干旱气象 ›› 2022, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (1): 146-155.DOI: 10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2022)-01-0146
基于SCTP-RF算法的甘肃省短期定量降水客观预报方法研究
刘娜( ), 黄武斌(
), 黄武斌( ), 杨建才, 王基鑫, 王一丞, 张君霞
), 杨建才, 王基鑫, 王一丞, 张君霞
- 兰州中心气象台,甘肃 兰州 730020
Objective forecast method of short-term quantitative precipitation in Gansu Province based on SCTP-RF algorithm
LIU Na( ), HUANG Wubin(
), HUANG Wubin( ), YANG Jiancai, WANG Jixin, WANG Yicheng, ZHANG Junxia
), YANG Jiancai, WANG Jixin, WANG Yicheng, ZHANG Junxia
- Lanzhou Central Meteorological Observatory, Lanzhou 730020, China
摘要:
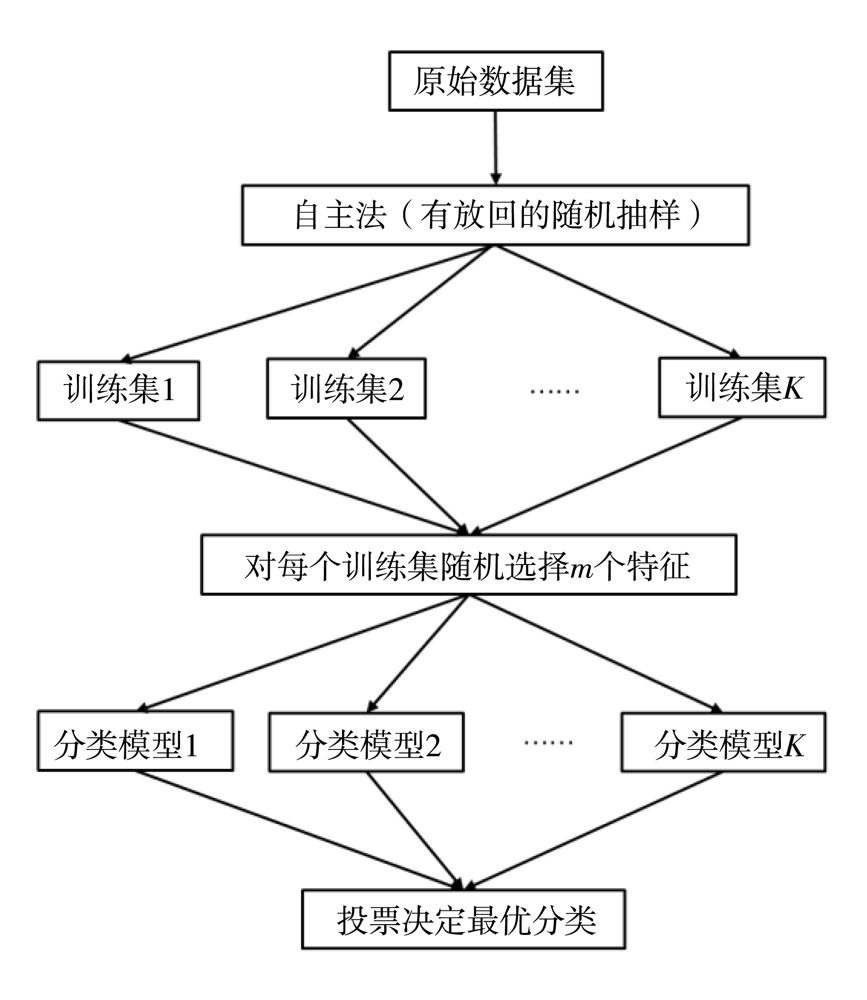
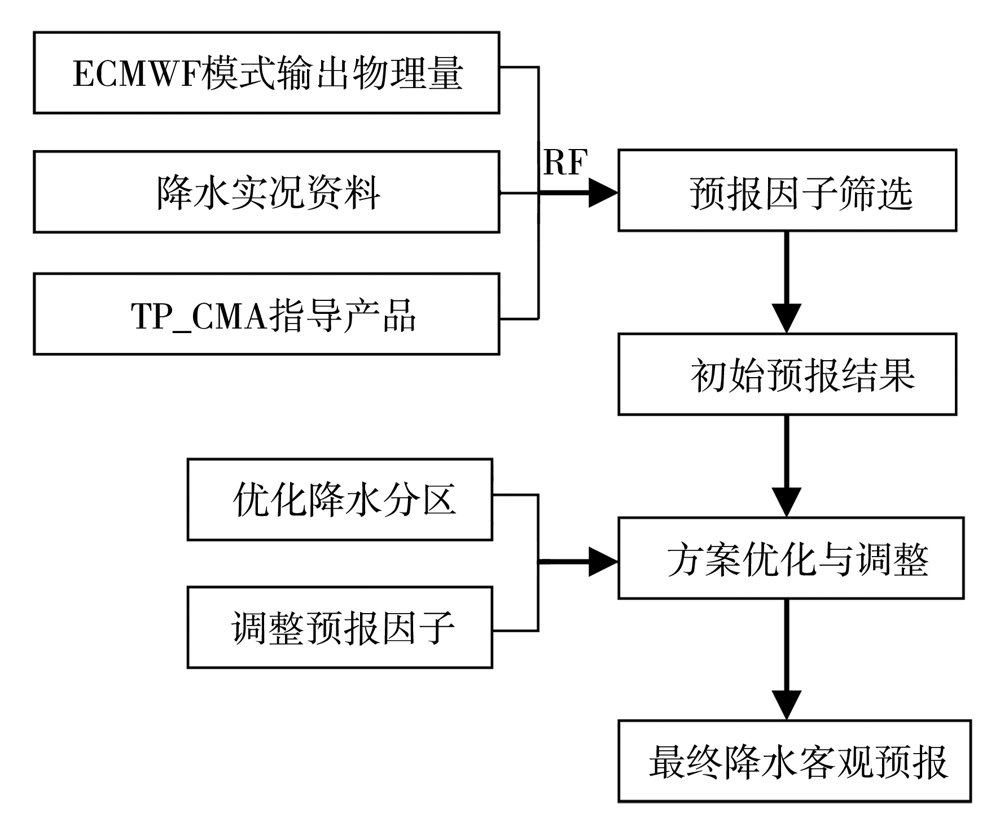
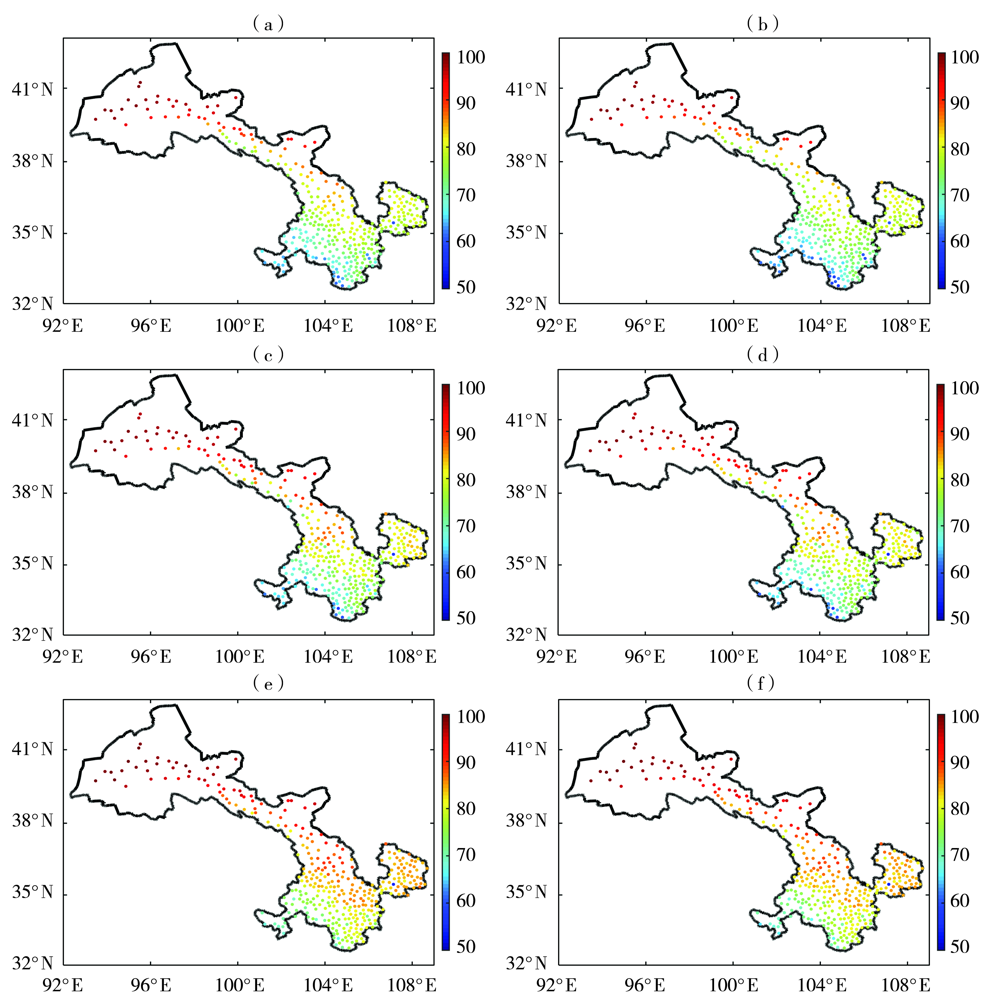
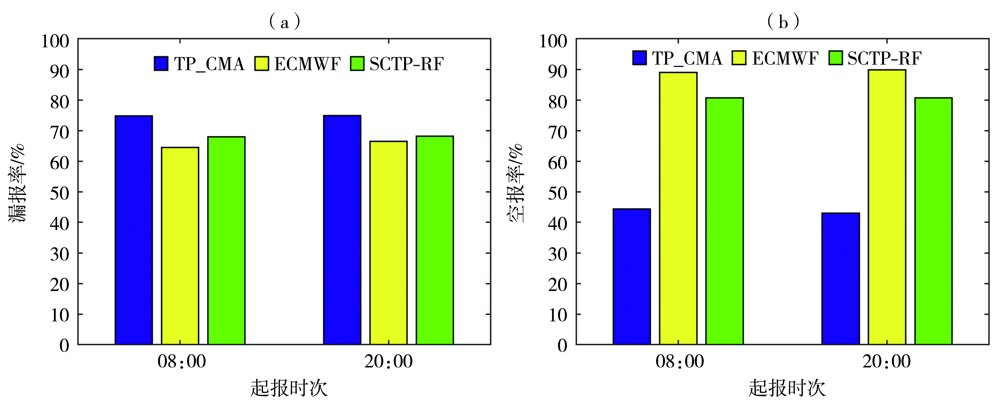
基于欧洲中期天气预报中心(ECMWF)的精细化数值预报产品、中国气象局下发的降水指导产品(TP_CMA)及甘肃省340个气象站点降水实况数据,利用泰森多边形与K-means空间聚类方法(spatial cluster and Tyson polygon,SCTP),对2017—2019年4—9月甘肃省340站降水资料进行客观分区。在此基础上,采用随机森林算法(random forest,RF),筛选出与降水相关的物理量因子构建模型,开展甘肃省短期定量降水客观预报订正试验,并进行预报效果检验。结果表明:(1)甘肃省4—9月降水客观分区依次为7、6、14、13、14和11个。(2)就晴雨预报而言,SCTP-RF订正产品对甘肃省汛期的晴雨预报能力较TP_CMA指导产品和ECMWF模式产品有一定提升,提升幅度分别为6.1%、4.2%;在空间上,SCTP-RF算法对甘肃省340站的晴雨预报均具有一定的订正能力,大部分站点晴雨预报准确率提升了5%,特别是河东地区。(3)在分级降水预报中,SCTP-RF订正产品对中雨和大雨的预报能力均优于TP_CMA指导产品和ECMWF模式产品,且全省大部的订正效果较好,特别是河东中部及陇东南地区,但在强降水过程中对小雨和暴雨的预报订正不稳定,尤其是陇东南地区的小雨。
中图分类号: