干旱气象 ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (3): 426-436.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2024)-03-0426
山西极端暴雨环流特征及水汽异常研究
周晋红1( ), 王秀明2(
), 王秀明2( ), 田晓婷1, 张泽秀1, 李树文1, 蔡晓芳1
), 田晓婷1, 张泽秀1, 李树文1, 蔡晓芳1
- 1.太原市气象局,山西 太原 030082
2.中国气象局气象干部培训学院,北京 100081
-
收稿日期:2022-11-17修回日期:2023-09-28出版日期:2024-06-30发布日期:2024-07-11 -
通讯作者:王秀明(1977—),女,湖南长沙人,博士,正高级工程师,主要从事灾害性强对流天气形成机理和数值模拟研究。E-mail: wangxm@cma.gov.cn 。 -
作者简介:周晋红(1968—),女,山西太原人,硕士,正高级工程师,主要从事灾害性天气形成机理及预报技术研究。E-mail: zjhlwh@sohu.com。 -
基金资助:山西省科技厅山西省应用基础研究计划面上自然基金项目(201901D111464)
Study on circulation characteristics and water vapor anomaly of extreme rainstorm events in Shanxi Province
ZHOU Jinhong1( ), WANG Xiuming2(
), WANG Xiuming2( ), TIAN Xiaoting1, ZHANG Zexiu1, LI Shuwen1, CAI Xiaofang1
), TIAN Xiaoting1, ZHANG Zexiu1, LI Shuwen1, CAI Xiaofang1
- 1. Taiyuan Meteorological Bureau, Taiyuan 030082, China
2. China Meteorological Administration Training Centre, Beijing 100081, China
-
Received:2022-11-17Revised:2023-09-28Online:2024-06-30Published:2024-07-11
摘要:
研究山西极端暴雨发生规律对开展预报预警、灾害防御具有重要意义。本文利用常规观测资料和欧洲中期天气预报中心(European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts,ECMWF)第五代大气再分析资料(ERA5),采用标准化距平作为异常度,运用环流分析和物理量诊断等方法,研究1981—2018年6—9月山西17次极端暴雨的气候特征、环流影响系统和水汽异常特征。结果表明:山西极端暴雨主要出现在7—8月,暴雨区主要位于中南部,2010年以来极端暴雨明显多发;影响系统主要是700 hPa低涡和台风系统,有偏南和偏东两支水汽通道。极端暴雨过程中,低层水汽含量明显偏高,从暴雨区平均比湿的过程最大值看,大部分过程850 hPa超过14.2 g·kg-1,700 hPa则可超过9.8 g·kg-1、对应暴雨区平均异常度达1.6 以上;水汽的极端性在低层水汽通量辐合中心表现突出,17次极端暴雨700、850 hPa暴雨区水汽通量辐合中心过程最大值的异常度均值分别达-8、-6,其中台风减弱低压影响下的极端暴雨850 hPa水汽通量辐合中心最大异常度达-12。根据以上环流和水汽特征建立极端暴雨概念模型,并给出极端暴雨低层水汽含量和水汽通量辐合强度预报参考指标。
中图分类号:
引用本文
周晋红, 王秀明, 田晓婷, 张泽秀, 李树文, 蔡晓芳. 山西极端暴雨环流特征及水汽异常研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(3): 426-436.
ZHOU Jinhong, WANG Xiuming, TIAN Xiaoting, ZHANG Zexiu, LI Shuwen, CAI Xiaofang. Study on circulation characteristics and water vapor anomaly of extreme rainstorm events in Shanxi Province[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2024, 42(3): 426-436.
| 序号 | 时段 | 日期 | ≥50 mm站数 | ≥100 mm站数 | 暴雨中心 降水量/ mm | 暴雨中心 站点 | 本站暴雨中心降水量排位 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20:00—20:00 | 1981-08-15 | 27 | 13 | 187.5 | 永和 | 1 |
| 2 | 20:00—20:00 | 1982-07-30 | 17 | 4 | 207.0 | 垣曲 | 3 |
| 3 | 20:00—20:00 | 1989-08-16 | 30 | 5 | 151.7 | 沁源 | 2 |
| 4 | 20:00—20:00 | 1992-08-31 | 23 | 6 | 160.0 | 汾西 | 1 |
| 5 | 20:00—20:00 | 1993-08-4 | 29 | 6 | 131.6 | 灵石 | 1 |
| 6 | 20:00—20:00 | 1996-07-31 | 13 | 5 | 178.8 | 安泽 | 1 |
| 7 | 20:00—20:00 | 1996-08-04 | 27 | 6 | 163.8 | 和顺 | 1 |
| 8 | 20:00—20:00 | 2001-07-27 | 49 | 8 | 127.9 | 黎城 | 1 |
| 9 | 20:00—20:00 | 2003-08-26 | 29 | 12 | 117.3 | 安泽 | 5 |
| 10 | 20:00—20:00 | 2005-09-20 | 39 | 5 | 165.5 | 安泽 | 2 |
| 11 | 08:00—08:00 | 2007-07-29 | 24 | 4 | 313.3 | 垣曲 | 1 |
| 12 | 08:00—08:00 | 2011-07-02 | 27 | 6 | 141.0 | 绛县 | 1 |
| 13 | 20:00—20:00 | 2012-07-21 | 19 | 5 | 126.4 | 偏关 | 1 |
| 14 | 20:00—20:00 | 2012-07-31 | 37 | 3 | 221.2 | 晋城 | 1 |
| 15 | 20:00—20:00 | 2013-07-10 | 16 | 5 | 158.4 | 阳城 | 1 |
| 16 | 08:00—08:00 | 2016-07-08 | 18 | 6 | 169.3 | 交口 | 2 |
| 17 | 08:00—08:00 | 2016-07-19 | 39 | 10 | 223.3 | 阳泉 | 1 |
表1 1981—2018年6—9月山西省极端暴雨个例统计
Tab.1 Statistics of the extreme rainstorm events in Shanxi Province from June to September during 1981-2018
| 序号 | 时段 | 日期 | ≥50 mm站数 | ≥100 mm站数 | 暴雨中心 降水量/ mm | 暴雨中心 站点 | 本站暴雨中心降水量排位 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20:00—20:00 | 1981-08-15 | 27 | 13 | 187.5 | 永和 | 1 |
| 2 | 20:00—20:00 | 1982-07-30 | 17 | 4 | 207.0 | 垣曲 | 3 |
| 3 | 20:00—20:00 | 1989-08-16 | 30 | 5 | 151.7 | 沁源 | 2 |
| 4 | 20:00—20:00 | 1992-08-31 | 23 | 6 | 160.0 | 汾西 | 1 |
| 5 | 20:00—20:00 | 1993-08-4 | 29 | 6 | 131.6 | 灵石 | 1 |
| 6 | 20:00—20:00 | 1996-07-31 | 13 | 5 | 178.8 | 安泽 | 1 |
| 7 | 20:00—20:00 | 1996-08-04 | 27 | 6 | 163.8 | 和顺 | 1 |
| 8 | 20:00—20:00 | 2001-07-27 | 49 | 8 | 127.9 | 黎城 | 1 |
| 9 | 20:00—20:00 | 2003-08-26 | 29 | 12 | 117.3 | 安泽 | 5 |
| 10 | 20:00—20:00 | 2005-09-20 | 39 | 5 | 165.5 | 安泽 | 2 |
| 11 | 08:00—08:00 | 2007-07-29 | 24 | 4 | 313.3 | 垣曲 | 1 |
| 12 | 08:00—08:00 | 2011-07-02 | 27 | 6 | 141.0 | 绛县 | 1 |
| 13 | 20:00—20:00 | 2012-07-21 | 19 | 5 | 126.4 | 偏关 | 1 |
| 14 | 20:00—20:00 | 2012-07-31 | 37 | 3 | 221.2 | 晋城 | 1 |
| 15 | 20:00—20:00 | 2013-07-10 | 16 | 5 | 158.4 | 阳城 | 1 |
| 16 | 08:00—08:00 | 2016-07-08 | 18 | 6 | 169.3 | 交口 | 2 |
| 17 | 08:00—08:00 | 2016-07-19 | 39 | 10 | 223.3 | 阳泉 | 1 |
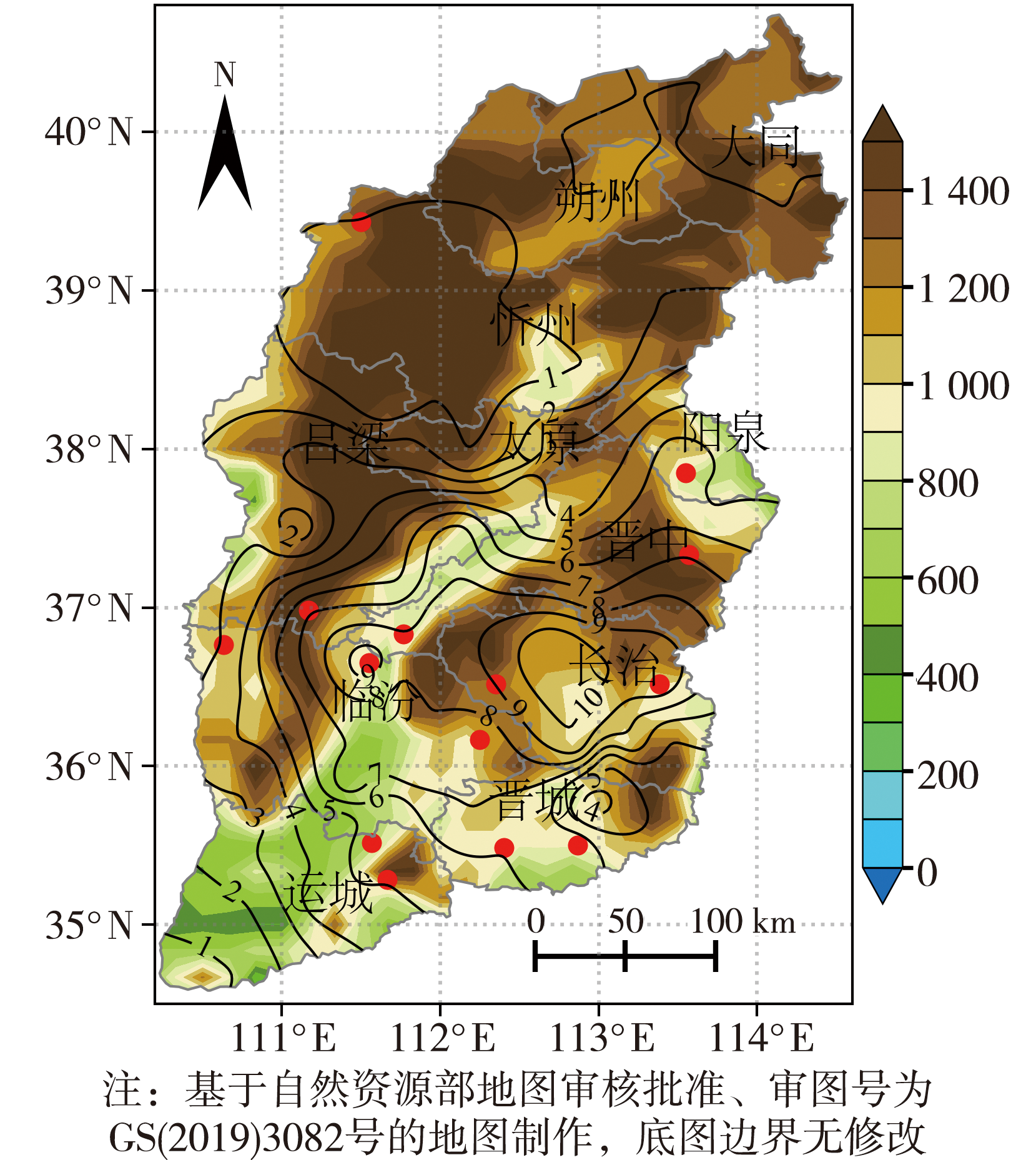
图1 1981—2018年6—9月山西省17次极端暴雨过程50 mm及以上暴雨站次(实线,单位:次)及暴雨中心站点(红色圆点)分布 (彩色填色为地形高度,单位:m)
Fig.1 The distribution of rainstorm stations frequency (solid lines, Unit: times) with daily precipitation equal to and more than 50 mm and rainstorm center stations (red dots) of 17 extreme rainstorm processes in Shanxi Province from June to September during 1981-2018 (The color shaded is terrain height,Unit: m)
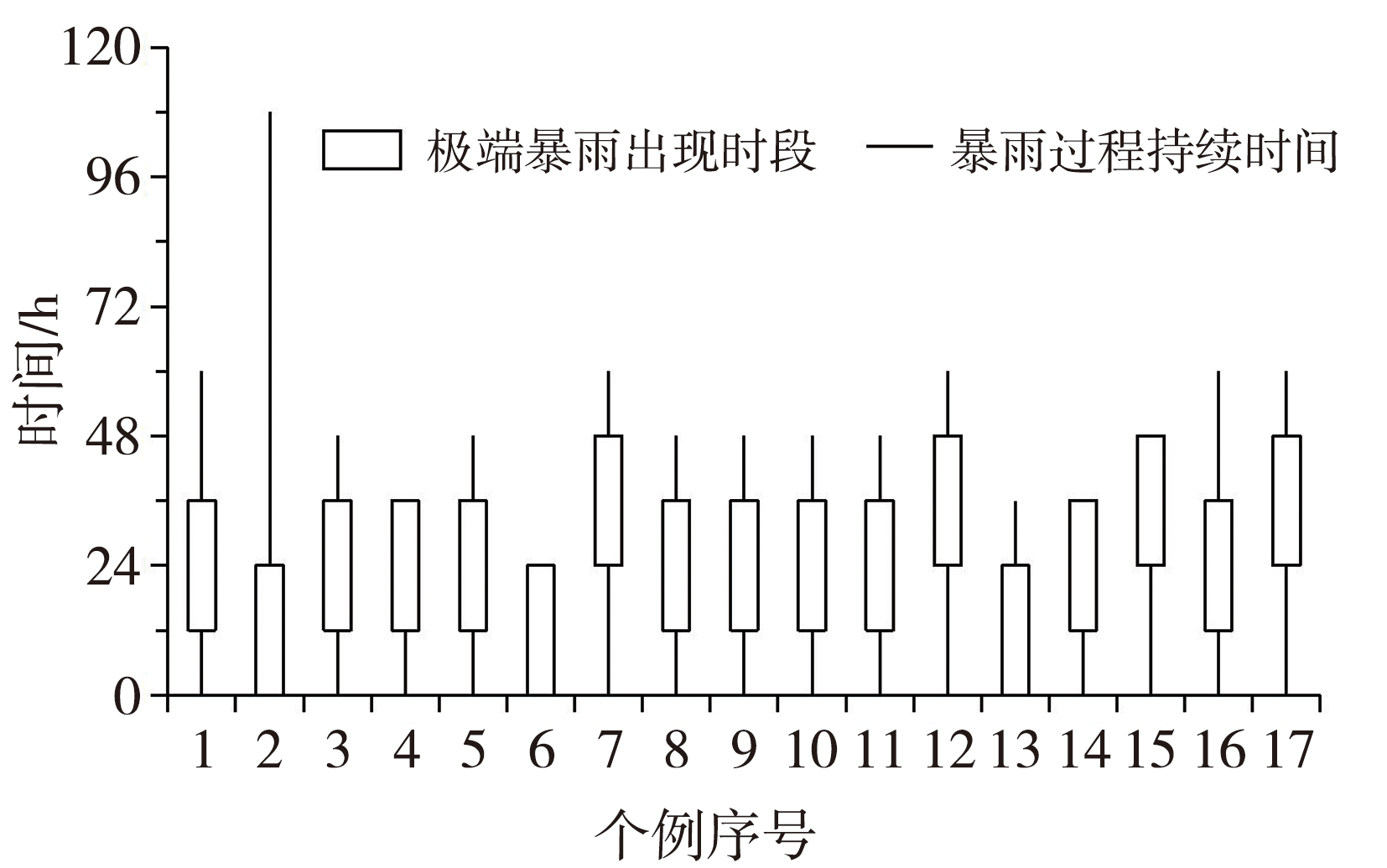
图2 1981—2018年6—9月山西省17次极端暴雨出现时段及对应暴雨过程持续时间
Fig.2 The occurrence time of 17 extreme rainstorms and the duration of corresponding rainstorm processes in Shanxi Province from June to September during 1981-2018
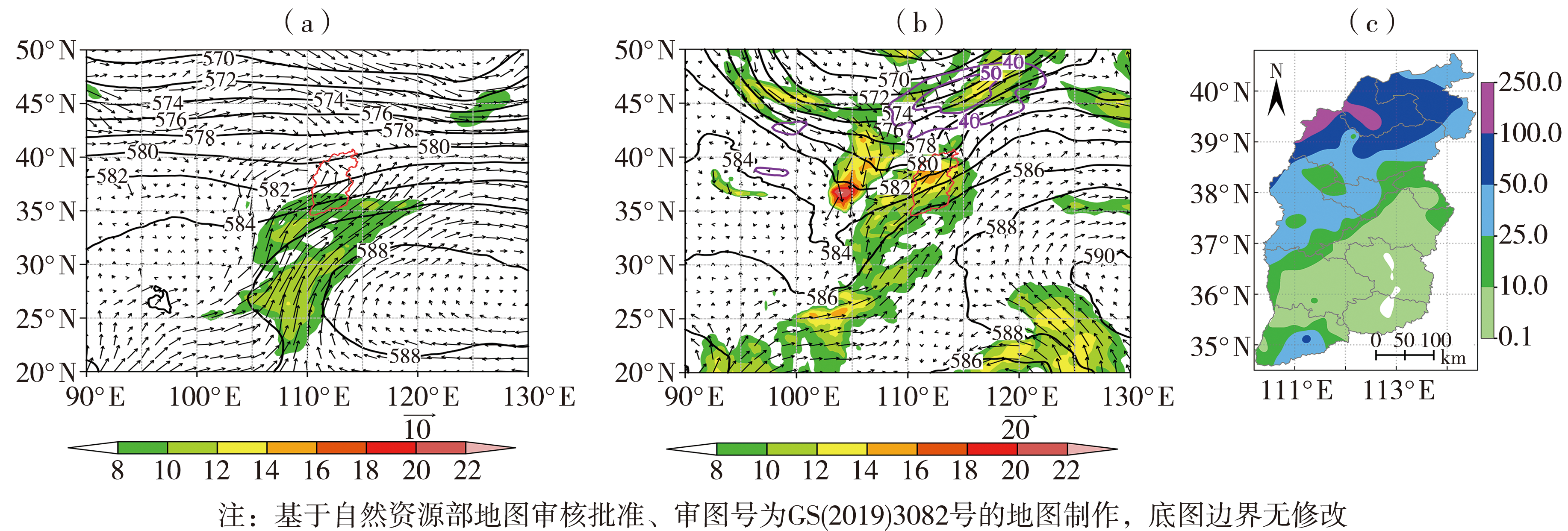
图3 700 hPa低涡型极端暴雨发生期间环流合成场(黑色实线为500 hPa平均位势高度,单位:dagpm;箭矢和彩色填色分别为700 hPa平均风场和风速,单位:m·s-1)(a),2012年7月21日08:00 500 hPa位势高度(黑色实线,单位:dagpm)、700 hPa风场(箭矢)和风速(彩色填色)(单位:m·s-1)、200 hPa≥40 m·s-1风速区(紫色实线,单位:m·s-1)(b),2012年7月20日20:00—21日20:00山西省降水量(单位:mm)空间分布(c) (红色实线区域为山西省。下同)
Fig.3 Circulation composite field during the occurrence of 700 hPa low vortex pattern extreme rainstorms (black solid lines represent average geopotential height on 500 hPa, Unit: dagpm; arrow vectors and color shaded represent 700 hPa average wind field and wind speed, respectively, Unit: m·s-1) (a), 500 hPa geopotential height field (black solid lines, Unit: dagpm), 700 hPa wind field (arrow vectors) and wind speed (color shaded) (Unit: m·s-1), the area of wind speed greater than or equal to 40 m·s-1 on 200 hPa (purple solid lines, Unit: m·s-1) at 08:00 on 21 July 2012 (b), the spatial distribution of precipitation (Unit: mm) in Shanxi Province from 20:00 on 20 to 20:00 on 21 July 2012 (c) (The red solid line area is Shanxi Province. the same as below)

图4 西风带低槽(涡)与台风相互作用型极端暴雨发生期间环流合成场(黑色实线为500 hPa平均位势高度,单位:dagpm;箭矢和彩色填色分别为700 hPa平均风场和风速,单位:m·s-1)(a),1992年8月31日08:00 500 hPa位势高度(黑色实线,单位:dagpm)、700 hPa风场(箭矢)和风速(彩色填色,单位:m·s-1)(b),1992年8月30日20:00—31日20:00山西省降水量(单位:mm)空间分布(c)
Fig.4 Circulation composite field during the extreme rainstorms of interaction pattern between westerly low trough (vortex) and typhoon (black solid lines represent average geopotential height on 500 hPa, Unit: dagpm; arrow vectors and color shaded represent 700 hPa average wind field and wind speed, respectively, Unit: m·s-1) (a), 500 hPa geopotential height field (black solid lines, Unit: dagpm), 700 hPa wind field (arrow vectors) and wind speed (color shaded) (Unit: m·s-1) at 08:00 on 31 August 1992 (b), the spatial distribution of precipitation (Unit: mm) in Shanxi Province from 20:00 on 30 to 20:00 on 31 August 1992 (c)
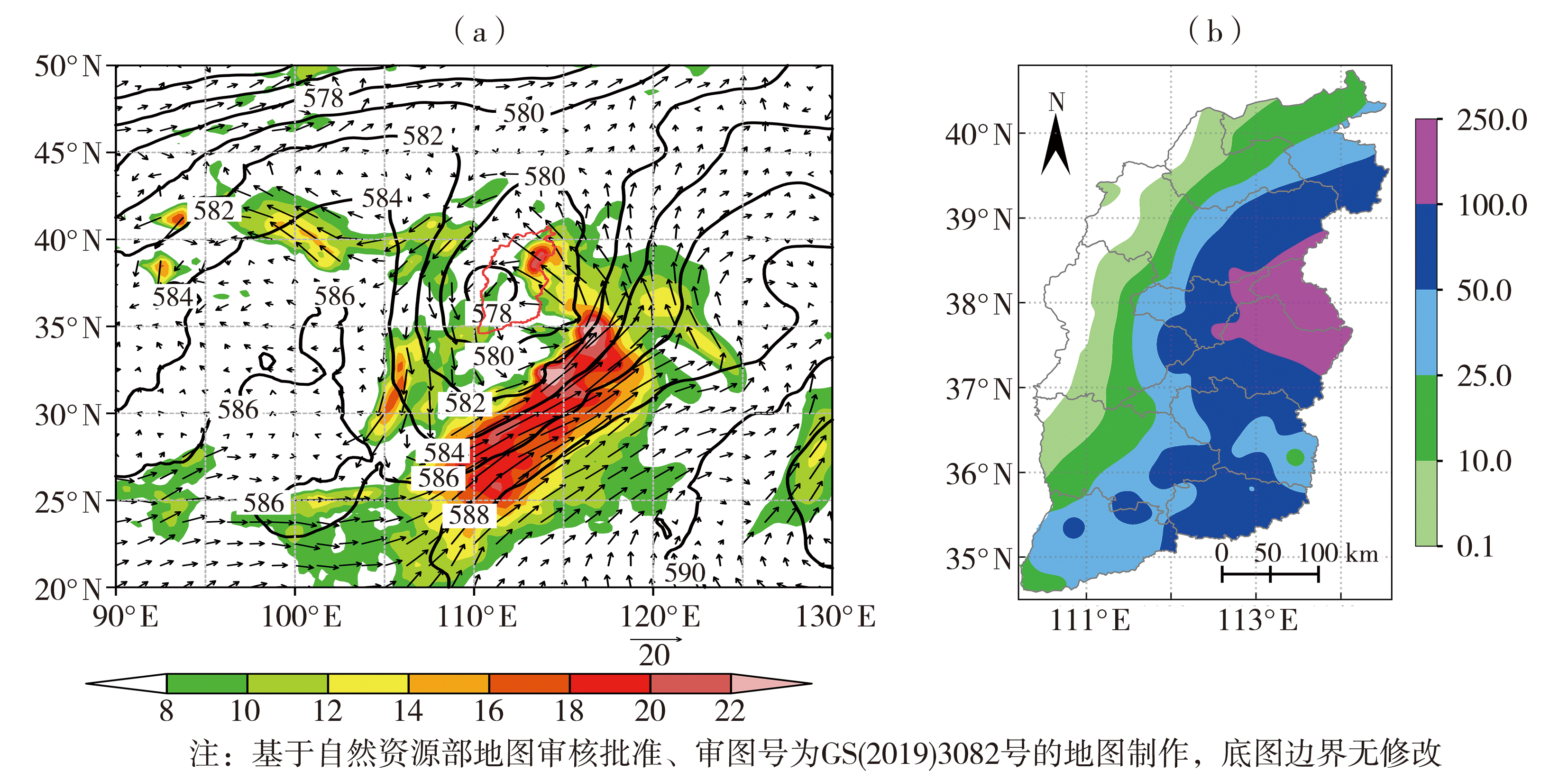
图5 2016年7月19日20:00 500 hPa位势高度场(黑色实线,单位:dagpm)、700 hPa风场(箭矢)及风速(彩色填色)(单位:m·s-1)(a),2016年7月19日08:00—20日08:00山西省降水量(单位:mm)空间分布(b)
Fig.5 The 500 hPa geopotential height field (black solid lines, Unit: dagpm), wind field (arrow vectors) and wind speed (color shaded) (Unit: m·s-1) on 700 hPa at 20:00 on 19 July 2016 (a), the spatial distribution of precipitation (Unit: mm) in Shanxi Province from 08:00 on 19 to 08:00 on 20 July 2016 (b)

图6 1996年8月4日08:00 500 hPa位势高度场(黑色实线,单位:dagpm)、700 hPa风场(箭矢)及风速(彩色填色)(单位:m·s-1)(a),1996年8月3日20:00—4日20:00山西省降水量(单位:mm)空间分布(b)
Fig.6 The 500 hPa geopotential height field (black solid lines, Unit: dagpm), wind field (arrow vectors) and wind speed (color shaded) (Unit: m·s-1) on 700 hPa at 08:00 on 4 August 1996 (a), the spatial distribution of precipitation (Unit: mm) in Shanxi Province from 20:00 on 3 to 20:00 on 4 August 1996 (b)
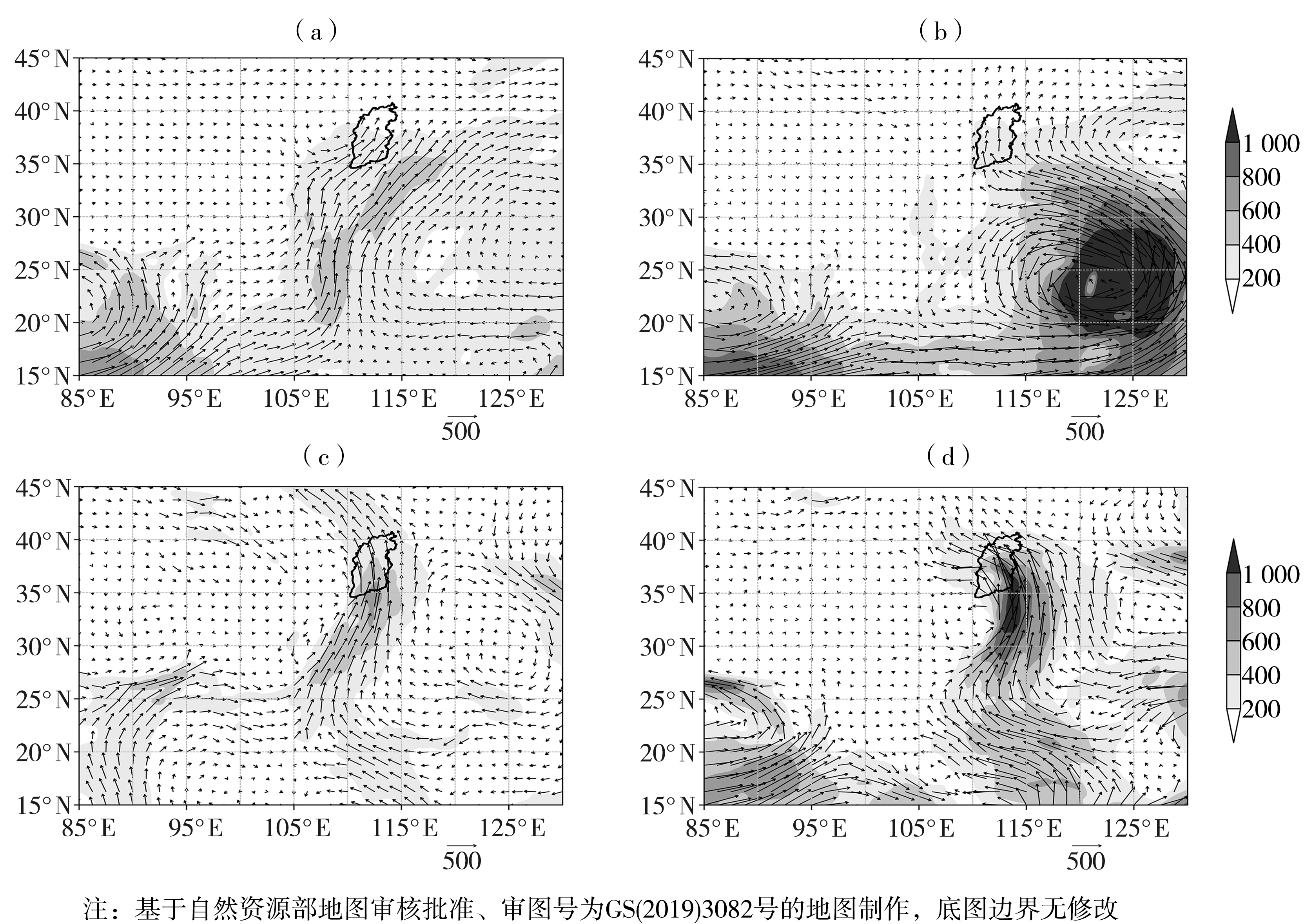
图7 700 hPa低涡型(a)、西风带低槽(涡)与台风相互作用型(b)极端暴雨发生期间地面至300 hPa垂直积分水汽通量合成场(箭矢及阴影,单位:kg·m-1·s-1),冷涡型典型个例2007年7月29日20:00(c)、台风低压型个例1996年8月4日08:00(d)地面至300 hPa垂直积分水汽通量(箭矢及阴影,单位:kg·m-1·s-1) (黑色实线区域为山西省)
Fig.7 The composite fields of vertical integrated vapor flux from the ground to 300 hPa (arrows and shaded, Unit: kg·m-1·s-1) during extreme rainstorms of 700 hPa low vortex pattern (a) and interaction pattern between westerly low trough (vortex) and typhoon (b), the