干旱气象 ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (2): 217-227.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2024)-02-0217
金沙江下游高温天气的环流分型和诊断
黄瑶1,2( ), 袁梦1,3(
), 袁梦1,3( ), 郭洁1,2, 宋雯雯1,2,4, 刘新超1,2
), 郭洁1,2, 宋雯雯1,2,4, 刘新超1,2
- 1.高原与盆地暴雨旱涝灾害四川省重点实验室,四川 成都 610072
2.四川省气象服务中心,四川 成都 610072
3.四川省农村经济综合信息中心,四川 成都 610072
4.中国气象局大气探测重点开放实验室,四川 成都 610225
Synoptic circulation patterns clustering analysis and physical diagnosis of high temperature weather in the lower reaches of the Jinsha River
HUANG Yao1,2( ), YUAN Meng1,3(
), YUAN Meng1,3( ), GUO Jie1,2, SONG Wenwen1,2,4, LIU Xinchao1,2
), GUO Jie1,2, SONG Wenwen1,2,4, LIU Xinchao1,2
- 1. Heavy Rain and Drought-Flood Disasters in Plateaus and Basin Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Chengdu 610072, China
2. Sichuan Meteorological Service Centre, Chengdu 610072, China
3. Sichuan Rural Economy Comprehensive Information Center, Chengdu 610072, China
4. Key Laboratory of Atmosphere Sounding, China Meteorological Administration, Chengdu 610225, China
摘要:
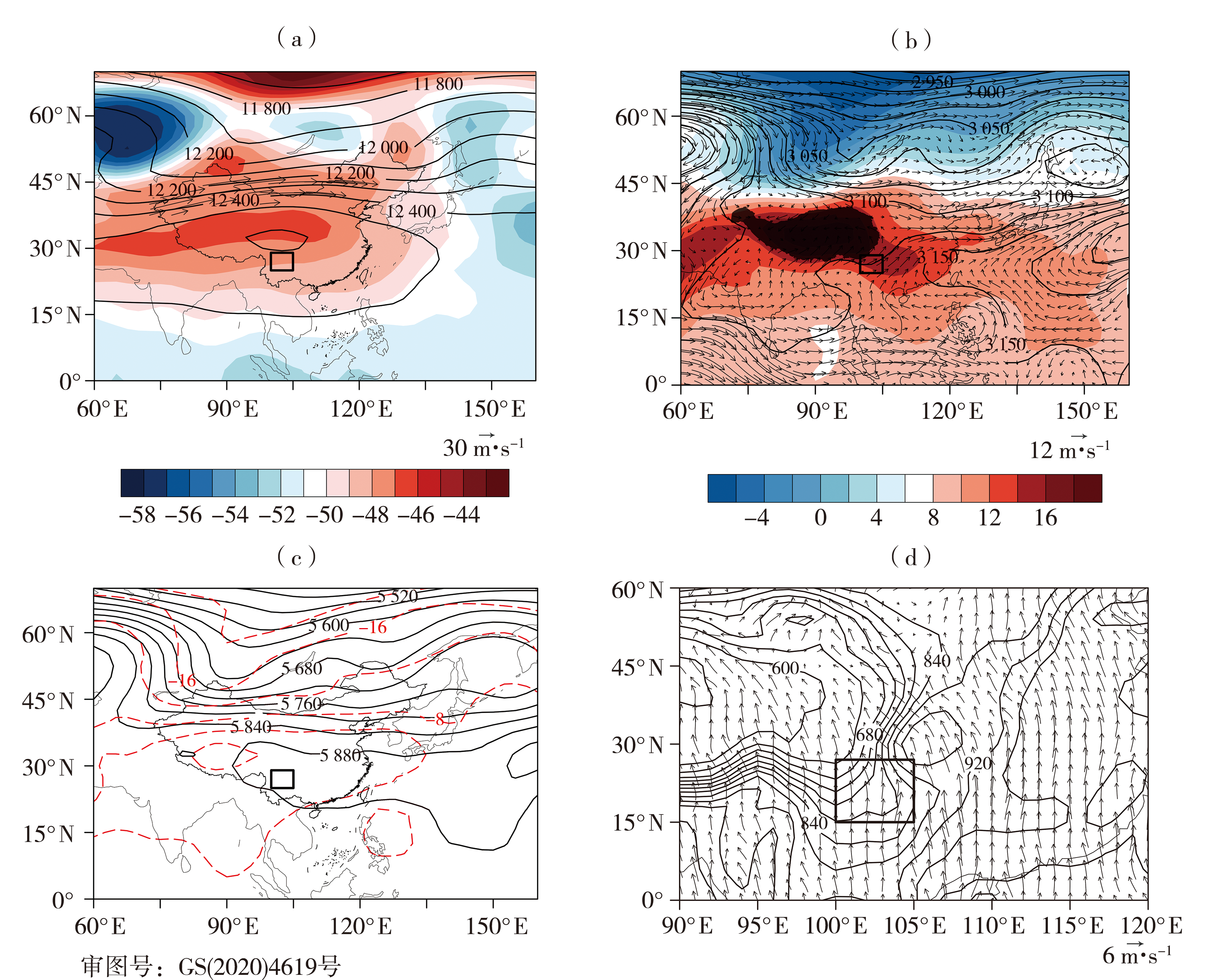
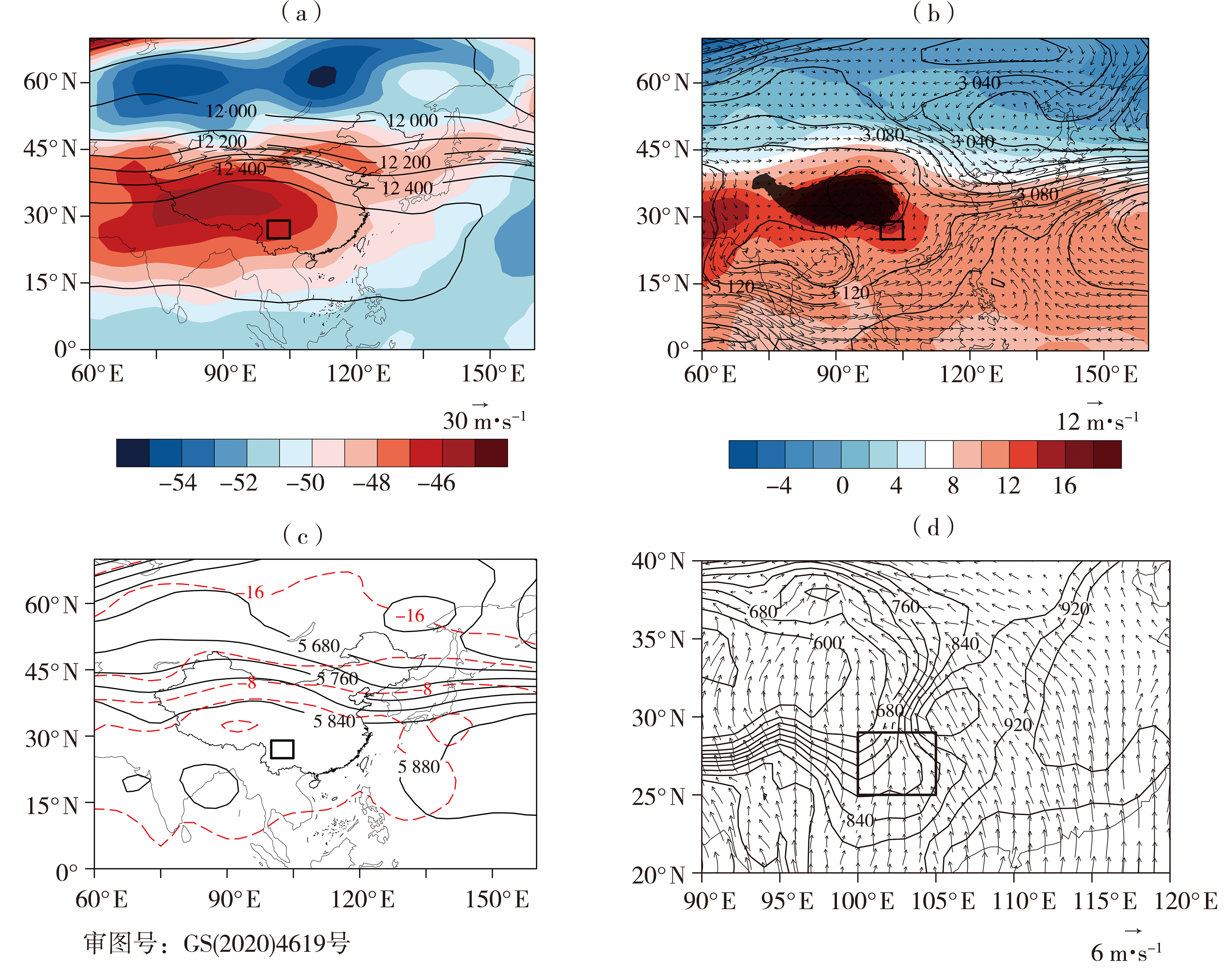
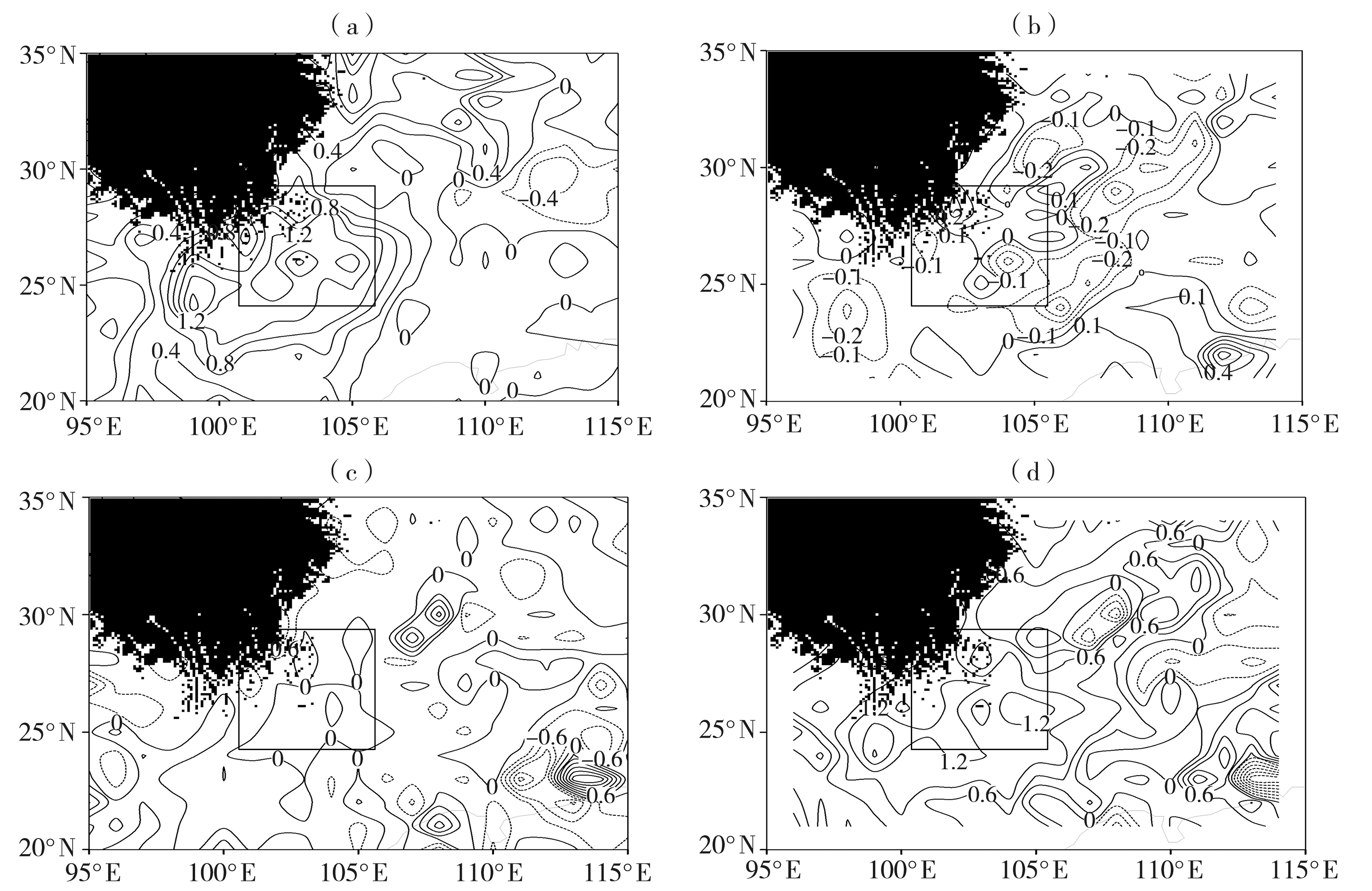
金沙江流域作为我国重要的生态屏障和清洁能源输出地,其下游干热河谷地段是高温频发地区,针对该区域开展高温天气环流特征和诊断对提高高温灾害预报水平和提高该区域能源调度效率具有重要意义。利用1981—2020年逐日最高气温资料和欧洲中期天气预报中心(the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts, ECMWF)第五代大气再分析数据集ERA5(Reanalysis v5),通过K-means聚类分析法对金沙江下游高温天气环流形势进行分型,并对各类高温天气的动力和热力因子进行诊断,提炼出各型高温的物理量阈值。结果表明:金沙江下游高温天气的环流背景可分为暖脊型、副热带高压-青藏高压型和青藏高压型3种类型。高温期间中高层均有≥0.25 Pa·s-1的下沉气流,天空晴朗无云,晴空辐射强,且近地面受到≤800 hPa强度的热低压直接加热作用。热力诊断发现金沙江下游高温主要由非绝热加热引起,温度平流对局地升温的贡献为负,垂直绝热变化贡献接近于0,但下沉气流有利于地面接收更多太阳辐射,使近地层非绝热加热增加,从而导致金沙江下游出现高温天气。
中图分类号: