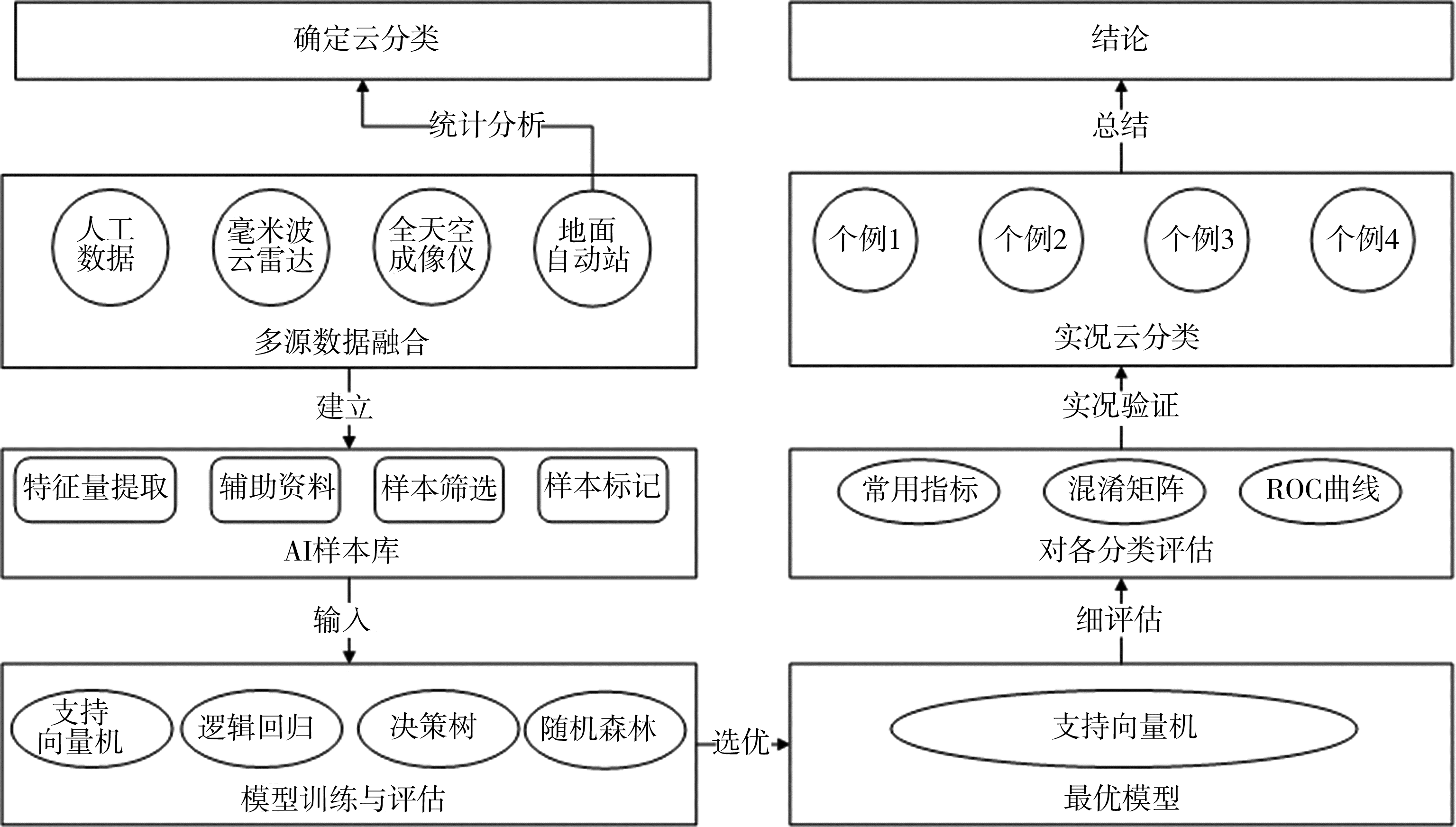
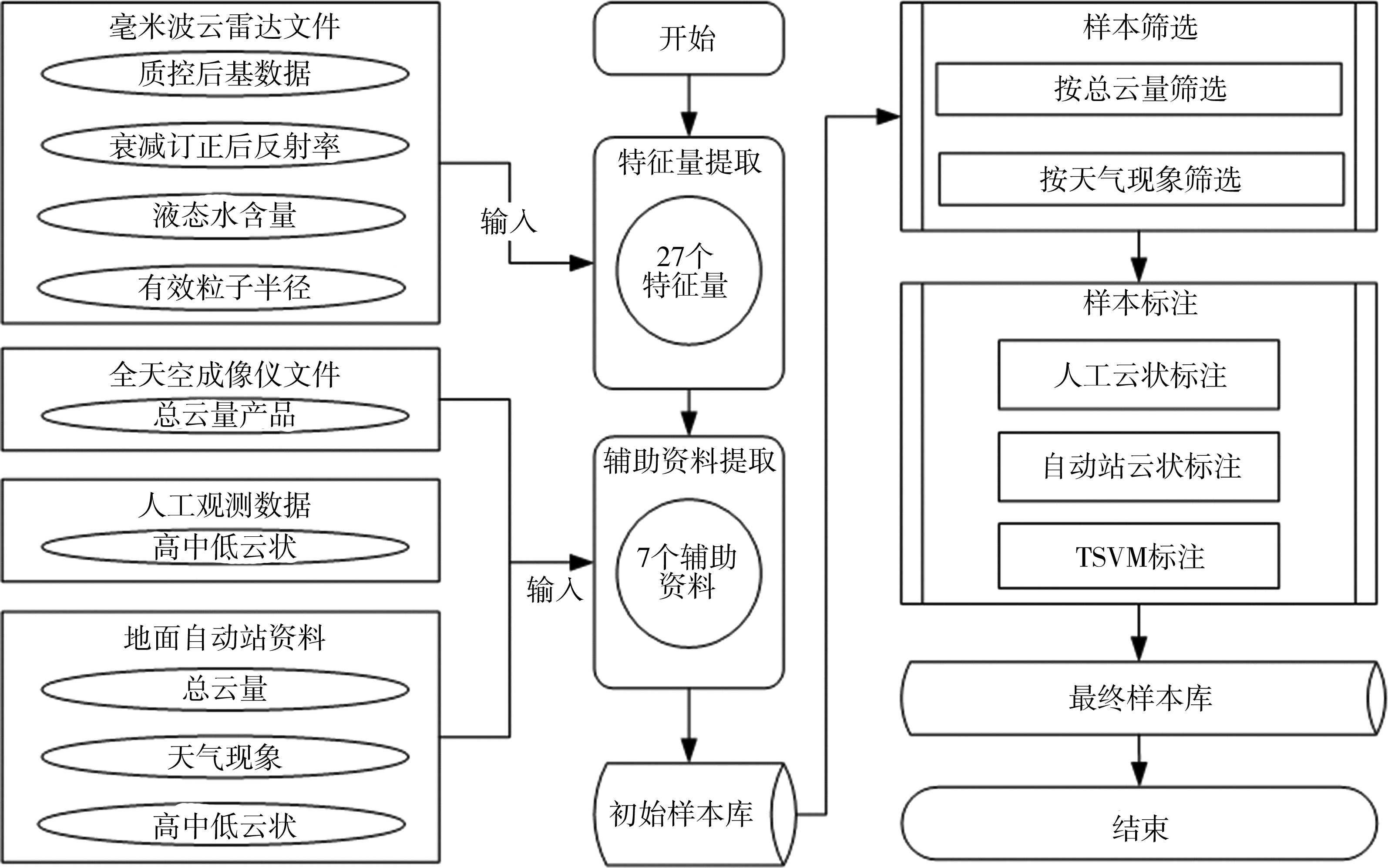
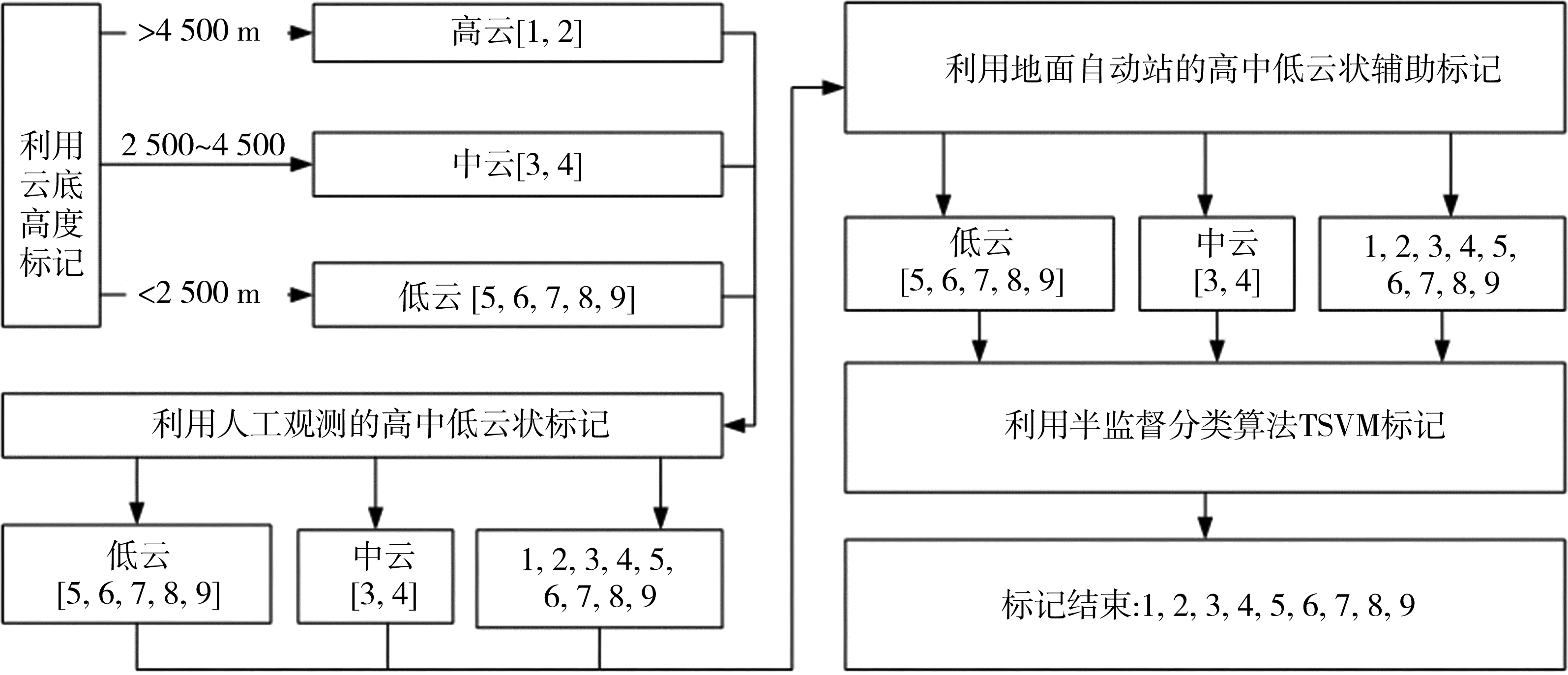
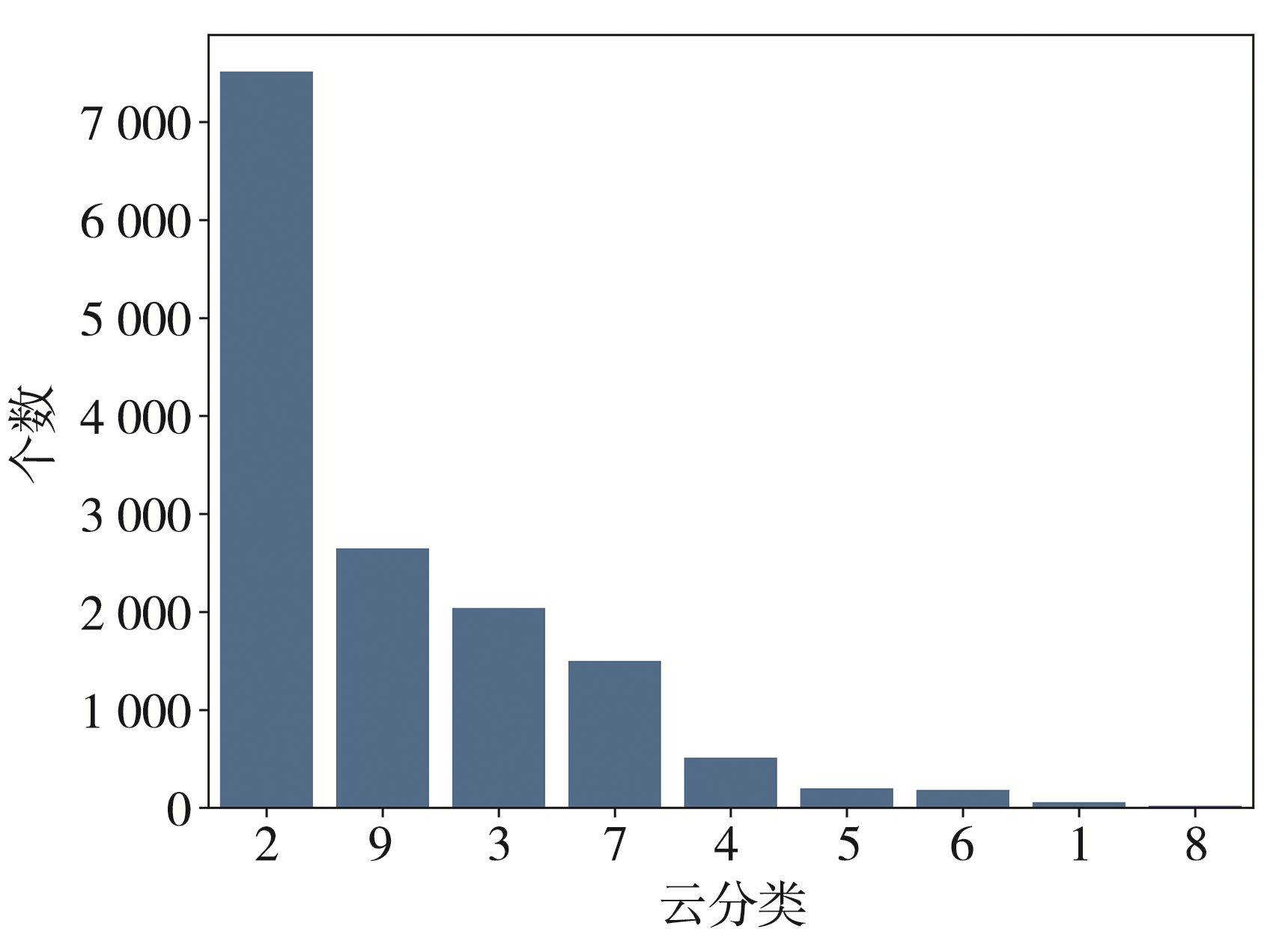
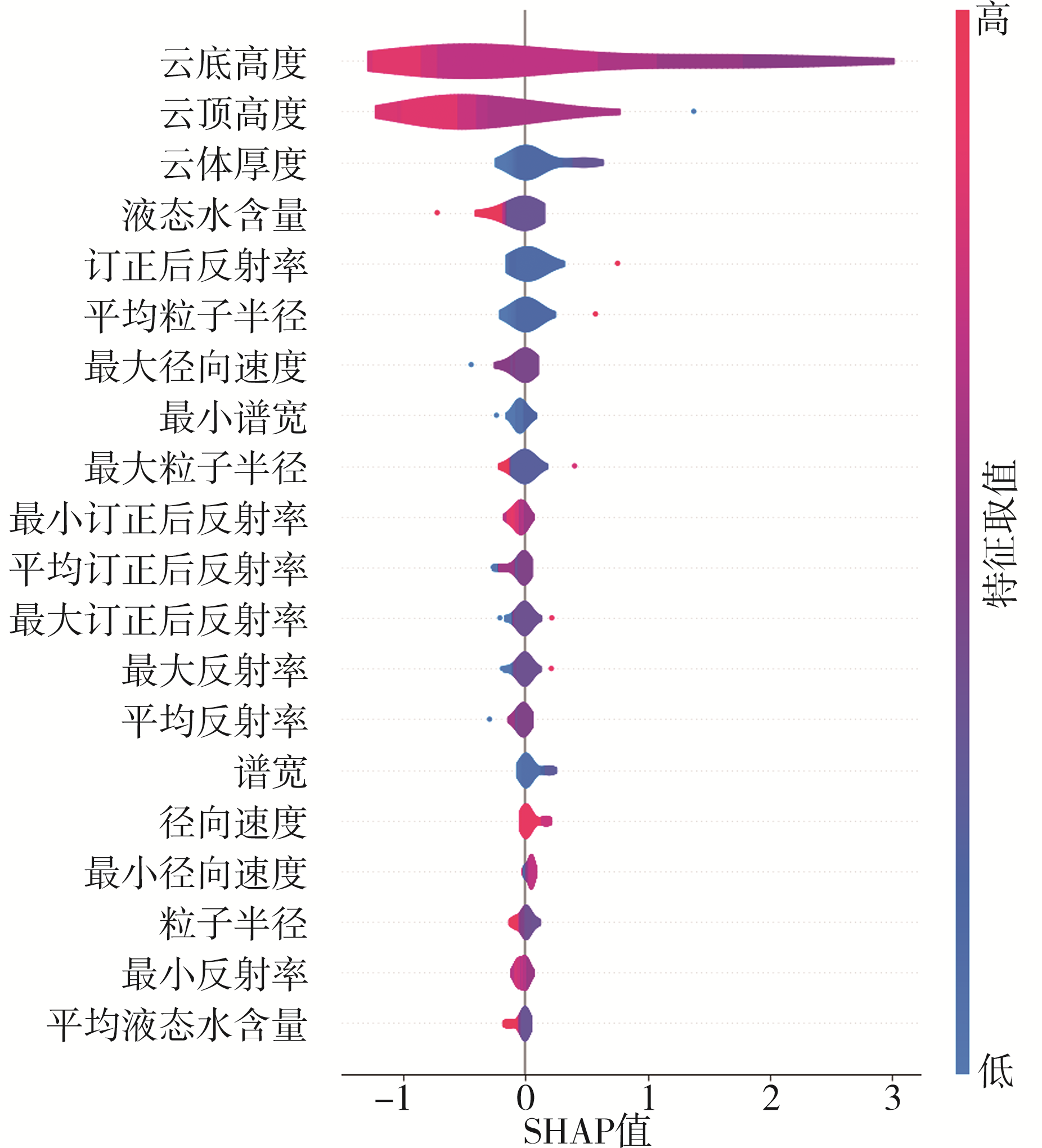
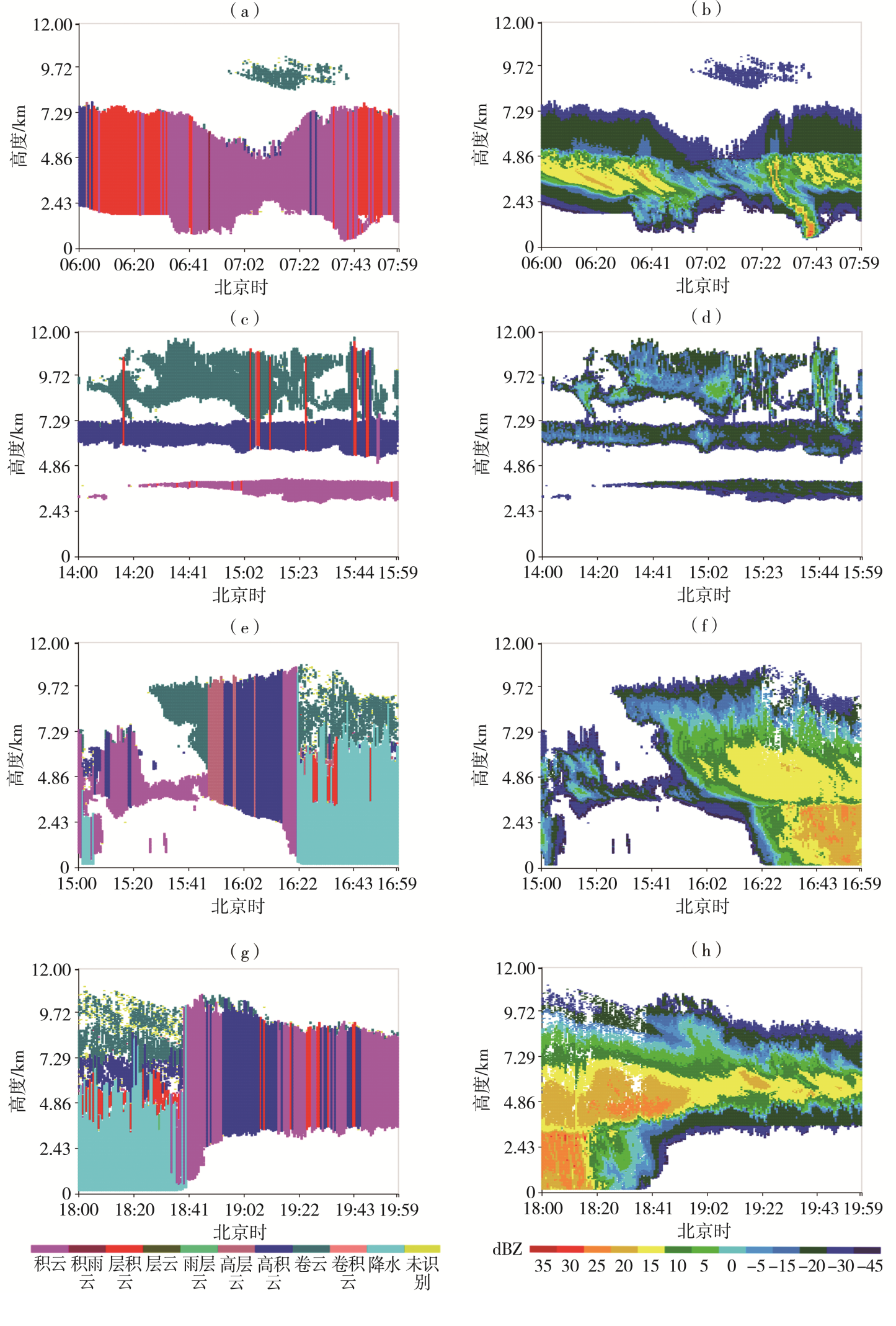
