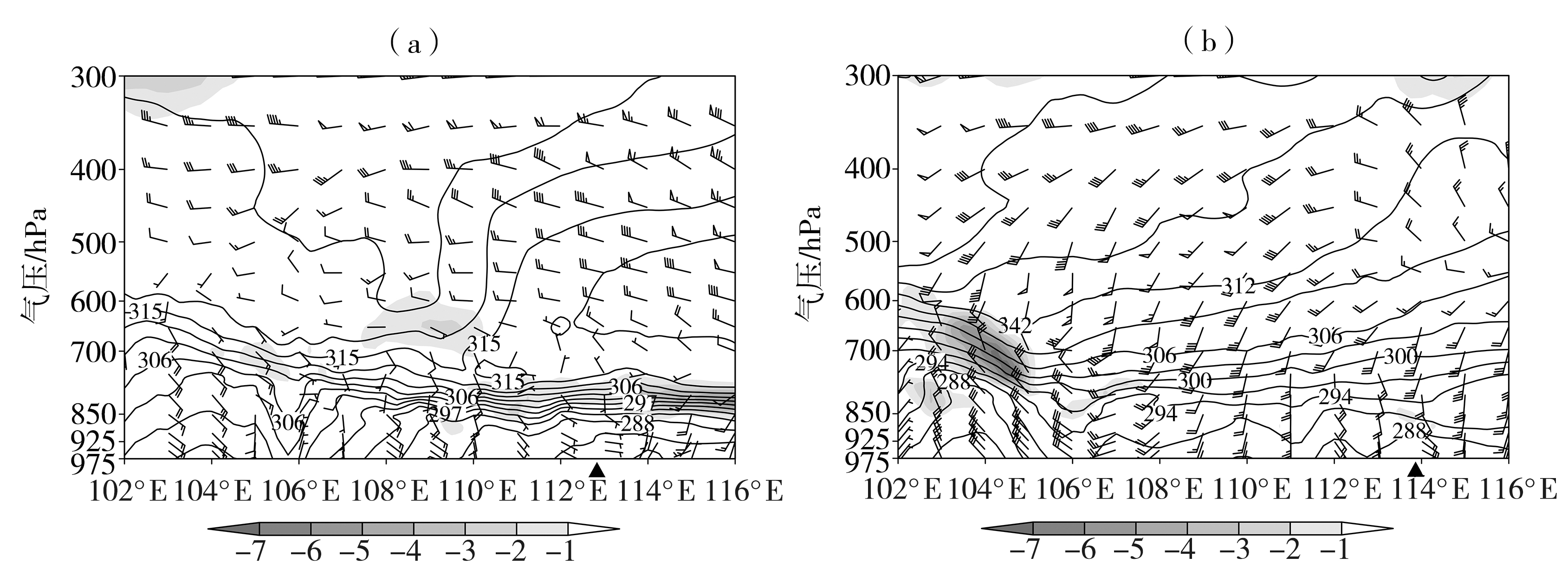
图4 2021年2月24日08:00沿35.8°N(a)和2021年2月27日14:00沿37.9°N(b)的假相当位温(黑色实线,单位:K)、湿斜压对称不稳定(灰色填色,单位:10-6 m2·s-1·K·kg-1)及风场(风矢,单位:m·s-1)的经度-高度剖面 (黑色三角为暴雪中心所在经度)
Fig.4 The longitude-height sections of the pseudo-equivalent potential temperature (black solid lines, Unit: K),wet baroclinic symmetric instability (the grey shaded, Unit: 10-6 m2·s-1·K·kg-1) and wind field (wind vectors, Unit: m·s-1) along 35.8°N at 08:00 on February 24 (a) and along 37.9°N at 14:00 on February 27 (b), 2021 (the black triangle represents the longitude of the center of the snowstorm)

图5 2021年2月24日16:00(a)、16:30(c)和2月28日16:00(b)、16:30(d)红外云图黑体亮温(a、b)及雷达组合反射率因子(c、d)