vertical integrated vapor flux from the ground to 300 hPa (arrows and shaded, Unit: kg·m-1·s-1) at 20:00 on 29 July 2007 for typical case of cold vortex pattern (c), and 08:00 on 4 August 1996 for the case of typhoon low pressure pattern (d) (The black solid line area is Shanxi Province)
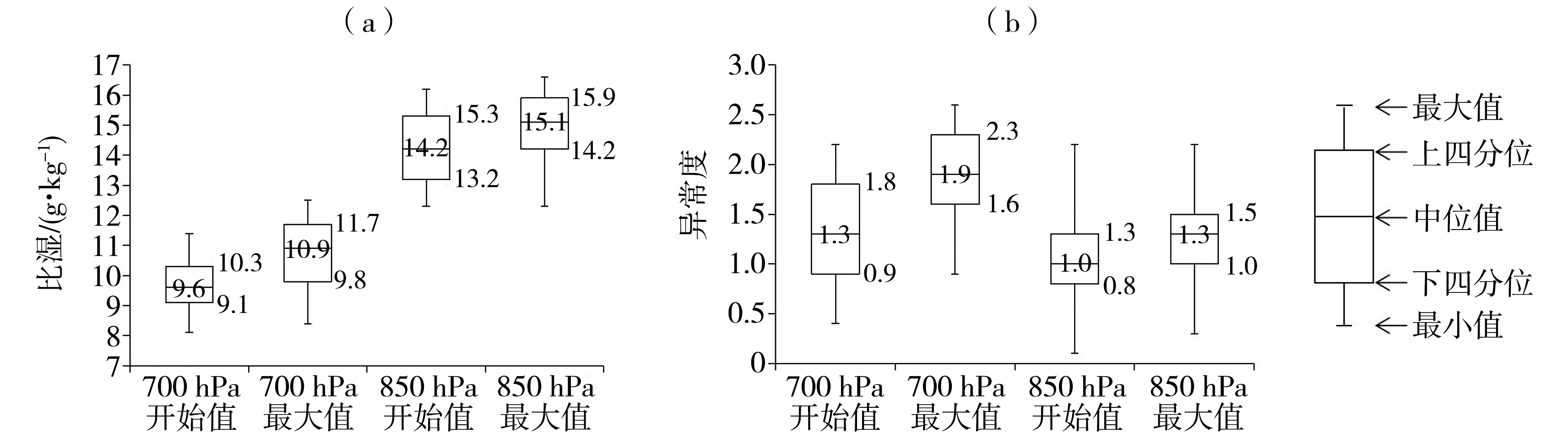
图8 1981—2018年6—9月山西省17次极端暴雨过程850、700 hPa暴雨区降水开始时刻、过程最大平均比湿(a,单位:g·kg-1)及其平均异常度(b)箱线图
Fig.8 The box plot of average specific humidity at the rain beginning and the maximum average specific humidity during the process over the rainstorm area on 850, 700 hPa (a, Unit: g·kg-1) and the corresponding average abnormal degree (b) of 17 extreme rainstorm processes in Shanxi Province from June to September during 1981-2018
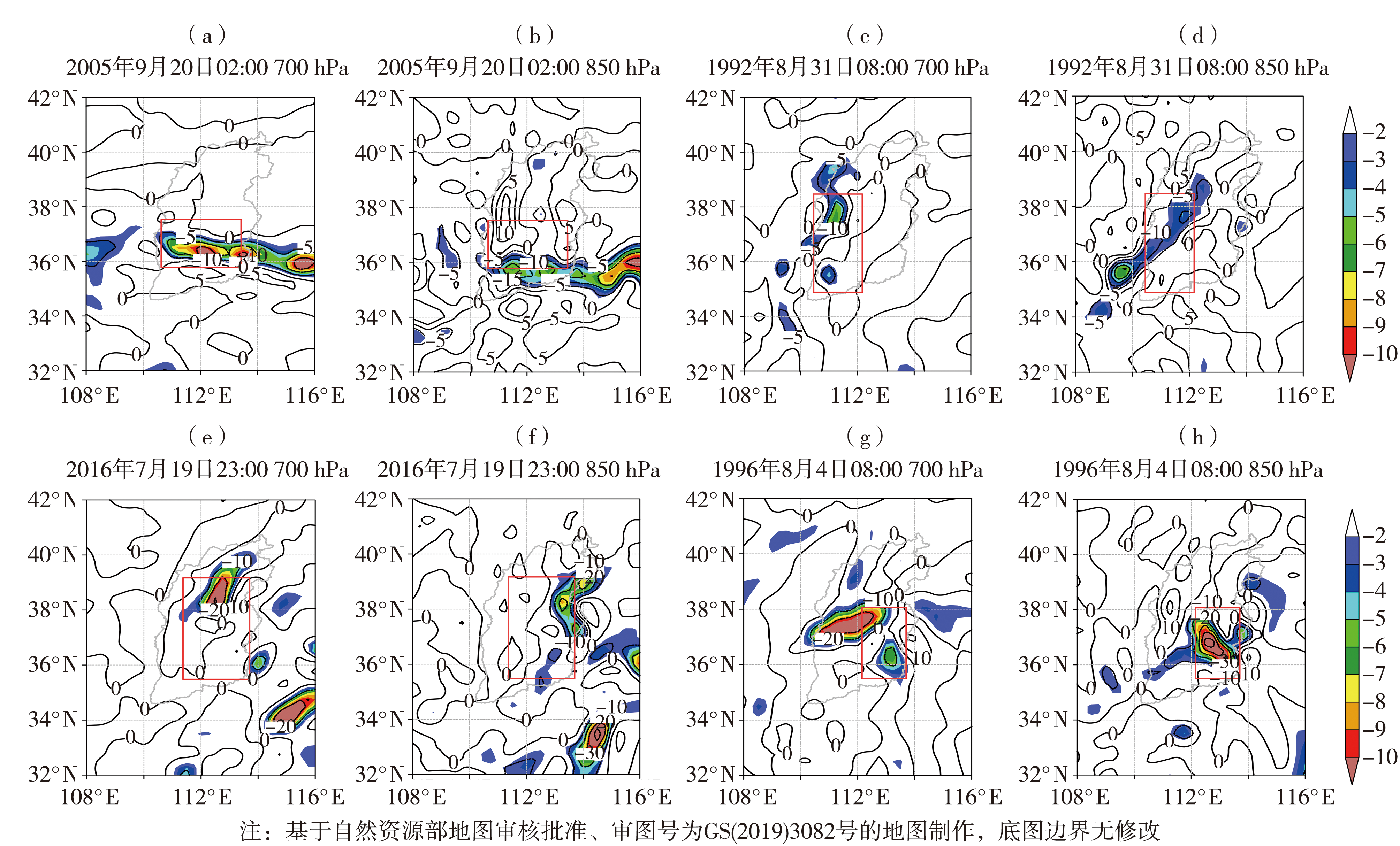
图9 700 hPa低涡型(a、b)、西风带低槽(涡)与台风相互作用型(c、d)、冷涡型(e、f)极端暴雨典型个例及台风低压型(g、h)极端暴雨700、850 hPa水汽通量散度(黑色实线,单位:10-7 g·cm-2·s-1·hPa-1)及其负异常度(彩色填色) (红色方框为暴雨区)
Fig.9 The water vapor flux divergence (black solid lines, Unit: 10-7 g·cm-2·s-1·hPa-1) on 700, 850 hPa and its negative abnormal degree (color shaded) of extreme rainstorm typical case of 700 hPa low vortex pattern (a, b), interaction pattern between westerly low trough (vortex) and typhoon (c, d), cold vortex pattern (e, f), and typhoon low pressure pattern (g, h) extreme rainstorm (The red box is rainstorm area)
| 统计量 | 700 hPa | 850 hPa | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水汽通量辐合中心过程最大值/(10-7g·cm-2·s-1·hPa-1) | 异常度 | 水汽通量辐合中心过程最大值/(10-7g·cm-2·s-1·hPa-1) | 异常度 | |
| 700 hPa低涡型均值 | -18 | -8 | -29 | -6 |
| 西风带低槽(涡)与台风相互作用型均值 | -12 | -6 | -18 | -4 |
| 冷涡型均值 | -19 | -9 | -33 | -7 |
| 台风低压型 | -24 | -11 | -55 | -12 |