| [1] |
陈冬冬, 赵静, 王柏林, 等, 2019. FY-2F卫星和毫米波云雷达云高观测的个例对比分析[J]. 气象科技, 47(3):495-501.
|
| [2] |
陈挺, 刘香君, 臧璇, 等, 2025. 深度特征选择方法研究综述[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 42(7):1-11.
|
| [3] |
顾桃峰, 岳海燕, 伍光胜, 等, 2023. 毫米波云雷达与激光云高仪气象探测性能对比分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 43(1):275-283.
|
| [4] |
郭立平, 刘姝, 李敬海, 等, 2024. 毫米波云雷达在高影响天气中的预警应用[J]. 干旱气象, 42(3):465-472.
DOI
|
| [5] |
胡树贞, 曹晓钟, 陶法, 等, 2020. 船载毫米波云雷达观测西太平洋云宏观特征对比分析[J]. 气象, 46(6):745-752.
|
| [6] |
胡树贞, 陶法, 张雪芬, 等, 2022. 基于毫米波云雷达的寒潮过程回波特征分析[J]. 气象水文海洋仪器, 39(1):8-11.
|
| [7] |
黄兴友, 陆琳, 洪滔, 等, 2020. 利用毫米波云雷达数据反演层云微物理参数和云内湍流耗散率[J]. 大气科学学报, 43(5):908-916.
|
| [8] |
姬雪帅, 王丽婧, 郭宏, 等, 2022. 基于多源观测资料对张家口一次雨雪天气降水相态特征的分析[J]. 干旱气象, 40(3):507-515.
DOI
|
| [9] |
李晨蕊, 伏晶, 刘维成, 等, 2022. 应用FY卫星产品分析陇东半干旱区特大暴雨事件云特征[J]. 干旱气象, 40(6):954-967.
DOI
|
| [10] |
李海飞, 乐满, 杨飞跃, 等, 2017. 基于地基云雷达资料的淮南地区冬季云宏观特征[J]. 干旱气象, 35(6):1 011-1 014.
|
| [11] |
李慧, 郑旭程, 苏立娟, 等, 2023. 基于毫米波云雷达的黄河流域内蒙古段云宏观特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 41(3):434-441.
DOI
|
| [12] |
李郅琴, 杜建强, 聂斌, 等, 2019. 特征选择方法综述[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 55(24):10-19.