Fig.5 The black body temperature on infrared cloud images (a, b) and composite radar reflectivity factors (c, d) at 16:00 (a), 16:30 (c) on February 24, 2021 and 16:00 (b), 16:30 (d) on February 28, 2021
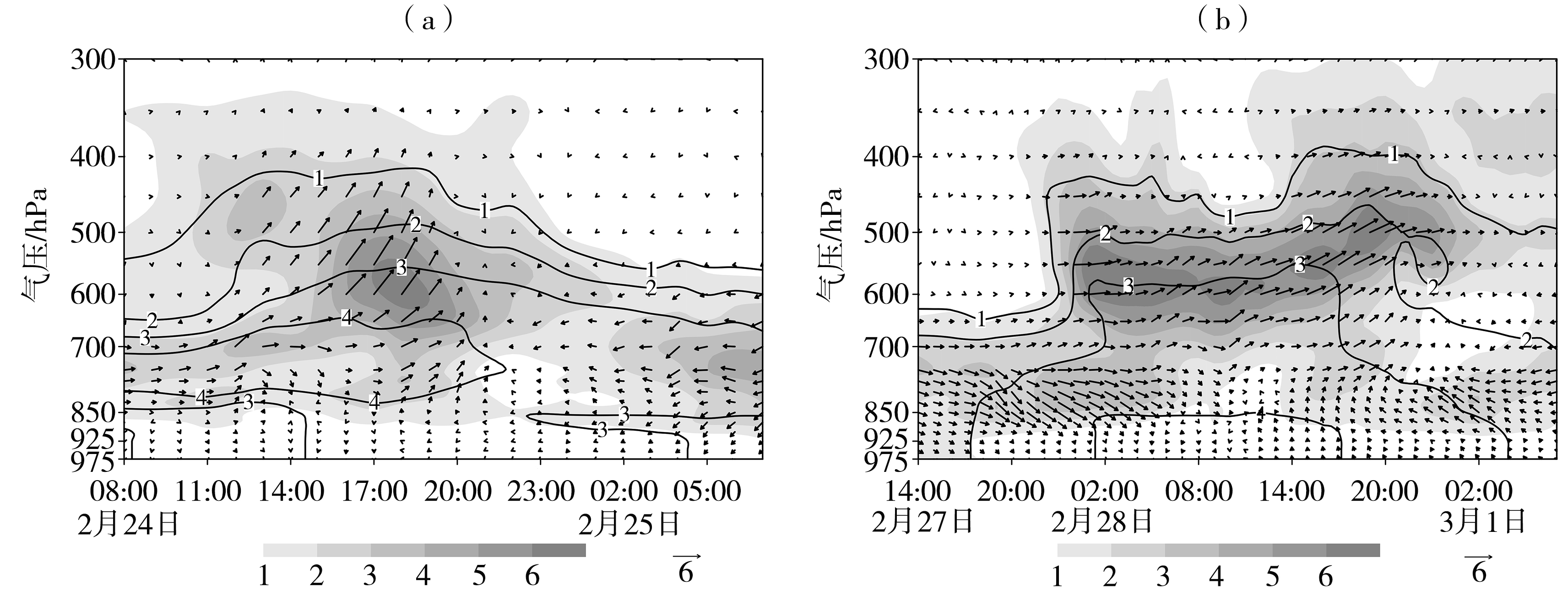
图6 过程Ⅰ(a)和过程Ⅱ(b)沿降水中心[过程Ⅰ(112.9°E, 35.8°N)、过程Ⅱ(113.7°E, 37.9°N)]的比湿(黑色实线,单位:g·kg-1)、水平水汽通量(灰色填色区)和经向垂直水汽通量(箭头)(单位:10-5 kg·m-1·hPa-1·s-1)的时间-高度剖面
Fig.6 The time-height sections of specific humidity (solid black lines, Unit: g·kg-1), horizontal water vapor flux (the gray shaded area), and meridional vertical water vapor flux (arrows) (Unit: 10-5 kg·m-1·hPa-1·s-1) along the precipitation centers of Process Ⅰ (112.9°E, 35.8°N) (a) and Process Ⅱ (113.7°E, 37.9°N) (b)
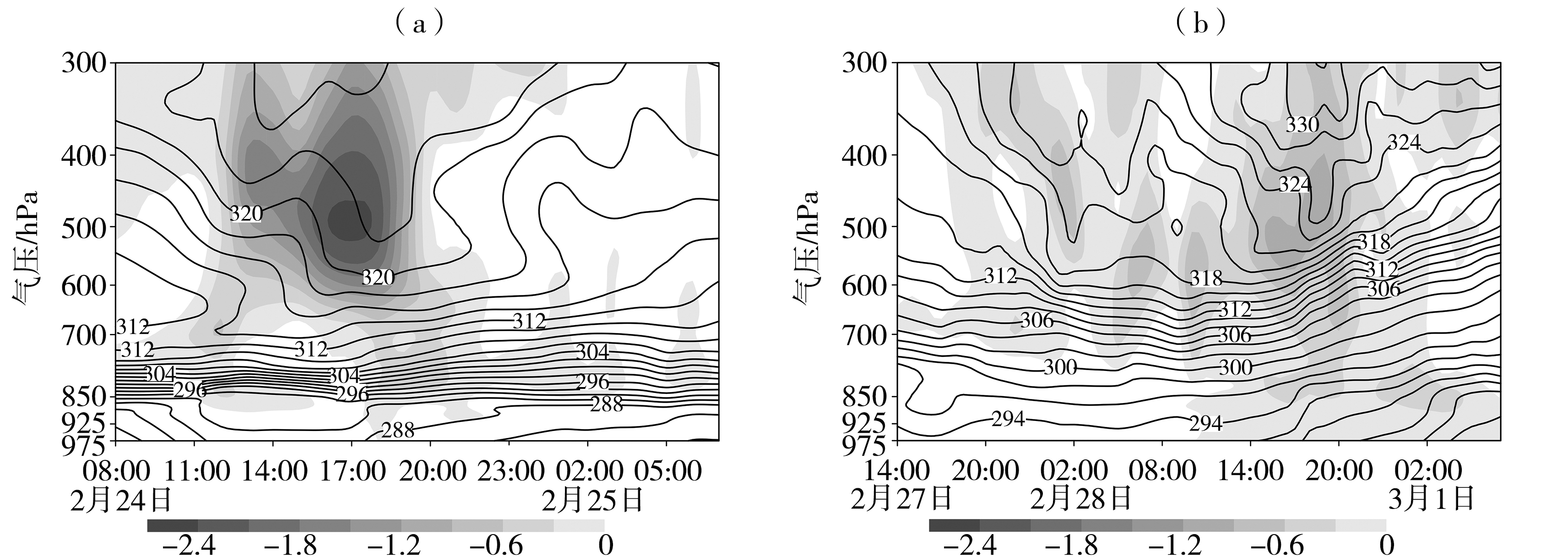
图7 过程Ⅰ(a)和过程Ⅱ(b)沿降水中心[过程Ⅰ(112.9°E, 35.8°N)、过程Ⅱ(113.7°E, 37.9°N)]的假相当位温(黑色实线,单位:K)和垂直速度(灰色填色区,单位:Pa·s-1)的时间-高度剖面
Fig.7 The time-height sections of the pseudo-equivalent potential temperature (solid black lines, Unit: K) and vertical velocity (the gray shaded, Unit: Pa·s-1) along the precipitation centers of the Process Ⅰ (112.9°E, 35.8°N) (a) and the Process Ⅱ (113.7°E, 37.9°N) (b)
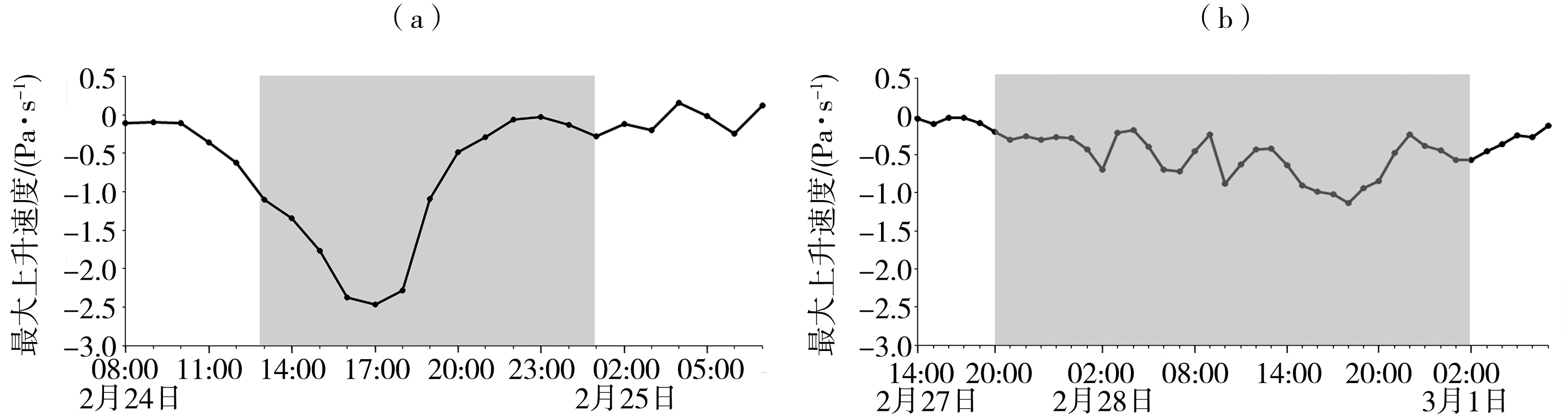
图8 过程Ⅰ(a)和过程Ⅱ(b)500 hPa以下最大上升速度随时间演变 (灰色矩形框表示过程降水时段)
Fig.8 The evolution of maximum ascending velocity under 500 hPa during the Process Ⅰ (a) and the Process Ⅱ (b) (the gray box represents the period of snowfall)