表2 不同环流分型下山西极端暴雨700、850 hPa暴雨区水汽通量辐合中心过程最大值及其异常度统计
Tab.2 The statistics of the maximum value of water vapor flux convergence center during the process and its abnormal degree over the rainstorm area on 700, 850 hPa in Shanxi extreme rainstorm under different circulation classifications
| 统计量 | 700 hPa | 850 hPa | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水汽通量辐合中心过程最大值/(10-7g·cm-2·s-1·hPa-1) | 异常度 | 水汽通量辐合中心过程最大值/(10-7g·cm-2·s-1·hPa-1) | 异常度 | |
| 700 hPa低涡型均值 | -18 | -8 | -29 | -6 |
| 西风带低槽(涡)与台风相互作用型均值 | -12 | -6 | -18 | -4 |
| 冷涡型均值 | -19 | -9 | -33 | -7 |
| 台风低压型 | -24 | -11 | -55 | -12 |
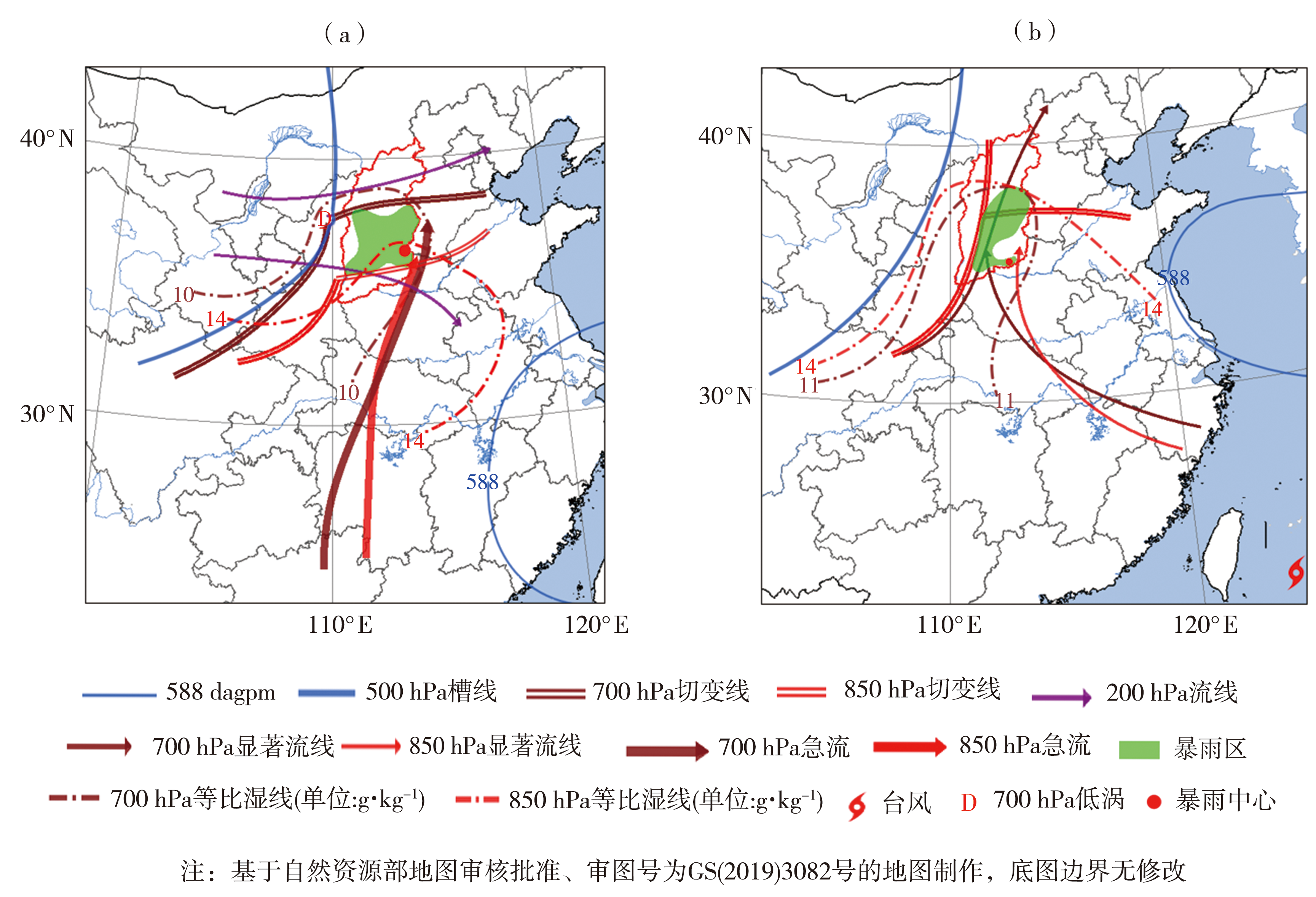
图10 700 hPa低涡型(a)、西风带低槽(涡)与台风相互作用型(b)极端暴雨典型个例概念模型
Fig.10 Conceptual model of extreme rainstorm typical case of 700 hPa low vortex pattern (a), interaction pattern between westerly low trough (vortex) and typhoon (b)
| [1] | 陈涛, 林建, 张芳华, 等, 2017. “16·7”华北极端强降水过程对流尺度集合模拟试验不确定性分析[J]. 气象, 43(5): 513-527. |
| [2] | 谌芸, 孙军, 徐珺, 等, 2012. 北京721特大暴雨极端性分析及思考(一)观测分析及思考[J]. 气象, 38(10):1255-1 266. |
| [3] | 丁一汇, 2019. 中国暴雨理论的发展历程与重要进展[J]. 暴雨灾害, 38(5): 395-406. |
| [4] | 董伯纲, 于洋, 2022. 近60年山西省极端降水时空变化特征[J]. 水土保持学报, 36(1):135-141. |
| [5] | 符娇兰, 马学款, 陈涛, 等, 2017. “16·7”华北极端强降水特征及天气学成因分析[J]. 气象, 43(5):528-539. |
| [6] | 高蓉, 宋连春, 钟海玲, 2018. 2016年汛期中国降水极端特征及与1998年对比[J]. 气象, 44(5):699-703. |
| [7] | 郝寿昌, 秦爱民, 李馗峰, 等, 2016. 山西省天气预报技术手册[M]. 北京: 气象出版社:102-105. |
| [8] | 李兆奇, 赵桂香, 赵彩萍, 2022. 山西近40年极端降水特征分析[J]. 海洋气象学报, 42(3):88-98. |
| [9] |
苗爱梅, 郝振荣, 贾利冬, 等, 2014. “0702”山西大暴雨过程的多尺度特征[J]. 高原气象, 33(3):786-800.
DOI |
| [10] | 苗爱梅, 贾利冬, 吴蓁, 等, 2008. 070729特大暴雨的地闪特征与降水相关分析[J]. 气象, 34(6):74-80. |
| [11] |
苗爱梅, 王洪霞, 武捷, 2020. 山西不同历时强降水的统计特征及趋势变化[J]. 高原气象, 39(4): 796-807.