DOI
|
| [13] |
刘光普, 黄思源, 梁莺, 等, 2019. 毫米波雷达在港口海雾观测和能见度反演中的应用[J]. 干旱气象, 37(6):993-1 004.
|
| [14] |
路志英, 王长桥, 王萍, 等, 2000. 用小波分析提取云图纹理梯度特征[J]. 模式识别与人工智能, 13(4):434-438.
|
| [15] |
倾鹏程, 陶法, 胡树贞, 等, 2022. 联合毫米波测云仪和全天空成像仪云分类方法[J]. 广东气象, 44(2):73-77.
|
| [16] |
全国气象仪器与观测方法标准化技术委员会, 2017. 地面气象观测规范总则:GB/T 35221—2017[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社.
|
| [17] |
任丹阳, 曹梅, 王瑞英, 等, 2023. 毫米波云雷达及探空反演的云垂直结构对比分析[J]. 陕西气象(6):1-9.
|
| [18] |
宋冬昊, 王文明, 王敏仲, 等, 2025. 基于轻量级梯度提升机对毫米波雷达云回波数据分类[J]. 科学技术与工程, 25(17):7 072-7 079.
|
| [19] |
孙学金, 刘磊, 高太长, 等, 2009. 基于模糊纹理光谱的全天空红外图像云分类[J]. 应用气象学报, 20(2):157-163.
|
| [20] |
王卫民, 徐八林, 雷勇, 等, 2024. Ka波段毫米波云雷达对青藏高原东南缘降水回波的分析[J]. 气象, 50(3):291-302.
|
| [21] |
夏德深, 金盛, 王健, 1999. 基于分数维与灰度梯度共生矩阵的气象云图识别(Ⅱ):灰度梯度共生矩阵对纹理统计特征的描述[J]. 南京理工大学学报, 23(4):289-292.
|
| [22] |
徐路扬, 翟亮, 王媛媛, 等, 2023. 多源遥感数据在北京春季沙尘天气监测中的应用评估[J]. 干旱气象, 41(2):318-327.
DOI
|
| [23] |
杨晓, 黄兴友, 杨军, 等, 2019. 毫米波雷达云回波的自动分类技术研究[J]. 气象学报, 77(3):541-551.
|
| [24] |
余安安, 吴雪菲, 李栋, 等, 2021. 基于神经网络的毫米波测云雷达云状识别研究[J]. 国外电子测量技术, 40(4):82-86.
|
| [25] |
喻皓, 2024. 基于卷积神经网络的地基云人工智能分类器研究[J]. 自动化与仪器仪表(2):24-28.
|
| [26] |
张德玉, 秦三杰, 魏荣妮, 等, 2024a. 天气雷达实时回波省级直显系统设计与应用[J]. 计算机技术与发展, 34(11):21-28.
|
| [27] |
张德玉, 魏荣妮, 张强, 等, 2024b. 天气雷达基数据通用工具包设计与实现[J]. 信息技术与信息化(5):153-156.
|
| [28] |
张德玉, 张启超, 张强, 等, 2024c. 基于天擎的天气雷达基数据显示分析系统[J]. 气象水文海洋仪器, 41(4):112-115.
|
| [29] |
张晋茹, 杨莲梅, 2019. 基于毫米波云雷达的伊犁河谷两次强降雪过程云特征观测分析[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 13(5):41-48.
|
| [30] |
张艳品, 章文星, 吕达仁, 等, 2014. 卫星(IASI探测仪)观测云顶高与地基云雷达观测的对比验证[J]. 大气科学, 38(5):874-884.
|
| [31] |
张志坚, 张静, 蔡英琪, 2020. 毫米波云雷达系统观测试验结果分析[J]. 气象水文海洋仪器, 37(3):17-20.
|
| [32] |
周著华, 白洁, 刘健文, 等, 2005. MODIS多光谱云相态识别技术的应用研究[J]. 应用气象学报, 16(5):678-684.
|
| [33] |
MING H, WANG M Z, WEI M, et al, 2021. Study on the clouds detected by a millimeter-wave cloud radar over the hinterland of the Taklimakan Desert in April-June 2018[J]. Journal of Meteorological Research, 35(6): 1 074-1 090.
DOI
|
| [34] |
TAN Z H, WANG J, GUO J P, et al, 2024. Improving satellite-retrieved cloud base height with ground-based cloud radar measurements[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 41(11): 2 131-2 140.
DOI
|
 ), 胡树贞2(
), 胡树贞2( ), 秦三杰3, 张强1, 白明1, 庞成1, 魏荣妮1
), 秦三杰3, 张强1, 白明1, 庞成1, 魏荣妮1
 ), HU Shuzhen2(
), HU Shuzhen2( ), QIN Sanjie3, ZHANG Qiang1, BAI Ming1, PANG Cheng1, WEI Rongni1
), QIN Sanjie3, ZHANG Qiang1, BAI Ming1, PANG Cheng1, WEI Rongni1