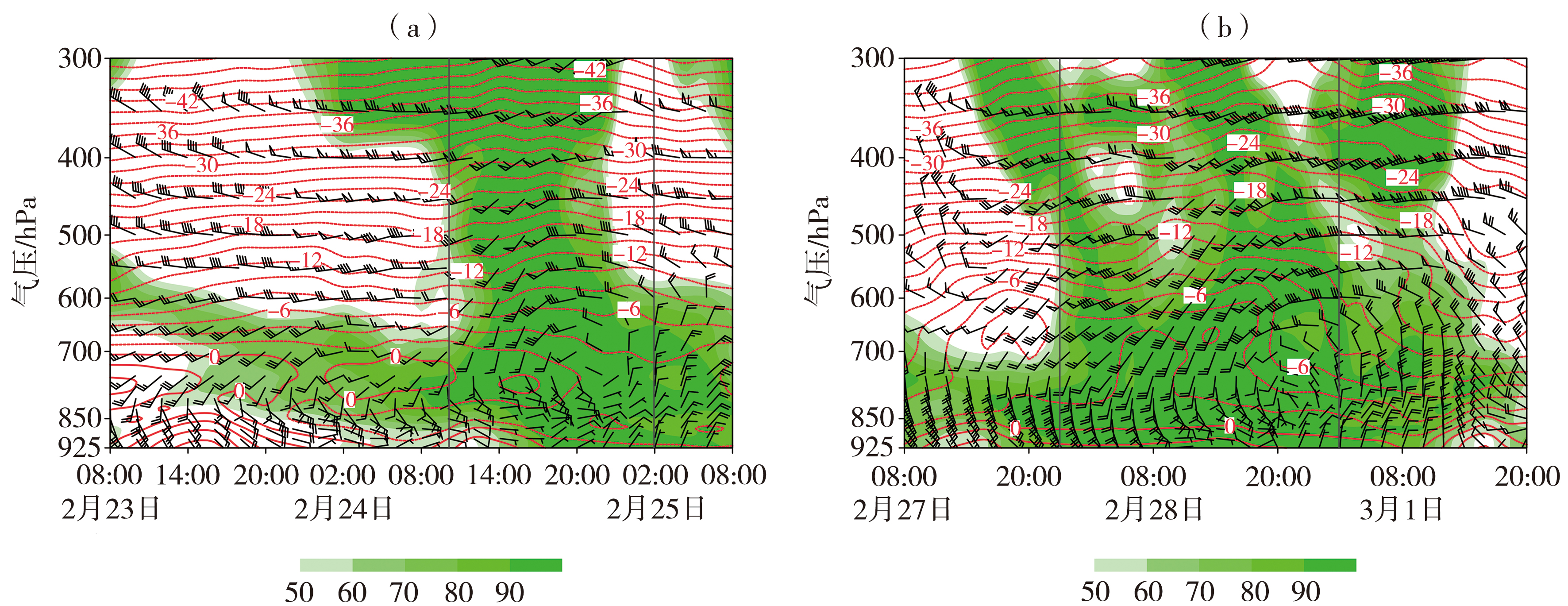
图9 2021年2月23—25日(a)、2月27日—3月1日(b)高平站(112.9°E,35.8°N)温度场(红线,单位:℃)、水平风场(风矢,单位:m·s-1)和相对湿度(填色,单位:%)的时间-高度剖面 (两条竖线之间为降水时段)
Fig.9 The time-height sections of temperature (red lines, Unit: ℃), horizontal wind field (wind vectors, Unit: m·s-1), and relative humidity (the color shaded, Unit: %) at Gaoping Station (112.9°E, 35.8°N) from 23 to 25 February (a) and from 27 February to 1 March (b), 2021 (Between the two vertical lines is the precipitation period)
| [1] | 杜佳, 杨成芳, 戴翼, 等, 2019. 北京地区4月一次罕见暴雪的形成机制分析[J]. 气象, 45(10):1363-1 374 |
| [2] |
郭英香, 冯晓莉, 刘畅, 等, 2023. 1961-2021年青藏高原前后冬强降雪特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 41(5): 723-733.
DOI |
| [3] | 胡宁, 符娇兰, 孙军, 等, 2021. 北京一次冬季极端降水过程中相态转换预报的误差分析[J]. 气象学报, 79(2): 328-339. |
| [4] | 胡鹏, 蔡哲, 张永靖, 等, 2015. 一次伴有雷暴的暴雪天气成因机理分析[J]. 气象科学, 35(2): 210-215. |
| [5] | 李典南, 许东蓓, 苟尚, 等, 2019. 甘肃中部一次冷锋后高架雷暴天气过程综合诊断[J]. 干旱气象, 37(5): 809-816. |
| [6] | 孟雪峰, 孙永刚, 霍志丽, 等, 2022. 内蒙古一次极端暴雪事件中冻雨成因分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 16(4): 22-30. |
| [7] | 任伟, 任燕, 全林生, 等, 2024. 山东西北部一次极端暴雪的动力和热力特征[J]. 陕西气象(2): 8-15. |
| [8] | 王喜, 王琴, 向阳, 等, 2020. 2018年1月江苏3次致灾暴雪成因对比分析[J]. 海洋气象学报, 40(1): 134-143. |
| [9] | 王一颉, 赵桂香, 马严枝, 2019. 降水相态转换机制及积雪深度预报技术研究[J]. 干旱气象, 37(6): 964-971. |
| [10] | 徐娟娟, 郝丽, 刘嘉慧敏, 等, 2020. 2018年1月陕西区域性暴雪过程诊断[J]. 干旱气象, 38(1): 117-125. |
| [11] |
闫慧, 赵桂香, 张朝明, 等, 2015. 山西中部一次暴雪天气过程分析[J]. 干旱气象, 33(5): 838-844.
DOI |
| [12] | 阎琦, 崔锦, 杨青, 2019. 2018年辽宁两次雨转暴雪过程对比分析[J]. 干旱气象, 37(6): 944-953. |
| [13] | 杨成芳, 李泽椿, 2018. 近十年中国海效应降雪研究进展[J]. 海洋气象学报, 38(4): 1-10. |
| [14] | 杨军, 2014. 2013年卫星遥感应用技术交流论文集[M]. 北京: 气象出版社: 136-150. |
| [15] | 杨淑华, 赵桂香, 程海霞, 等, 2021. 山西两类暴雪过程的雷达产品特征比较及降雪量估测[J]. 干旱气象, 39(3): 436-447. |
| [16] |
张桂莲, 刘澜波, 孟雪峰, 等, 2022. 冷垫背景下回流暴雪成因与雷达回波特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 40(3): 500-506.
DOI |
| [17] |
张入财, 王君, 陈超辉, 等, 2023. 印度双低涡对青藏高原西部一次典型暴雪过程的影响[J]. 干旱气象, 41(3): 463-473.
DOI |
| [18] |
赵桂香, 2014. 诊断分析技术在山西强降雪预报中的应用[J]. 高原气象, 33(3): 838-847.