DOI |
| [12] | 苗爱梅, 武捷, 赵海英, 等, 2010. 低空急流与山西大暴雨的统计关系及流型配置[J]. 高原气象, 29(4):939-946. |
| [13] | 苗青, 白自斌, 王洪霞, 等, 2021. 山西秋季一次极端暴雨过程的异常特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 39(6):984-994. |
| [14] | 孙继松, 何娜, 王国荣, 等, 2012. “7.21”北京大暴雨系统的结构演变特征及成因初探[J]. 暴雨灾害, 31(3):218-225. |
| [15] | 孙继松, 雷蕾, 于波, 等, 2015. 近10年北京地区极端暴雨事件的基本特征[J]. 气象学报, 73(4):609-623. |
| [16] | 孙建华, 张小玲, 卫捷, 等, 2005. 20世纪90年代华北大暴雨过程特征的分析研究[J]. 气候与环境研究, 10(3):492-506. |
| [17] | 孙军, 谌芸, 杨舒楠, 等, 2012. 北京721特大暴雨极端性分析及思考(二)极端性降水成因初探及思考[J]. 气象, 38(10):1267-1 277. |
| [18] |
唐懿, 蔡雯悦, 翟建青, 等, 2022. 2021年夏季中国气候异常特征及主要气象灾害[J]. 干旱气象, 40(2): 179-186.
DOI |
| [19] | 田付友, 杨舒楠, 郑永光, 等, 2021. 北京地区两次极端特大暴雨过程中短时强降水环境条件对比分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 40(1):27-36. |
| [20] |
王佳津, 肖红茹, 杨康权, 等, 2023. 四川盆地一次持续性暴雨的水汽输送特征[J]. 干旱气象, 41(3): 474-482.
DOI |
| [21] | 王婧羽, 崔春光, 王晓芳, 等, 2014. 2012年7月21日北京特大暴雨过程的水汽输送特征[J]. 气象, 40(2) :133-145. |
| [22] |
王思慜, 赵桂香, 赵瑜, 等, 2017. 2016年7月山西一次大暴雨天气过程的多尺度系统相互作用分析[J]. 干旱气象, 35(5): 857-867.
DOI |
| [23] | 肖递祥, 杨康权, 俞小鼎, 等, 2017. 四川盆地极端暴雨过程基本特征分析[J]. 气象, 43(10):1165-1 175. |
| [24] |
邢蕊, 杨健博, 田梦, 等, 2023. 不同边界层参数化方案对台风“烟花”北上阶段暴雨模拟的影响试验[J]. 干旱气象, 41(1): 91-102.
DOI |
| [25] |
许敏, 沈芳, 刘璇, 等, 2022. 京津冀“7·5”强对流天气形成的环境条件及中尺度特征[J]. 干旱气象, 40(6): 993-1 002.
DOI |
| [26] |
张桂莲, 仲夏, 韩经纬, 等, 2018. 内蒙古中西部地区一次极端大暴雨特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 36(1): 17-26.
DOI |
| [27] | 张文龙, 崔晓鹏, 2012. 近50a华北暴雨研究主要进展[J]. 暴雨灾害, 31(4):384-391. |
| [28] | 赵桂香, 赵建峰, 杨东, 等, 2013. 山西一次大暴雨过程云图及环境场的特征分析[J]. 高原气象, 32(6):1747-1 757. |
| [29] | 赵思雄, 孙建华, 2019. 我国暴雨机理与预报研究进展及其相关问题思考[J]. 暴雨灾害, 38(5):422-430. |
| [30] | 赵思雄, 孙建华, 鲁蓉, 等, 2018. “7·20”华北和北京大暴雨过程的分析[J]. 气象, 44(3):351-360. |
| [31] | 朱乾根, 林锦瑞, 寿绍文, 等, 2000. 天气学原理和方法[M]. 3版. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [32] | HART R E, GRUMM R H, 2001. Using normalized climatological anomalies to rank synoptic-scale events objectively[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 129(9): 2 426-2 442. |
| [33] | TAO S Y, DING Y H, 1981. Observational evidence of the influence of the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Plateau on the occurrence of heavy rain and severe convective storms in China[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 62(1):23-30. |
| [34] | XIA R D, ZHANG D L, 2019. An observational analysis of three extreme rainfall episodes of 19-20 July 2016 along the Taihang Mountains in North China[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 147(11): 4 199-4 220. |
| [1] | 井 宇 , 陈 闯 , 赵 强 , 刘菊菊. 陕西雷暴大风时空分布和气象条件分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(4): 576-587. |
| [2] | 魏娟娟, 万瑜, 潘宁, 肖俊安. 伊犁河谷春季极端暴雨水汽特征与不稳定机制分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2024, 42(3): 395-404. |
| [3] | 傅朝, 刘维成, 宋兴宇, 徐丽丽, 沙宏娥, 马莉, 崔宇. 西北干旱区一次极端暴雨局地性增强的对流环境特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(6): 909-921. |
| [4] | 刘新伟,王澄海,郭润霞,杨晓军,狄潇泓. 1981—2018年甘肃省极端暴雨天气过程的气候与环流特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(5): 750-758. |
| [5] | 翁之梅,周雪君,甘晶晶,王凯. 浙江省春季不同类型暖区天气降水特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(5): 766-774. |
| [6] | 周雅蔓, 孙迪, 赵勇, 李桉孛, 郭玉琳. 新疆北部夏季大范围极端降水及其环流异常特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2021, 39(2): 215-224. |
| [7] | 李常德, 王磊, 李晓霞, 赵建华, 曾鼎文. 黄土高原4月旱涝环流特征及前期强迫信号分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2020, 38(1): 14-21. |
| [8] | 丁江钰, 陈小婷, 王建鹏, 葛森, 纪晓玲. 福州长乐机场雷暴及风切变天气特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2019, 37(2): 270-276. |
| [9] | 蔡荣辉, 陈静静, 文萍, 何炜炜, 陈红专, 李蔚. 2017年湖南一次特大致洪暴雨过程的水汽特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2019, 37(2): 288-300. |
| [10] | 胡春丽1,李荣平1,王婷1,李菲2,李琳琳1. 辽宁水稻年景预报模型研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2018, 36(3): 501-. |
| [11] | 张桂莲,仲夏,韩经纬,赵斐,包福祥,李瑞青. 内蒙古中西部地区一次极端大暴雨特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2018, 36(1): 17-26. |
| [12] | 乔娟,张雅斌,程龙,黄蕾,白国强. 西安地区高温天气分月精细化预报指标[J]. 干旱气象, 2018, 36(1): 141-149. |
| [13] | 姚蓉, 黎祖贤, 许霖, 唐杰, 陈静静. 湖南冻雨预报关键技术指标及应用[J]. 干旱气象, 2014, 32(3): 366-372. |
| [14] | 潘冬梅,田忠锋. 近 50a阿勒泰地区大风的环流分型及预报[J]. 干旱气象, 2014, 32(1): 108-113. |
| [15] | 王清川,寿绍文,许敏,张绍恢. 河北省廊坊市初冬雨雪相变特征及预报指标初探[J]. 干旱气象, 2012, 30(2): 276-282. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