DOI |
| [19] | 赵桂香, 2007. 一次回流与倒槽共同作用产生的暴雪天气分析[J]. 气象, 33(11): 41-48. |
| [20] | 赵桂香, 2021. 山西省大雪天气研究[M]. 北京: 气象出版社:172-175. |
| [21] | 赵桂香, 程麟生, 李新生, 2007. “04.12”华北大到暴雪过程切变线的动力诊断[J]. 高原气象, 26(3): 615-623. |
| [22] | 赵桂香, 杜莉, 范卫东, 等, 2011a. 山西省大雪天气的分析预报[J]. 高原气象, 30(3): 727-738. |
| [23] | 赵桂香, 杜莉, 范卫东, 等, 2011b. 一次冷锋倒槽暴风雪过程特征及其成因分析[J]. 高原气象, 30(6):1516-1 525 |
| [24] | 赵桂香, 杜莉, 郝孝智, 等, 2013. 3次回流倒槽作用下山西大(暴)雪天气比较分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 29(32): 337-349. |
| [25] | CHEN G X, WANG W C, CHENG C T, et al, 2021. Extreme snow events along the coast of the northeast United States: Potential changes due to global warming[J]. Journal of Climate, 34(6): 2 337-2 353 |
| [26] | O’GORMAN P A, 2014. Contrasting responses of mean and extreme snowfall to climate change[J]. Nature, 512: 416-418. |
| [27] |
QUANTE L, WILLNER S N, MIDDELANIS R, et al, 2021. Regions of intensification of extreme snowfall under future warming[J]. Scientific Reports, 11(1): 16621. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-95979-4.
PMID |
| [28] | ZHAO Y, FU L, YANG C F, et al, 2020. Case study of a heavy snowstorm associated with an extratropical cyclone featuring a back-bent warm front structure[J]. Atmosphere, 11(12): 1272. DOI: 10.3390/atmos11121272. |
| [1] | 王一丞, 刘维成, 宋兴宇, 张文光. 卫星降水产品在陇东2022年7月特大暴雨事件中的适用性评估[J]. 干旱气象, 2023, 41(6): 997-1007. |
| [2] | 张君霞, 黄武斌, 杨秀梅, 刘维成, 周子涵, 沙宏娥. 陇东半干旱区一次特大暴雨事件的降水极端性分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(6): 922-932. |
| [3] | 高兴艾, 朱凌云, 闫世明, 裴坤宁, 张逢生, 王淑敏, 成鹏伟. 典型高碳排放城市临汾温室气体时空分布特征及影响因素[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(2): 256-265. |
| [4] | 李清华, 孟洁, 李劲松, 刘月丽, 常清, 姜敏, 郭栋. 山西省不同重现期下电线覆冰厚度空间分布及区划[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(1): 156-165. |
| [5] | 董春卿, 武永利, 郭媛媛, 马丽, 苗青. 山西强对流天气分类指标与判据的应用[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(2): 345-355. |
| [6] | 王君 . 豫北两次特大暴雨事件的物理量极端性和中尺度特征王君[J]. 干旱气象, 2019, 37(3): 419-. |
| [7] | 刘耀龙, 张华明,黄晓丽,常媛媛, 张建新. 山西省冰雪运动气候适宜性评价[J]. 干旱气象, 2019, 37(1): 173-179. |
| [8] | 李军霞,李培仁,晋立军,李义宇,郑煜,刘志宏. 地基微波辐射计在遥测大气水汽特征及降水分析中的应用[J]. 干旱气象, 2017, 35(5): 767-775. |
| [9] | 郭立平,乔林,李成才,周玉都. 河北廊坊“恒温”天气特征及其可预报性分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2016, 34(1): 195-201. |
| [10] | 郭媛媛,董春卿,苗爱梅. 东亚副热带夏季风与山西省夏季降水的关系[J]. 干旱气象, 2014, 32(1): 32-37. |
| [11] | 赵俊荣, 郭金强. 天山北坡中部一次罕见特大暴雪天气成因[J]. J4, 2010, 28(4): 438-442. |
| [12] | 刘耀文 , 张红英 , 史云飞 , 尹振保 , 马子平. 山西省秋季罕见大暴雪天气过程诊断[J]. J4, 2010, 28(3): 332-337. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
